加密貨幣革命承諾將財務自主權歸還給個人,免除對傳統銀行及第三方的依賴。然而,數百萬人發現這項承諾同時意味着令人卻步的責任:必須親自保護自己的數位資產。與傳統銀行不同,密碼忘記可以重設、遺失的卡片可以補發;加密貨幣遵循的是一旦金鑰遺失,資產即永久消失的嚴苛原則。
對使用非託管錢包的人而言,情況非常嚴峻——若同時丟失密碼與種子短語,通常就意味著永遠無法再取回資產。Ledger分析師指出,全球估計有230萬至370萬枚 比特幣(BTC) 處於遺失狀態,代表數十億美元永久無法取回。這些驚人的數據凸顯了一個自比特幣誕生以來始終存在的核心難題:普通人該如何安全有效地管理自己的財務主權?
解方在於不斷進化的錢包技術,每種方案都在安全、易用性與控制權之間尋求平衡。從主宰市場十多年的傳統種子短語系統,到精妙的多重簽署機制,再到最前沿的多方計算協議,我們見證著數位資產存取方式的變革。
這場進化反映的不僅是技術上的突破,更顛覆了我們對信任、控管與風險的認知。當大眾正站在加密貨幣主流應用的門檻前,理解這些技術不僅是加密愛好者的需求,更是每一位預備迎接數位資產為全球經濟核心者的必修課。
基石:認識種子短語
欲理解錢包科技的創新,首先需明白自加密貨幣誕生以來一直作為基礎的系統——種子短語。把種子短語想像成開啟龐大數位保險箱的主鑰匙。種子短語又稱為助記詞,是你掌握加密資產的關鍵,能在裝置遺失、被竊或損壞時提供恢復的保險。
當你建立加密貨幣錢包,其實是在生成一對密鑰,包括公鑰(作為錢包地址)與私鑰(證明你擁有資產並能花費)。種子短語實際上是私鑰的人類可讀化表示,通常由12或24個從標準字典挑選的單詞組成。這些詞彷彿隨機——比如「abandon ability able about above absent absorb abstract absurd abuse access accident」——但它們蘊藏你所有加密地址和私鑰的數學基礎。
此系統之美在於其簡單與通用性。即使你遺失了錢包(如硬體錢包不見或手機損壞),也可以透過助記詞恢復存取。這組種子短語能於任意相容設備、全球任何地點隨時找回錢包,帶來傳統銀行系統做不到的財務移轉性。
然而,這種設計的優雅也帶來重大責任:種子短語代表對資產完全且不可撤回的掌控力。不同於銀行帳戶可驗證身份恢復存取權,加密貨幣講求的是數學證明而非信用證明。倘若他人取得你的種子短語,可瞬間盜光你的錢包,沒有客服專線、沒有所謂防詐機制、而且沒辦法逆轉交易。
此責任所帶來的現實議題許多用戶已親身體驗。我們發現,多數參與者對種子短語存在重大誤解,增加了嚴重安全風險——例如,僅43%可正確認出種子短語圖片,多數人以為若遺失可以重設。這些誤區反映出一個更深層的問題:安全保管種子短語所需的複雜度,遠超過一般用戶的技術知識。
僅僅談存放就夠頭痛了。最安全做法是用紙抄下種子短語,並分散存放於多個離線安全地點。有些加密貨幣用戶甚至把助記詞存於銀行保險箱或寄存箱,以防竊盜及天災等風險。然而這同時衍生另一套問題:如何在冗餘備份與曝光風險間取捨?若發生意外,家人該如何取回資產?如何在防範天災的同時保持存取便利?
數位存放雖相對方便,卻帶來其他風險。把助記詞儲存在電腦或雲端會大幅提高遭駭或惡意軟體入侵的機率。加密社群中不乏因截圖、存在密碼管理器或郵件草稿裡,結果全數資產血本無歸的案例。
更陰險的是種子短語管理造成的心理弱點。騙徒往往會假設受害人有誤解或貪圖小利,進而套取助記詞。高段騙局專挑用戶對助記詞一知半解,設下複雜圈套讓受害人自願洩露,誤以為是在幫忙或領取獎勵。
「人」或許是種子短語體系最大的弱點。人會犯錯、會健忘、會信錯人、也會在壓力下做出事後後悔的決定。儘管22%的參與者表示曾為恢復帳戶而分享過種子短語,許多人都認同規劃帳戶恢復重要性,但並未採取合適措施。
這些困難促成了所謂「易用性—安全性取捨」。儲存越安全,取用就越不便;越便利,風險也越高。這根本性的張力驅動了替代方案發展——在維持安全的同時,降低用戶個人負擔。
儘管種種困難,種子短語依舊為加密貨幣自主保管的基礎。它展現加密貨幣的核心理念:由個人而非機構掌控資產。所有錢包創新皆需在此原則下思考如何讓其更易用、更安全、更適合大眾普及。
進化:多重簽署安全機制
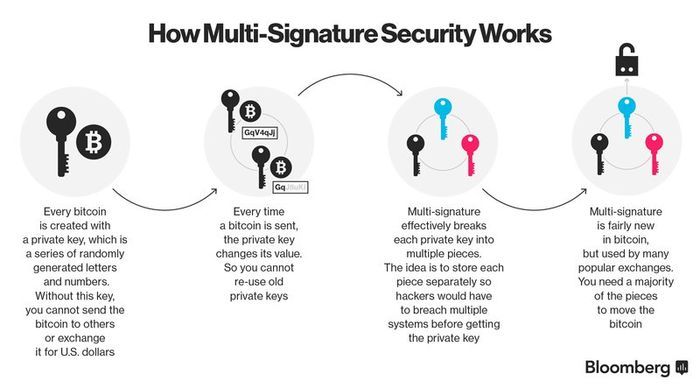
單一簽署錢包的限制日益顯著後,加密社群參考了傳統銀行模式:交易需多方核准。多重簽署,或稱「multisig」,是超越基礎種子短語後的第一項重大進化,將權力分散的原則引入加密貨幣安全領域。
要理解多重簽名錢包,不妨想像企業帳戶每張支票都需兩人簽名。這種雙重控管避免單人盜領,卻又不妨礙合法交易進行。多重簽名錢包是專為提升交易安全設計,必須多個簽名才能執行轉帳。
技術上是創建由多把私鑰共同控管的特殊加密貨幣地址,而非單一密鑰。常見的「M-of-N」模型,例如2-of-3多簽錢包:三人各自持鑰,需任兩人簽名始可交易,使安全性與彈性兼具。
多重簽署提升的安全明顯可見。如果使用得當,可消除只靠單一密鑰的單點失效風險。駭客若想竊取資金,必須同時入侵多人的私鑰,且這些鑰匙通常分處不同地點,難度與協調成本大幅提升。
除了安全外,多簽錢包更開創前所未有的金融管理模式。新創團隊可設立多簽金庫,大額支出需多位創辦人同意;組織得以協作、透明地控管資產;家庭可建立共管帳號以規劃遺產或大額消費;投資團體可杜絕單人未經授權的操作。
多簽技術已證實其價值。Safe多簽錢包成為Vitalik Buterin(以太坊共同創辦人)及眾多Web3項目守護百億美元資產的首選。這層級的機構級採用,證明多簽錢包已非實驗性技術,而成為大型加密資產儲存的可靠解決方案。
然而,多簽錢包也產生全新挑戰…… of challenges and limitations. The most obvious is coordination complexity. Every transaction requires multiple parties to be available and willing to sign. If you need 3-of-5 signatures and two of your co-signers are traveling without access to their keys, legitimate transactions can be blocked. This coordination overhead can make multisig wallets impractical for day-to-day use.
挑戰與限制。最明顯的是協調的複雜性。每一筆交易都需要多方同時出席且願意簽署。如果你採用 5 人中 3 人簽名(3-of-5)的設定,而其中兩位共同簽署人正在外旅行且無法存取他們的私鑰,合法的交易就可能被擋下。這樣的協調負擔讓多重簽章錢包在日常使用上變得不切實際。
The technical implementation also varies significantly between different blockchains. It is difficult for multisig wallet providers to securely support new chains as the few cryptocurrency protocols that support multisig have distinct implementations from one another. Bitcoin's multisig implementation differs from Ethereum's, which differs from newer blockchains like Solana or Cardano. This fragmentation means that multisig solutions often work well on one blockchain but require completely different implementations for others.
不同區塊鏈間的技術實現也差異很大。對多重簽章錢包的提供者來說,要安全地支援新鏈並不容易,因為少數支援多重簽章的加密貨幣協議彼此間實作方式各異。比特幣的多重簽章方式與以太坊不同,以太坊又與像 Solana 或 Cardano 這類新興鏈不同。這種分裂情形意味著多重簽章解決方案通常只在單一鏈上運作良好,若要支援其它鏈則必須重新打造一套完全不同的技術。
There's also the question of key management distribution. While multisig eliminates the single point of failure, it multiplies the seed phrase management problem. Now instead of securing one seed phrase, you have multiple parties each responsible for securing their own keys. It is essential to distribute multi-sig private key access among distinct entities. A multi-sig setup where a single entity holds multiple private keys and stores them in a single location is essentially the same as a single-key wallet.
還有金鑰管理分配的課題。多重簽章雖然消除了單一故障點,卻讓助記詞管理問題加劇。現在不再是保管一組助記詞,而是有多位個體,各自要負責保管自己的私鑰。分散多重簽章私鑰存取權給不同主體是至關重要的。如果一個多重簽章錢包,卻由單一人持有多把私鑰且儲存在同一地方,本質上就等同單一私鑰錢包。
The user experience challenges extend beyond technical complexity to social and organizational dynamics. Who controls the keys? How do you handle disputes? What happens if one of the key holders becomes unavailable or unwilling to cooperate? What if relationships change or someone becomes malicious? These human factors can be more challenging to manage than the technical aspects.
使用體驗上的挑戰遠不只技術複雜度,還包括社會與組織層面的動態。誰負責掌控金鑰?遇到爭議時如何處理?如果某位持有金鑰的人無法取得聯繫,或拒絕配合,該怎麼辦?如果人際關係變動或有人變得惡意,總要如何應對?這些與人有關的問題,往往比技術難題更棘手。
Despite these limitations, multisig wallets have found their niche in scenarios where the benefits outweigh the complexity. If you're looking for the best crypto multisig wallets, Sparrow Wallet stands out for its comprehensive features and high level of security. Safe Wallet, formerly known as Gnosis Safe, is a popular multi-signature smart contract wallet. These established solutions demonstrate that multisig technology has matured and found practical applications.
儘管有上述限制,多重簽章錢包還是在利益超過複雜成本的場景中找到了利基。若你尋找最佳加密貨幣多重簽章錢包,Sparrow 錢包因為其功能全面及高安全性而脫穎而出。Safe Wallet(前稱 Gnosis Safe)則是熱門的多簽智慧合約錢包。這些成熟的方案證明多重簽章技術已經逐漸成熟並落地應用。
The institutional adoption of multisig technology has been particularly significant. BitGo is a multi-sig wallet solution tailored for institutional investors and businesses. It supports a wide range of cryptocurrencies and offers enterprise-grade security features, including multi-user access and advanced policy controls. This corporate adoption has driven improvements in user interfaces, policy management, and integration with existing business processes.
機構端對多重簽章技術的採用尤其顯著。BitGo 是專為機構投資人及企業設計的多重簽章錢包解決方案,支援多種加密貨幣,並提供企業級安全功能,包括多人存取與進階政策控管。這類企業級應用推動了使用介面、政策管理和與現有商業流程整合的進步。
Yet even as multisig wallets have gained acceptance, their limitations have pointed toward the need for more sophisticated solutions. The coordination overhead, blockchain-specific implementations, and social complexities of managing multiple keys have led researchers and developers to explore alternatives that could provide multisig's security benefits without its operational drawbacks.
即使多重簽章錢包已漸受市場接受,其種種限制仍令人期待更進階的解決方案。繁瑣的協調負擔、每條鏈不同的技術實現,以及多鑰管理的人際複雜性,都驅使研究人員與開發者探索能兼具多重簽章安全性、卻沒有營運缺點的替代方案。
The Cutting Edge: Multi-Party Computation Wallets
前沿技術:多方計算(MPC)錢包
As the cryptocurrency ecosystem matured and institutional adoption accelerated, the limitations of both single-signature and multi-signature approaches became increasingly apparent. The industry needed a solution that could provide enterprise-grade security without the operational overhead of traditional multisig, while still maintaining the self-custody principles that make cryptocurrency valuable. The answer emerged from an advanced area of cryptography called multi-party computation, or MPC.
隨著加密貨幣生態系統逐漸成熟、機構採用加速,單一簽章以及多重簽章兩種模式的限制也日益明顯。業界亟需一種解決方案,能提供企業級安全防護,卻不會帶來傳統多簽的運作成本,同時保有加密貨幣最珍貴的自我保管原則。這個答案來自密碼學中的一門先進領域——多方計算(Multi-Party Computation, MPC)。
MPC enables multiple parties – each holding their own private data – to evaluate a computation without ever revealing any of the private data held by each party (or any otherwise related secret information). In the context of cryptocurrency wallets, this means that multiple parties can collaborate to sign transactions without any single party ever having access to the complete private key.
MPC 允許多方各自保有自己的私密資料下共同運算,過程中不會向其他人透露自己的私密資料(或相關機密資訊)。套用到加密貨幣錢包上,這代表多方能協作完成交易簽名,卻沒有人能單獨取得完整的私鑰。
This represents a fundamental shift in how we think about key management. Traditional wallets store a complete private key somewhere, whether on a device, on paper, or in someone's memory. Even multisig wallets require complete private keys to be held by each party. MPC wallets, by contrast, split the private key into mathematical shares that are distributed among multiple parties, ensuring that no single party has access to the complete private key, eliminating single points of failure.
這徹底改變了我們對金鑰管理的思維。傳統錢包必須完整儲存一組私鑰,不論是在裝置、紙本或記憶裡。即使多重簽章,每個合作者也需要各自擁有完整私鑰。MPC 錢包則不同,它將私鑰數學切片後分配給多個個體,確保沒有人能接觸完整私鑰,消除了單一故障點。
The technical elegance of MPC lies in its use of cryptographic protocols that allow computation on encrypted data. Think of it as a way for multiple people to jointly solve a mathematical equation without any of them knowing all the inputs. Each party holds a piece of the puzzle, and they can work together to create valid signatures without reconstructing the complete key. This process happens through sophisticated mathematical techniques involving threshold cryptography and distributed key generation.
MPC 的技術精妙之處在於它能在加密資料上進行運算的密碼協議。你可以想像成多人一起解一道數學題,但沒有人知道所有的輸入。每個人只拿到拼圖的一部分,他們卻能合作生成有效簽名,無需還原出完整私鑰。這一切仰賴門檻密碼學(threshold cryptography)與分散式金鑰生成等進階數學技術。
The core mechanism that underpins MPC wallets is a sophisticated blend of distributed key generation (DKG) and threshold cryptography, two pillars of modern cryptography that enhance security and privacy in digital transactions. When you create an MPC wallet, the system generates key shares rather than a complete private key. These shares are mathematically related to each other in such a way that a predetermined threshold number of them can be combined to create valid signatures, but fewer than the threshold reveals no information about the key.
MPC 錢包的核心機制融合了分散式金鑰產生(Distributed Key Generation, DKG)以及門檻密碼學,這兩大現代密碼學支柱大幅提升了數位交易的安全與隱私。當你建立 MPC 錢包時,系統產生的是一組相關聯的金鑰切片,而不是一組完整私鑰。只要達到預設門檻數的切片參與簽名,就可組合出有效簽名,若不足門檻,則無法獲得任何私鑰資訊。
The security benefits are substantial. Unlike traditional wallets (EOAs), that solely rely on a single private key, MPC wallets meaning use advanced cryptographic technology, to ensure that the private key is neither exposed to nor stored in a single direction, adding an extra layer of security. An attacker would need to compromise multiple independent systems simultaneously to steal funds, and even then, the compromise would be mathematically complex rather than simply copying a file or seed phrase.
其安全性大幅提升——不同於僅靠單一私鑰的傳統錢包(EOA),MPC 錢包運用先進密碼學技術,確保私鑰既不會以任何單一形式暴露,也不會集中儲存,等於多加了一層保護。攻擊者想竊取資產,必須同時破解多套獨立系統,且這個過程極端複雜,遠非複製檔案或助記詞那麼簡單。
Perhaps more importantly, MPC wallets eliminate many of the usability problems that have plagued traditional approaches. Unlike multisig wallets, which require coordination among multiple parties for every transaction, MPC wallets can be configured so that a subset of key shares can authorize transactions. This means that legitimate users can transact smoothly while still maintaining security against compromise of any individual component.
更重要的是,MPC 錢包排除了傳統金鑰管理上的許多痛點。傳統多簽錢包每一筆交易都得由多方協調參與,MPC 錢包則可設定部分金鑰切片即具交易授權力。這讓合法用戶能順利付款或操作,同時依然具備任一單點失效無法攻破的安全性。
The technology has rapidly gained adoption among institutional players who need to balance security with operational efficiency. Fireblocks has established itself as the gold standard for institutional MPC wallets. The platform is trusted by banks, hedge funds, and asset managers because of its multi-layered security, automated transaction workflows, and compliance-first approach. This institutional validation demonstrates that MPC has moved beyond academic research to become practical technology for managing large-scale cryptocurrency operations.
MPC 技術已被有高度安全與營運效率追求的機構廣泛採用。Fireblocks 已成為機構級 MPC 錢包的黃金標準──其平台獲得銀行、避險基金、資產管理人信任,理由包括層層防護的安全措施、自動化交易流程,以及合規優先的設計。這代表 MPC 已從學術研究階段,躍昇成大規模加密貨幣資產管理的實用技術。
The blockchain compatibility advantages of MPC are particularly significant. The MPC system developed in-house at Coinbase supports both ECDSA and EdDSA protocols. This means the wallet can handle cryptographic signing for almost any blockchain, and users don't have to pay for gas transactions since there is zero overhead. Unlike multisig implementations, which must be built specifically for each blockchain's architecture, MPC signatures are indistinguishable from regular signatures at the blockchain level.
MPC 在區塊鏈兼容性上的優勢尤其明顯。Coinbase 自行開發的 MPC 系統同時支援 ECDSA 與 EdDSA 協議,代表這類錢包幾乎適用各種區塊鏈的簽章需求,且用戶無需額外支付交易手續費,因為沒有鏈上負擔。與必須因應各鏈架構客製化的多簽不同,MPC 的簽章在鏈上表現與一般簽章無異。
This universal compatibility is crucial as the cryptocurrency ecosystem becomes increasingly multi-chain. Unlike Multi-sig, MPC happens off-chain with only one single signature broadcast on-chain. It's data-light meaning it is cheaper and faster to execute, and much more secure. Users can manage assets across dozens of different blockchains using the same MPC wallet infrastructure, without needing to understand the specific multisig implementations of each chain.
這種普遍相容性在加密貨幣生態走向多鏈化時尤其關鍵。不像多簽需各鏈逐一支援,MPC 在鏈下執行,最後只需單一簽章上鏈。這讓運作更輕盈,執行成本低也更快速安全。用戶能用同一組 MPC 錢包基礎設施管理數十條鏈上的資產,無需熟悉各鏈獨特的多簽細節。
The user experience improvements extend beyond technical compatibility to fundamental usability enhancements. Many MPC wallets are eliminating seed phrases entirely, instead using alternative recovery methods. Web3Auth: Wallet-as-a-service infrastructure that is friendly both to dedicated developers and end-users, Web3Auth uses MPC technology to bring improved security to users without the need for seed phrases. This represents a potential solution to one of cryptocurrency's most persistent user experience problems.
MPC 對使用體驗的改善不只是技術方面,更提升了根本的易用性。許多 MPC 錢包已經完全捨棄助記詞,改用其他備援方法。Web3Auth:一個兼顧專業開發者與終端用戶的錢包即服務基礎架構,透過 MPC 技術讓用戶不再需要備份助記詞,安全性還能提升。這有潛力解決加密貨幣領域最根深蒂固的體驗問題之一。
Recovery mechanisms in MPC wallets can be far more sophisticated than traditional approaches. Instead of relying on users to safely store seed phrases, MPC wallets can implement social recovery, biometric authentication, or institutional backup services. Phantom and Bitget Wallet are leading the way in smart recovery, experimenting with hybrid MPC and account abstraction to provide seamless and user-friendly recovery options. These approaches maintain the security properties of self-custody while dramatically reducing the risk of user error.
MPC 錢包的備份與恢復機制遠比傳統方案靈活。用戶不必再自行妥善保管助記詞,MPC 可導入社交恢復、生物特徵驗證或機構備援。Phantom 及 Bitget Wallet 正在積極推動智慧恢復,利用 MPC 與帳戶抽象技術,提供無縫、易用的恢復選擇。這些方法既維持「自我保管」的安全性,又能大幅減少使用者出錯的風險。
The governance capabilities of MPC wallets also represent a significant advancement over traditional approaches. Create as many custom rules and policies as you want for different situations. Setting up well defined rules ensures that not a single transaction can be executed without the approval of the appointed persons. Organizations can implement complex approval workflows, spending limits, time locks, and other sophisticated controls that would be difficult or impossible with traditional wallet architectures.
MPC 錢包在治理能力上亦遠超過傳統架構。你可以針對各種情境設定無數自訂規則與政策。界定清楚後,每筆交易都需經指定人員核可才可執行。組織可實施複雜的審批流程、消費上限、時間鎖等進階防護,這些在傳統錢包架構下往往難以甚至無法達成。
However, MPC wallets are not without their challenges and limitations. The computational overhead, while manageable for institutions, can impact performance compared to simpler alternatives. While offering increased security, MPC wallets might slow down processes and
然而,MPC 錢包也並非毫無挑戰或限制。雖然計算負擔對於機構而言大致可控,但與更簡易方案相比還是會帶來效能影響。雖然安全性提升,MPC 錢包可能會導致某些流程變慢,並且require more communication compared to simpler methods. The cryptographic protocols require coordination among multiple parties, which can introduce latency, particularly in high-frequency trading scenarios.
相較於較為簡單的方法,這些方式需要更多的溝通協調。密碼學協議需要多方協作,在高頻交易等情境下,這可能導致延遲。
The complexity of MPC implementations also raises questions about auditability and trust. It's also worth noting that not all MPC wallets are open-source or interoperable, which could limit their usability and compatibility with other systems. Users must trust that the cryptographic implementations are correct and secure, which can be challenging to verify without deep mathematical expertise.
MPC 實作的複雜性同時帶來可稽核性與信任問題。值得注意的是,並非所有 MPC 錢包都是開源或可互通的,這可能會限制其實用性以及與其他系統的相容性。使用者必須相信其密碼學實作是正確且安全的,而這在沒有深厚數學背景的情況下,往往難以自行驗證。
Despite these challenges, the trajectory of MPC wallet development suggests that they represent the future of cryptocurrency self-custody. In 2025, several MPC wallets stand out for their unique features and user benefits. Institutional platforms such as Ledger Vault, Fordefi, and Coinbase WaaS are leveraging MPC to secure billions in digital assets with multi-user access and hardware-grade protection.
儘管有這些挑戰,MPC 錢包的發展趨勢顯示其代表加密貨幣自我託管的未來。到了 2025 年,有數款 MPC 錢包因其獨特功能與用戶利益而脫穎而出。像 Ledger Vault、Fordefi 和 Coinbase WaaS 這類機構級平台運用 MPC 技術,讓多用戶存取並達到硬體等級保護,確保數十億美元等級的數位資產安全。
Comparative Analysis: Security, Usability, and Control
Understanding the relative strengths and weaknesses of seed phrase, multisig, and MPC approaches requires examining them across multiple dimensions that matter to real users and organizations. Each technology represents different tradeoffs between security, usability, cost, and control, and the optimal choice depends heavily on the specific use case and user requirements.
要瞭解助記詞、多重簽名和 MPC 等方法的相對優劣,需從實際用戶與組織所重視的多個面向加以審視。每種技術都在安全性、易用性、成本和控制權間有不同權衡,最適切的選擇高度取決於具體情境與使用者需求。
From a pure security standpoint, the progression from seed phrases to multisig to MPC represents a clear evolution toward more sophisticated threat models. Seed phrases, while cryptographically sound, create a single point of failure that has proven vulnerable to both technical attacks and human error. The simplicity that makes seed phrases accessible also makes them fragile. A single moment of carelessness – a screenshot saved to the cloud, a handwritten phrase left visible, a moment of confusion during a phishing attack – can result in complete loss of funds.
純粹從安全性的角度來看,從助記詞、多重簽名再到 MPC 的演進,清楚反映出對進階威脅模型的發展。助記詞雖具備密碼學安全性,但卻創造了單點失效,證明容易受到技術攻擊與人為失誤影響。促使助記詞易於普及的簡單性,同時也使其脆弱。一時的不慎——如將截圖儲存於雲端、手寫助記詞暴露在外、或釣魚攻擊中的混亂——都可能導致資金完全損失。
Multisig wallets address this single point of failure by distributing control, but they do so in a way that increases surface area for certain types of attacks. While it becomes much harder for an attacker to compromise multiple independent keys, the coordination required for legitimate transactions creates new vulnerabilities. Social engineering attacks can become more sophisticated, targeting relationships between key holders rather than technical infrastructure. The human factors that make multisig appealing – the ability to involve trusted parties in financial decisions – also create new attack vectors that don't exist with individual custody.
多重簽名錢包透過分散控制來解決單點失效問題,但也因此增加了某些攻擊的面向。雖然攻擊者要同時入侵多個獨立密鑰的難度增加,合法交易所需的協調卻帶來新的弱點。社交工程攻擊變得更複雜,可能針對持鑰人的關係而非純粹技術基礎設施。讓多重簽名具有吸引力的人為因素——如讓可信賴的人共同參與財務決策——也創造出個人自託管下原本不存在的新攻擊途徑。
MPC wallets represent a significant advancement in addressing both technical and human vulnerabilities. By ensuring that complete private keys never exist in any single location, they eliminate entire categories of attacks while maintaining usability. The mathematical properties of MPC mean that compromising individual key shares reveals no useful information to attackers, making the system resilient to partial breaches. However, the complexity of MPC implementations introduces new categories of potential vulnerabilities related to protocol implementation and coordination mechanisms.
MPC 錢包在處理技術與人為弱點方面有重大突破。由於完整私鑰從未在任何單一位置存在,這消除了整類型的攻擊,同時保有易用性。MPC 的數學特性意味破壞個別密鑰分片並無法提供攻擊者有用資訊,讓系統能抵抗局部滲透。然而,MPC 實作的複雜性也引入了協議實施與協調機制等新型態潛在弱點。
The usability spectrum tells a different story. Seed phrases, despite their security limitations, offer unmatched simplicity for individual users who understand their responsibilities. There are no coordination requirements, no technical protocols to understand, and no dependencies on other parties or services. This simplicity has enabled the grassroots adoption of cryptocurrency and remains crucial for scenarios where complete individual sovereignty is paramount.
易用性方面的情況則不同。雖然助記詞存在安全限制,但對明瞭自身責任的個體用戶來說,其易用性無可匹敵。使用者不需協調、不需理解技術協議,也不依賴其他人或服務。這種簡單性促進了加密貨幣的草根擴散,在追求完整個人主權的場景下依然具有決定性意義。
Multisig wallets sacrifice individual simplicity for organizational robustness. The coordination overhead that makes them less suitable for individual day-to-day use becomes an advantage in scenarios where deliberate friction is desirable. Corporate treasuries, DAO governance, and family inheritance planning all benefit from requiring multiple parties to agree on transactions. However, this coordination requirement can make multisig wallets impractical for scenarios requiring quick response to market movements or frequent transactions.
多重簽名錢包則犧牲個人使用的簡易性,換取組織運作上的強健穩定。雖然協調成本使其不利於個人日常操作,卻在需要有意設置阻力的情境(如公司金庫、DAO 治理及家族傳承規劃)中展現優勢。然而,這種協調需求也使其在需要迅速應對市場動態或頻繁交易的情境下變得不切實際。
MPC wallets aspire to combine the security benefits of multisig with the usability of individual wallets, and in many respects they succeed. The ability to set flexible threshold requirements means that routine transactions can be frictionless while maintaining protection against compromise. Advanced features like programmable policies and automated compliance checking can actually make MPC wallets more usable than traditional alternatives for sophisticated use cases.
MPC 錢包旨在結合多重簽名的安全益處與個人錢包的易用性,並在許多方面確實做到了。可彈性設定門檻,讓日常交易流暢無阻,同時維持防護效果。具備可編程策略、自動合規檢查等先進功能,甚至讓 MPC 錢包在進階應用情境下比傳統方案更易用。
The cost considerations vary significantly across these technologies and use cases. Seed phrase management appears free but actually involves hidden costs in the form of security infrastructure, backup procedures, and risk management. Users who properly secure seed phrases often invest in safety deposit boxes, fireproof safes, or professional storage services. The psychological cost of constantly worrying about seed phrase security also represents a real burden for many users.
這幾種技術與應用場景的成本考量也有巨大差異。助記詞管理看似免費,但實際隱含了安全設備、備份流程與風險管理等隱性成本。妥善保存助記詞的用戶往往會投資保險箱、防火保管箱或專業存儲服務。長期憂慮助記詞安全的心理壓力,也是不少使用者極大的負擔。
Multisig wallets have explicit coordination costs in terms of time and communication, but they can actually reduce total security costs by distributing responsibility. Instead of each individual bearing the full burden of perfect security practices, the risk is shared among multiple parties. However, the blockchain-specific nature of multisig implementations can create significant development and maintenance costs for organizations operating across multiple chains.
多重簽名錢包的協調成本體現在時間與溝通上,但其透過分攤責任,實際能降低總體安全成本。不再需要每個人都做到極致安全,因為風險由多人分攤。不過,多重簽名因必須針對不同鏈各自實作,組織跨鏈運作時會產生可觀的開發和維運成本。
MPC wallets often have higher upfront costs due to their technical sophistication, but they can provide significant operational savings for organizations with complex security requirements. The ability to implement automated compliance checking, flexible approval policies, and universal blockchain compatibility can reduce ongoing administrative overhead. For institutional users, the reduced insurance and audit costs often justify the technology premium.
MPC 錢包由於技術複雜,前期成本通常較高,但對安全需求複雜的組織而言,能帶來重大運營節省。自動合規檢查、彈性審批政策與跨鏈相容等能力都能降低長期管理負擔。對機構用戶來說,保險和稽核成本的降低,往往足以抵消所需技術溢價。
The control dimension reveals fundamental philosophical differences between these approaches. Seed phrases represent the purest form of individual sovereignty – complete control with complete responsibility. This aligns perfectly with cryptocurrency's original vision of eliminating trusted intermediaries, but it places enormous burdens on individual users. The "not your keys, not your crypto" principle reaches its logical conclusion with seed phrase management, but this absolute control comes at the cost of flexibility and error recovery.
各方案在控制權層面則展現出根本性的理念差異。助記詞代表最純粹的個人主權——完全掌控,完全負責。這與加密貨幣消除信託中介的原始願景不謀而合,但也對個人用戶造成巨大壓力。所謂「Not your keys, not your crypto」的原則,到了助記詞管理可謂達到極致,但絕對的掌控也意味著缺乏彈性與容錯能力。
Multisig wallets introduce structured interdependence while maintaining self-custody principles. Control is distributed by design, which can be either a feature or a limitation depending on the use case. For organizations, this structured sharing of control enables governance and risk management practices that would be impossible with individual keys. For individuals, it can provide security benefits while requiring trust in other parties.
多重簽名錢包則在自託管原則下,引入有結構的相互依存。設計上控制權分散,對不同情境來說可視為優點或限制。對組織而言,這種結構化的控制分配可執行治理與風險管理,是單一密鑰體系下做不到的。對個人而言,也能提升安全性,但須信任其他人。
MPC wallets offer perhaps the most nuanced approach to control. They can provide individual control that feels like traditional seed phrase management while actually distributing security responsibilities across multiple components. This hidden distribution can provide security benefits without requiring users to actively manage relationships with other parties. However, it also introduces dependencies on service providers and technical infrastructure that some users may find philosophically inconsistent with self-custody principles.
MPC 錢包或許在控制權方面給出了最細緻的做法。它能讓用戶享有類似傳統助記詞的控制體驗,實際上卻將安全責任隱性分散於多個組件。這種隱形分散能提升安全性,同時不必讓用戶主動經營與他者關係。然而,這也使其依賴服務提供商及技術基礎設施,對部分講究自我託管理念的用戶而言,可能產生理念上的不一致。
The accessibility implications of these technologies extend beyond individual users to broader cryptocurrency adoption. Seed phrases, despite their conceptual simplicity, have proven to be a significant barrier to mainstream adoption. We found that the majority of our participants harbored significant misconceptions about seed phrases that could expose them to significant security risks — e.g., only 43% could correctly identify an image of a seed phrase, many believed they could reset their seed phrase if they lost them.
這些技術在可近性上的影響,也遠超出個別用戶,進一步影響加密貨幣的大規模普及。助記詞雖概念單純,卻證明是大眾採用的重要障礙。我們發現,多數受訪者對助記詞存在嚴重誤解,使他們暴露於高風險之中——例如,只有 43% 能正確辨認助記詞圖片,許多人甚至認為遺失後可以重設助記詞。
Multisig wallets require even higher levels of technical and social sophistication, making them suitable primarily for organizations or technically savvy individuals. The coordination requirements alone eliminate many potential users, and the blockchain-specific implementations create additional barriers to entry.
多重簽名錢包則需更高的技術與社會素養,因此主要適用於組織或技術高明的個人。光是協調需求就排除了許多潛在用戶,而鏈特定的實作更是進一步設下門檻。
MPC wallets show the most promise for bridging the gap between sophisticated security and mainstream accessibility. By abstracting away cryptographic complexity and eliminating seed phrase management, they could enable widespread self-custody adoption among users who would otherwise rely on centralized exchanges or custodial services.
MPC 錢包則被認為最有機會彌合高階安全與大眾可近性的鴻溝。藉由抽象掉密碼學複雜性及移除助記詞管理,其有望推動廣泛自我託管,使原本只能仰賴中心化交易所或託管服務的用戶,也能獨立保管資產。
Trust Models and Decentralization Philosophy
The evolution of wallet technologies reflects deeper questions about the nature of trust in decentralized systems. While all three approaches maintain the fundamental principle of self-custody – meaning users retain ultimate control over their assets – they implement dramatically different trust models that have profound implications for both security and philosophical consistency with cryptocurrency's founding principles.
錢包技術的演進,其實體現了去中心化系統當中「信任」本質的進一步思考。三種方法都維持了自我託管這一核心原則——即使用者最終掌控其資產——但在信任模型實作上截然不同,這對安全實踐及與加密貨幣創始原則的理念一致性都產生深遠影響。
Seed phrase wallets represent the most radical interpretation of trustlessness. In this model, trust is not distributed or managed – it is eliminated as much as possible. The user trusts only in mathematics and cryptography, not in any external parties, services, or coordination mechanisms. This aligns perfectly with the cypherpunk philosophy that inspired Bitcoin's creation, where the goal was to create a system that could function without requiring trust in governments, banks, or other traditional institutions.
助記詞型錢包體現了對「無需信任」最極端的詮釋。在這種模式中,信任既非分散也非管理,而是盡可能被消滅。使用者只信賴數學與密碼學,不需信託任何外部人員、服務或協調機制。這與啟發比特幣誕生的 cypherpunk 精神如出一轍,目標正是打造一個無需信任政府、銀行或其他傳統機構的運作系統。
The
(後續內容未完,若需繼續請告知。)哲學上這種做法的純粹性非常吸引人,但它同時給使用者帶來了巨大的實際負擔。當你排除了外部信任後,你就必須將所有責任內化。每一個安全決策、每一個備份步驟、每一個存取權限機制,都將變成個人的責任。如果你犯錯,系統也無法協助你,因為協助意味著需要引入可以被攻破或腐化的信任元素。
這種消除信任的方式既具有強大力量,也帶來諸多問題。它讓加密貨幣能夠跨越政治邊界運作、抵禦監管攻擊,並為被傳統金融體系排除在外的人群提供財務自主。然而,它也因用戶操作失誤導致巨額損失,並造成了阻礙主流採用的壁壘,進而限制加密貨幣在社會層面的潛在影響力。
多簽錢包在力求維持去中心化原則的同時,引入了結構化的信任關係。與其說它是消除信任,不如說是把信任透過明確協議與技術控制分散到多方。這種作法介於個人自主與集體安全之間,然而也帶來了難以管理的社會複雜性。
多簽系統中的信任模型,極度依賴持鍵人之間的關係。在企業環境中,這種關係通常受到雇傭契約、信託責任和法律框架的規範。這種信任是結構化且有法律約束力的,因此相對可預測、易於管理。而在非正式場域——如家庭遺產規劃或社區金庫——信任關係則更具個人色彩,也可能更加脆弱。
多簽系統的技術信任假設基本上是被充分理解且符合去中心化原則的。區塊鏈本身會強制執行多簽要求,沒有外部個體能夠覆蓋支配交易授權的數學規則。然而,協調機制通常仰賴外部溝通渠道與決策程序,這可能引入受信任的要素。
MPC 錢包則代表了信任管理最為複雜的方式,利用密碼學技術建立起既分散又對使用者隱形的信任關係。這種作法嘗試在不用讓用戶積極管理社會關係或協同機制的情況下,為他們提供分散信任帶來的安全效益。
MPC 系統中的技術信任模型,結構複雜且隨各種實作顯著不同。門檻型 MPC 系統將信任分散在多個計算方,但使用者必須信任這些方會持續可用且誠實。多方計算協議必須保證兩個基本特性:隱私性——協定執行過程中各方持有的私密資訊不會被推知;正確性——即使有部分成員在協定執行中分享資訊或偏離指令,MPC 仍不允許他們逼使誠實方產生不正確的結果。
然而,MPC 系統在實務上的信任需求,會依據實作方式劇烈變化。自營型 MPC 系統(用戶自行運行 MPC 節點),保持強烈的去中心化特性,但需要高度技術專業。託管型 MPC 服務(第三方負責計算基礎設施)則提供更佳易用性,卻引入與服務商間的信任關係,這不見得與純粹的自託管原則一致。
這些不同信任模型的哲學意涵,不僅關於個別的安全考量,也涉及未來金融主權的議題。助記詞(seed phrase)體系是個人金融自主權最激進的體現,但實務上的限制使其適用於技術門檻極高的少數用戶。
多簽系統則示意金融主權可與結構化社會關係與組織治理並存。這對於希望保留自託管、又要進行集體決策的機構與社群,或許更為適合。多簽系統在企業與 DAO 場景的成功,證明去中心化並非要消滅一切結構信任。
MPC 系統則帶來最複雜的哲學提問,因為它可用密碼抽象層遮蔽信任關係。一方面,它可能維持高度安全性與極佳易用性,進而推動自託管理念進入主流。另一方面,它也可能削弱許多人認為加密貨幣價值主張不可或缺的透明度與用戶控制權。
可審計性(auditability)問題,成為衡量這些信任模型時的關鍵。助記詞體系完全可由用戶自行審查——任何人都可用開源軟體驗證助記詞與私鑰間的數學關係。多簽系統則是部分可審計——用戶可驗證多簽安排的技術屬性,但協同機制則須依靠社會信任。
MPC 系統的可審計性則面臨最大挑戰,因為密碼協定複雜,而分散式計算基礎設施對用戶而言可能不透明。值得注意的是,並非所有 MPC 錢包都是開源或可互操作的,這可能限制其易用性,以及與其他系統的相容性。這層不透明未必代表有問題,但會讓用戶必須信任數學證明與實作品質,而非直接檢驗安全特性。
而這些信任模型的去中心化意涵,也差距顯著。助記詞系統在個人層面達到了極致去中心化,但若其難度過高反而可能驅使用戶選擇託管服務,使生態系統趨向中心化。多簽系統以多方分權維持去中心化,但必要的協同機制可能引進中心化成分。
MPC 系統理論上有潛力同時兼顧高度去中心化與易用性,但這會顯著取決於具體實作。中心化 MPC 服務提供了更好的用戶體驗,卻可能背離去中心化目標;而去中心化 MPC 網絡則能保持哲學一致性,同時也會帶來全新的技術與經濟挑戰。
真實世界應用與案例
不同錢包技術的理論優缺點,若從真實世界應用角度檢視,將更加明確。不同組織與個人因自身的安全需求、操作限制及風險容忍度差異,往往傾向於選擇不同方案,於是創造出一個多元並存、各自服務不同需求的錢包技術生態系。
個人零售用戶是錢包技術最大的潛在市場,但其需求依技術熟悉度、資產規模及使用習慣而天差地別。對於交易頻率低、且已養成良好安全習慣的用戶來說,助記詞錢包仍是極具吸引力的方案。它的簡單性與完全控制權,正好呼應了許多人最初被加密貨幣吸引的哲學動機。
然而,助記詞管理對於剛接觸加密貨幣或缺乏技術背景的用戶來說格外困難。我們發現多數研究參與者對助記詞抱有嚴重誤解,導致高風險暴露於安全漏洞之下。這形成一大主流採用障礙,因許多潛在用戶會被助記詞的安全責任嚇退。
對這些用戶來說,MPC 錢包提供了一個有前景的替代方案,既維持自託管性質,又大幅降低金鑰管理負擔。Zengo 錢包就是一個讓用戶不須記住助記詞或金鑰即可創建自託管錢包的解決方案。這種做法消除了最重要的用戶體驗瓶頸之一,同時仍保有金鑰分散存儲所帶來的安全優勢。
企業金庫管理是多簽技術最成功的應用場景之一。持有大量加密資產的公司,必須在安全性與作業效率之間取得平衡,並滿足監管與稽核要求。BitGo 是一款為機構投資人及企業量身打造的多簽錢包解決方案,支援各種加密貨幣,並具備企業級安全特性,例如多用戶存取和進階政策控管。
企業應用案例展現多簽技術如何透過結構化授權流程,提升易用性並滿足法規合規性需求。不必讓個別員工為企業資產管理助記詞,多簽系統讓公司能導入符合內部既有流程的審批機制,同時維持密碼學層面的安全。
不過,企業需求同時也促使多簽技術朝向 MPC 系統演進,獲得許多類似好處,卻有更高運營效率。Fireblocks 已成為機構 MPC 錢包的業界標竿。該平台因其多層級安全設計、自動化交易流程及重視合規的理念,受到銀行、對沖基金及資產管理機構的信賴。其實現複雜的Here is the requested translation in zh-Hant-TW, with markdown links left untranslated as instructed:
政策與自動化合規檢查使MPC(多方計算)系統對於擁有複雜營運需求的機構特別具有吸引力。
加密貨幣交易所和託管服務代表了另一個重要的應用情境,在這些情境下,不同的錢包技術用於滿足不同的營運需求。許多交易所對其熱錢包採用多重簽名系統,因為由於交易是由自動化系統而非人工操作員處理,因此協調開銷是可控的。多重簽名的分散性帶來安全性優勢,而其營運開銷則可由自動化基礎設施吸收。
對於大額資產的冷錢包存儲,許多機構級託管機構已轉向MPC系統,這類系統在維持營運彈性的同時,提供更佳的安全性。Fireblocks是一家機構級數位資產託管商,提供支援超過30種區塊鏈協議與1,100種代幣的MPC錢包。這種通用的區塊鏈相容性,對需要支援多元客戶資產組合的託管服務業者來說格外重要,因為無需為每個區塊鏈分別維護基礎設施。
去中心化自治組織(DAO)對錢包技術來說是一個有趣的測試場域,因為它們將加密貨幣的去中心化理念與實用的治理需求結合起來。許多DAO為其金庫採用了多重簽名系統,發現多重簽名的協調需求與其治理流程十分契合。要求金庫交易必須收集多份簽章這一設計,創造了自然的檢查點,可以防止未經授權的支出,同時確保合法的治理決策得以實施。
然而,也有一些DAO正在實驗MPC系統,以實現更進階的治理模型。能夠執行可程式化政策及自動化合規檢查,能夠支援更複雜的治理架構,同時降低阻礙DAO運作的協調開銷。
家庭與遺產規劃是錢包技術中最具挑戰性的應用之一,因為它必須在安全性、可及性與社會互動間取得平衡。傳統的助記詞(seed phrase)方法在遺產規劃上製造了不少困難,因其必須在生前共享敏感資訊,或是冒著意外發生時資產永久遺失的風險。
多重簽名系統在遺產規劃方面有一定優勢,因為可讓家人參與安全防護,但不需完全的信任。22%的受訪者曾為帳號復原目的分享過助記詞,許多人雖然明白預先規劃復原方案的重要性,但卻未付諸行動。不過,多重簽名的協調需求,在親屬分布於不同地區或缺乏技術知識時,容易帶來現實上的困難。
MPC系統在遺產規劃上的潛力則更大,因其可實現更先進的復原機制,而無需家人之間的主動協調。社交復原系統、生物特徵認證、甚至機構備援服務,都能提供多元的資產復原路徑,同時維持防止未經授權存取的安全性。
跨境支付與匯款也是錢包技術應用的重要情境,技術選擇將帶來明顯的實務影響。對於跨國匯款的個人用戶來說,助記詞系統因其簡單與普遍性而具有優勢,因為不需要與其他人協調,也無需依賴不一定在各地都能獲得的服務提供者。
但在國際旅遊過程中,或是政局不穩地區,資安風險與助記詞管理的挑戰性特別高。能提供恢復機制並減少對實體儲存依賴的MPC系統,對這些用戶可能更為實用。
遊戲與NFT生態系已成為錢包技術的重要試驗場所,因為它們融合了高交易量與大量初次接觸加密貨幣的新手用戶。傳統助記詞管理方式在遊戲應用裡已被證明是一大採用障礙,因為用戶預期能像傳統App一樣輕鬆上手。
整合進遊戲App的MPC錢包,可賦予用戶自我託管的好處,無需理解複雜的金鑰管理概念。此外,Coinbase、幣安(Binance)和Web3Auth等平台提供的嵌入式錢包方案,已經把MPC整合到SDK中,讓應用和遊戲能提供安全且支援社交或生物辨識復原的自託管錢包。這種嵌入式路線,可能是將自託管普及至主流消費者應用的關鍵。
技術深入剖析:這些系統實際是如何運作
理解不同錢包技術的實務實現,需要了解其背後的密碼學與運算機制,這些機制決定了它們的安全性質。儘管一般用戶無需懂得所有技術細節也能有效使用這些系統,但細節上的實作差異對安全性、效能與長期可行性有重大影響。
助記詞系統依賴歷經數十年發展且已被驗證的密碼學標準。過程從熵值產生開始,錢包軟體會創建一組隨機數據,其熵足以確保密碼安全。此熵之後會按照BIP-39標準轉換為一串單詞,該標準定義了2048個單詞的清單及熵到單詞序列的數學關係。
助記詞作為一個輸入,會經過金鑰衍生函數產生實際用於交易的金鑰。BIP-32標準定義了如何從單一助記詞衍生出多組金鑰,讓錢包能為隱私或組織分化無限產生地址。助記詞與衍生金鑰間的數學關係具確定性,意味著同一助記詞可在不同裝置上永遠產生相同金鑰,從而實現錢包備份與恢復。
助記詞系統的安全性,完全仰賴最初熵值的隨機性與助記詞本身的保密。其底層密碼演算法經過長期測試,被認為可防禦所有已知攻擊,但系統本身不能防止助記詞被盜,因此這是驅動其他技術方案發展的本質弱點。
多重簽名系統是在基礎密碼學模型上擴展,要求多個簽名才能授權交易。雖然不同區塊鏈的技術實作差異很大,但總體原則為:建立一種特殊交易型別,指定多組公開金鑰,以及要求簽名的門檻數。
在比特幣中,多重簽名交易使用腳本操作碼(script opcodes)將簽名要求直接寫入區塊鏈交易。例如2-of-3多簽交易會包含三組公開金鑰,並要求其中兩個對應私鑰的有效簽名。比特幣網路審核這些簽名時,使用和單簽交易相同的密碼演算法,但適用於多組金鑰。
以太坊的多重簽名則不同,它主要仰賴智慧合約而非原生區塊鏈特性。以太坊多重簽名錢包實際上是智慧合約,裡面存有多組公開金鑰,並透過合約邏輯驗證簽名才執行交易。這種方式在政策設計上更有彈性,但同時需要更多運算資源與更高的gas費用。
多重簽名系統的安全性假設為:攻破多組互不關聯的私鑰,比攻破單一金鑰困難許多。這在現實中大多成立,但前提是各私鑰要真正獨立——存放地點不能相同、由不同人管理、並採用不同的安全措施保護。
MPC系統則運用更先進的密碼學技術,讓多方能共同簽署交易,但任何一方都無法獲得完整私鑰。其技術實作需要多個高級密碼學概念協同運作以達到理想的安全屬性。
門檻式秘密分享法(threshold secret sharing)是大多數MPC實作的基礎。這種方式可將一份秘密(私鑰)拆分成多份,只要收集到某一門檻數即可重構私鑰,少於門檻數則無法取得任何資訊。例如在3-of-5門檻方案中,任意三份即可重組私鑰,僅有兩份則對攻擊者無意義。
然而,單純將私鑰拆分、之後再合併,其實違背MPC初衷,因為某一時刻仍需還原完整私鑰。真正的MPC協議,會運用安全多方計算(secure multiparty computation)等方法,直接在分散的份額上執行密碼操作,而無需重建完整私鑰。
MPC簽名的實際運作通常採用多輪協議,由持有份額的多方交換特殊訊息,最終能共同產生合法簽名。具體協議內容依簽名演算法與安全要求不同而有所差異,但大致原理是,每方在本地對自己的份額運算,然後分享中間成果,最終綜合生成最終簽章。
---The two basic properties that a multi-party computation protocol must ensure are: Privacy: The private information held by the parties cannot be inferred from the execution of the protocol. Accuracy: If a number of parties within the group decide to share information or deviate from the instructions during the protocol execution, the MPC will not allow them to force the honest parties to output an incorrect result.
一個多方計算(MPC)協議必須確保的兩個基本特性為:隱私性:各方持有的私人資訊不能從協議的執行過程中被推知。準確性:如果群組中的某些成員在協議執行期間決定共享資訊或偏離指令,MPC 仍不會允許他們強迫誠實的參與者輸出錯誤的結果。
The distributed key generation process in MPC systems is particularly sophisticated because it must create key shares without ever creating the complete private key. This involves cryptographic protocols where multiple parties contribute randomness and perform joint computations to generate key shares that are mathematically related but individually reveal no information about the final key.
MPC 系統中的分散式金鑰生成流程特別複雜,因為它必須在從未產生完整私鑰的狀態下,創建金鑰分片。這涉及密碼學協議,多方共同提供隨機性並執行聯合計算,以產生彼此具數學關聯、卻無法獨立揭露最終金鑰資訊的金鑰分片。
The performance implications of these different approaches vary significantly. Seed phrase systems have minimal computational overhead because they use standard cryptographic operations that are highly optimized in most software and hardware implementations. The only performance consideration is the key derivation process, which is intentionally designed to be computationally expensive to slow down brute force attacks, but this only affects wallet creation and recovery, not routine transactions.
這些不同方案在效能上的影響差異顯著。助記詞系統的運算負擔極低,因為其採用的標準密碼學操作在大多數軟體與硬體中都已高度優化。唯一需考慮的效能問題是金鑰推導過程,此過程設計上刻意增加運算量,是為了降低暴力破解攻擊的可能性,但這只會影響錢包的創建和恢復,不會連帶影響日常交易。
Multisig systems have moderate performance overhead compared to single-signature transactions because they require multiple signature verifications. In Bitcoin, this primarily affects transaction size and validation time. In Ethereum, multisig transactions can require significantly more gas because they involve smart contract execution rather than simple signature verification.
多簽系統與單一簽名交易相比,效能負擔屬於中等,因為其需進行多重簽章驗證。在比特幣中,這主要會影響交易檔案的大小和驗證所需的時間;而在以太坊中,多簽交易可能需要明顯更多的 Gas,因為它涉及智能合約執行,而非單純的簽名驗證。
MPC systems have the highest computational overhead because they require multiple rounds of communication and cryptographic computation to generate each signature. While offering increased security, MPC wallets might slow down processes and require more communication compared to simpler methods. However, this overhead is generally acceptable for most applications, and ongoing research is focused on optimizing MPC protocols to reduce latency and computational requirements.
MPC 系統在所有方案之中具備最高的運算負擔,因為每筆簽名都需多輪溝通與密碼學運算。儘管能提供更高的安全性,MPC 錢包相較於較簡單的方法,過程可能更耗時且溝通需求更高。然而,大多數應用場景下這種負擔在可以接受的範圍,且目前研究也持續優化 MPC 協議以降低延遲與運算需求。
The network communication requirements also differ significantly between these approaches. Seed phrase systems require no coordination, making them ideal for offline or air-gapped environments. Multisig systems require coordination among key holders but only at the time of transaction authorization. MPC systems require more extensive communication between parties during the signature generation process, which can create challenges in high-latency or unreliable network environments.
這些方案在網路溝通需求上也有極大差異。助記詞系統無需協調,適合離線或隔離設備環境;多簽系統則僅在交易授權時需要金鑰持有人間協調;MPC 系統於產生簽名時需要參與方大量溝通,這在高延遲或網路不穩環境下可能帶來挑戰。
The blockchain compatibility implications are particularly important as the cryptocurrency ecosystem becomes increasingly multi-chain. Seed phrase systems work universally because they generate standard private keys that are compatible with any blockchain using the same cryptographic algorithms. Multisig systems require blockchain-specific implementations because each blockchain handles multisig transactions differently.
隨著加密貨幣生態系步入多鏈時代,區塊鏈相容性變得格外重要。助記詞系統具高度通用性,因為其產生的標準私鑰可用於任何採相同密碼學演算法的區塊鏈。多簽則需根據各鏈實現,因每個公鏈處理多簽交易的方式不同。
Unlike Multi-sig, MPC happens off-chain with only one single signature broadcast on-chain. It's data-light meaning it is cheaper and faster to execute, and much more secure. This blockchain-agnostic property makes MPC systems particularly attractive for organizations that need to operate across multiple blockchain ecosystems without maintaining separate infrastructure for each.
與多簽系統不同,MPC 在鏈下運作,最終只需將一筆簽章上鏈。這種「輕量資料」特性讓執行成本更低、速度更快、安全性也大幅提升。這種不依賴特定區塊鏈的性質,對於需要跨多鏈營運的組織極具吸引力,因為不須為各條鏈分別維護基礎設施。
Economic Implications and Market Impact
經濟層面影響與市場衝擊
The evolution of wallet technologies is reshaping the economic landscape of cryptocurrency in ways that extend far beyond individual user security. The different approaches to key management create distinct cost structures, risk profiles, and market dynamics that influence everything from institutional adoption to the development of new financial products and services.
錢包技術的演化,正以超越個人用戶資安的方式,重塑加密貨幣的經濟格局。不同金鑰管理方案形塑出明顯不同的成本結構、風險輪廓與市場動態,進而影響機構採用、甚至到新型金融產品與服務的誕生。
The direct costs associated with different wallet technologies vary significantly and often include hidden expenses that become apparent only through long-term use. Seed phrase management appears to have minimal direct costs, but proper security requires investments in storage infrastructure that many users underestimate. Professional-grade storage solutions such as bank safety deposit boxes, fireproof safes, or specialized storage services can cost hundreds or thousands of dollars annually for users with significant assets.
不同錢包技術的直接成本存在極大差異,且常伴隱性開支,需長期使用後才能顯現。助記詞管理看似成本極低,但若要確保安全,仍需投資儲存相關基礎設施——這點經常被用戶低估。專業級存取方案如銀行保管箱、防火保險箱或專業存儲服務,對於持有大量資產的用戶而言,每年可能需花費數百甚至數千美元。
The insurance implications are particularly important for institutional users. Traditional insurance policies generally don't cover cryptocurrency losses, and specialized cryptocurrency insurance is expensive and often requires specific security measures. Seed phrase systems typically receive the lowest insurance coverage because of the single point of failure risk, while multisig and MPC systems can qualify for better coverage terms due to their distributed security models.
保險層面的影響對機構用戶尤為重要。傳統保險通常不承保加密貨幣損失,而專用加密保險成本高昂,且常需符合特定安全措施。由於單點故障風險,助記詞方案基本拿不到好條件保險;相較之下,多簽與 MPC 系統因為其分散式安全架構,更可能獲得更優惠的保險條款。
In 2023 alone, approximately $3.8 billion worth of cryptocurrency was stolen through various cyberattacks, with a significant portion attributed to single-signature wallet vulnerabilities. Multisig wallets have proven to be an effective deterrent, reducing the risk of unauthorized access by over 60%. These statistics translate directly into insurance pricing and risk assessment, making advanced wallet technologies increasingly attractive from a total cost of ownership perspective.
僅在 2023 年,就有約 38 億美元的加密貨幣因各種網路攻擊被盜,其中有大量案例與單一簽名錢包漏洞有關。多簽錢包已證明能有效降低風險,未經授權存取的事件減少超過 60%。這些數據直接影響保險定價與風險評估,使得進階錢包技術在整體擁有成本層面變得更具吸引力。
The operational costs associated with different wallet technologies create different economic incentives for various types of organizations. Small individual users may find seed phrase management to be the most cost-effective approach despite the risks, while larger organizations often discover that the coordination and security costs of multisig systems are justified by the risk reduction they provide.
不同錢包技術在運營成本上的差異,會給不同組織帶來各自的經濟誘因。小型與個人用戶可能認為助記詞管理最省錢,儘管風險較高;而規模較大的組織則常認為多簽方案雖然協同及安全成本高,但能有效分散風險,成本是值得的。
MPC systems typically have higher upfront costs due to their technical complexity, but they can provide significant operational savings for organizations with complex security requirements. What sets Fireblocks apart is its network of 1,800+ institutions, allowing instant, secure settlements without counterparty risk. This network effect creates economies of scale that can make MPC systems more cost-effective than traditional approaches for institutions that frequently transact with other network participants.
MPC 系統因技術複雜度較高,前期建置費用也會較多,但對於安全需求高且複雜的組織來說,能在後續運營成本中帶來顯著節省。Fireblocks 的獨特之處,在於其 1,800 家以上的機構網絡,讓用戶之間可即時且低風險地完成結算。這種網絡效應帶來的規模經濟,甚至可能讓 MPC 系統對經常與網絡內成員交易的機構來說,比傳統方案更具成本優勢。
The impact on transaction costs varies significantly between blockchain networks and transaction types. Bitcoin multisig transactions are larger than single-signature transactions, resulting in higher transaction fees during periods of network congestion. Ethereum multisig transactions require more gas because they involve smart contract execution, making them significantly more expensive than simple transfers.
交易成本的變化也因區塊鏈類型及交易種類而大有不同。比特幣多簽交易的資料體積高於單一簽名,若遇鏈上壅塞,費用也會增加。以太坊多簽交易需消耗較多 Gas ,因為涉及智能合約運行,成本遠高於單純轉帳。
A key feature of TotalSig is its ability to optimize transaction fees, potentially reducing them by 3 to 5 times. This is especially valuable during periods of high gas prices, allowing users to save significant amounts per transaction and providing cost-effective solutions during network congestion. This demonstrates how advanced wallet technologies can actually reduce transaction costs through optimization techniques that aren't available with simpler approaches.
TotalSig 的一大特點是能最佳化交易手續費,最高能減少 3 到 5 倍。這在高 Gas 價期間尤其有價值,讓用戶每筆交易都能省下可觀成本,並在網路壅塞時提供更有競爭力的解決方案。這說明了進階錢包技術如何通過優化,做到簡單方案難以達成的手續費降低。
The market impact of wallet technology evolution extends to the development of new financial products and services. The security limitations of seed phrase systems have created a large market for custodial services, where institutions manage cryptocurrency on behalf of users who don't want to handle key management themselves. This custodial market represents billions of dollars in assets under management and generates significant fee revenue for service providers.
錢包技術的推進,已帶動新型金融產品與服務的誕生。例如,助記詞系統的安全瓶頸催生了託管服務市場,由機構代替不願自行管理金鑰的用戶來保管加密資產。目前託管市場已累積數十億美元資產規模,為服務提供者創造豐厚使用費收入。
However, the emergence of more user-friendly self-custody solutions could potentially disrupt this market. If MPC wallets and other advanced technologies can provide institutional-grade security with consumer-friendly usability, they might enable users to maintain self-custody without sacrificing convenience. This could reduce demand for custodial services and shift value to wallet infrastructure providers.
然而,若能有更易用的自我託管技術問世,託管市場結構將受顛覆。若 MPC 錢包和其他進階技術,能同時具機構級安全與消費者友善體驗,用戶將有機會維持自主管理權又不失便利。如此將減少對第三方託管的依賴,價值也會逐漸轉移到錢包基礎設施供應商手上。
The institutional adoption patterns reveal important economic dynamics in the wallet technology market. Early institutional adopters often chose multisig solutions because they were the most mature alternative to single-signature wallets. However, many institutions are now migrating to MPC systems as they mature and offer better operational efficiency.
機構用戶的採用趨勢,顯現了錢包技術市場內特有的經濟動態。早期機構多選用多簽方案,因其是最成熟的單簽方案替代選擇。但如今,隨著 MPC 系統的成熟和營運效率提升,越來越多機構開始轉向 MPC。
Looking ahead to the second half of 2025, several developments are expected. Bitcoin.com Wallet will integrate deeper Zano support for private payments and improve smart recovery features. Binance Web3 Wallet will add gasless transaction support and biometric recovery tools. MetaMask Institutional will expand its MPC custodian integrations, offering more control and compliance-ready infrastructure. This institutional migration toward MPC systems reflects their economic advantages for complex organizational use cases.
展望 2025 年下半年,相關錢包還將有多項新發展。例如 Bitcoin.com Wallet 將深度整合 Zano 支援以強化匿名支付,並優化智慧恢復機制;Binance Web3 Wallet 會加入免 Gas 轉帳和生物辨識恢復等功能;MetaMask Institutional 則會擴大 MPC 託管整合,帶來更高控管性與合規基礎設施。機構大舉遷往 MPC 系統,正體現其在複雜組織場景下的經濟效益。
The competitive dynamics in the wallet technology market are being shaped by the different value propositions of these technologies. Seed phrase wallets compete primarily on simplicity and cost, making them attractive for individual users and small organizations with limited security budgets. Multisig solutions compete on proven security and regulatory compliance, appealing to institutions that need established solutions with clear audit trails.
錢包市場競爭格局,正受各技術的不同價值主張所牽引。助記詞錢包以操作簡單、成本低廉為競爭重點,對安全預算有限的個人與小型組織具吸引力;多簽方案主打安全性及法規合規,吸引需明確稽核軌跡的大型機構。
MPC systems compete on the promise of combining the security benefits of multisig with the usability of single-signature systems, but they must overcome higher costs and technical complexity to achieve market adoption. The success of MPC providers will likely depend on their ability to deliver on this value proposition while building ecosystem partnerships that justify the technology premium.
MPC 系統主打結合多簽安全與單簽易用性的雙重優勢,但若要廣泛普及,仍需克服高成本及技術複雜度等門檻。MPC 供應商的成功與否,關鍵在於能否實現這一價值主張,並且與生態圈內合作夥伴協力,讓其技術保費有實質依據。
The network effects associated with different wallet technologies create interesting economic dynamics. Seed phrase systems benefit from universal compatibility and the large ecosystem of
不同錢包技術帶來的網絡效應,也創造出獨特的經濟現象。助記詞系統享有高普遍相容性,以及龐大的生態圈資源。supporting tools and services. Multisig systems benefit from institutional adoption and regulatory acceptance, creating credibility that drives further adoption.
MPC systems are attempting to create network effects through platform strategies, where multiple services build on common MPC infrastructure. The public crypto exchange's MPC wallet enables a large and growing number of users to access the Web3 ecosystem in a safe, reliable, and secure manner. If successful, these platform strategies could create powerful economic moats that favor early MPC adopters.
MPC 系統正在嘗試透過平台策略來創造網絡效應,在這些策略下,多個服務可建立於共同的 MPC 基礎設施之上。公共加密貨幣交易所的 MPC 錢包讓越來越多的用戶能夠以安全、可靠且保護良好的方式進入 Web3 生態系。如果這些平台策略成功,將能為早期 MPC 採用者打造強大的經濟護城河。
The impact on cryptocurrency adoption more broadly may be the most significant economic implication of wallet technology evolution. The complexity and risk associated with seed phrase management has been identified as a major barrier to mainstream cryptocurrency adoption. If advanced wallet technologies can reduce this barrier while maintaining the self-custody benefits that make cryptocurrency valuable, they could unlock much larger markets.
加密貨幣錢包技術的演進對更廣泛的加密貨幣普及可能造成最為深遠的經濟影響。助記詞管理的複雜性與風險已被認為是加密貨幣大眾化的主要障礙之一。如果先進的錢包技術能降低這個門檻,同時維持加密貨幣的自我託管優勢,就能解鎖更龐大的市場規模。
However, the economic incentives around wallet technology development create potential conflicts with decentralization principles. Companies that invest in developing advanced wallet technologies need to generate returns on their investments, which may lead them toward business models that concentrate control or extract value in ways that contradict cryptocurrency's philosophical foundations.
然而,錢包技術開發周邊的經濟誘因可能會與去中心化原則產生潛在衝突。投入資源開發先進錢包技術的公司需要獲得回報,因此可能會採用集中控制或萃取價值的商業模式,有違加密貨幣的哲學基礎。
The regulatory implications of different wallet technologies also have significant economic consequences. Regulators are generally more comfortable with multisig systems because they provide clear audit trails and can implement compliance controls that are difficult or impossible with individual seed phrase management. MPC systems may offer even better compliance capabilities while maintaining user control, potentially reducing regulatory friction for cryptocurrency businesses.
不同錢包技術的監管層面同樣帶來顯著的經濟影響。監管機構通常對多重簽章系統較為接受,因其能提供清晰的稽核紀錄並可執行合規控管,這在單一助記詞管理中難以實現。MPC 系統則有機會提供更佳的合規能力,同時維持用戶的主控權,有潛力進一步降低加密貨幣事業的監管摩擦。
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the technological advances represented by multisig and MPC wallets, each approach faces significant challenges that limit their applicability and effectiveness in certain scenarios. Understanding these limitations is crucial for making informed decisions about wallet technology adoption and for identifying areas where further innovation is needed.
儘管多重簽章與 MPC 錢包在技術層面上有顯著的進展,兩種方式仍面臨重大挑戰,這些挑戰限制了它們在特定場景下的應用性與效能。理解這些限制對於智慧採用錢包技術及辨識未來創新方向具有關鍵意義。
User education remains a fundamental challenge across all wallet technologies, but the nature of the educational burden varies significantly. While seed phrase management appears conceptually simple, many believed they could reset their seed phrase if they lost them, indicating that even basic concepts are widely misunderstood. This educational gap contributes to security vulnerabilities and user losses that undermine confidence in self-custody approaches.
用戶教育依舊是所有錢包技術的核心挑戰,但其教育負擔的性質有很大差異。雖然助記詞管理在概念上看似簡單,很多用戶卻誤以為遺失後可以重設助記詞,顯示出連基本原理都廣泛被誤解。這種教育落差導致安全漏洞與用戶損失,削弱了對自我託管方式的信心。
Multisig systems introduce different educational challenges because users must understand not only the technical aspects of key management but also the social dynamics of coordination and governance. The technical knowledge required to set up and maintain multisig wallets is often beyond the capabilities of individual users, limiting adoption to organizations with dedicated technical resources.
多重簽章系統則有另一種教育難題,因為用戶除了需理解密鑰管理的技術層面,還要熟悉協作與治理的社會動態。設置與維護多重簽章錢包所需的技術知識,對多數個人用戶來說門檻太高,使應用侷限於有專業技術團隊的組織。
MPC systems present perhaps the greatest educational challenge because they abstract away the underlying security mechanisms in ways that can be difficult for users to verify or understand. While this abstraction can improve usability, it can also create false confidence or inappropriate trust in systems that users cannot fully evaluate. The complexity of the underlying cryptography makes it difficult for users to distinguish between well-implemented and poorly-implemented MPC systems.
MPC 系統帶來的教育挑戰更大,因為其會將底層安全機制抽象化,讓用戶難以驗證或理解。這種抽象雖提升了易用性,但也可能讓用戶對難以評估的系統產生錯誤信心或不當信任。底層密碼學的複雜性也讓用戶難以辨別 MPC 系統實作的優劣。
The standardization challenges facing the wallet technology ecosystem create fragmentation that limits interoperability and increases development costs. While seed phrase systems benefit from well-established standards like BIP-39 and BIP-32, multisig implementations vary significantly between different blockchains and wallet providers. It is difficult for multisig wallet providers to securely support new chains as the few cryptocurrency protocols that support multisig have distinct implementations from one another.
錢包技術生態系的標準化挑戰造成分裂,限制了互通性並推高開發成本。助記詞系統受惠於如 BIP-39 及 BIP-32 等完善標準,然而多重簽章實作在不同區塊鏈與錢包提供者間有很大差異。因為少數支持多重簽章的加密貨幣協定彼此實作不同,多重簽章錢包要安全支援新鏈變得困難。
MPC systems face even greater standardization challenges because the technology is newer and the implementation space is more complex. Different MPC protocols offer different tradeoffs between security, performance, and functionality, making it difficult to establish universal standards. The lack of standardization creates vendor lock-in risks and makes it difficult for users to migrate between different MPC providers.
MPC 系統面臨更嚴峻的標準化問題,因為相關技術較新,實作領域也更加複雜。不同的 MPC 協定在安全性、效能和功能面上各有取捨,難以訂立統一標準。缺乏標準化使業者綁定風險提高,用戶要轉移到不同 MPC 供應商也變得困難。
Recovery and inheritance planning present persistent challenges across all wallet technologies, but the specific obstacles vary significantly. Seed phrase systems require users to securely share sensitive information with trusted parties or accept the risk of permanent loss. The social dynamics of sharing seed phrases often conflict with security best practices, creating difficult tradeoffs between accessibility and protection.
恢復與遺產規劃是在所有錢包技術中持續存在的挑戰,但具體困難各不相同。助記詞系統要求用戶需將敏感資訊安全地與可信任對象分享,否則就只能接受資產永久損失的風險。助記詞分享的社會層面經常與資安最佳實踐衝突,使可用性與保護之間的取捨變得棘手。
Moreover, only a minority have engaged in any estate planning for their crypto assets. This lack of planning creates significant risks for asset recovery and inheritance, particularly given the irreversible nature of cryptocurrency transactions. Traditional legal frameworks for inheritance often don't accommodate the unique properties of cryptographic assets, creating additional complexity for families and estates.
而且,只有少數人曾替自己的加密資產進行遺產規劃。這種規劃的缺乏創造了重大資產恢復與繼承風險,尤其在加密貨幣交易不可逆的情境下更為嚴重。傳統法律體系對加密資產的獨特性往往無法完全適用,為家族與遺產管理造成更多的複雜性。
Multisig systems can provide better inheritance planning capabilities by allowing multiple parties to be involved without sharing complete control, but they introduce coordination challenges that can be difficult to manage across generations or changing family relationships. The technical requirements for maintaining multisig wallets over long periods can create dependencies on specific service providers or technical expertise that may not be sustainable.
多重簽章系統可讓多方共同參與資產管理而無需完全分享控制權,因此在遺產規劃上較具優勢。但也會帶來難以跨世代或家族關係變更時管理的協調難題。長期維護多重簽章錢包的技術要求,可能使其依賴特定服務供應商或專業人才,這些依賴未必可長期維持。
MPC systems offer promise for addressing inheritance challenges through sophisticated recovery mechanisms, but they often require trust in service providers or infrastructure that may not be available indefinitely. The long-term viability of MPC services is difficult to evaluate, creating risks for users who depend on them for asset recovery.
MPC 系統透過精密的恢復機制,有潛力解決遺產問題,但通常需要依賴服務提供者或基礎設施,而這些資源未必能長期可用。MPC 服務的長期可持續性難以評估,對於仰賴它們做資產恢復的用戶,風險亦隨之增加。
Performance and scalability limitations affect different wallet technologies in different ways. Seed phrase systems have minimal performance overhead for individual use, but they don't scale well to organizational use cases that require coordination among multiple parties. The lack of built-in authorization controls makes seed phrase systems unsuitable for complex governance requirements.
各種錢包技術的效能與擴展性限制各有不同。助記詞系統在個人使用情境下效能負擔極小,但若應用於需多人協作的組織場景則表現不佳。缺乏內建授權控管使助記詞系統無法滿足複雜治理的需求。
Multisig systems can handle complex authorization requirements effectively, but the coordination overhead limits their scalability for high-frequency transactions. The blockchain-specific nature of multisig implementations also creates scalability challenges for organizations operating across multiple networks.
多重簽章系統能有效處理複雜授權需求,但協作負擔卻限制了其於高頻交易中的擴展性。此外,不同區塊鏈的多重簽章實作專屬性,對於跨多鏈運作的組織來說亦是擴展上的挑戰。
The process of transaction authorization in MPC wallets, which requires collaboration among multiple parties, can introduce delays, especially in high-frequency trading environments. While MPC systems offer better scalability than traditional multisig for many use cases, the computational overhead and communication requirements can create bottlenecks in scenarios requiring rapid transaction processing.
MPC 錢包的交易授權流程需要多人協作,可能導致延遲,尤其是在高頻交易環境下。儘管 MPC 系統在許多場景下較傳統多重簽章具更佳的可擴展性,但其運算負擔與通信需求,在需高速處理交易的情境中仍可能造成瓶頸。
Regulatory uncertainty creates challenges for all advanced wallet technologies, but the specific risks vary. Multisig systems are generally well-understood by regulators because they provide clear audit trails and can implement compliance controls. However, the distributed nature of key management can create challenges for meeting certain regulatory requirements, particularly in jurisdictions with strict custody regulations.
監管不確定性對所有先進錢包技術造成挑戰,但各自的風險不盡相同。多重簽章系統因提供清楚的稽核紀錄且可執行合規控管,通常較受監管機關理解。然而,其金鑰管理分散的特性,可能使其難以符合法規嚴格的託管規定。
MPC systems present more complex regulatory challenges because the distributed nature of key management may not fit cleanly into existing regulatory frameworks. Regulators may struggle to understand which parties have custody and control over assets in MPC systems, potentially creating compliance challenges for institutional adopters.
MPC 系統則面臨更複雜的監管難題,因金鑰管理分散的架構,未必能直接套用現有的監管體系。監管機關可能難以釐清在 MPC 架構下,哪些方實際掌控資產,這對機構用戶造成合規困難。
The technical debt and maintenance challenges associated with different wallet technologies create long-term sustainability concerns. Seed phrase systems benefit from their simplicity and the maturity of supporting infrastructure, making them relatively easy to maintain over long periods. However, the security challenges associated with individual key management may become more severe as attack techniques evolve.
不同錢包技術的技術債與維運問題,帶來長期可持續性的隱憂。助記詞系統因結構單純、支援基礎設施成熟,長期維運相對容易。不過與個人密鑰管理有關的安全風險,隨著攻擊手法演進,可能會越來越嚴峻。
Multisig systems require ongoing maintenance to stay current with blockchain protocol changes and security best practices. The blockchain-specific nature of multisig implementations creates technical debt that can be expensive to maintain as the ecosystem evolves.
多重簽章系統需持續維護,才能跟上市場上的區塊鏈協議與資安最佳實踐。多重簽章系統的區塊鏈專屬性會累積技術債,隨生態發展維護成本也會提高。
MPC systems face the greatest maintenance challenges due to their complexity and the rapid evolution of the underlying technology. The cryptographic protocols that underpin MPC systems continue to evolve, potentially requiring significant updates or migrations to maintain security and performance. The dependency on specialized expertise for maintenance makes MPC systems particularly vulnerable to technical debt accumulation.
MPC 系統的複雜性及底層技術快速推進,使其面臨最嚴峻的維護挑戰。支撐 MPC 的密碼學協定不斷進化,為維持安全和效能,可能需大幅更新或遷移。此一維護對專業技術極度依賴,使 MPC 系統特別容易累積技術債。
Interoperability challenges limit the effectiveness of all wallet technologies in the increasingly multi-chain cryptocurrency ecosystem. While seed phrase systems provide good compatibility across different blockchains, they don't offer built-in solutions for cross-chain transactions or unified management of multi-chain portfolios.
日益多鏈化的加密貨幣生態下,互通性挑戰限制了各種錢包技術的效用。助記詞系統雖然能在不同區塊鏈間提供良好相容性,但無法內建支援跨鏈交易或多鏈資產統一管理方案。
Integrating MPC wallets seamlessly with the existing infrastructure of blockchain and cryptocurrency ecosystems can be difficult. This lack of interoperability might limit their widespread adoption as users and services look for solutions that can easily work within the current landscape.
MPC 錢包要無縫整合到區塊鏈及加密貨幣生態現有基礎架構並不容易。這種互通性的缺乏,可能會限制 MPC 技術的推廣,尤其在用戶與服務尋求與現有生態輕鬆整合方案時。
The cost and accessibility barriers associated with advanced wallet technologies create challenges for widespread adoption. While (譯至此)the total cost of ownership may favor advanced systems for institutional users, the upfront costs and technical complexity can be prohibitive for individual users and small organizations. This creates a potential bifurcation in the market where advanced security is available primarily to well-resourced users.
整體擁有成本對於機構用戶而言,可能會更傾向選擇先進系統,但對個人用戶和小型組織來說,高昂的前期成本與技術複雜性卻可能造成進入門檻過高。這導致市場可能出現分化,先進的安全防護主要只對資源充足的用戶開放。
Future Developments and Emerging Trends
The trajectory of wallet technology development suggests that we are approaching a period of rapid innovation and convergence, where the distinct categories of seed phrase, multisig, and MPC wallets may begin to blur as new hybrid approaches emerge. Several technological and market trends are shaping this evolution in ways that could fundamentally transform how people interact with cryptocurrency.
錢包技術的發展趨勢顯示,我們正進入一個快速創新和趨同的時期,種子短語、多簽與MPC錢包這些明顯區分的類型,隨著新型混合方案的出現,界線將逐漸模糊。多項技術和市場趨勢正在推動這一演化,有可能從根本上改變人們與加密貨幣的互動方式。
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into wallet security represents one of the most promising areas of development. AI systems can potentially provide intelligent risk assessment, automated policy enforcement, and predictive security monitoring that could make all types of wallets more secure and user-friendly. Machine learning algorithms could analyze transaction patterns to detect suspicious activity, optimize fee structures, and even provide personalized security recommendations based on individual usage patterns.
將人工智慧(AI)與機器學習技術整合到錢包安全中,是最具前景的發展領域之一。AI系統有望提供智慧風險評估、自動化政策執行以及預測性安全監控,從而讓各類錢包更加安全且易用。機器學習演算法還可以分析交易模式來偵測可疑活動、優化手續費結構,甚至根據個人使用習慣提供客製化的安全建議。
Biometric authentication is becoming increasingly sophisticated and accessible, creating opportunities to replace or supplement traditional authentication methods across all wallet types. Advanced biometric systems could provide the security benefits of hardware tokens while offering the convenience of always-available authentication. The combination of biometric authentication with MPC systems could enable truly seamless self-custody experiences that don't require users to manage any traditional credentials.
生物辨識驗證技術越來越精密且普及,為各類錢包提供取代或補充傳統身份驗證方式的機會。先進的生物特徵系統能帶來類似硬體金鑰的安全性,同時具備隨時可用的便利性。如果將生物特徵認證與MPC技術結合,將能實現真正無縫且無需管理傳統憑證的自我託管體驗。
Phantom will roll out smarter token and NFT data tools and test MPC-based recovery. Coinbase Wallet will continue embedding MPC-backed wallets into third-party apps through its WaaS SDK. This integration of MPC technology into consumer applications represents a significant trend toward making advanced security invisible to end users while maintaining the benefits of self-custody.
Phantom將推出更聰明的代幣與NFT數據工具,並測試基於MPC的恢復方案。Coinbase Wallet則透過其WaaS SDK持續將MPC支持的錢包嵌入第三方應用中。這類將MPC技術整合進消費級應用的趨勢,代表先進的安全性正逐漸對終端用戶變得無感,但同時保有自我託管的優勢。
The development of account abstraction on Ethereum and other smart contract platforms is creating new possibilities for wallet functionality that blur the lines between traditional categories. Account abstraction (AA) is a blockchain feature that allows smart contracts to function as fully customizable wallets, removing the need for externally owned accounts (EOAs) like traditional Ethereum wallets. This capability enables wallets to implement complex authorization logic, automated transactions, and recovery mechanisms that were previously impossible.
以太坊及其他智能合約平台上的帳戶抽象(Account Abstraction, AA)發展,正創造讓錢包功能模糊傳統類別界線的新可能。帳戶抽象允許智能合約像錢包一樣被完全自訂,免除過去需要外部帳戶(EOA,例如傳統以太坊錢包)的需求。這一功能讓錢包可實作更複雜的授權邏輯、自動化交易以及以前難以實現的恢復機制。
Account abstraction could enable hybrid systems that combine elements of multisig and MPC technology while adding programmable features like automated compliance checking, conditional transactions, and social recovery mechanisms. These capabilities could make sophisticated wallet security accessible to mainstream users without requiring them to understand the underlying complexity.
帳戶抽象還能催生結合多簽和MPC技術元素的混合系統,並增添可編程功能,如自動合規檢查、條件式交易和社交恢復機制。這些能力可以讓大眾用戶享有高級錢包安全性,且不必深入理解複雜的運作機制。
The emergence of decentralized identity systems could provide new foundations for wallet security and recovery that don't depend on traditional seed phrases or centralized service providers. Decentralized identity could enable reputation-based recovery mechanisms, social attestation systems, and cross-platform identity verification that could make wallet management both more secure and more user-friendly.
去中心化身份系統的出現,為錢包安全性與恢復提供了不依賴傳統助記詞或中心化服務的新基礎。去中心化身份認證可以讓聲譽式恢復、社交背書、跨平台身份驗證成為可能,使錢包管理更安全也更易用。
Cross-chain interoperability continues to evolve rapidly, with new protocols and standards emerging to enable seamless asset management across multiple blockchain networks. The wallet technologies that can most effectively integrate with these interoperability solutions will likely have significant advantages in the increasingly multi-chain cryptocurrency ecosystem.
跨鏈互通性持續快速進化,帶來支援多鏈資產管理的全新協議與標準。能和這些跨鏈解決方案緊密整合的錢包技術,在多鏈加密生態中將具有明顯優勢。
The revamped wallet is also gearing up to support all blockchains compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and select others, such as Solana. This trend toward universal blockchain support will likely favor MPC systems and account abstraction approaches that can provide consistent interfaces across different blockchain architectures.
全新設計的錢包也正準備支援所有與以太坊虛擬機(EVM)相容的區塊鏈以及部分其他鏈(如Solana)。這種邁向區塊鏈通用支援的趨勢,應有利於MPC系統及帳戶抽象方案,因為它們能在異質區塊鏈間提供一致的介面體驗。
The regulatory landscape is evolving in ways that could significantly impact wallet technology development. As governments around the world develop more sophisticated cryptocurrency regulations, wallet providers will need to implement compliance features that can satisfy regulatory requirements without compromising the benefits of self-custody.
監管環境的變化可能對錢包技術發展帶來重大影響。各國政府持續推出更精細的加密貨幣管制規章,錢包服務供應商必須設計出既能符合法規、又不犧牲自主管理優勢的合規功能。
The development of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) could create new requirements for wallet interoperability and compliance monitoring that influence the design of all wallet technologies. While CBDCs may operate on different technical principles than existing cryptocurrencies, the wallet infrastructure that supports them will likely need to integrate with existing cryptocurrency systems.
央行數位貨幣(CBDC)的發展,可能會對錢包互通性及合規監控提出全新要求,進而影響所有錢包技術的設計。儘管CBDC在技術層面或許與現有加密貨幣有所不同,但相應的錢包基礎設施仍須與現有加密系統實現整合。
Privacy-preserving technologies continue to advance, with new cryptographic techniques enabling stronger privacy protection without sacrificing security or compliance capabilities. Zero-knowledge proofs, homomorphic encryption, and other advanced cryptographic techniques could enable wallet systems that provide complete transaction privacy while still supporting regulatory compliance and audit requirements.
隱私保護技術亦持續進步,新的密碼學方法能在不犧牲安全或合規性的前提下,增強隱私防護。零知識證明、同態加密及其他先進加密技術,有望打造既能完全隱藏交易細節、又可符合法規與稽核需求的新型錢包系統。
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and edge computing capabilities could enable new forms of distributed wallet security that take advantage of multiple connected devices. Rather than relying on centralized servers or coordination between human parties, future wallet systems could leverage the computational resources of multiple devices to provide distributed security while maintaining usability.
物聯網(IoT)裝置和邊緣運算能力的導入,將帶來利用多設備優勢的新型分散式錢包安全。未來的錢包系統不需再依賴中心化伺服器或人為協作,而是能調用多個設備的計算資源,同時提供分散式安全性和良好使用體驗。
Quantum computing represents both a threat and an opportunity for wallet technology development. While quantum computers could potentially break existing cryptographic algorithms, they could also enable new forms of cryptographic security that are fundamentally more secure than current approaches. Wallet technologies that can adapt to post-quantum cryptography will have significant advantages as quantum computing capabilities advance.
量子運算對錢包技術而言,同時是威脅也是機會。雖然量子電腦有可能破解現有密碼演算法,但它也能催生比現有方案更堅不可摧的新型密碼安全體系。能因應後量子密碼學錢包技術,將隨著量子運算進展而具備重大優勢。
The development of more sophisticated hardware security modules (HSMs) and trusted execution environments (TEEs) could enable new forms of secure computation that combine the benefits of hardware security with the flexibility of software-based systems. These technologies could enable MPC systems that provide better security guarantees while reducing the coordination overhead associated with current implementations.
更先進的硬體安全模組(HSM)和可信執行環境(TEE)技術的發展,能結合硬體安全優勢與軟體彈性,實現新型安全運算方式。這些技術可助MPC系統在提升安全性的同時,降低現有多方協作的協調成本。
Social recovery mechanisms are becoming more sophisticated and may represent a convergence point between different wallet approaches. Bitget Wallet will introduce a new "smart recovery" feature combining MPC and social login. These systems could provide the security benefits of distributed control while eliminating the coordination challenges that have limited multisig adoption.
社交恢復機制日益成熟,或將成為各種錢包技術趨同的關鍵。Bitget Wallet將推出結合MPC與社交登入的「智慧恢復」功能。這類系統可在兼具分散式控制安全性的同時,消除多簽普及受限的協作難題。
The gamification of wallet security could make good security practices more engaging and accessible to mainstream users. By incorporating elements of gaming, achievement systems, and social interaction, wallet providers could encourage users to adopt better security practices while making the overall experience more enjoyable.
錢包安全性的遊戲化設計,能讓良好安全習慣變得更加有趣並易於大眾接受。藉由導入遊戲、成就系統和社交互動等元素,錢包服務商能引導用戶養成更佳安全規範,同時提升整體使用樂趣。
Automated compliance and reporting capabilities are becoming more sophisticated, potentially enabling wallet systems that can satisfy complex regulatory requirements without requiring manual intervention from users. These systems could automatically generate audit trails, enforce spending policies, and report transactions to relevant authorities while maintaining user privacy and control.
自動化合規與報告功能趨於成熟,有望讓錢包系統在無須用戶手動操作下,滿足複雜的監管規範。這些系統可以自動產生稽核記錄、執行消費政策,並將必要交易回報有關機關,同時維持用戶隱私與主控權。
Recommendations and Best Practices
Navigating the complex landscape of wallet technologies requires a strategic approach that considers individual needs, risk tolerance, and technical capabilities. The decision between seed phrase, multisig, and MPC approaches should be based on careful evaluation of specific use cases rather than assuming that any single technology is universally optimal.
在錢包技術這個複雜領域中導航,需要結合策略性思維,考量個人需求、風險容忍度與技術能力。選擇種子短語、多簽或MPC方案時,應根據實際使用情境仔細分析,而不是一味假設某一技術對所有人都最適合。
For individual users who are new to cryptocurrency or have limited technical expertise, the primary considerations should focus on balancing security with usability while minimizing the risk of permanent loss due to user error. Traditional seed phrase management may be appropriate for users who can commit to developing strong security practices and who value maximum control over their assets. However, this approach requires significant ongoing attention to security details and backup procedures.
對於加密貨幣新手或技術能力有限的個人用戶,首要考量應是在安全性與易用性之間取得平衡,並盡量降低因操作失誤造成永久損失的風險。傳統助記詞管理適合有恆心養成嚴謹安全習慣、且重視資產完全控制權的用戶,但這種方式需要長期投入心力在安全細節與備份程序上。
As soon as you create a new wallet or key, make sure to record your recovery phrase with your preferred method. Self-custody wallet providers, including BitPay, do not save or take responsibility for your seed phrase. Users who choose seed phrase systems must immediately implement proper backup procedures and should never delay this critical security step.
每當你建立新錢包或金鑰時,應立刻用自己習慣的方式記錄恢復短語。包括BitPay在內的自我託管錢包服務商,都不會幫你保存或負責你的助記詞。選擇助記詞方式的用戶必須馬上執行適當備份,切勿拖延這個至關重要的安全步驟。
For individual users who prioritize convenience or who are concerned about their ability to manage seed phrases safely, MPC wallets offer an increasingly attractive alternative. Zengo: With an excellent record as a safe self-custodial MPC wallet, Zengo makes asset management easier while providing stronger protection against unauthorized access. These systems can provide institutional-grade security while eliminating many of the user experience challenges associated with traditional key management.
若注重便利性或擔心自己無法妥善管理助記詞,可考慮MPC錢包。Zengo:作為一款知名的安全自管MPC錢包,Zengo使資產管理變得簡單,同時擁有更強的未經授權訪問防護。這類系統能帶來機構級安全力,且解決了傳統金鑰管理帶來的種種體驗難題。
However, users considering MPC systems should carefully evaluate the long-term viability and trustworthiness of the service providers they depend on. The distributed nature of MPC security provides protection against many types of attacks, but users must still trust that the service infrastructure will remain available and secure over time.
然而,考慮採用MPC系統時,必須審慎評估所依賴服務商的長期可用性與可信度。雖然MPC的分散安全性可以防禦多種攻擊,但用戶仍需信賴服務基礎設施能長久維持可用與安全。
For organizations and institutions, the choice between multisig (機構和組織用戶的多簽/...... 後文省略,請補全內容以便繼續翻譯)and MPC systems often depends on specific operational requirements and regulatory constraints. Organizations with established governance processes and clear authorization hierarchies may find that multisig systems align well with their existing procedures while providing clear audit trails and regulatory compliance.
決定使用多重簽名(multisig)還是多方計算(MPC)系統,往往取決於具體的操作需求與法規限制。已建立治理流程及明確授權層級的組織,通常會發現多重簽名系統與既有流程高度契合,同時能提供清晰的審計紀錄與法規遵循。
The Safe multisig wallet is a secure crypto wallet trusted by Vitalik Buterin (Ethereum cofounder) and other leading Web3 projects to secure over USD 100 billion in crypto assets. This level of institutional adoption demonstrates that multisig technology has proven itself in high-stakes environments and can provide the security and governance capabilities that organizations require.
Safe 多重簽名錢包是一款安全的加密貨幣錢包,獲以太坊共同創辦人 Vitalik Buterin 及多個頂尖 Web3 專案信賴,協助保管超過一千億美元的加密資產。如此規模的機構採用證明了多重簽名技術已能在高風險環境下站穩腳步,並提供組織需求的安全性與治理能力。
However, organizations that need to operate across multiple blockchain networks or that require high transaction throughput may find that MPC systems provide better operational efficiency. Fireblocks' institutional MPC wallet maximizes security and service level agreements (SLAs) while minimizing operational overhead. The universal blockchain compatibility and automated policy enforcement capabilities of advanced MPC systems can provide significant operational advantages for complex organizational use cases.
然而,若組織需在多條區塊鏈網路間運行,或有高交易量需求,MPC 系統往往能帶來更佳的運營效率。Fireblocks 的機構級 MPC 錢包可最大化安全性與服務水平協議(SLA),同時將營運負擔降至最低。先進的 MPC 系統提供全面的區塊鏈相容性與自動化政策執行,對於複雜的組織應用案例能帶來顯著的營運優勢。
Estate planning and inheritance considerations should be a priority for all cryptocurrency users, regardless of which wallet technology they choose. Moreover, only a minority have engaged in any estate planning for their crypto assets. This lack of planning creates significant risks not only for individual users but also for the broader adoption of cryptocurrency as a store of value.
不論選擇哪種錢包技術,資產傳承規劃都應是所有加密貨幣用戶的優先考量。然而,實際上僅少數人有為其加密資產進行遺產規劃。這種規劃的缺乏,不只對個人用戶帶來重大風險,也影響加密貨幣作為價值儲存工具的廣泛採用。
Users of seed phrase systems should implement comprehensive estate planning that includes secure storage of seed phrases in locations accessible to trusted family members or legal representatives. This often requires balancing the security risks of sharing sensitive information against the risks of assets becoming permanently inaccessible.
使用助記詞錢包的用戶,應實施全面的遺產規劃,例如將助記詞以安全方式儲存於受信任家人或法律代表可存取的位置。這通常需要在分享敏感資訊的安全風險,與資產永久無法取得的風險間取得平衡。
Multisig systems can provide better inheritance planning capabilities by allowing family members or legal representatives to be included as key holders without requiring them to have complete access to assets during the account holder's lifetime. However, this approach requires careful planning to ensure that the necessary technical knowledge and coordination capabilities will be available when needed.
多重簽名系統可提升遺產規劃能力,允許家人或法律代表擔任密鑰持有者,卻無需在帳號持有人生前就能完全存取資產。但此方式需細心規劃,以確保屆時具備所需的技術知識與協作能力。
MPC systems may offer the most flexible inheritance planning options through sophisticated recovery mechanisms that can be configured to provide access to designated parties under specific circumstances. However, users should ensure that these recovery mechanisms are properly documented and that designated beneficiaries understand how to use them.
MPC 系統則可藉由高度彈性的恢復機制,根據特定情境設定指定人員的存取權限,提供最具彈性的遺產規劃選項。然而,用戶需確保這些恢復機制有完整紀錄,並讓受益人清楚瞭解如何操作。
Security practices should be adapted to the specific characteristics of each wallet technology while maintaining fundamental principles of defense in depth. For seed phrase systems, this means implementing multiple backup methods, using dedicated hardware for key generation and storage, and regularly testing recovery procedures to ensure they work correctly.
安全管理要因應不同錢包技術的特性,同時維持縱深防禦的基本原則。對於助記詞系統,這表示需實施多重備份、以專用硬體產生及儲存密鑰,並定期測試還原流程以確保萬無一失。
Use an offline backup method that can't be hacked, like copied on a piece of paper or engraved onto steel; store either at a secret location within a fire-proof personal safe or safety deposit box. Physical security measures remain crucial even for the most advanced wallet technologies, and users should implement multiple layers of protection against both digital and physical threats.
請使用無法被駭的離線備份方式,例如將助記詞抄寫在紙張,或刻在不鏽鋼板上,並存放於耐火個人保險箱或保險箱的秘密位置。即使是最先進的錢包技術,實體安全防護依舊極為關鍵,建議用戶針對數位與實體威脅實施多層保護。
For multisig systems, security practices should focus on ensuring the independence of key holders and the security of coordination mechanisms. Key holders should use different devices, different storage methods, and different communication channels to minimize the risk of correlated failures. Regular testing of transaction authorization procedures can help identify potential coordination problems before they affect critical operations.
多重簽名系統的安全管理應著重於密鑰持有者的獨立性和協作機制的安全。密鑰持有者應使用不同裝置、不同儲存方式及不同通訊管道,以降低同時失效的風險。定期測試交易授權程序,也有助預先辨識協作上的潛在問題,避免影響關鍵運作。
MPC systems require users to understand the trust assumptions associated with the specific implementation they choose. While the cryptographic protocols provide strong security guarantees, users must trust the service providers, software implementations, and communication infrastructure that enable the MPC functionality. Regular security audits and ongoing monitoring of service provider security practices are essential for maintaining confidence in MPC systems.
MPC 系統要求用戶瞭解其所選實作所涉及的信任前提。即使密碼學協議提供了強大防護,用戶仍需信任服務提供者、軟體實作以及支援 MPC 功能的通訊基礎建設。定期執行安全稽核和持續監控服務供應商的安全措施,是維持 MPC 系統信心的關鍵。
Risk management strategies should be tailored to the specific threats that are most relevant to each user's situation and wallet technology choice. Individual users in stable political and economic environments may focus primarily on protecting against theft, loss, and user error. Users in less stable environments may need to prioritize portability, censorship resistance, and protection against physical threats.
風險管理策略也應針對每位用戶情境與錢包技術做適當調整。政經穩定環境下的個人用戶,主要防範竊盜、遺失與操作錯誤;身處不穩定環境者,則更須關注可攜性、抗審查力與實體安全。
Institutional users typically face more complex risk management requirements that may include regulatory compliance, fiduciary responsibilities, and protection against insider threats. The wallet technology choices should align with the organization's broader risk management framework and should be regularly reviewed as business requirements and threat landscapes evolve.
機構用戶普遍面臨更複雜的風險管理要求,例如法規遵循、信託責任及防範內部人員威脅。錢包技術的選擇須與組織總體風險管理架構呼應,並應隨業務需求與威脅情勢持續檢討調整。
Diversification across multiple wallet technologies can provide additional security benefits while reducing dependence on any single approach. Users with significant cryptocurrency holdings might consider distributing their assets across different wallet types to reduce the impact of any single point of failure. This approach requires additional complexity and coordination, but it can provide significant risk reduction benefits.
跨多種錢包技術進行資產多元配置,不僅能提升安全層級,也有助降低對單一技術的依賴。持有大量加密貨幣者可考慮將資產分散於不同類型錢包,以減少任何單點失效造成的損失。這麼做雖然增加管理複雜度與協作需求,但帶來的風險降低效益相當可觀。
However, diversification should be implemented carefully to avoid creating new vulnerabilities through increased complexity. Each additional wallet system introduces new attack vectors and management overhead that must be carefully evaluated against the security benefits provided.
然而,多元配置必須謹慎執行,以免因複雜度提升反而引入新的弱點。每新增一種錢包系統,都可能產生新的攻擊面和管理負擔,需要仔細衡量其安全效益是否大於潛在風險。
Final thoughts
The evolution of cryptocurrency wallet technologies from simple seed phrases to sophisticated multi-party computation systems represents more than just incremental security improvements. It reflects a fundamental maturation of the cryptocurrency ecosystem as it grapples with the challenge of making self-custody both secure and accessible to mainstream users. Each technological approach embodies different philosophical perspectives on the balance between individual sovereignty, collective security, and practical usability.
加密貨幣錢包從簡單的助記詞到複雜的多方計算系統,其發展不僅僅是安全性的漸進提升,更蘊含著整個加密生態邁向成熟——嘗試讓自主管理既安全又容易普及。每一種技術路線,體現了對個人主權、集體安全與實用性間平衡的不同哲學觀點。
Seed phrases will likely remain relevant for users who prioritize maximum individual control and who have the knowledge and commitment required to manage them safely. Their simplicity and universal compatibility ensure that they will continue to serve as the foundation for cryptocurrency self-custody, even as more sophisticated alternatives become available. However, their limitations in terms of user experience and error tolerance suggest that they will increasingly become a niche solution rather than the default choice for most users.
對於極度重視個人掌控權、具備相關知識與承諾能安全管理的用戶來說,助記詞仍會有其存在價值。簡單性與普遍相容性使其仍是自主管理加密資產的根基,即使未來有更多進階選項也不會消失。然而,在使用體驗與容錯能力的侷限下,助記詞預期將逐漸由主流選擇退居成利基市場方案。
Multisig wallets have found their niche in organizational and institutional contexts where the coordination overhead is justified by the security benefits and governance capabilities they provide. The proven track record of multisig technology in securing large-scale cryptocurrency assets demonstrates its value for specific use cases, even as its limitations prevent it from becoming a universal solution.
多重簽名錢包則在組織及機構場景中發揮了其優勢——高度安全性與治理能力,充分補償了協作上的複雜性。多重簽名在保護大規模加密資產上已有豐富實績,對特定需求展現價值,雖仍難成為通用解決方案。
The rapid development and adoption of MPC wallet technology suggests that it may represent the future of mainstream cryptocurrency self-custody. By providing institutional-grade security with consumer-friendly usability, MPC systems could enable the widespread adoption of self-custody principles without requiring users to become cryptographic experts. However, the success of this approach depends on the development of sustainable business models, robust technical standards, and long-term trust relationships between users and service providers.
MPC 錢包技術的快速發展與採用,顯示它有望成為主流加密貨幣自主管理的未來。MPC 系統結合機構級安全與友善操作介面,有機會普及自主管理,不必讓用戶都成為密碼學專家。但這一途徑是否成功,仍取決於永續商業模式、穩健技術標準及用戶與服務商間的長期信任關係。
In conclusion, 2025 marks a significant shift towards MPC wallets, which offer enhanced security and user experience. Whether for individuals or institutions, MPC wallets provide a smart, adaptive gateway to self-sovereign finance, making crypto management safer and simpler. This technological shift could be the key that unlocks mainstream cryptocurrency adoption by eliminating the security and usability barriers that have limited adoption to date.
總結來說,2025 年將是 MPC 錢包大幅普及的重要轉捩點。其增強的安全性與用戶體驗,無論是個人還是機構,都能作為通向自我主權金融的智慧、彈性入口,讓加密資產管理更安全、更簡易。這一技術轉折,有望消除阻礙主流採用至今的安全與易用障礙,成為推動加密貨幣大規模主流化的關鍵。
The convergence of wallet technologies with other emerging innovations such as account abstraction, decentralized identity, and cross-chain interoperability suggests that the future of cryptocurrency self-custody will be characterized by hybrid systems that combine elements from multiple approaches. Rather than competing technologies, we may see seed phrases, multisig, and MPC systems evolving into complementary components of more comprehensive security frameworks.
錢包技術融合帳戶抽象、去中心化身份認證、跨鏈互通等創新,預示著未來的加密貨幣自主管理將以混合型系統為主,整合多種技術方案。不會只是彼此競爭的技術,而是助記詞、多重簽名與 MPC 會成為更完善安全架構的互補組件。
The implications of this technological evolution extend beyond individual user security to fundamental questions about the future of money and financial sovereignty. As wallet technologies become more sophisticated and user-friendly, they enable new forms of financial organization and governance that were previously impossible. The ability to implement programmable compliance, automated governance, and sophisticated risk management through wallet technology could transform not just how individuals manage their money, but how organizations, communities, and even governments organize their financial systems.
這場技術進化影響的不僅是個人資安,更牽涉金錢未來及金融主權的根本議題。錢包技術的持續升級與人性化,將開啟過去難以想像的全新金融組織與治理模式。藉由錢包技術實現可程式化法規遵循、自動化治理、複雜風險控管,不僅能改變個人的資金管理方式,更可能徹底翻轉組織、社群甚至政府的金融體系運作。
However, this technological progress also introduces new risks and challenges that must be carefully managed. The complexity of advanced wallet systems can create new forms of vendor dependence and systemic risk that could undermine the decentralization principles that make cryptocurrency valuable. The need to balance innovation with philosophical consistency will be an ongoing challenge for the cryptocurrency community.
然而,技術的進步也引入了新的風險與挑戰,必須謹慎應對。進階錢包的複雜性,可能帶來全新型態的供應商依賴與系統性風險,甚至破壞加密貨幣賴以為基的去中心化價值。如何在創新與核心理念間取得平衡,將是整個加密貨幣社群持續面臨的重大課題。
The path forward requires continued investment in user education, technical standards development, and 未來之路,需持續投入用戶教育、技術標準制定與...regulatory clarity to ensure that advanced wallet technologies can realize their potential while maintaining the principles of financial sovereignty and decentralization that define cryptocurrency's value proposition. The choices made by wallet developers, users, and regulators over the next few years will likely determine whether cryptocurrency achieves its promise of democratizing financial access or remains a niche technology for specialists.
最終,任何錢包技術的成功,不僅僅取決於其技術能力,還取決於其是否能夠賦予個人和組織掌控自己財務生活的能力,同時在日益複雜的數位經濟中安全且有效地運作。能夠最有效實現這一基本目標,並隨著用戶需求和技術能力的變化而調整的錢包技術,將更廣泛地塑造加密貨幣和數位金融的未來。
As we stand at this technological crossroads, the decisions made by individual users, organizations, and service providers will collectively determine which path the cryptocurrency ecosystem follows. The technologies exist to make self-custody both secure and accessible; the challenge now is implementing them in ways that honor cryptocurrency's founding principles while meeting the practical needs of a global financial system. The future of money may well depend on getting this balance right.