數十億損失。三大資產暴跌。八天漏洞窗口。讓你深入了解上周這場史無前例加密幣災難,究竟是一場單純市況崩盤,還是一個針對全球最大交易所的精密打擊。
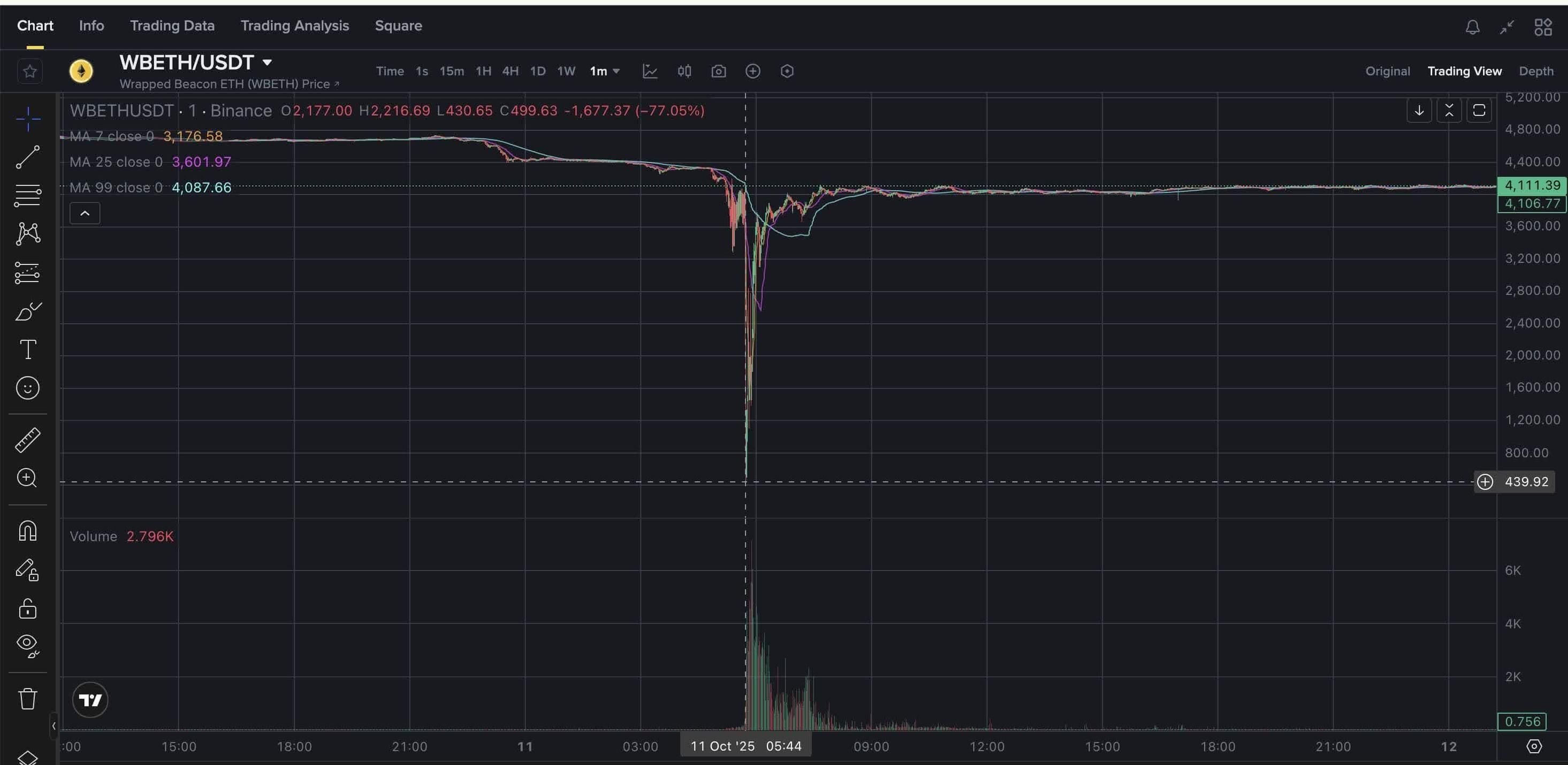
2025年10月10日晚上,幣安的交易員眼睜睜看著手上資產蒸發。40分鐘內,三款數位資產價值幾乎歸零:原本應固定一美元的 Ethena USDe 穩定幣暴瀉至 65 美仙;Wrapped Beacon ETH 急挫至僅值 0.2 美元;Binance Staked SOL 更下探僅剩 0.13 美元。近一百七十萬交易員被強平,創下加密史上最大一次強制清算,損失逾一百九十億美元。
這場混亂正值市場全面拋售之際。美國總統特朗普宣布自11月1日起全面徵收100%中國進口關稅,引發金融市場劇烈震盪。比特幣在幾天前才創下$125,000新高,當天卻急挫逾13%。以太幣暴跌18%。但幣安上的情況遠比傳統市況調整還要惡劣。
多款加密貨幣(包括 Enjin 與 Cosmos)於短時間內價格暴跌近乎清零,部分用戶形容系統出現過載。交易員報告交易賬戶凍結、止損委託失效,甚至在市場大跌時無法成交數分鐘。
當塵埃落定,一個具爭議的理論浮現。知名加密記者吳說區塊鏈(Colin Wu)指出,這次崩盤或非偶然,而是針對幣安及其做市商的協同攻擊,利用了交易所統一賬戶保證金制已知漏洞。時機極為可疑——事故正好發生在幣安宣佈將進行重大安全升級與實施升級之間的狹窄空窗期。
三大受影響資產於幣安24小時內成交量達35至40億美元,推算損失介乎五億至十億美元之間。若攻擊理論屬實,這將成為加密市場史上最複雜的漏洞利用案例之一——一場將原本為提升資金效率而設的基建武器化的精密打擊。
危機時間線
要明白10月11日大崩盤始末,需要回溯至前幾天,當時幣安風險團隊發出一則無意間向細心人士曝光漏洞的公告。
10月6日:預言機升級公告
10月6日,幣安公告將調整部分保證金交易抵押品的定價機制,由內部撮合價格改用更可靠的外部數據,預計10月14日生效。
這項公告對幣安來說只是增強技術、提升價格準確度的例行優化,特別適用於權益型衍生品及高息穩定幣等保證金抵押資產。但它同時揭示了關鍵:風險團隊已察覺相關資產用於強平時的定價存在漏洞。他們知道問題存在,需要修正,更公開宣佈這個八天的風險空窗期。
10月10至11日:攻擊窗口
美國時間10月10日深夜,市況急轉直下。比特幣從日內高位$122,456跌至低見$105,262,跌幅近7%。以太幣跌超12%;XRP由$2.83插水至$1.89,損失13%。
但幣安保證金系統的花樣,更令人愕然。雖然比特幣和主流山寨幣於各交易所普遍急跌,但幣安有三款特定資產出現死亡螺旋。市場波動加劇下,使用幣本位槓桿頭寸的交易戶損失被突如其來的抵押品崩潰進一步放大。USDe 應聲暴跌至65美仙、wBETH 跌至20美仙、BnSOL 見13美仙——而這些資產同期在其他交易所和鏈上協議價格遠高於此。
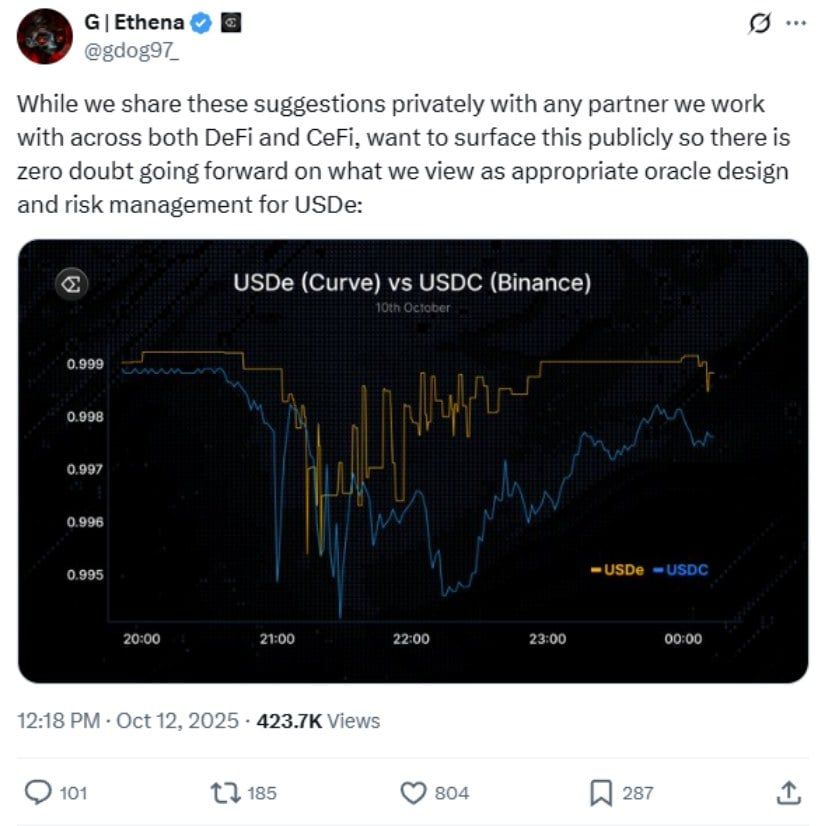
鏈上Aave預言機的USDe資料依然一比一掛鉤,說明混亂只限於幣安內部定價,並非整體市場真正崩潰。正是這種價差,成為協同攻擊理論重點。
隨著大量強平,不少幣安山寨幣資產亦出現極端閃崩,IOTX 一度見零。觀察人士指,謠傳源於主流中心化交易所自動清算交叉保證金倉位抵押品觸發急劇下跌。
10月11-12日:系統故障與回應
強平潮加劇下,幣安系統不堪重負。交易所承認系統因市場活躍而出現延誤和顯示異常,強調用戶資金安全。
幣安聯合創辦人何一發表聲明,承認事故並承諾檢討、補償由系統故障直接導致的損失。聲明指,市場劇震與大量新用戶湧入,令部分交易戶遇上成交問題。
數據顯示,幣安期貨比特幣、以太幣、BNB USDT 永續合約共用保險基金由12.3億美元跌至10.4億,期間動用1.88億應對極端風險。
10月14日:預言機修正
10月14日如期,幣安實施預言機升級,改用外部價格數據,並將贖回價納入三類受影響代幣的指數計價。漏洞窗口正式關閉,但損失已無法挽回。
幣安統一賬戶保證金系統運作原理
為了解幣安怎會暴露風險,必須明白其統一賬戶保證金制度的運作,及其與傳統保證金模式最大分別。
統一保證金的承諾
幣安投資組合保證金(Portfolio Margin),即統一賬戶,將不同交易產品的保證金計算及要求合併。交易員可用多種資產作抵押,令整體交易策略更靈活。
傳統保證金一般有兩種:USDT本位,交易員以泰達幣借出、償還;或幣本位,以比特幣或其他幣作抵押及標價。前者主打穩定,後者則給交易員持續曝險其選擇資產。
幣安統一賬戶打破傳統。它不限於穩定資產作抵押,也無需每個交易對各自分開保證金池,交易員基本上可用任何支持資產在現貨、期貨及衍生品全線倉位掛保證金,大大提升資金效率——整個投資組合皆可作保證金,而無需分隔於各子賬戶。
Unified Maintenance Margin Ratio(uniMMR)
統一賬戶保證金核心是“統一維持保證金比例”(uniMMR),用來綜合評估整體倉位風險,涵蓋賬戶內所有調整後權益與維持保證金需求。
uniMMR 越高,風險越低;相反則風險及被強平機會增加。此比率為調整後權益除以統一維持保證金。
uniMMR 低於 1.05(即105%)即會觸發強平;當 uniMMR 跌至或低於 1.5 會第一次追繳,1.2 會第二次追繳,並自動將賬戶設定為只可平倉,無法再開新倉或加按。
抵押品比率與資產評價
統一保證金下,抵押品並非一視同仁。依據交叉保證金錢包中各資產數量,部分抵押品會按折扣比率(Collateral Ratio)計算,該比例即資產作為抵押時的認可幅度。
幣安於此設計存有關鍵取捨。雖然比特幣、以太幣等主力資產的抵押比率甚高(多數達95%或以上),但交易所亦允許權益型衍生品及帶息穩定幣如 wBETH、BnSOL、USDe 作抵押。
接納這些資產原理看似合理。譬如 wBETH 代表質押以太幣外加累積收益,一枚 wBETH 等於一枚質押ETH及自2023年4月27日起所有收益,其價值會隨收益遞增。
同理,幣安 Staked SOL 代表質押SOL加上獲取的收益,資產可交易、可轉讓,讓用戶持續獲取質押獎勵,同時仍... liquidity
而 Ethena 的 USDe,雖然並非傳統以法幣作抵押的穩定幣,但透過一套複雜的「Delta Neutral」對沖策略來維持與美元掛鉤,當中以已質押的以太幣作為抵押品,在衍生品市場開立相應的空倉以對沖風險。
理論上,即使市場波動時,這類資產都應該保持相對穩定。但現實係,佢哋隱藏住一個致命漏洞。
計價的問題
「統一保證金」系統嘅致命缺陷就在這裡浮現。唔同於其他交易所,Binance 用自家內部訂單簿(即係平台上的買賣盤)嚟為保證金交易定價。當交易量稀薄時,就會出現問題。
對於流動性深且買賣差距細嘅資產,內部定價尚算有效。但對於啱啱推出、流動性低的新資產(例如 PoS 衍生品),內部訂單簿很容易同真實市價脫節。市面一有壓力,這個價差可以瞬間擴大。
Ethena Labs 創辦人 Guy Young(USDe 開發商)曾解釋,USDe「脫鈎」原因,就係因為 Binance 嘅計價系統只依賴自家有限流動性,冇去比對其他主流交易所的價格。
這個設計缺陷造成一個閉環:Binance 以自家訂單簿制定清算價格,訂單簿又可以畀人操控或因集體拋售而受壓,引發進一步清算,更多資產再壓向同一個已經乾涸的訂單簿,進一步形成惡性循環。
就好似計時炸彈一樣,只係等緊「合適」嘅環境或者「適當」嘅攻擊者將佢引爆。
脆弱點與攻擊理論
自 10 月 11 日開始,幣圈分析師一直在追問:今次閃崩究竟係系統毀滅性失誤,定係更黑暗——精明攻擊者精心利用 Binance 結構性漏洞發動既狙擊?
攻擊假說
根據吳說區(Colin Wu)分析,今次崩盤似乎有人早有預謀,目標針對 Binance 同其一個最大做市商。核心弱點就係統一賬戶保證金制度,容許用戶用波動性高的資產作抵押。
一場協同攻擊需要幾個步驟:一,發現漏洞——即識破 Binance 以自家現貨訂單簿,來判斷流動性有限資產的清算價。二,建立可在價格閃崩時賺錢的倉位。三,有足夠資金同協調能力去集中砸盤,令目標資產訂單簿招架不住。
據報當特朗普宣佈關稅計劃後,加密貨幣市場普遍下行,攻擊者就集中向 Binance 狂沽 USDe、wBETH 同 BnSOL,令它們價格只在 Binance 出現大幅脫鈎,其他交易所同鏈上價格卻相當穩定。
攻擊的時間點更為「主動出擊」理論增添佐證——剛好介乎於 Binance 10 月 6 日宣佈會更新預言機價格同 10 月 14 日正式實施之間,令攻擊者有一個明顯的空窗期。雖然 Binance 風控組已察覺有風險,但遲遲未執行措施,結果漏洞就比人捉到。
循環借貸與槓桿放大效應
攻擊成效會被循環借貸(Recursive Lending)進一步放大。所謂循環借貸,即用戶存入抵押品借錢,再以借來的錢買同款抵押品,如此循環,倍數增加槓桿。
如果攻擊者預先用 wBETH、BnSOL、或 USDe 做抵押品疊倉,然後引爆閃崩,清算壓力會自我增強——當抵押品價值下跌,槓桿倉位達清算線,系統被迫在乾涸訂單簿沽貨,進一步壓低價格,引發更多清算。
去中心化預言機攻擊的平行案例
今次手法同以前不少 DeFi(去中心化金融)預言機操控案非常相似。2022 年 10 月,Mango Markets 被人操控預言機拉高原生 MNGO 幣價,再以虛高抵押價值借錢走資超過一億美元。2021 年 8 月,Cream Finance 遭受多次預言機操控,損失逾 1.3 億美元。
Binance 今回則係另一版本——犯人唔係操控外部預言機,而係利用 Binance 自身同等於預言機的訂單冊,變成透過集中砸盤去內部玩價。
反方意見:純屬系統失靈
唔係所有人都同意「組織攻擊」說法。反方理論係設計缺陷加罕見市場壓力交錯,唔涉及刻意操控。
這個觀點認為,Binance 接受有收益(即帶息)資產做抵押,其實本質上誤判了這類資產於動盪市況下的真實行為。比特幣、以太幣橫跨幾十平台,流動性極高;PoS 衍生品同合成穩定幣市場卻細得多,壓力情況下買賣差價可以瞬間擴大,剩下的流動性隨時蒸發。
BitMine 主席 Tom Lee 對 CNBC 指,幣市自四月升 36%,今次回調其實早就應該發生。他說 VIX 波動指數罕有日升 29%,屬歷來百份之一最大單日波幅,形容拋售屬「健康洗牌」。
根據這種分析,特朗普宣佈關稅屬初始震盪。當 BTC 同山寨幣全線插水,Binance 上用 wBETH、BnSOL、USDe 做抵押開槓桿的交易員即時被追保——比特幣已跌 13%,孖展倉本已虧損,轉頭連抵押資產都大幅下調。
大家爭住賣抵押資產去補保證金或直接平倉,結果在 Binance 幾乎無流動性的訂單簿,巿價被急速拉低,進一步引發更多清算,惡性循環,無需任何協同。
正反證據並存
真相好可能係兩邊都有啲道理。有分析指今次事件證據偏向兩種解釋——有人集中做局,同埋時機不幸加上系統弱點同時爆發。
支持攻擊理論的:明顯趁著已知漏洞空窗期出手、出現價格只在 Binance 崩潰、三隻資產貿易量暴增、需要高級理解至識 exploit 內部定價機制。
支持系統失靈一說的:特朗普消息帶動大市急跌、用收益資產抵押的已知缺陷、任何交易所大規模爆倉都有技術困難,以及 Binance 官方只承認系統問題並無認定惡意攻擊。
但無論怎樣,都證明 Binance 的基建無論是靠自然還是人為,都未能頂得住極端壓力測試。
崩潰內幕:三大爆倉資產
10 月 11 日災難核心集中於三款資產,各自代表著不同類型的加密金融創新——亦揭示一旦遇到壓力,複雜金融工程如何可以全面崩壞。
Ethena USDe:合成美金
Ethena USDe 屬合成美元穩定幣,靠原生加密對沖策略維穩,同時可透過 Staking 同衍生品市場提供收益。佢唔同於 USDC 等傳統法幣抵押穩定幣,而係以加密資產例如已質押 ETH,以及 ETH 永續期貨空倉來對沖價格波動。
呢個協議有雙重設計——一係以 ETH、stETH 等抵押保證;二係用 ETH 永續合約開空倉減低價格波幅,令抵押物美金價穩定。收益來源包括 Staking 派息以及杠杆交易者支付的 funding rates。
截至 2025 年 10 月,USDe 市值已超過 120 億美金,成為全球最大穩定幣之一,其飛快擴張同時引發行業欽佩及風險擔憂。
不過質疑 USDe 穩定性的聲音一直存在——若空倉需求突然大於多倉(例如熊市常見),資金費用會轉負,Ethena 需補貼空倉,USDe 有可能跌穿一美元。
10 月 10-11 日,這個隱憂成了現實:USDe 預期 65 美仙閃崩,與 wBETH 和 BnSOL 同時爆煲。但鏈上 Aave 的 USDe 預言機價格仍然一對一,未見大規模清算,僅限 Binance 內部。
呢種價差正正暴露咗風險核心: USDe並沒有在基本層面脫鉤。協議的對沖機制依然正常運作。真正的問題是幣安的內部訂單簿買盤流動性不足,無法承接集中賣壓,導致該交易所價格脫離了市面上其他交易平台的走勢。
Ethena Labs創辦人Guy Young解釋說,這次脫鉤是因為幣安的定價系統過於依賴自身有限的流動性,而不是綜合多個大型交易所的價格。
Wrapped Beacon ETH (wBETH):質押獎勵出錯
Wrapped Beacon ETH是一種能累積價值的流動質押代幣,一個wBETH代表一個被質押的ETH,以及自2023年4月27日以來累積的質押獎勵。用戶可以在ETH質押頁面以零手續費質押ETH或將BETH兌換成wBETH,亦可把wBETH贖回為ETH。
BETH和wBETH的兌換初始比例在2023年4月27日為一比一,但隨著時間過去,隨質押獎勵累積,一個wBETH的價值會逐漸高於一個ETH。該比率每日更新,以反映被質押ETH所產生的獎勵。
wBETH的設計旨在解決權益證明(PoS)機制中的一個根本問題:質押的資產通常被鎖定,流動性低。通過將質押以太坊代幣化為可交易資產,幣安讓用戶在賺取質押獎勵的同時,仍然可以交易、借出或將其用作抵押品。
不過,這項創新同時帶來了新風險——這些風險在10月崩盤時變得明顯。當時幣安的wBETH價格一度急挫至430美元,發生在星期五21:40 UTC,相較同期ETH與USDT現貨價格高於3,800美元,折讓幅度高達88%。
像wBETH這類代幣,本設計用來緊貼其基礎資產的現貨價格。幣安按照現貨價格為這些包裝資產定價。正常情況下,套利者會同時買入低水資產和賣出高水資產,協助市場維持合理價差。
但10月10日的情況並不正常。以太坊在整體市場拋售之下下跌,wBETH受到雙重衝擊。首先,基礎資產本身貶值。其次,當交易員為應付保證金追繳或平倉而爭相賣盤時,他們在幣安的訂單簿拋售wBETH,拋售速度遠快於套利者反應。
包裝代幣崩潰之際,幣安的基礎設施亦告失效,市場莊家難以穩定價格。系統依賴幣安的內部訂單簿,缺乏外部價格參考,使wBETH在混亂期間無法緊貼ETH的實際價值。
Binance Staked SOL (BnSOL):Solana被平倉
Binance Staked SOL代表被質押的SOL及其產生的獎勵,並以可交易及可轉讓的形式存在。該代幣會通過BnSOL兌換SOL的比率,累計質押獎勵,即使用於幣安其他產品或外部DeFi應用亦不受影響。
SOL的質押年化回報(APR)採動態機制,與鏈上質押獎勵同步,約每兩至三日隨Solana每個epoch更新,會視乎整體網絡質押情況及驗證者表現而有所波動。
BnSOL與wBETH具備相同結構特點:設計為同時提供收益和流動性的流動質押衍生品。在10月崩盤時亦表現出同樣的脆弱性。
Binance Staked SOL價格亦曾急跌至34.90美元,遠低於Solana現貨價,同期其他交易所Solana報價在150至160美元徘徊,BnSOL跌穿35美元,折讓超過75%。
如同USDe和wBETH,BnSOL的基本價值沒變——底層質押Solana繼續產生獎勵,協議機制運作正常。這場危機純粹是交易所層面的定價和流動性問題。
共通點:內部定價與外部現實的落差
三種資產的崩盤都源於幣安內部定價與外部市場現實之間的差距。USDe跌至0.65美元,wBETH墮至0.20美元,BnSOL去到0.13美元——但同類資產在其他平台的價格一直高企。
在其他交易所及鏈上,這些資產相對穩定,亦顯示混亂主要限於幣安的流動性。危機地理集中,主要侷限於單一交易所的內部定價系統——或可視為最佳證據,顯示幣安基礎設施某些結構性問題,令崩盤失控。
Oracle價格差距與時機問題
如果10月11日的崩盤屬協同攻擊,時機反映了對幣安風險管理時序的高水平策劃與深厚認知。
八日脆弱窗口
10月6日,幣安宣布將修正其後被利用的定價問題,指出將由自身訂單簿價格改用更可靠的外部數據來源,實施日期訂於10月14日。
這個宣布原旨在安撫用戶,表明幣安正主動處理潛在風險,卻無意中公開了已知漏洞和補救時間表。
攻擊就發生在幣安宣布調整oracle價格和實施間的期間,給予攻擊者一個明確的操作窗口。
對於任何密切留意幣安公告的市場參與者,10月6日這個聲明猶如路線圖:這些特定資產存在定價漏洞,交易所知道,且八天內都不會修復。如果想利用內部定價脆弱位,10月6日至13日就是最佳時機。
Oracle升級欲解決的問題
預定的oracle升級本來旨在透過引入外部價格參考,納入平倉計算,修補核心漏洞。幣安宣布將轉用換算比定價去評估包裝代幣,即不再按波動劇烈及受壓的現貨交易價格,而是按照每個包裝代幣對應的質押比例作定價,反映實際ETH份額。
交易所亦提出三項修訂:將贖回價納入三個受影響代幣的指數計算,為USDe設定價值下限,以及提高風控檢查頻次。
這些改動本可割斷抵押品估值與薄弱、易受操控的內部訂單簿的聯繫,防止連鎖平倉。即使幣安wBETH現貨市場跌至0.20美元,oracle依然會將每單位wBETH認定為特定數量、驗證可查的以太幣。
但10月10日時,這個保護措施尚未生效。
內部警報與風控延誤
幣安風控團隊在崩盤前其實注意到部分敞口,但修正推遲令漏洞敞開,致被利用。
這就引發了對幣安風控流程的隱憂。如果團隊已識別足夠嚴重的漏洞,甚至需公開披露及系統修正,為何維持長達八天的延誤?為何不即時上調風險參數或臨時增加受影響資產的抵押要求?
答案或許在於一個處理每日數十億美元交易現場基建變更的複雜性。足夠測試、分階段推出及多系統協調都需時。但這種現實操作生成了一段具體高風險時期——根據攻擊理論,被人非常精準地利用。
延遲會否本身就是陷阱?
一個較為悲觀的解讀認為,公開宣布八天後才部署安全升級,屬於資訊安全基本常識上的嚴重錯誤。傳統金融領域的主要系統漏洞,會先完成修補才會公開,以免讓人有機可乘。
幣安做法——先公開,再計劃實施——可能出於透明度以及與用戶溝通的考慮。使用相關資產作抵押的用戶理應提前知曉定價機制轉變。但高度透明同時犧牲了操作安全。
無論是熟悉高級戰術者協同把握機會,還是單純市場力量衝擊弱點,公告與落實間這八天,後果都極其嚴重。
系統設計缺陷還是協同攻擊?
對10月11日是遇襲還是結構性故障的討論,反映了更深層次的加密貨幣市場架構、交易所設計,以及金融創新底線的問題。
刻意利用的證據
有多項因素支持協同者刻意利用幣安漏洞的說法。
時機精準:崩盤剛好落在已公告的漏洞窗口期間,顯示有人緊貼幣安公告作出部署。在這特定八天內而非之前或之後發生機會性市況,機率極低。
資產選擇:幣安統一保證金系統眾多抵押品之中,只有三種出現災難性脫鈎。它們正正就是最容易受內部價格操控的資產,原因在於其limited liquidity and reliance on Binance's order book for valuation.
有限流動性,以及依賴Binance交易所嘅訂單簿作為資產估值嘅依據。
Coordinated Selling: Attackers reportedly bombarded Binance with sell orders for USDe, wBETH, and BnSOL, causing their prices to depeg massively on just Binance's exchange while remaining stable elsewhere. This pattern suggests concentrated, coordinated selling rather than diffuse market panic.
協同拋售:有消息指攻擊者向Binance大舉拋售USDe、wBETH同BnSOL,導致呢啲資產嘅價格喺Binance平台大幅脫鈎,而喺其他平台則維持穩定。呢種模式顯示係有組織、集中嘅拋售,而唔係市場恐慌所致。
Profitability: If actors established short positions or removed collateral before initiating the crash, they could profit from both the price collapse and the liquidation cascade. Market rumors suggested that hours before Trump announced 100 percent China tariffs, a 2011 Bitcoin whale opened billion-dollar shorts on BTC and ETH, earning around 200 million dollars as markets plunged.
利潤可圖:如果相關人士喺引發暴跌之前已經開咗空倉,或者提前移除咗抵押品,佢哋可以靠資產價格崩潰同埋清算連鎖賺大錢。根據市場傳言,特朗普宣布對中國徵收一百巴仙關稅之前幾個鐘,一條2011年嘅比特幣鯨魚喺BTC同ETH上開咗數十億美元嘅空單,趁市場暴跌賺咗二億美元左右。
Sophisticated Knowledge Required: Exploiting this vulnerability required understanding Binance's internal pricing mechanisms, margin calculation formulas, and the specific weaknesses of using yield-bearing assets as collateral during volatility - knowledge suggesting insider information or sophisticated market surveillance.
需要高端知識:要利用呢個漏洞,必須好熟悉Binance內部嘅定價機制、保證金計算公式,以及用收益型資產做抵押品喺市場動盪時出現咩問題——呢啲知識有機會源自內部消息,或者係十分專業嘅市場監控能力。
The Case for Systemic Failure
Equally compelling evidence suggests the crash resulted from structural flaws interacting with market stress rather than deliberate manipulation.
同樣有說服力嘅證據指出,今次崩盤主要係結構性缺陷遇上市場壓力所致,而唔係純粹人為操控。
Macro Catalyst: Trump's tariff announcement provided a genuine, exogenous shock to markets. The announcement triggered a selloff of 18 billion dollars in cryptocurrency according to CNN, with effects rippling across all risk assets. This real market event could explain the initial downward pressure without requiring coordination.
宏觀觸發:特朗普公布加徵關稅,為市場帶嚟真正、外來嘅衝擊。據CNN報道,此消息引發咗超過一百八十億美元嘅加密貨幣拋售,影響波及所有高風險資產。呢個真實事件可以解釋初期個市下跌,唔需要有協同作為前提。
Universal Exchange Stress: Binance wasn't the only exchange to experience outages and frozen transactions. Coinbase and Robinhood reported similar issues. This suggests the problem stemmed from unprecedented volume and volatility rather than targeted attack on one platform.
平台普遍現壓力:唔止Binance出現系統癱瘓同交易凍結,Coinbase、Robinhood都出現同樣問題。呢啲現象反映根本原因係成交量激增同市況極端波動,而唔係針對某一個平台嘅攻擊。
Predictable Failure Mode: Financial engineers have long understood that accepting volatile or illiquid assets as collateral creates pro-cyclical risk. During stress, collateral loses value precisely when it's needed most, forcing liquidations that create more stress. No coordination is required for this dynamic to spiral out of control.
可預見失效模式:金融工程師早就知道,用高波動性或流動性低嘅資產做抵押,會產生順周期風險。市況跌得最勁嗰陣,抵押品偏偏會大跌價,逼大家被動清算,造成進一步的賣壓。整個過程無需協同操控,都可以自動惡化。
Arbitrage Failures: Market makers and arbitrageurs, who normally prevent large price discrepancies between venues, faced their own liquidity and risk management constraints during the chaos. Their inability to close the gaps between Binance prices and external markets could reflect overwhelming volatility rather than deliberate manipulation.
套利機制失靈:平時會做價差套利嘅莊家同套利者,喺今次混亂之下,自己都捱唔住流動性危機同風險限制,無法平抑Binance同其他市場資產價格差距。咁嘅情況反映出極端波動性,而非人為操控。
Insufficient Infrastructure: Binance's system delays and transaction failures, while criticized by users, are consistent with inadequate infrastructure for handling extreme volume spikes. Binance stated that platform modules briefly experienced technical glitches, and certain assets had depegging issues due to sharp market fluctuations.
基建不足:Binance系統塞車、交易失敗,雖然畀用戶鬧爆,但正正係平台缺乏應對極端成交量嘅基礎設施所致。Binance聲稱部份平台模組出現短暫技術故障,部份資產因市場急劇波動而脫鈎。
Hybrid Explanations
The most plausible explanation may involve elements of both theories. Natural market stress provided the initial catalyst - Trump's tariff announcement was real, Bitcoin's decline was genuine, and trading volumes genuinely spiked across all exchanges.
最合理嘅解釋應該係兩種理論都有影響。首先,市場本身已經有壓力——特朗普真係公布咗關稅,比特幣也確實下跌,交易量全線爆升。
But sophisticated actors may have recognized that this macro event created ideal conditions for exploiting Binance's known vulnerability. By adding concentrated selling pressure on the three vulnerable collateral assets at the precise moment when the exchange's systems were already stressed, they could amplify natural market forces into a catastrophic cascade.
但有實力嘅玩家可能睇中咗呢個宏觀市況下Binance嗰個已知弱點,專門喺交易所壓力最大嘅時候,針對三種抵押品大手沽貨,令本來嘅市場驚惶演變成災難級連鎖反應。
This hybrid model doesn't require advance knowledge of Trump's announcement or the ability to create market-wide panics from scratch. It simply requires:
呢種混合型操縱手法,唔使提前知特朗普出咩招,更唔需要自己「造市」嚟製造恐慌。只要做到:
-
Monitoring Binance's announcements to identify the vulnerability window
-
盯緊Binance公告,捕捉到漏洞窗口
-
Positioning to profit from a price collapse in the three vulnerable assets
-
預早部署,可以喺三種資產崩價時賺錢
-
Waiting for any significant market downturn to provide cover
-
等待重大市場回調,作為入手時機
-
Executing concentrated selling during the chaos to overwhelm internal order books
-
喺最亂嗰陣瘋狂沽售,擊潰平台訂單簿
-
Allowing the recursive liquidation spiral to do the rest
-
等清算鏈反應自動發揮威力
Whether purely coordinated attack or opportunistic exploitation of structural weakness during natural market stress, the result was the same: Binance's infrastructure failed catastrophically, and traders paid the price.
無論係純粹協同攻擊,定係趁市況差搵平台漏洞嚟搞事,結論都一樣:Binance基建出咗大問題,最終所有交易員都要埋單俾錢。
Regulatory and Industry Implications
Crypto.com CEO Kris Marszalek called for regulators to investigate exchanges with high liquidation volumes, noting that 20 billion dollars in losses hurt many users.
Crypto.com行政總裁Kris Marszalek呼籲監管機構調查清算量極大嘅交易所,指二十億美元損失重創好多人。
The October 11 crash has renewed calls for enhanced regulatory oversight of cryptocurrency exchanges, particularly regarding:
10月11日事件令社會再次要求加強對加密貨幣交易所嘅監管,特別係以下幾方面:
-
Collateral requirements: Should exchanges face restrictions on accepting volatile or illiquid assets as margin collateral?
-
抵押要求:交易所有冇需要限制高波動性或流動性差嘅資產充當保證金?
-
Pricing methodology: Should regulators mandate the use of external oracles or composite price feeds rather than internal order books?
-
定價方法:監管機構應否規定平台必須用外部預言機或綜合報價,而唔可以只靠自家訂單簿?
-
Transparency requirements: Should exchanges disclose known vulnerabilities more carefully, or implement fixes before public announcement?
-
透明度要求:平台應唔應該對已知漏洞更公開披露,或者先修正再公布?
-
Insurance funds: Are current exchange insurance funds adequate to cover losses from extreme events?
-
保險金:平台現有保險基金足唔足夠應付極端事件帶來嘅損失?
-
System resilience: Should exchanges face uptime and performance requirements during high-volume periods?
-
系統強韌性:平台喺高交易量時段要唔要有正常運作同效能保證?
These questions will likely shape the evolution of cryptocurrency regulation in the coming years, as policymakers seek to prevent future incidents while preserving the innovation that makes crypto markets distinctive.
呢啲問題好可能會影響加密貨幣監管未來幾年嘅發展,當局得平衡好防災同創新兩頭。
Market-Wide Impact and Contagion
While the most severe damage concentrated on Binance, the October 11 crash sent shockwaves through the entire cryptocurrency ecosystem, raising questions about market structure and interconnectedness.
雖然損失最嚴重發生喺Binance,但呢次10月11日崩盤都令成個加密貨幣生態圈震撼,引發對市場結構同連結性嘅反思。
The Scope of Losses
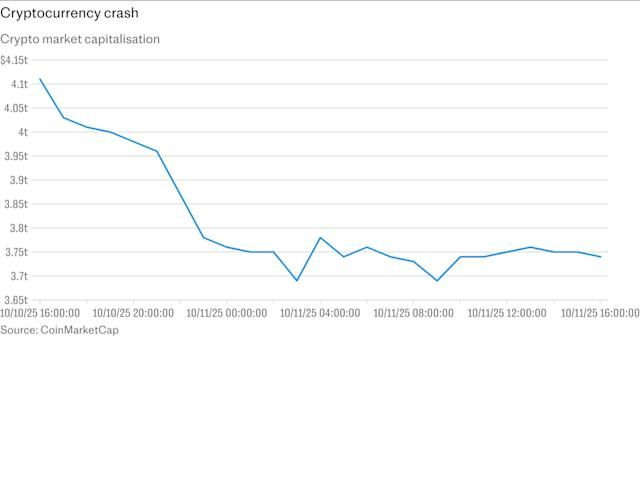
The crash resulted in 19 billion dollars liquidated on the crypto market in 24 hours, with more than 1.6 million traders liquidated. CoinGlass data showed that 7 billion dollars was flushed in a single hour during the peak of the crisis.
今次崩盤24小時內加密市場共被清算190億美元,超過160萬名交易員被爆倉。根據CoinGlass數據,危機高峰時單一小時就有70億美元被清算。
Bitcoin, having reached an all-time high of 125,000 dollars earlier in the week, fell to around 105,000 dollars before partially recovering to trade in the 110,000 to 115,000 dollar range. Ethereum fell 12.15 percent, Binance Coin dropped 9.87 percent, and XRP plunged 13.17 percent.
比特幣當周一度見125,000美元歷史高位,之後急插落105,000美元,隨後反彈至110,000至115,000美元區間徘徊。以太坊跌咗12.15%,幣安幣跌9.87%,XRP插13.17%。
Altcoins bore the brunt of the selloff. Altcoins tumbled between 30 percent and 80 percent as liquidations mounted. Some tokens experienced flash crashes to near-zero values before rebounding.
山寨幣成為重災區,大部分山寨幣淨跌幅介乎30%至80%,部份代幣一度閃崩見零,隨後先反彈。
Contagion or Containment?
Despite the severity of losses, the crisis displayed both concerning contagion effects and surprising resilience in certain areas.
雖然損失慘重,但市場一方面出現咗連鎖反應跡象,另一方面某啲環節又顯現一定韌力。
A recent market meltdown exposed vulnerabilities in centralized price oracles, such as Chainlink and Pyth, which feed dollar prices to exchanges, DEXs, and DeFi apps. While longs were liquidated and shorts hit liquidity boundaries, blockchains themselves remained stable, handling DeFi trades and swaps flawlessly.
今次市況考驗咗集中式預言機(如Chainlink、Pyth)為交易所、去中心化交易所(DEX)同DeFi應用提供報價嘅可靠性。雖然好多多頭被清算、淡倉亦打到無貨出,但底層區塊鏈系統依然暢順,DeFi產品照常撮合同兌換。
This divergence reveals an important characteristic of the October 11 crash: it was primarily an exchange-level crisis rather than a protocol-level failure. Ethereum continued processing transactions normally. Solana's validators kept producing blocks. DeFi protocols on multiple chains functioned as designed.
呢種分歧突顯咗10月11日崩盤一個本質特點:事件主要係交易所軟件層出事,而唔係區塊鏈協議層失效。以太坊嘅交易照舊處理,Solana驗證器一直有生產區塊,多條鏈上DeFi協議都無出現停擺。
The crisis remained largely confined to centralized exchanges, with Binance bearing the most extreme impact due to its specific infrastructure vulnerabilities. This containment suggests that cryptocurrency markets have developed some resilience against systemic collapse, even as individual platforms remain vulnerable.
今次危機主要局限於中心化交易所,其中Binance因為本身有明顯結構性問題,受到最大衝擊。事件未有外溢至整個生態反映咗市場對系統性崩潰具某程度抗壓力,雖然單一平台依然好易出事。
Impact on DeFi and Stablecoins
As liquidations mounted, many users of centralized crypto exchanges reported failed orders, with some traders unable to close positions before blowups. This experience drove renewed interest in decentralized alternatives.
大量清算期間,好多中心化交易所用戶報告訂單失敗,有啲人甚至未能趁爆倉前平倉,令大家再次關注去中心化方案。
In the wake of the chaos, Binance acknowledged disruptions and said it would compensate losses directly caused by system failures. The promise of compensation may partially mollify affected users, but the crisis has intensified the long-standing debate over custody, counterparty risk, and the trade-offs between centralized and decentralized trading venues.
風波後,Binance承認平台出現問題,承諾會賠償因系統問題直接造成嘅損失。雖然有賠償承諾可以平息部分怨氣,但今次事件令關於資產託管、對手風險、中心化同去中心化交易所取捨嘅討論再度升溫。
For stablecoins, the crash provided a mixed stress test. Traditional fiat-backed stablecoins like USDT and USDC maintained their pegs throughout the crisis, demonstrating the value of simple, well-collateralized designs during extreme volatility. BUSD remained hard-pegged during the crisis, in contrast to the synthetic and yield-bearing alternatives that collapsed.
對穩定幣而言,這次事件也算係一場複雜嘅壓力測試。傳統法幣抵押的穩定幣如USDT、USDC,全程保持掛鉤,反映資產簡單透明同足額抵押喺極端環境下夠紮實。BUSD一樣頂得住,但同期倒下的多數都係合成型或者帶收益嘅新派穩定幣。
USDe's failure to maintain its peg on Binance, even as it held firm on other venues and in DeFi protocols, highlighted the risks of algorithmic and synthetic stablecoins during liquidity crises - but also suggested these risks may be more exchange-specific than protocol-level.
至於USDe雖然喺其他平台同DeFi協議維持咗掛鉤,但偏偏喺Binance大幅脫鉤,突顯算法型、合成型穩定幣遇上流動性危機時有咩風險——而且呢類風險更多係交易所層面所致,而非全網級別。
Market Sentiment and Recovery
Tom Lee, chairman of BitMine, characterized the market pullback as overdue after a 36 percent gain since April, calling the sell-off a healthy shakeout and suggesting short-term returns could turn positive soon.
BitMine主席Tom Lee認為,市場自四月以來已升咗36%,今次回調其實係健康調整,短線可能很快重拾升勢。
Some analysts suggested that while retail fear dominated, institutions were quietly accumulating, mirroring the pattern seen after the March 2020 COVID crash, which later sparked one of the biggest altcoin seasons in history.
部分分析指,雖然小散愈嚟愈驚,機構反而乘勢默默吸貨,類似2020年疫情股災之後,當時爆咗史上最大規模嘅山寨幣牛市。
By October 12-13, markets had partially stabilized. Bitcoin recovered from its lows, trading back above 112,000 dollars. Many altcoins retraced a portion of their losses. Trading volumes remained elevated but orderly, suggesting the panic phase had passed.
到10月12至13日,市場已經部份回穩。比特幣重上112,000美元以上,好多山寨幣都反彈返一大截。成交量雖然仲高,但秩序已經回復,市場恐慌基本過咗。
However, the longer-term impacts on market structure and investor confidence remain uncertain. The crash served as a harsh reminder of the risks inherent in leveraged cryptocurrency trading and the potential for infrastructure failures during stress.
但係長遠嚟講,市場結構同投資者信心會唔會受損,依家仲難定論。今次事故絕對係一個重要警號:加密貨幣槓桿交易有幾大風險,平台基建失誤隨時爆煲。
Expert Commentary and Regulatory Implications
The October 11 crash has prompted
10月11日崩盤之後,引發咗......widespread analysis from industry observers, raising fundamental questions about exchange design, risk management, and the role of regulation in cryptocurrency markets.
行業觀察者廣泛分析,提出了關於交易所設計、風險管理,以及監管在加密貨幣市場中角色的根本問題。
Risk Management Failures
Analysts pointed to a clear failure in how margin collateral and liquidation pricing were structured, flaws that made the system easy to exploit.
分析人士指出,保證金抵押品及清算價格設定上存在明顯失當,令系統容易被人利用。
The choice of margin collateral and the design of liquidation pricing became key points tested by this market event, with experts noting that financial product innovation requires greater prudence, and exchanges still have much to improve in their risk management systems.
今次市場事件正正考驗了交易所如何選擇保證金抵押品及設計清算價格,專家認為金融產品創新需要更審慎,交易所在風險管理系統上仍有很大改進空間。
The crisis exposed several specific risk management failures:
- Collateral Acceptance Standards: Binance's decision to accept proof-of-stake derivatives and yield-bearing stablecoins as margin collateral without accounting for their liquidity characteristics during stress created unnecessary systemic risk.
- Pricing Methodology: Relying on internal order book prices for assets with limited liquidity created a closed loop vulnerable to manipulation or simply inadequate for calculating true market value during volatility.
- Vulnerability Disclosure: Publicly announcing a known security issue eight days before implementing the fix created a window of exploitation that sophisticated actors could monitor and potentially weaponize.
- Insurance Fund Adequacy: While Binance deployed 188 million dollars from its insurance fund during the crisis, estimated losses ranged between 500 million and 1 billion dollars, raising questions about whether current insurance mechanisms provide adequate protection.
這場危機揭示出數個具體的風險管理失誤:
- 抵押品接受標準:Binance 選擇接受權益證明衍生品及帶息穩定幣作為保證金抵押品,卻沒有考慮到這些資產在市場壓力下的流動性特性,為系統帶來了不必要的系統性風險。
- 價格制定方法:依賴內部訂單簿價格來估算流動性有限的資產,形成封閉循環,容易被操控,亦難以反映市場震盪時的真正價值。
- 漏洞公開披露:在落實修補前八日公開已知的安全漏洞,給了有心人觀察和潛在利用的「空窗期」。
- 保險基金充足性:雖然 Binance 在今次危機動用了 1.88 億美元保險基金,但估算損失達 5 億至 10 億美元,引發外界質疑現有保險機制是否足夠保障用戶。
Calls for Enhanced Oversight
The magnitude of losses and the nature of the crash have intensified calls for regulatory intervention in cryptocurrency exchange operations.
巨額損失及事件本身的特性,加劇了要求政府介入加密貨幣交易所監管的聲音。
Crypto.com CEO Kris Marszalek called for regulators to investigate exchanges with high liquidation volumes, noting that 20 billion dollars in losses hurt many users.
Crypto.com 行政總裁 Kris Marszalek 呼籲監管機構調查高清算量的交易所,指出今次損失達 200 億美元,對大量用戶造成傷害。
Specific regulatory proposals emerging from industry discussions include:
- Standardized Risk Disclosures: Requirements for exchanges to clearly disclose how they calculate liquidation prices, what assets are accepted as collateral, and the specific risks of using illiquid assets in margin systems.
- External Oracle Requirements: Mandating that exchanges use external, manipulation-resistant price feeds for liquidation calculations rather than relying solely on internal order books.
- Collateral Concentration Limits: Restricting the percentage of margin collateral that can consist of illiquid or volatile assets to prevent cascading liquidations.
- Stress Testing and Scenario Analysis: Requiring exchanges to conduct and publish regular stress tests showing how their systems would perform during extreme market events.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts: Enhanced surveillance systems to detect unusual trading patterns that might indicate manipulation or coordinated attacks.
行業討論中提出的具體監管建議包括:
- 標準化風險披露:要求交易所清楚披露如何計算清算價格、接受哪些資產作爲抵押品,以及在保證金系統使用非流通資產的具體風險。
- 外部預言機要求:強制交易所使用外部、防範操控的價格數據源作清算計算,而不是只依賴內部訂單簿。
- 抵押品集中度限制:限制保證金抵押品中非流通或高波動資產所佔比例,以防止連鎖式清算。
- 壓力測試及場景分析:要求交易所定期執行及公開壓力測試,展示系統在極端市場情況中的表現。
- 實時監察及警示:強化監控系統,偵測不尋常交易模式,及早發現潛在操縱或協同攻擊。
The Precedent of Traditional Finance
Regulators examining the October 11 crash have relevant precedents from traditional financial crises to draw upon.
監管機構審視 10 月 11 日事件時,可借鏡傳統金融界的相關先例。
The 2008 financial crisis revealed similar dynamics around collateral valuation during stress. Mortgage-backed securities that had traded at par suddenly became illiquid, forcing fire sales that created spiral effects throughout the banking system. Regulatory responses included enhanced collateral haircuts, stress testing requirements, and restrictions on accepting complex securities as margin.
2008 年金融危機正正揭示了壓力情況下抵押品估值的同類問題。以往按面值交易的按揭支持證券突然失去流動性,被迫割價沽售,引發銀行體系連鎖反應。監管方隨後加強了抵押品減值(haircut)、壓力測試及限制複雜證券作為抵押品。
The 2010 Flash Crash demonstrated how automated trading systems can amplify volatility during periods of stress. Subsequent regulations introduced circuit breakers, revised market maker obligations, and enhanced monitoring to prevent similar incidents.
2010 年閃電崩盤則反映,當市場受壓時自動化交易系統可加劇波動。事後監管採用熔斷機制、修訂做市商職責及加強監管,以防止同類事情重演。
The lessons from traditional finance suggest that cryptocurrency exchanges may face increasing regulatory requirements around risk management, transparency, and system resilience - particularly for platforms offering leveraged trading and accepting complex assets as collateral.
傳統金融業的經驗指出,加密貨幣交易所(特別是提供槓桿交易和複雜抵押品的)將面對更嚴格的風險管理、透明度及系統韌性的監管要求。
Industry Self-Regulation vs. Government Oversight
The cryptocurrency industry faces a choice between proactive self-regulation and reactive government intervention.
加密貨幣行業正面對主動自律與被動接受政府監管之選擇。
Some exchanges have already announced enhancements following the October 11 crash. Binance implemented its planned oracle updates and compensation program. Other platforms have reviewed their own collateral policies and risk management frameworks.
部分交易所已因應 10 月 11 日事件宣佈提升措施,Binance 落實了預言機更新及賠償計劃,其它平台亦審視自身的抵押品政策與風險管理架構。
However, voluntary industry improvements may not satisfy regulators or protect users adequately. The concentration of risk in large centralized exchanges, combined with the potential for cascading failures across markets, suggests that comprehensive regulatory frameworks may be inevitable.
不過,業界自發改進或未必能令監管方滿意,亦不足以全面保障用戶。風險集中於大型中心化交易所,加上潛在的市場連鎖反應,意味著更全面的監管框架很可能無可避免。
The key question is whether regulatory intervention can preserve innovation while preventing catastrophic failures. Overly restrictive rules could drive trading activity to unregulated offshore venues or entirely decentralized platforms, potentially increasing rather than decreasing systemic risk. Finding the right balance between safety and innovation will challenge policymakers in the years ahead.
關鍵問題在於監管能否在防止災難性失敗同時,保留創新空間。過度嚴苛的規則或會驅使交易活動轉移到無監管的離岸市場或完全去中心化平台,反令系統性風險增加而非減少。如何在安全與創新之間取得平衡,將成未來政策制定的重要挑戰。
Comparative Lessons from Past Crises
The October 11, 2025 crash joins a growing list of catastrophic events in cryptocurrency history, each offering lessons about the interaction between innovation, risk, and system design.
2025 年 10 月 11 日的崩盤,成為加密貨幣歷史上又一嚴重大事件,每一次災難都為創新、風險及系統設計的互動提供教訓。
The Luna-UST Collapse (May 2022)
The question of whether USDe is truly backed one-to-one remains hanging. The Luna-UST collapse proved how bad things can get when pegs fail. Back then, Binance lost money defending UST near 70 cents.
至今 USDe 是否真正一對一資產儲備仍存疑問。Luna-UST 的崩潰證明當錨定失效,後果可以有多嚴重。當時 Binance 為捍衛 UST 幣值接近 70 美分亦有損失。
The Terra Luna ecosystem's implosion in May 2022 provides the most direct parallel to Binance's October 11 crisis. Terra's algorithmic stablecoin UST maintained its dollar peg through a mechanism involving minting and burning the LUNA token. When confidence wavered and selling pressure intensified, the system entered a death spiral: UST lost its peg, triggering LUNA issuance to restore it, flooding the market with new LUNA tokens, destroying LUNA's value, further undermining confidence in UST, and accelerating the collapse.
2022 年 5 月 Terra Luna 生態系統的爆破,與今次 Binance 危機最為相似。Terra 的算法穩定幣 UST 透過鑄造及銷毀 LUNA 代幣來維持美元掛鉤。一旦信心動搖、拋售加劇,系統即進入死亡螺旋:UST 失去錨定,引發 LUNA 鑄幣試圖回復價值,結果大量 LUNA 湧入市場,幣值滅頂,進一步打擊信心,令崩潰加速。
The parallel to October 11 lies in the feedback loops. In Terra, loss of peg triggered issuance, which accelerated the collapse. On Binance, collateral devaluation triggered liquidations, which caused more selling, which devalued collateral further, creating a similar spiral.
兩者相似點在於負面反饋循環:Terra 方面,失去錨定引發新幣發行,反加速災難;Binance 方面,抵押品貶值觸發清算,造就更多拋售,抵押進一步貶值,出現近似螺旋。
Both crises revealed the danger of closed-loop systems where the mechanism designed to restore stability can amplify instability under stress. Terra's fix - burning LUNA to restore UST - created more problems than it solved. Binance's system - liquidating collateral to protect margin requirements - similarly intensified the very crisis it was designed to prevent.
兩場危機均顯示出封閉循環系統的風險:原用於維持穩定的機制,在壓力下反而加劇問題。Terra 將銷毀 LUNA 當作 UST 的解決方法,結果引發更大危機;Binance 以清算作爲防守機制,同樣無意中加劇本應避免的危機。
The key difference: Terra's collapse stemmed from fundamental protocol design flaws. The system was mathematically destined to fail under sufficient stress. Binance's crisis reflected infrastructure and operational shortcomings rather than unavoidable protocol failures. Better pricing mechanisms, adequate liquidity, and proper risk management could have prevented or mitigated the cascade.
最大分別在於,Terra 崩潰根本起因是協議設計失誤,從數學上必然會在壓力下爆煲;Binance 危機則主要涉及基建和營運層面的漏洞,只要有合適的定價機制、流動性及風險管理,是有望預防或減輕災情。
Mango Markets Oracle Manipulation (October 2022)
In October 2022, a trader exploited Mango Markets, a Solana-based decentralized exchange, by manipulating the oracle price for its native MNGO token. The attacker built large positions, used those positions to manipulate the token's price upward through thin order books, borrowed against the artificially inflated collateral value, and withdrew more than 100 million dollars before the protocol could respond.
2022 年 10 月,一名交易員在 Solana 生態的去中心化交易所 Mango Markets 利用預言機價值操縱本地代幣 MNGO。他先建立大型倉位,利用缺乏流動的訂單簿推高價格,令自己的抵押品表面暴升,再大額借貸並套現超過 1 億美元,協議設計未及時反應。
The Mango attack demonstrates how oracle manipulation can create leverage out of thin air. By controlling the price feed used for collateral valuation, the attacker made worthless positions appear valuable enough to support massive loans.
Mango 事件證明,操控預言機即可「平地起槓桿」:攻擊者只需控制用於抵押估值的價格來源,就可以將無價值資產包裝成能支持巨額貸款的「黃金」。
The October 11 Binance crash, whether coordinated or not, involved similar dynamics. Binance's reliance on internal order book prices for collateral valuation created a closed system where concentrated selling could drive artificial price movements disconnected from external market reality. The primary difference: Mango involved deliberately manipulating prices upward to borrow more, while the alleged Binance attack manipulated prices downward to trigger liquidations.
今次 10 月 11 日 Binance 事件,無論是否有組織,都有近似情況。Binance 用內部訂單簿作抵押估值,令集中拋售時價格可脫離外部市場現實。主要分別在於,Mango 是故意推高價格以放大借貸,而今次 Binance 事件則指向下壓價格以觸發清算。
Both incidents highlight the critical importance of using robust, manipulation-resistant price oracles for any system involving collateralized lending or margin trading.
兩件事皆說明任何涉及抵押借貸或保證金交易的系統,必須採用堅實、防範操縱的價格預言機。
FTX Collapse (November 2022)
The FTX exchange's spectacular failure in November 2022 revealed how concentrated risk and inadequate separation of customer funds from exchange operations could lead to catastrophic losses.
2022 年 11 月 FTX 交易所的轟然倒閉,暴露出風險集中的問題,及用戶資金與交易所運作未有嚴格劃分,會導致災難性損失。
While FTX's collapse stemmed primarily from fraud and misappropriation of customer funds, it shares with the October 11 Binance crash a common thread: concentrated risk in large centralized platforms creates systemic vulnerabilities that can cascade through markets when confidence breaks.
雖然 FTX 垮台主因是欺詐及挪用客戶資金,但與 Binance 事件共通點是:大型中心化平台的風險集中,一旦信心動搖,所產生的系統性漏洞可波及整個市場。
FTX demonstrated that even well-regarded, heavily-used platforms can harbor critical weaknesses invisible to users until crisis strikes. The parallels to Binance are imperfect - there's no evidence of fraud or misappropriation in the October 11 event - but both cases reveal how dependent cryptocurrency markets remain on the operational integrity of centralized intermediaries.
FTX 事件證明,即使再受歡迎、用戶眾多的平台也可能潛藏用戶難以察覺的重大問題,直到危機爆發才顯現。Binance 今次並未涉及欺詐或挪用,但二者都反映加密幣市場高度依賴中心化中介機構的營運誠信。
Cream Finance Repeated Exploits (2021)
Cream Finance, a DeFi lending protocol, suffered multiple exploits in 2021 that collectively drained more than 130 million dollars. Most involved flash loan attacks combined with oracle manipulation or reentrancy vulnerabilities.
2021 年,DeFi 借貸協議 Cream Finance 多次被攻擊,總損失超過 1.3 億美元,大多涉及閃電貸結合預言機操縱或重入漏洞。
The relevance to October 11 lies in the recurring theme: complex financial systems built on fragile foundations become vulnerable to sophisticated exploitation. Cream's fundamental protocol design wasn't necessarily flawed, but the implementation details - how prices were
(原文未完,暫停於此)calculated, which assets were accepted as collateral, and how quickly the system could respond to anomalies - created opportunities for attackers.
計算方式、接受哪些資產作為抵押品,以及系統回應異常情況的速度,都為攻擊者製造了可乘之機。
Binance's October 11 crisis similarly reflects the gap between design intent and implementation reality. In theory, accepting yield-bearing assets as collateral makes sense if properly risk-adjusted. In practice, the details of pricing methodology, liquidity requirements, and stress scenario planning determined whether the system could withstand volatility.
Binance於10月11日發生的危機,亦同樣反映設計意圖與實際執行之間的落差。理論上,如果風險調整得當,接受有收益資產作為抵押品是合情合理的。但現實上,評價方法的細節、流動性要求及壓力情境規劃,才決定了系統能否抵擋波動。
The Recurring Pattern: Innovation Outpacing Risk Management
重複出現的模式:創新遠超過風險管理
These historical crises share a common pattern: financial innovation in cryptocurrency markets consistently outpaces the development of robust risk management frameworks.
這些歷史危機有一個共同點:加密貨幣市場的金融創新一再超越穩健風險管理框架的發展速度。
Terra pioneered algorithmic stablecoins without fully stress-testing the death spiral scenario. Mango built a sophisticated derivatives platform without adequately securing its price oracles. FTX scaled to become the second-largest exchange without implementing proper controls on fund movements. Cream pushed the boundaries of DeFi lending without anticipating complex attack vectors.
Terra率先推出算法穩定幣,但未有充分測試死亡螺旋的壓力情景。Mango建立了先進的衍生品平台,但未有為價格預言機提供足夠保障。FTX成為第二大交易所的同時,卻沒有完善的資金流動管控。Cream則在DeFi借貸領域不斷突破,卻未能預計複雜的攻擊手法。
And Binance, seeking to offer maximum capital efficiency through unified margin across diverse assets, created a system where collateral valuation could become disconnected from market reality during stress.
至於Binance,為了以統一保證金制度提升資本效率,卻令壓力情況下抵押品價值與市場實際情況脫節。
The lesson isn't that innovation should cease. Liquid staking derivatives, synthetic stablecoins, and cross-margin systems all offer genuine benefits when properly implemented. The lesson is that each innovation creates new failure modes that must be anticipated, tested, and guarded against before they cause catastrophic losses.
教訓並不是創新應該停止。只要落實得宜,流動質押衍生品、合成穩定幣、交叉保證金制度等都是有實質好處的。真正的教訓是,每一次創新都會帶來新的失敗型態,必須預先預計、測試並防範,否則就會釀成災難性損失。
Key Terms Explained
重要術語解釋
Understanding the October 11 crash requires familiarity with several technical concepts that define modern cryptocurrency trading. Here are concise explanations of the key terms central to this event.
要理解10月11日的崩盤,首先要熟悉幾個主導現代加密貨幣交易的技術概念。以下是對相關主要術語的簡明解釋:
Proof-of-Stake Derivatives: These are tokenized representations of cryptocurrency staked in proof-of-stake blockchains. When users stake assets like Ethereum or Solana, they lock those tokens to help secure the network and earn rewards. Proof-of-stake derivatives like wBETH and BnSOL make this staked value liquid and tradable, allowing stakers to use their assets while still earning rewards. The derivatives' value typically equals the underlying staked asset plus accumulated rewards.
權益證明(PoS)衍生品:這類產品是將在權益證明區塊鏈質押的加密資產代幣化。用戶質押例如Ethereum或Solana等資產時,實際上是鎖定這些代幣,用以協助保護網絡並賺取回報。像wBETH和BnSOL這些權益證明衍生品,就令被質押的價值變得流通及可交易,用戶可以邊持有邊賺取獎勵。這些衍生品的價值,通常等於底層質押資產加上累積回報。
Yield-Bearing Stablecoins: Unlike traditional stablecoins backed by dollars in bank accounts, yield-bearing stablecoins like Ethena's USDe generate returns for holders. USDe maintains its dollar peg through delta-neutral hedging - holding crypto collateral while simultaneously shorting that same crypto in derivatives markets, neutralizing price volatility. The yield comes from staking rewards on the collateral and funding rates from the derivatives positions. These stablecoins offer advantages over non-yielding alternatives but introduce additional complexity and risk.
有收益穩定幣:這類穩定幣(如Ethena的USDe)與傳統由銀行存款美元支持的穩定幣不同,持有人可以賺取回報。USDe透過「Delta中性對沖」維持其美元掛鈎——即同時持有加密資產作為抵押,並在衍生品市場做空同一資產,以抵消價格波動。收益來自抵押資產的質押回報,以及衍生品頭寸的資金費率。這些穩定幣比傳統無息穩定幣有優勢,但同時帶來更多複雜性和風險。
Margin Collateral: This refers to assets deposited to secure leveraged trading positions. When traders borrow funds to amplify their positions, they must post collateral that the exchange can liquidate if the trade moves against them. Margin collateral acts as a buffer protecting lenders from borrower defaults. The type of assets accepted as collateral and how those assets are valued critically affects system stability during volatility.
保證金抵押品:指用戶為槓桿交易而存入作擔保的資產。當交易者借入資金擴大倉位時,必須提供交易所可隨時變現的抵押品,以防交易虧損。保證金抵押品就像為借出方設下的保護緩衝。至於接受哪些資產作抵押,以及評價的方法,直接影響系統在波動市況下的穩定性。
Liquidation: When a leveraged position loses too much value, the exchange automatically closes it by selling the collateral to repay the borrowed funds. This process, called liquidation, prevents borrowers from owing more than their collateral is worth. Liquidations occur automatically when predetermined thresholds are breached. During the October 11 crash, cascading liquidations created a feedback loop where forced selling drove prices lower, triggering more liquidations.
強制平倉(清算):當槓桿倉位損失過多時,交易所會自動平掉持倉,把抵押品賣出,用以償還借入資金。這個過程稱為清算,目的是避免借款人欠下超過其抵押品價值的債務。當預設門檻被觸發時,清算會自動進行。10月11日崩盤期間,連環清算令拋盤自我強化,價格愈跌愈快,引發更多清算。
Oracles: In cryptocurrency systems, oracles provide external data to smart contracts and trading systems. Price oracles specifically supply information about asset values from various sources. Oracle design proves critical because systems rely on these feeds to calculate collateral values, trigger liquidations, and execute automated strategies. Poorly designed oracles can be manipulated or may fail to reflect true market conditions, as occurred with Binance's reliance on internal order books.
價格預言機:在加密貨幣系統中,預言機為智能合約和交易系統提供外部資料,價格預言機專門匯集多方資產價格資訊。預言機設計至關重要,因為系統依賴這些資料計算抵押品價值、觸發清算及執行自動化策略。若設計不當,預言機可被操控,或未能真實反映市況,就如Binance僅依賴自家訂單簿那次一樣。
Recursive Borrowing: This strategy involves depositing collateral, borrowing against it, using borrowed funds to acquire more collateral, depositing that additional collateral, and repeating the cycle. Recursive borrowing creates highly leveraged exposure with relatively little initial capital but amplifies both gains and losses. During crashes, recursive positions face compounding liquidations as each layer of borrowed collateral loses value.
遞歸借貸:即先存入抵押品借錢,然後再用借來的錢買更多抵押品,不斷重複。這種方式可用相對少的本金,提高槓桿倍數,大大放大潛在收益和損失。當市況崩潰時,這種倉位會因多層重疊而引發連環強平。
Hard Pegs vs. Soft Pegs: A hard peg means an asset maintains a fixed exchange rate through direct redemption mechanisms or regulatory guarantees. For example, BUSD maintained a hard peg because it could be redeemed one-to-one for dollars. A soft peg uses market mechanisms, arbitrage, or algorithmic adjustments to maintain approximate value. USDe uses a soft peg through delta-neutral hedging. During extreme stress, soft pegs can break while hard pegs generally hold - as occurred on October 11 when BUSD remained stable while USDe depegged on Binance.
硬掛鈎 vs. 軟掛鈎:硬掛鈎指資產通過直接兌換機制或監管保證保持固定兌換率。例如,BUSD可1:1兌換美元,因此屬於硬掛鈎。軟掛鈎則透過市場、套利或算法機制來維持近似價值。USDe就是用Delta中性對沖來維持軟掛鈎。遇到極端壓力時,軟掛鈎隨時斷裂,而硬掛鈎一般能維持——正如10月11日BUSD保持穩定,USDe在Binance脫鈎。
Unified Margin: Also called portfolio margin or cross-margin, unified margin allows traders to use their entire portfolio as collateral for positions across multiple markets and products. Rather than siloing margin requirements for each position, unified margin calculates risk holistically, enabling greater capital efficiency. The October 11 crash exposed how this efficiency comes at the cost of interconnected risk - problems in one part of the portfolio can trigger liquidations across all positions.
統一保證金:又叫組合保證金或交叉保證金,允許交易者用整個資產組合作為多市場、產品的抵押品。不再每個倉位單獨計算保證金,而是整體考慮風險,提高資本效率。10月11日的崩盤揭示了這種效率其實令風險互相連繫,一處出事,可觸發全盤清算。
Delta-Neutral Hedging: This strategy maintains exposure to non-price factors like yield or funding rates while eliminating exposure to price movements. For example, USDe achieves delta neutrality by holding long ETH exposure through staked collateral while simultaneously holding equal short ETH exposure through derivatives. If ETH rises or falls, gains in one position offset losses in the other. This approach works well during normal market conditions but can fail if hedge ratios slip or if one leg of the position becomes illiquid.
Delta中性對沖:這種策略旨在消除價格波動的風險,只保留收益或資金費率等非價格因素的敞口。例如,USDe通過質押持有ETH多頭,同時在衍生品市場做空等額ETH,達成Delta中性。當ETH升跌時,一邊賺一邊蝕,實現對沖。正常情況下有效,但若對沖比例偏離或其中一邊變得不流通,策略就會失效。
These technical concepts, while offering genuine innovation and efficiency gains, create complex systems where failures can cascade in unpredictable ways. The October 11 crash demonstrated how even well-intentioned financial engineering can produce catastrophic outcomes when implementation details prove inadequate for extreme stress scenarios.
以上技術雖帶來創新和提升效率,但同時令系統變得複雜,一旦出事,失敗可以連鎖式蔓延,難以預計。10月11日的崩盤說明了,即使出發點良好的金融工程,只要細節未能應對極端壓力,仍可釀成災難性後果。
Aftermath and Open Questions
後續與待解難題
As the cryptocurrency industry processes the October 11 crash, numerous critical questions remain unanswered, and the full scope of consequences continues to unfold.
隨著加密貨幣行業消化10月11日的崩盤,眾多關鍵問題依然未有答案,而真正影響仍在持續發酵。
The Compensation Question
賠償問題
Binance announced it would review and compensate losses directly caused by its system failures, with co-founder Yi He stating that the exchange would review accounts individually, analyze situations, and provide compensation accordingly.
Binance表示會就直接由系統故障引致的損失進行賠償,共同創辦人何一指交易所會逐一審查帳戶,分析具體情況,再相應作出賠償。
Binance stated that payouts would equal the difference between the market price at midnight on October 11 and each user's liquidation price, with distribution planned within 72 hours.
Binance表示,賠償金額為每位用戶在10月11日午夜市價與其清算價之間的差額,計劃於72小時內完成分發。
However, significant ambiguities remain regarding compensation:
但關於賠償,仍有不少重大疑點:
-
Scope: Will Binance compensate all users who suffered losses during the crash, or only those who can demonstrate that specific system failures directly caused their losses? How will the exchange distinguish between losses caused by market volatility versus infrastructure failures?
-
範圍:Binance會否賠償所有崩盤期間蒙受損失的用戶,還是僅賠償那些能證明具體系統故障直接導致其損失的人?交易所又打算如何分辨市況波動造成的損失與基建失誤造成的損失?
-
Methodology: How will Binance calculate the "true" market price for assets like wBETH and USDe when their prices diverged dramatically between Binance and other venues? Using external prices could increase compensation costs substantially; using Binance's distorted internal prices would shortchange affected users.
-
計算方法:由於wBETH及USDe等資產當時內外價差巨大,Binance將怎樣界定「真實」市價?如果用外部市場價格,賠償成本可能大增;如用自己市價又會令受害人蝕底。
-
Coverage Amount: With estimated losses ranging from 500 million to 1 billion dollars, can Binance's insurance fund and balance sheet absorb the full cost? What happens if total claims exceed available funds?
-
金額上限:外界估計損失介乎5億至10億美元,Binance的保險基金和資產負債表能否承受?賠償總額超出儲備又怎辦?
-
Timing: As of mid-October 2025, many users report delays in receiving compensation and uncertainty about claim status. The 72-hour timeline has elapsed, yet questions persist about when and how much users will ultimately receive.
-
時間表:至2025年10月中,許多用戶仍未收到賠償,也不確定最新申索進度。72小時時限早已過去,最終賠償金額及發放日期均未明。
System Changes and Risk Management Reforms
系統改革及風險管理措施
Binance announced it has shifted to using conversion-ratio pricing for wrapped assets and added redemption prices to index calculations for all three affected tokens.
Binance稱已改用換算比例定價包裝資產,並將贖回價納入三隻受影響代幣的指數計算。
The exchange implemented three specific fixes: adding redemption prices to index calculations, setting a minimum price threshold for USDe, and increasing the frequency of risk control reviews.
交易所實施了三項針對性補救措施:納入贖回價、為USDe設最低價格門檻、及提高風控審查頻率。
These changes address the immediate technical vulnerability but raise larger questions:
這些措施雖可暫時堵塞技術漏洞,但同時帶來更大問題:
-
Collateral Policy: Has Binance revised its standards for which assets qualify as margin collateral? Will proof-of-stake derivatives and yield-bearing stablecoins face higher haircuts or lower maximum loan-to-value ratios?
-
抵押政策:Binance有否修訂抵押品資格標準?權益證明衍生品及有息穩定幣會否被提高折讓或調低最高貸款成數?
-
Liquidity Requirements: Will the exchange implement minimum liquidity thresholds for assets accepted as collateral, ensuring sufficient depth in order books to handle stress scenarios?
-
流動性要求:交易所會否為抵押資產設最低流動性標準,以確保在壓力情況下訂單簿也有足夠深度?
-
Circuit Breakers: Does Binance plan to implement automatic trading halts or volatility controls that would pause liquidations during extreme price dislocations?
-
熔斷機制:Binance打算設自動停市或波幅限制機制,在極端價格波動時暫停清算嗎?
-
Third-Party Audits: Will independent risk management firms review Binance's updated systems to verify they can withstand future stress?
-
第三方審核:有沒有獨立風險管理公司替Binance新系統審核、確保可抵抗未來危機?
The Investigation Question
調查問題
Perhaps the most consequential unanswered question: will there be a formal investigation into whether the October 11 crash involved market manipulation or coordinated attack?
或許最重要卻仍未有答案的問題是:10月11日的崩盤,究竟會否展開正式調查,查明有否涉及市場操控或有組織攻擊?
Crypto.com CEO Kris Marszalek Below is the translation, following your instructions (markdown links skipped):
呼籲監管機構調查清算量高的交易所。
有多個潛在調查方向:
- 鏈上取證:區塊鏈分析公司可以追蹤交易模式,以確定集中的拋售是否來自協作錢包,或是否出現暗示有蓄意操控的模式。
- 交易所數據分析:擁有傳召權的監管機構可以審查Binance內部的交易數據,識別在崩盤前建立頭寸並從中獲利的賬戶。
- 通訊監控:如果出現協調行為,相關人士可能經過加密信息或社交媒體聯絡,留有數碼足跡,調查人員可以追查。
- 時間分析:詳細重建時間線可以揭示賣單是否出現與算法執行、人為協作,還是簡單恐慌反應一致的模式。
截至2025年10月中,主要監管機構尚未宣布正式啟動調查。美國監管機構會否基於Binance複雜的合規背景而介入調查,仍屬未知之數。該交易所的離岸屬性以及缺乏總部亦令司法管轄問題變得複雜。
更廣泛的市場結構問題
10月11日的崩盤觸發了對加密貨幣市場結構根本問題的新討論:
中心化與去中心化:這次危機是否顯示即使有理論上的去中心化選擇,加密貨幣市場依然危險地依賴中央化交易所?政策應鼓勵往去中心化平台遷移,抑或中央化平台有足夠優勢以支撐其主導地位?
Oracle標準化:行業是否應該建立標準化的預言機網絡,所有交易所必須以此進行清算計算,類似傳統金融依賴LIBOR或SOFR等確立參考利率?
保險機制:現時交易所級別的保險基金是否足夠?抑或行業應成立跨交易所保險池,或仿照傳統銀行的FDIC強制要求保險方案?
槓桿限制:加密貨幣交易所應否面臨最高槓桿率的監管限制,特別針對散戶,好像外匯或股票市場的槓桿限制?
實時風險披露:交易所應否公開實時數據看板,顯示其保險基金餘額、清算量及系統健康狀況,好讓用戶評估對手風險?
給市場參與者的啟示
對於經歷10月11日崩盤的交易者和投資者,有幾個實用教訓:
抵押品種類有分別:在壓力時期,並非所有抵押品都一樣。帶息資產及衍生品在平時或許穩定,一旦流動性蒸發則可能劇烈波動。
交易所特有風險:同一資產在極端情況下於不同交易所價格可以嚴重背馳。同時在多個平台持倉或理解平台特有風險變得關鍵。
槓桿放大失敗模式:高槓桿倉位不只承受市場風險,還要面對執行風險、預言機風險和對手風險。每層額外槓桿都造就新失敗點。
系統韌性有異:10月11日的崩盤證明去中心化協議和區塊鏈表現可靠,反觀中央化交易所基礎設施卻失效。這提示大家多元化不僅在資產,也在平台類型與託管安排。
安全升級時機要注意:已知漏洞若有公佈修復日期,便成為被利用的窗口。交易者應留意平台公告並了解系統何時特別脆弱。
結語:創新之價
2025年10月11日的加密貨幣崩盤,很可能被視為分水嶺——關鍵不在於損失了多少資金(儘管數字相當驚人),而在於事件暴露了加密貨幣市場基建的成熟度及脆弱之處。
這次崩盤揭示了加密貨幣創新核心的一種基本矛盾。同一批令市場更有效率的工具——統一本位、流動質押衍生品、帶息穩定幣——同時亦令系統複雜,故障一旦發生便可能層層蔓延。資本效率與系統關聯性原來是同一枚硬幣的兩面。
有投資者將此次崩盤比作Luna爆煲,並指出問題在於交易所用非法幣穩定幣作高價值抵押,讓風險無限蔓延。警告強調,將市場定價與高抵押率結合,是最危險的組合,特別當中心化交易所的套戥機制本身有缺陷時。
不論10月11日究竟是針對已知漏洞的協調攻擊,還是市場自然壓力下的風險管理崩潰,最大啟示是加密貨幣市場在某些關鍵層面依然未臻成熟,甚或仍極度脆弱,儘管用戶與交易量大幅增長。
至於「攻擊」抑或「失效」的爭拗,其實不及事件教訓本身重要。無論是被蓄意利用還是結構崩壞,接納流動性差、波動大資產作抵押,卻無足夠定價護欄,都屬不可接受風險。依賴內部Orderbook作清算參數,在流動性稀薄時也等同自製災難。金融創新,必須以健全的風險管理配套支撐。
對行業來說,10月11日是一個選擇。這次崩盤可以成為推動交易所設計、風險管理及監管架構重大改進的契機——交易所可制定更嚴格的抵押品標準、更可靠的預言機系統及更完善的壓力測試流程;監管機構則可設計合情合理的監管以增強安全而非扼殺創新;交易者亦可要求更高透明度,轉向重視系統韌性勝於極致槓桿的平台。
或者,行業只把這次事件視為偶發事故,針對被利用漏洞作局部技術修補,繼續原本模式,直到下次危機揭示新一輪系統性弱點。
傳統金融市場歷經百年危機,每次的啟示都涉及風險、槓桿及系統設計。加密貨幣市場才不過十五年,卻以驚人速度經歷這個學習過程。10月11日崩盤,只是新添又一筆昂貴教訓,告訴大家當創新拋離風險管理時會出現甚麼問題。
重要的問題是:行業會否真正反思總結,還是繼續追逐下個創新,並帶著令10月11日成為可能的同一組結構性弱點。
隨著加密貨幣市場日漸成熟,與傳統金融更緊密連接,做好風險管理的成敗影響越來越大。10月11日損失的數億甚至數十億美元,對受影響的交易者是慘痛教訓,但與將來若同類漏洞在更大規模下發生所造成之損失相比,仍算局部可控。
未來之路需在兩大目標中取得平衡──既保存市場創新與效率價值,也要打造防止災難性失效所需的穩健基建與風險管理架構。能否做到這個平衡,將決定加密貨幣能否成為全球金融體系值得信賴的一環,還是只會不時爆發危機,侵蝕公眾信心,甚至帶來嚴苛監管。
2025年10月11日,為加密貨幣行業帶來又一次學習機會。這次機會會否被把握還是錯失,仍有待觀察。





