XRP Ledger 啟用了一項挑戰區塊鏈架構基本假設的代幣標準:即合規與監管應在應用層透過智能合約來實現。
多功能代幣(MPT)標準則提出了不同的做法。它將授權規則、轉帳限制、元資料管理和恢復機制直接內建於協議本身。
這個變革意義重大,因為機構代幣化已到達一個轉捩點。根據業界數據,實體資產代幣化市場三年來成長近五倍,目前已有超過 280 億美元資產被表示於區塊鏈。
然而,即使市場大幅擴張,金融機構在發行鏈上合規證券時仍然反覆遇到同樣的問題:客製化智能合約稽核成本高昂、監管不確定性(不確定哪一層代碼需負法律責任),以及跨不同應用確保合規控制正確運作的技術複雜度。
MPT 標準試圖徹底標準化帳本層級的合規,將這些功能變為原生特性,而非可選功能。對於探索代幣化的機構而言,從智能合約的複雜性轉為協議級保障,可能意味著專案能否突破法務審查階段並真正上線。
從更廣義的區塊鏈架構看,這重新喚起一個十年前的爭議:合規應由應用開發者透過智能合約執行?還是由協議設計者將規則嵌入共識機制?
作為基礎建設的代幣標準:以 Ethereum 的演進為例
要理解 MPT 架構的重要性,需回顧代幣標準在過去八年於 Ethereum 如何演進。
ERC-20 標準於 2015 年出現,是一個簡單的介面規範,定義任一可替代性代幣合約需實作的六個功能:查詢餘額、轉移代幣,以及授權第三方移轉。正因其設計簡單,開發者得以輕鬆創建代幣,錢包與交易所無須為每一種資產寫客製化代碼即可整合。ERC-20 因此迅速普及,推動 2017 年 ICO 熱潮,並確立可替代性代幣為區塊鏈基石。
但 ERC-20 是為無需許可的資產設計,沒有持幣資格限制、無法附加監管資訊、也無法讓發行方控管(如凍結、追回資產)。對於一般用途代幣無妨,對證券類資產則不夠。
隨後的證券型代幣潮嘗試將合規性補丁套在 ERC-20 上。ERC-1400 草案(由 Polymath、Harbor 等公司制定)引入「分割單元」概念。單一 ERC-1400 代幣可細分為多個 tranche(如合格投資人、創辦人鎖倉股、可自由交易部分),每個分區有不同轉讓規則。此標準還加上文件管理,發行方可將法律文件等附加於鏈上代幣。
ERC-1400 雖提升了合規層級,但本質仍屬智能合約標準。每個發行方都需自行布署合約、管理合規邏輯,帶來實作差異。不同發行人的 ERC-1400 代幣在特殊情境下可能行為不同,增加平台整合難度。
ERC-3643,獲以太坊社群正式認可並納入主線 GitHub,另闢新徑。它捨棄分區,改採「ONCHAIN ID」的身份驗證層。代幣轉帳前,驗證合約會查核傳送方與接收方是否具備可信發行方的身份憑證,如已完成 KYC、符合投資人資格、或居於核准地區。發行人在合約層定義轉讓規則,身份系統則確保只有合格對象能交易。
ERC-3643 於實際應用大獲成功,已有逾 280 億美元資產透過此框架代幣化。其優勢在於利用區塊鏈安全性驗證合規,全數轉帳驗證皆發生於鏈上,為監管市場帶來稽核記錄與密碼學確證。
儘管如此,以太坊證券型代幣標準仍有結構性侷限——全部實作於智能合約中。每個發行方都需布署合約,且需持續維護、升級;若合約邏輯有錯,資產恐遭竊或凍結,而協議層無法自動補救。
於以太坊執行複雜合規邏輯還有燃料費成本:約定每次身份驗證、分割轉移、文件雜湊查詢都需 ETH 支付 gas。對高價低頻證券尚可,對大量小額或頻繁驗證的場景,手續費很快累積。
這些以太坊經驗教會我們三件事:一、代幣化需要標準化,否則整合成本將無法負擔。二、合規設計必須內建,不能事後補救。三、身份與資訊揭露與代幣本身同等重要,因為監管要求清楚知道資產持有人與發行資訊。
MPT 標準正是在思考:會否有更好的方式,而非讓數以千計機構各自重寫這一切智能合約?
深入 MPT 標準:協議層級的代幣化
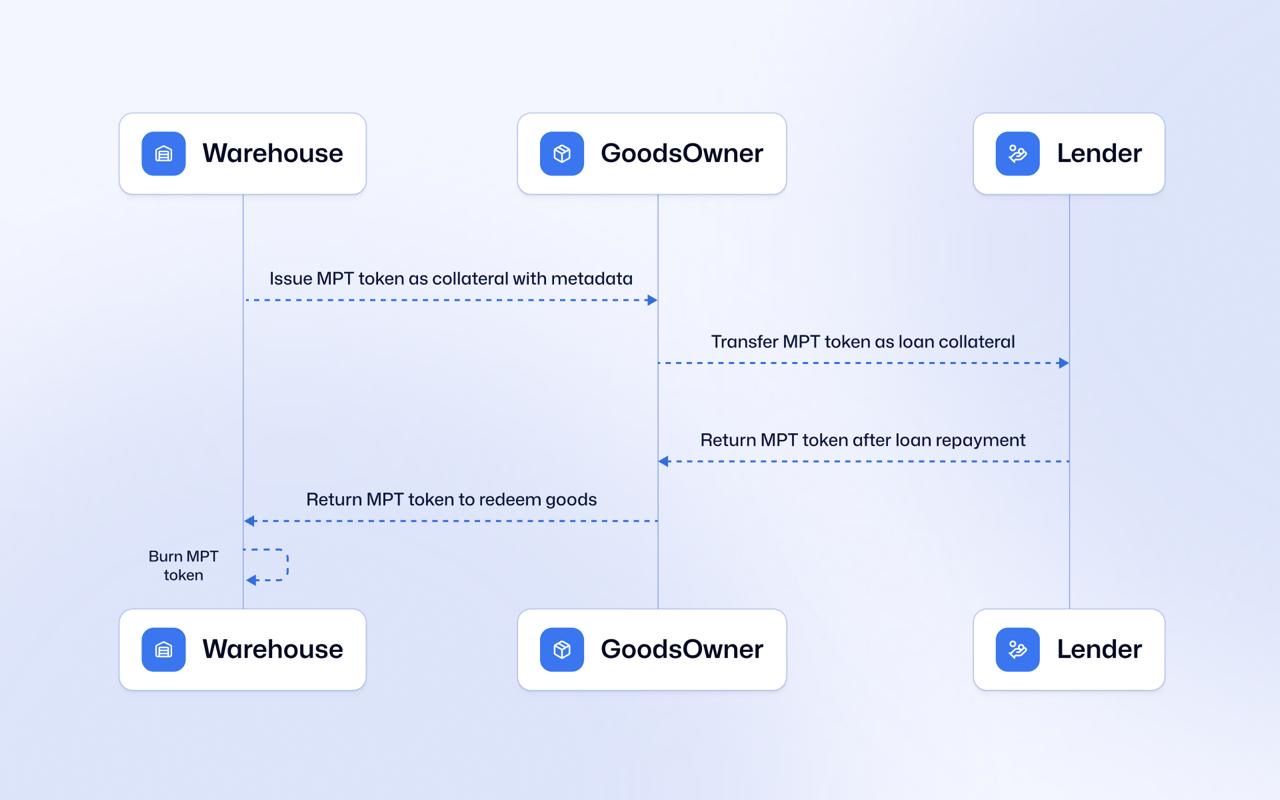
多功能代幣(MPT)標準代表根本不同的架構選擇。它不是定義讓開發者實作的智能合約介面,而是直接將代幣發行能力加入 XRP Ledger 協議。
當發行方創建 MPT 時,並非布署智能合約,而是創建一個新的帳本物件,類似於為 XRP Ledger 新增帳戶。MPT 及其規則會儲存在帳本狀態樹中,並由共識協議的交易處理邏輯統一管理。
這一差異,關鍵在於代碼執行的位置。以太坊上的 ERC 標準,代幣轉移會調用發行方或平台商撰寫的合約代碼,此代碼執行於 EVM,需要燃料,且可能有程式漏洞。MPT 則由每個驗證節點執行核心帳本程式碼來處理轉帳,同一套驗證 XRP 支付的邏輯也被用於處理 MPT 轉移,按每個代幣的設定條件套用規則。
MPT 規格定義了每一代幣在創建時都可選用的一套固定能力工具箱,作為標準化合規與控制配備。
可轉讓性控制決定誰能轉移代幣及在何種情境下轉移。MPT 可設定成不可轉讓,表示持有人只能將代幣還給發行方,適合封閉循環系統——發行方只准大家賺取或購買該代幣,不允許二級市場自由流通。若資產要流通,可將「Require Auth」旗標設為允許列表,只有經發行方批准的地址才能領取並持有,未經授權轉帳寫入帳本時會於協議層自動拒絕。
供給管理讓發行方直接設定代幣最大流通數量。與以太坊 ERC-20 需在合約內寫死最大供給上限、如果合約有 bug 還可能被突破不同,MPT 的供給上限由帳本強制執行。上限達到即無法再鑄造,只有「銷毀」機制可減少流通供給並釋出額度,但總數絕不可能超出預設上限。
轉移手續費允許發行方在地址間轉移時抽取一定比例之費用。此費用的實現方式為銷毀代幣,而非收取並累積至發行方錢包,如此可避免因資金留存產生的稅務或監管問題。費用從 0 至 50%(以 0.0001% 為單位)供細緻調控。回收給發行方時則不收費,確保持有人能無損贖回。
合規控制提供發行方因應監管要求或安全事件的機制。「Can Lock」旗標可針對單一或全體 freezes. An issuer can lock a specific holder's balance, preventing any transfers in or out except returns to the issuer. Or they can globally freeze all tokens of that issuance, halting all transfers across the network. These capabilities mirror traditional financial institution powers, like blocking accounts suspected of fraud or complying with asset seizure orders.
凍結。 發行人可以鎖定某特定持有者的餘額,防止任何轉入或轉出,僅允許將資產退回給發行人。亦或,他們可以全域凍結該發行批次的所有代幣,停止全網的所有轉帳。這些能力反映了傳統金融機構的權限,例如封鎖涉嫌詐騙帳戶,或配合法院資產扣押令等操作。
The "Can Clawback" flag goes further, allowing issuers to forcibly transfer tokens from a holder's account back to the issuer. This addresses scenarios where tokens are stolen, sent to the wrong address, or held by an account whose keys have been lost. In traditional securities systems, transfer agents can cancel and reissue certificates. Clawback gives token issuers equivalent powers on-chain.
“可收回(Clawback)”標誌則更進一步,允許發行人強制性地將代幣自持有人帳戶轉回發行人。這設計用來應對代幣被竊、誤轉地址,或私鑰遺失後持有帳戶失控等狀況。在傳統有價證券系統中,登記機構可以註銷並重新發行證書;Clawback 功能則讓區塊鏈代幣發行人也擁有等價的鏈上處理權限。
Metadata Management provides 1024 bytes of arbitrary data storage per token issuance. By convention, this should contain JSON conforming to a schema that defines fields like asset name, description, issuer identity, legal documents, and custom properties. Because this metadata is stored in the ledger, it is replicated across all validators and becomes part of the permanent record. Platforms can rely on this data being present and consistently formatted, unlike systems where metadata lives off-chain and might become unavailable.
中繼資料管理 每一次代幣發行可使用 1024 字節任意資料儲存。依照慣例,這段內容應該是符合特定架構(Schema)的 JSON,定義資產名稱、描述、發行人身分、法律文件和自訂屬性等欄位。因為這些中繼資料寫入帳本,會在所有驗證者間同步並成為永久記錄。不同於中繼資料儲存在鏈外且可能消失的系統,平台可以依賴這些資訊恆常存在且格式一致。
Decimal Precision settings allow tokens to represent fractional ownership. An MPT's "asset scale" determines where to place the decimal point when displaying balances. A token with scale 2 represents cents, with scale 6 represents millionths, and so on. This matters for assets like bonds, where par value might be $1,000 but secondary market trading happens in hundredths of par.
小數精度 設置允許代幣表現出分數化持有權。MPT 的「資產刻度」決定餘額顯示時小數點的位置。例如,scale 2 則代表「分(cents)」、scale 6 則代表「百萬分之一」,等等。這對於像債券這類資產尤為重要,其票面價值可能為 1000 美元,但二級市場交易卻以百份之一為計量單位。
The key insight is that none of these capabilities require custom code. They are flags and parameters in a ledger object. The compliance logic, transfer rules, and restrictions are interpreted by the protocol's built-in transaction processors. Every validator runs the same code, ensuring consistent behavior across the network.
關鍵之處在於,以上這些功能都不需要自訂程式碼。它們僅是帳本物件的旗標與參數。合規邏輯、轉帳規則與限制,全部由協議內建的交易處理器解析。每一個驗證者運行相同程式碼,確保全網行為一致。
Issuers configure these settings when creating the token, and in the current MPT version, those settings are immutable. Once an MPT is created, its transferability rules, supply cap, and compliance controls cannot be changed. This immutability provides certainty to token holders about what rights they have and what controls exist, but also reduces flexibility if circumstances change.
發行人在建立代幣時就設定好這些選項,且當前 MPT 版本下,這些設定一經上鏈就不可更改。MPT 創建後,其可轉讓性規則、總量上限、合規控管權限都無法再變動。這種不可變性,給持有人明確保障──自己擁有什麼權利、發行方有什麼控制──不過也降低日後因應環境變化的彈性。
A proposed extension called XLS-94 Dynamic MPT would allow certain fields to be marked as mutable during token creation. The issuer could then update these fields later through special transactions that require their digital signature. This would enable scenarios like gradually lifting transfer restrictions as regulatory requirements change, or updating metadata to reflect corporate actions. The proposal aims to balance flexibility with the security of immutability by making mutability an opt-in choice during token creation.
未來提案「XLS-94 動態 MPT」允許發行人在創建代幣時將特定欄位標記為可變更。之後發行人只需提交帶數位簽章的特殊交易,即可更新這些欄位。這可支援如因應監管需求逐步放寬轉移限制,或更新中繼資料反映公司行動等情境。該提案目標是在建立代幣時讓“可變”變成可選項,以平衡彈性與不可變性的安全性。
Ethereum Versus XRP Ledger: Architecture and Trade-Offs
Ethereum 與 XRP Ledger:架構與取捨
The debate between smart contract flexibility and protocol standardization reflects competing visions of how blockchains should handle specialized use cases.
關於智慧合約彈性與協議標準化間的對比,展現了區塊鏈面對特殊應用時兩種不同願景的競合。
Ethereum's approach treats the base protocol as a general-purpose computation platform. The Ethereum Virtual Machine provides a Turing-complete execution environment where developers can implement any logic they can code. Token standards like ERC-20 or ERC-3643 are not enforced by the protocol. They are conventions that developers follow voluntarily because it makes their tokens compatible with wallets and exchanges.
以太坊的做法,是將底層協議設計成通用運算平台。以太坊虛擬機提供圖靈完備的執行環境,讓開發者只要能寫程式,就能實現任意邏輯。ERC-20、ERC-3643 等代幣標準並非協議強制執行,而僅是開發者自願依循的業界慣例,因這樣做能確保代幣與錢包和交易所相容。
This flexibility enables innovation. When developers encounter new requirements, they can write new contract code to address them. The ERC-3643 identity system, for instance, emerged from real-world experience issuing securities and discovering that simple token contracts were insufficient. Because Ethereum allowed arbitrary contract logic, developers could build and deploy this identity layer without needing protocol changes.
這種彈性能驅動創新。每當開發者遇到新需求,都可以透過新智能合約來解決。像 ERC-3643 身分層標準,就是源自於發行有價證券的實務經驗,發現單一代幣合約不夠用。因以太坊允許任意合約邏輯,開發者無需修改協議本身就能構建並部署此類身分層功能。
The downside is that every deployment is unique. Two tokens claiming to implement ERC-3643 might behave differently because their contracts interpret the standard differently or add custom extensions. Auditing each contract for security and regulatory compliance becomes necessary but expensive. And complex contracts increase gas costs, making some use cases economically impractical.
缺點在於,每次部署都是獨特的。兩個都聲稱支持 ERC-3643 的代幣,可能因智能合約對標準解讀不同,或加上自訂擴充,最後表現出不同行為。每一個合約都必須安全審查與合規檢驗,費用與複雜度大增。複雜合約還會提高 Gas 成本,令部分應用經濟上難以實現。
XRPL's approach treats specialized capabilities as protocol features. The ledger provides specific transaction types for specific purposes: payments, escrows, checks, AMM pools, and now Multi-Purpose Tokens. Rather than general computation, the protocol offers a curated set of primitives that cover common needs.
XRPL 則將專用功能直接納入協議。帳本針對不同目的,定義專屬交易類型:付款、託管、支票、AMM 池、及多用途代幣(MPT)等等。取代通用運算,協議直接提供涵蓋主流需求的精選基本功能。
This standardization reduces integration costs. A wallet that supports MPTs can handle any MPT issuance because all MPTs follow the same protocol rules. There are no custom contract ABIs to parse, no unique logic paths to test. Compliance capabilities like freezing or clawback work identically across all issuers because the protocol implements them, not contract code.
標準化大幅降低整合成本。支援 MPT 的錢包能直接處理所有 MPT 發行,因為它們一律遵循同一套協議規則。也無需解析自訂合約介面 (ABI),或測試獨立邏輯路徑。像凍結、收回等合規功能,在所有發行人間都一致,皆由協議而非合約程式實現。
The transaction cost benefit is significant. Because MPT operations are native protocol features, they cost only the base ledger transaction fee, currently around $0.0002 per transaction. There is no gas computation cost proportional to the complexity of compliance checks or transfer rules. This flat fee structure makes MPTs economically viable even for high-frequency or low-value transfers.
這帶來顯著的手續費優勢。MPT 操作屬於原生協議功能,只收基本帳本交易費,目前每筆約 US$0.0002。無需依據合規或轉帳規則的複雜度另計 Gas 費。這種平價收費結構,讓 MPT 即使高頻或小額轉帳也符合集經濟效益。
The main trade-off is reduced flexibility. Issuers can only use the compliance controls that MPT provides. If a use case requires authorization logic that does not fit MPT's allowlist model, there is no way to implement custom rules. The protocol's feature set constrains what is possible, for better and worse.
代價則是彈性下降。發行人只能採用 MPT 內建的合規控管。如果某種應用必須實現 MPT 白名單模式以外的授權邏輯,就無法自訂規則。協議內建功能集就決定了一切可行與不可行之處。
On Ethereum with ERC-3643, an issuer would deploy a token contract, an identity registry contract, and multiple validator contracts that check different eligibility criteria. Some validators might verify KYC attestations from approved identity providers. Others might check investor accreditation status or confirm residence in approved jurisdictions. The issuer configures which validators must approve transfers and can add or remove validators as requirements evolve. This modularity provides precise control over who can hold tokens and under what conditions.
以太坊及 ERC-3643 架構下,發行人會部署一個代幣合約、身分註冊合約,以及多個用來檢查資格標準的驗證合約。有些驗證合約會查核來自批准身分提供者的 KYC 證明,其他則確認投資人資歷、或是否位於合規法域。發行人可自主配置哪些驗證器必須通過才能轉帳,並隨需求加入或移除驗證器。此模組化設計讓誰能持有代幣及其條件,可以被精確掌控。
The implementation requires coordinating multiple contracts, each of which must be audited. Changes to eligibility rules require deploying new validator contracts or updating existing ones if they were built to be upgradeable. The gas cost of each transfer includes calling the token contract, which calls the identity registry, which queries potentially multiple validator contracts. This multi-step verification adds up, especially if validators perform complex checks.
然而實作上,所有這些合約皆需協同運作,而且逐一要審計。資格規則變動時,要不是重新部署全新驗證合約,就是更新現有(如果有設計可升級功能)。單筆轉帳的 Gas 費,會疊加代幣合約調用、身分註冊、再查多個驗證合約的流程。若驗證條件複雜,這多層檢查將大幅推高成本。
On XRPL with MPT, the issuer creates a token with the "Require Auth" flag enabled. They then authorize specific accounts to hold the token by sending MPTAuthorize transactions that add those accounts to the token's holder list. The authorization check happens at the protocol level during transfer processing. If the receiving account is not authorized, the transfer fails before any state changes.
XRPL 的 MPT 則是:發行人啟用「Require Auth」(授權後持有)標誌,透過 MPTAuthorize 交易,將指定帳戶加進代幣持有人清單。每一次轉帳時,協議層就會檢查收款帳戶是否已獲授權,若未授權,這次交易在狀態改變前就被拒絕。
The simplicity reduces deployment complexity and eliminates smart contract risk. But the authorization system is all-or-nothing. Either an account is authorized or it is not. The protocol provides no way to encode nuanced rules like "this holder can receive tokens only if their accreditation is current" or "transfers to this jurisdiction are limited to institutional investors." Those rules must be enforced off-chain, with the issuer deciding whether to authorize accounts based on their own eligibility checks.
此極簡設計降低部署難度並消除智能合約風險。然而,授權系統是絕對(全有全無)。要不是帳戶已經授權,就是未授權。協議層本身無法編碼像「此持有人必須證照未到期才可收受代幣」、「移轉至某地區僅限機構投資人」等細緻規則。這些需由發行人根據自家檢核流程,在鏈下審核後授權決定。
Some use cases fit naturally into MPT's model. A corporate bond where the issuer maintains a registry of qualified purchasers and authorizes them individually works well. The authorization list serves as a ledger-native representation of the bond's holder record.
有些場景天然地適合 MPT 模型。例如,公司債發行人持續維護一份合格購買人名冊並逐一授權──這正好符合 MPT 授權名單可作為債券持有人記錄的鏈上直觀表現。
Other use cases clash with MPT's constraints. A real estate fund that wants to implement detailed waterfall distributions, where different share classes receive proceeds in specific orders depending on performance metrics, cannot express that logic in MPT's fixed feature set. Such complexity would require either building it off-chain or using a different platform.
但另一些需求就會與 MPT 的限制衝突。例如不動產基金若要設計細緻的瀑布分配(不同股份依表現先後分收益),這種複雜條件在 MPT 固定功能集中難以表達。這就必須在鏈下實現,或選用其他平台。
The architectural choice reflects different philosophies about where complexity should live. Ethereum pushes complexity into smart contracts, giving developers freedom but requiring each implementation to be secured and audited individually. XRPL pulls common compliance patterns into the protocol, standardizing them but limiting what is possible to what the protocol designers anticipated.
這背後,是兩套設計理念的抉擇──複雜度應位於哪裡?以太坊將複雜性推給智能合約,由開發者自由發揮,卻要求每套都要獨立檢查與保護;XRPL 則把常見合規模式拉進協議層,做出標準化,卻讓可能性止步於協議設計者的預期。
Neither approach is objectively superior. The right choice depends on whether your use case fits within the protocol's feature set and whether you value reduced deployment complexity over implementation flexibility.
這兩種方式沒有絕對優劣。該選哪一種,取決於你的應用場景能否落在協議功能集內,還有你更重視降低部署複雜度,抑或是開發彈性。
Institutional Finance Use Cases: Where MPT Aims
機構金融應用場景:MPT 的核心目標
Ripple's positioning of MPT focuses specifically on use cases where regulated financial institutions are likely to issue tokens. The September 2025 institutional roadmap document outlined a clear vision: enable traditional finance to represent real-world assets on-chain without forcing banks and asset managers to become smart contract developers.
Ripple 推動 MPT 的定位,就針對受監管金融機構有發行代幣需求的場景。2025 年 9 月的機構化發展藍圖文件已明確描繪願景:讓傳統金融能將現實資產上鏈,而不用逼銀行和資產管理人變成智能合約開發者。
Fixed Income Securities represent perhaps the most straightforward MPT use case. A corporate bond traditionally consists of a promise to pay principal at maturity plus periodic coupon payments. Representing this on-chain has historically required either complex smart contracts that encode payment schedules or hybrid systems where on-chain tokens represent ownership but payments happen off-chain.
固定收益型證券 可算是 MPT 最直觀的應用實例。公司債傳統上就是承諾到期給付本金,並週期性支付利息。要把這套機制搬到鏈上,過往不是得靠編碼還本付息時程的複雜合約,就是導入鏈上代表所有權但付款還是在鏈下的混合系統。
MPT's metadata capabilities allow bond characteristics to be recorded on-chain. The 1024-byte metadata field can contain maturity dates, coupon rates, payment frequencies, and references to
MPT 的中繼資料功能,能將債券特性直接寫入區塊鏈。那個 1024 字節中繼資料欄位可記載到期日、票面利率、付息頻率及其相關資訊……legal documentation. 雖然協議本身並不會自動執行息票支付——這仍需發行人在適當的時間發送付款交易——但將債券條款編碼在帳本資料中,使其具備透明且可驗證的特性。
供應上限(supply cap)功能與債券發行自然契合。例如,若一家公司發行一筆面值 1,000 美元、總計 1 億美元的債券,只需設定 100,000 顆代幣的供應上限。這些代幣一旦鑄造並分配給投資人後,該筆發行就無法再創建額外的債券代幣,從數學上確保了債務總額的上限。
轉讓限制(transfer restrictions)可讓發行人落實監管規定。例如,美國境內的債券可能限於合格機構買方,歐洲則對合格投資人開放豁免發行。要求持有人獲得授權才能接收代幣,讓發行人能掌控投資者結構,並具體證明其遵從發行規範。
股票代幣化(Equity Tokenization) 過程中,關於股權種類與表決權的設計更為複雜。優先股可能擁有不同的股息率、清算權優先次序或贖回條款,和普通股有所區隔。有些股票會帶有表決權,而有些則沒有。
MPT 透過將每種股票類別視為獨立的代幣發行來應對這一點。公司可以為 A 類普通股發行一個 MPT,為 B 類優先股發行另一個 MPT,還可為無表決權的限售股單位發行第三個 MPT。每項發行各自有供應上限、轉讓規則及描述權益的 metadata。
其限制在於,股權類別間的法律關係——例如優先股對普通股的清算優先序——無法直接在代幣協議中編碼。這些契約關係仍存在於公司組織章程中,而代幣只是帳本原生的所有權證明。當公司出現分紅、贖回等公司行動時,必須利用帳本上的持有人資料來執行。
穩定幣及電子貨幣 完美契合 MPT 的設計。穩定幣發行人於鏈下建立相應儲備金後,創建 MPT,再隨用戶法幣入金鑄造代幣。供應上限可設為相當高以應對成長,或直接不設上限。
回收機制(clawback)回應了關鍵監管要求:能夠應執法單位請求或制裁而凍結、沒收資金。傳統金融機構在特定情況下必須能封鎖帳戶、逆轉交易。MPT 給穩定幣發行人同等權力,使其能在技術層面符合法規,如反洗錢規定。
XRPL 獨有的「Deep Freeze」功能提供進一步保護。此功能可使發行人阻止特定帳戶透過信任線發送、接收任何代幣,即使是經由去中心化交易所或自動做市商(AMM)路徑。如此全面封鎖回應了監管單位對資金可能經由未監控渠道流動的疑慮。
資產回收對機構級穩定幣採納很重要。如果用戶遺失私鑰,在標準區塊鏈架構下存款便成永久遺失。clawback 功能讓發行人能回收這些資產,經驗證之帳戶持有人可透過鏈下流程取回資金。雖然這導入集中化——發行人對資產有極大控制權——卻正符合傳統電子貨幣體系中銀行協助客戶取回帳戶權限的慣例。
代幣化貨幣市場基金(Tokenized Money Market Funds) 是近期機構應用中最被看好的領域之一。貨幣市場基金持有短期高品質債券,其收益略高於銀行存款,為企業及機構重要儲值工具,全球管理資產達數兆美元。
若能將貨幣市場基金份額代幣化,投資人可持有於鏈上的基金權益,透過代幣升值或分紅取得收益,甚至可將這些份額作為其他協議的抵押品。部分資產管理公司已在 Ethereum 上推出代幣化貨幣市場基金,證明市場需求存在。
MPT 協議層架構能降低這類產品上鏈之營運複雜度。基金管理人無需自行部署與維護智能合約,只需設定一份符合基金屬性的 MPT、授權合格投資人、根據申購贖回鑄造或銷毀代幣。帳本自動負責合規驗證與轉讓限制。
即將推出的 XRPL 貸款協議將開啟新應用場景。若貨幣市場基金份額以 MPT 表現,可直接於本地貸款系統用作抵押品,無須客製整合。協議層即了解 MPT 屬性,如代幣是否鎖定或已凍結,能在帳本層驗證抵押資格。
碎片化實體資產(Fractionalized Real-World Assets) 允許小規模投資人擁有高價資產(如房地產、藝術品、基礎建設)的部分所有權。比如,一棟價值 1,000 萬美元的不動產可細分為 10,000 顆每顆價值 1,000 美元的代幣,使更多投資人可參與持有。
MPT 的資產比例功能支持此類精確的分割所有權。若一大樓價值 1,000 萬美元,發行 1,000 萬枚代幣,則每枚代表 1 美元價值,並可進一步精確反映市價波動。
轉讓限制能協助管理碎片化房地產的監管複雜性。在許多法域,提供房地產碎片所有權須將產品登記為證券,或必須依豁免資格限定投資對象。協議層的授權要求可強制落實此規定。
碎片化資產的挑戰在於治理。代幣持有人需能對資產經營決策投票、領取租金收益,最終共同清算資產。MPT 雖記錄所有權,但未內建治理基礎設施。這些功能需在協議之上開發,可藉由鏈下流程將帳本作為持有人登記冊,或藉尚未實施的額外協議功能實現。
忠誠度與獎勵計畫(Loyalty and Rewards Programs) 屬於風險較低但仍可藉代幣化獲益的應用。航空公司、飯店、零售商等每年發行價值數十億美元的點數,但這些點數多數受困於業者專屬資料庫,不可轉讓,也難跨平台流通。
以 MPT 代幣化點數能讓其於不同平台間流動,同時維持發行人控制權。不可轉讓旗標可阻止點數在二級市場自由流通,避免業者擔憂的貶值。但發行人可選擇允許用戶將點數兌回,供客戶兌換獎勵。
供應上限與鑄造權可讓業者控管點數的發行屬性。若零售商欲限制點數負債總額,可設發行上限;若希望客戶消費即時發點,可隨需鑄造。
授權要求也支持分層會員制。例如,國際連鎖飯店可發行一個 MPT 代表一般點數,另一個 MPT 作為精英會員點,後者具更佳兌換權益。轉讓限制也可確保點數僅於原定會員系統內流通。
監管意涵:設計即合規
全球金融監管機構對於如何監管代幣化證券莫衷一是。此技術帶來了結更快、所有權透明、減少中介成本等優點,但也引發投資人保護、市場操縱防範、監管歸屬的新問題。
歐盟加密資產市場規則(MiCA)於 2024 年 12 月 30 日全面生效,為加密資產發行人及服務提供者建立完善規則。MiCA 規定,資產掛鉤型代幣與電子貨幣代幣發行人必須持有 1:1 儲備,公開詳細白皮書揭露風險,給予代幣持有人按票面價贖回權。服務業者則需取得執照、執行反洗錢控管,確保營運韌性。
對於代幣化證券,MiCA 大致仍適用既有金融服務監管。證券型代幣視為受 MiFID II 及相關規範的金融工具。監管焦點在於該筆債券或股票是否符合傳統證券要求,而非區塊鏈技術本身是否產生新型監管類別。
MPT 協議層合規控管對多項監管機構指引與執法行動提出的疑慮,給予具體解法。
投資人適格性(Investor Eligibility) 仍是大多數證券發行首要考量。規範常依財富、收入、投資經驗或專業資格限制投資人。在美國,Regulation D 發行若非大量揭露資訊,僅限於合格投資人;歐洲豁免經常要求專業或合格投資者。
於公開區塊鏈上落實這些限制一向困難。如果任何人都能創建錢包,且交易無須許可,發行人如何防止不合格投資人acquiring tokens on secondary markets? Smart contract solutions exist but require careful implementation. If the authorization logic contains bugs, tokens might transfer to unauthorized holders despite restrictions.
在二級市場取得代幣?雖然存在智能合約解決方案,但實施時必須非常謹慎。如果授權邏輯存在漏洞,即使有限制條件,代幣也可能會被轉移到未經授權的持有者手中。
MPT builds authorization into consensus rules. The protocol itself rejects transfers to unauthorized addresses. This makes investor eligibility technically enforceable in a way that provides greater certainty to both issuers and regulators.
MPT(多簽名資產標準)將授權機制內建於共識規則中。協議本身會拒絕轉移給未經授權的地址。這讓投資人資格得以在技術上被強制執行,為發行人與監管機關帶來更高的確定性。
Transfer Restrictions and Lock-Ups address regulatory requirements around holding periods and offering constraints. Regulation S offerings, which exempt U.S. issuers from registration for offshore sales, impose lock-up periods during which securities cannot be resold to U.S. persons. Founder shares often have vesting schedules or transfer restrictions to prevent premature sales.
轉讓限制與鎖定期(Lock-Up) 回應了關於持有期限與發行限制的監管要求。根據 Regulation S,允許美國發行人在向海外銷售證券時豁免註冊,但必須施加鎖定期,在此期間內證券不得再銷售給美國人士。創辦人股份也經常設有歸屬期或轉讓限制,以防止過早出售。
Implementing these restrictions through smart contracts requires encoding time-based logic and tracking transfer histories. MPT handles this through its transfer rules and authorization system. An issuer can simply decline to authorize transfers during lock-up periods, or use the non-transferable flag to prevent any secondary market sales.
透過智能合約實施這些限制需要編碼時間相關邏輯並追蹤轉帳歷史。MPT 則用轉帳規則與授權系統來處理。發行人可以於鎖定期間拒絕授權轉讓,或使用不可轉讓標誌,完全阻止任何二級市場銷售。
The limitation is that MPT does not natively support scheduled unlocking. If founder shares vest over four years, the issuer must manually authorize transfers as vesting milestones are reached rather than encoding the schedule in the token itself. The proposed XLS-94 Dynamic MPT extension could address this by allowing time-based rule changes.
限制是,MPT 原生並不支援自動化的定期解鎖。如果創辦人股份是四年期分批歸屬,發行人必須在每個歸屬時點手動授權轉讓,而不能直接將歸屬計畫編碼在代幣上。未來提出的 XLS-94 動態 MPT 擴充規範,則可能讓時間性規則的變更成為可能。
Issuer Controls and Emergency Powers matter for regulated securities in ways that defy permissionless blockchain principles. If a court orders asset seizure, if funds are stolen, or if an investor's account is compromised, traditional securities systems allow issuers and intermediaries to reverse transactions or freeze accounts.
發行人控制與緊急權力 在監管證券領域具有重大意義,這與區塊鏈去許可制原則背道而馳。當法院下令查封資產、資金遭竊,或投資人帳戶被入侵時,傳統證券體系可允許發行人或中介機構逆轉交易或凍結帳戶。
MPT's freeze and clawback capabilities provide these powers. An issuer can lock an account in response to a court order, preventing further transfers. They can claw back tokens sent to the wrong address due to user error. These interventionist capabilities run counter to cryptocurrency culture but align with how regulated securities work in traditional markets.
MPT 的凍結與追回(clawback)功能賦予發行人這些權力。發行人可以根據法院命令鎖定帳戶,防止進一步轉讓;或因用戶操作錯誤追回誤送的代幣。這些干預性功能雖與加密貨幣文化背道而馳,卻符合傳統金融市場中監管證券的實務操作。
The debate is whether these powers introduce unacceptable centralization or necessary regulatory compliance. Critics note that an issuer with clawback authority can arbitrarily seize tokens from holders, creating counterparty risk that does not exist with bearer assets like Bitcoin. Proponents counter that investors in regulated securities already trust issuers and transfer agents with similar powers, and that eliminating these capabilities makes blockchain unsuitable for institutional securities.
爭議在於:這些權力是否造成不可接受的中心化,還是遵循必要的監管法規。批評者認為,掌有追回權力的發行人可隨意沒收持有人代幣,這會產生像比特幣等持有式資產不存在的對手風險。支持者則指出,受監管證券的投資人本就必須信任發行人與過戶機構具備此類權力,移除這些能力反倒讓區塊鏈無法用於機構級證券發行。
MPT makes this a choice rather than a mandate. The "Can Lock" and "Can Clawback" flags can be disabled during token creation. An issuer that wants to create a maximally decentralized asset can omit these features. One that needs regulatory compliance can include them. The key is that the choice is explicit and immutable, giving holders certainty about what controls exist.
MPT 將其設計為選擇而非強制。於發行代幣時,「可鎖定」與「可追回」標誌皆能選擇關閉。想發行極度去中心化資產的發行人可以不開啟這些功能,有合規需求的發行人則可啟用。關鍵在於該選項為明確且不可更改,讓持有人確定清楚有哪些控管機制存在。
Transparency and Disclosure requirements permeate securities regulation. Issuers must provide offering documents, financial statements, material disclosures, and ongoing reporting. Traditionally these documents are filed with regulators and distributed to investors through various channels.
透明度與揭露規範貫穿所有證券監管法。發行人須提供發行文件、財務報表、重大訊息揭露及持續性報告。這些文件傳統由發行人遞交主管機關,並以多種方式提供給投資人。
MPT's metadata field provides on-chain disclosure storage. An issuer can include URLs pointing to offering documents, file hashes proving document authenticity, or even embed critical terms directly in the metadata JSON. Because this data is part of the ledger state, it is replicated across all validators and permanent.
MPT 的 metadata 欄位提供鏈上揭露存儲。發行人可納入指向發行文件的網址、驗證文件真偽的雜湊值,甚至直接將關鍵條款嵌入元資料(metadata)的 JSON 中。由於這些資料屬於帳本狀態(ledger state)的一部分,因此會永久保存在所有驗證人節點上。
The 1024-byte limit constrains what can be stored directly. Most legal documents exceed this size by orders of magnitude. But cryptographic hashes of documents fit easily, providing a tamper-evident way to link on-chain tokens to off-chain documentation. Regulators or investors can verify that the documents an issuer claims to have filed match the hashes embedded in the token metadata.
由於有 1024 字元的存儲限制,直接存放完整法律文件不太可能,大部分法律文件的容量遠超此限。不過,文件的密碼學雜湊值完全可以納入,也能做為鏈上代幣與鏈下文件的防篡改連結。監管機關或投資人可檢查發行人主張已申報的文件是否與代幣元資料中的雜湊相符。
AML and KYC Requirements create perhaps the sharpest tension between blockchain pseudonymity and regulatory mandates. Financial institutions must verify customer identities, screen against sanctions lists, monitor for suspicious activity, and report large or unusual transactions.
反洗錢(AML)與了解你的客戶(KYC) 是區塊鏈去識別化與監管法令間最尖銳的衝突之一。金融機構必須驗證客戶身份、篩查制裁名單、監控可疑活動,並回報大額或異常交易。
MPT does not directly implement KYC. The protocol has no concept of real-world identity or know-your-customer checks. What it provides is the infrastructure for issuers to enforce identity requirements through their authorization process.
MPT 並未直接實作 KYC。該協議並無現實身份或 KYC 查核的概念。它只提供發行人可透過授權程序強制身份條件的基礎設施。
An issuer could establish an off-chain KYC process where investors submit identification documents and undergo verification. Once approved, the issuer authorizes that investor's XRPL address to hold tokens. The ledger then enforces the restriction that only authorized addresses can receive tokens, but the determination of whether someone should be authorized happens off-chain through the issuer's compliance procedures.
發行人可建立鏈外 KYC 流程,讓投資人提交身份文件並通過驗證。經核可後,發行人授權該投資人的 XRPL 地址持有代幣。帳本會強制執行這一規則:只有經授權地址可接收代幣,但「是否應獲授權」的判斷過程,以及身份查核結果,皆發生於鏈下、由發行人的合規機制執行。
This hybrid approach keeps sensitive personal information off the public ledger while providing protocol-level enforcement of restrictions based on that information. The limitation is that the on-chain record provides no audit trail of why accounts were authorized or what identity verification occurred. Regulators must rely on issuers maintaining off-chain records.
這種混合型模式可讓敏感個資不會存放於公開帳本,同時又能根據這些資料從協議層級強制人員管制。不過,鏈上記錄不會保留授權原因或實際進行 KYC 的稽核足跡,監管機關僅能依賴發行人鏈下保存完整紀錄。
The Credentials feature, which activated separately from MPT, adds an identity layer to XRPL. Issuers can attest to specific facts about addresses, like "this address completed KYC with provider X on date Y" or "this holder is accredited according to SEC rules." These attestations are on-chain but designed to reveal only necessary information, preserving privacy while enabling compliance verification.
「憑證(Credentials)」此功能與 MPT 分開啟用,能為 XRPL 增添身份層。發行人可就地址認證特定資訊,如「本地址於 Y 年與 X 機構完成 KYC」,或「此持有人根據 SEC 規則為合格投資人」。這些鏈上證明只揭露必要資訊,在兼顧隱私下達成合規查核需求。
Protocol Versus Smart Contract: A Deeper Trust Model Debate
協議層級與智能合約層級之選擇:更深層的信任模式辯論
The choice between embedding capabilities in protocols versus leaving them to application-layer smart contracts reflects competing beliefs about security, flexibility, and where trust should be placed in blockchain systems.
關於應將關鍵能力設計在協議層或交由應用層智能合約處理,體現了對安全性、靈活性以及應該將信任託付於區塊鏈哪一層級的不同價值觀。
Protocol advocates argue that moving critical security and compliance logic into the base layer reduces the attack surface. Every XRPL validator runs the same core codebase. That code is developed by an open-source community, undergoes extensive review, and changes only through a formal amendment process requiring supermajority consensus. This shared codebase means MPT transfer restrictions, freeze capabilities, and authorization checks work identically everywhere. There is no way for an individual issuer's implementation to contain bugs that break these protections.
主張協議層架構的人認為,將安全與合規關鍵邏輯集中設計於基礎協議,能減小攻擊面。所有 XRPL 驗證人都運行同樣的核心程式,這些程式碼由開源社群維護,經過充分審查,且只有當獲得超過門檻共識時才得以變更。由於大家共用同一套代碼,MPT 的轉帳限制、凍結功能、授權檢查等到處都一致。發行人無法透過私人部署版本造成破壞保護機制的漏洞。
The argument continues that standardization protects users. With MPT, every token implements compliance the same way. A holder knows that if their account is frozen, no transfer attempts will succeed. If a token has a supply cap, mathematical certainty exists that no more than that cap can ever circulate. These guarantees come from protocol rules that cannot be subverted without the agreement of the validator network.
此論述還主張,標準化能保障用戶。所有 MPT 代幣的合規機制皆相同。持有人可以確信,若其帳號遭凍結,則任何轉帳指令都不會成功;若代幣有供給上限,則能數學上保證流通總量不會超標。且這些保障來自協議層規則,除非全驗證人網路協議,否則無法被竄改。
Smart contract advocates counter that flexibility matters more than standardization. Financial instruments are diverse. A municipal bond behaves differently than a real estate investment trust, which differs from preferred shares with conversion rights. Trying to design a protocol that accommodates every possible security structure is futile. Better to provide general computation capabilities and let developers build specialized logic as needed.
主張智能合約的人則反駁,靈活性往往比標準化更重要。金融工具種類繁多:市政債券、房地產投資信託、具轉換權之特別股等皆有其特殊制度。協議層若要包容所有可能結構,將成為不切實際的工程。更好的做法是提供一般化的可編程能力,讓開發者根據需求編寫專屬邏輯即可。
They note that bugs in protocol code affect everyone simultaneously. A vulnerability in MPT logic could potentially compromise all MPT tokens across the network. With smart contracts, a bug affects only that contract's users. The blast radius is contained. Yes, auditing thousands of contracts is more work than auditing one protocol, but distributed security review across many independent developers can be robust.
他們也指出,協議級程式碼一旦出現漏洞會同時波及所有人,若 MPT 架構上的邏輯出現破口,可能損害整體網路上的所有 MPT 代幣。智能合約的漏洞只影響個別用戶,災害範圍可控。雖然審核成千上萬個合約的工程量遠大於審核單一協議碼,但若由眾多獨立開發者分擔安檢審核,安全性未必遜色。
The upgrade path presents another trade-off. Protocol changes require coordination across validators, amendment proposals, voting periods, and community consensus. This process can take months or years. Smart contracts can be deployed instantly by their developers, enabling rapid iteration. If market needs change or regulations evolve, contract developers can adapt immediately. Protocol designers face much higher inertia.
升級路徑也是另一權衡。協議變更須跨驗證人協調、提案、表決及社群共識,可能數月到數年;而智能合約只要開發者一方便能即時部署,反應靈活。如果市場需求或監管規則變動,合約開發者可立刻調整;設計協議者的調整則阻力極大。
Yet this inertia can be a feature rather than a bug. Immutable protocol rules provide stability that some applications require. A bond issuer might want certainty that the token's compliance rules will not change unexpectedly. If those rules are in a smart contract, the contract owner could upgrade them, potentially in ways that harm token holders. If they are in the protocol, changes require network-wide consensus that the issuer does not unilaterally control.
但這種「惰性」反而可能是一種優勢,非缺陷。不變協議規則能帶來部分應用所需的穩定性。債券發行人可能要求代幣的合規條件不可隨意變動。智能合約中,合約持有人可隨時升級,甚至於不利持有人;協議級規則要調整,得獲得全網共識,發行人無法左右。
The integration cost consideration tilts toward protocols. A platform that wants to support tokenized securities must integrate with whatever token standards issuers use. With Ethereum, this means understanding multiple smart contract interfaces, handling differences between ERC-1400, ERC-3643, and various custom implementations, and potentially auditing each contract's code to ensure it behaves as expected.
就整合成本考量,協議層具有優勢。一個平台如要支援證券型代幣,必須整合各家發行人採用的標準。以以太坊為例,需支援多種智能合約介面,面對 ERC-1400、ERC-3643 與各式客製版本的差異,並可能一一審查合約碼以驗證行為正確。
With MPT, integration is uniform. A platform adds support for the MPT transaction types and ledger objects, then automatically supports all MPT issuances. The protocol documentation describes exact behavior, eliminating ambiguity about how features work.
MPT 模式下,介接作業變得統一。平台只需支援 MPT 的交易型態與帳本物件,即可同時支援所有 MPT 發行標的。協議文件詳細寫明每項功能行為,消除功能實作的歧義。
Transaction costs present a stark difference. Complex Ethereum smart contracts can cost significant gas to execute. A security token transfer that must query identity registries, check multiple compliance rules, and update partition balances might cost tens of dollars in gas during periods of network congestion. MPT transfers cost around one-fiftieth of one cent regardless of how many compliance checks apply, because protocol
交易成本也有顯著差異。以太坊複雜的智能合約執行時,需消耗大量 Gas;一筆涉及身分查詢、多重合規檢查、分帳更新的證券型代幣轉讓,在網路擁塞時甚至要價數十美元。MPT 的轉帳無論檢查多少合規規則,交易手續費約只需一分錢的五十分之一,因為該檢查由協議本身處理。features do not scale costs with complexity.
功能複雜度並不會隨著成本一同擴張。
For high-value, low-frequency transactions, this cost difference barely registers. Transferring shares of a private company worth hundreds of thousands of dollars does not become impractical because the blockchain transaction costs twenty dollars. For retail securities, payment tokens, or high-frequency trading, transaction costs matter significantly.
對於高價值、低頻率的交易來說,這樣的成本差異幾乎可以忽略。轉讓價值數十萬美元的私人公司股份,即使區塊鏈手續費達到二十美元,也不會變得不可行。反之,對於零售證券、支付型代幣或高頻交易,交易成本就顯得極為重要。
The philosophical question underlying this debate is whether blockchains should be general-purpose computing platforms or specialized transaction processors. Ethereum champions the former view: provide a Virtual Machine capable of arbitrary computation, then let developers build whatever they need. XRPL represents the latter: identify common use cases, implement them as optimized protocol features, and avoid the complexity and costs of general computation.
這場辯論背後的哲學問題,是區塊鏈應該是通用型計算平台,還是專門的交易處理器。以太坊主張前者:提供可執行任意運算的虛擬機,然後讓開發者隨心所欲建立他們需要的功能。XRPL 則屬於後者:找出常見的使用案例,將其實作成優化過的協定功能,避免通用運算帶來的複雜性與成本。
Neither philosophy is objectively correct. The right answer depends on whether your application fits within a protocol's feature set and whether you prioritize standardization over flexibility, integration simplicity over implementation control, and predictable costs over rapid iteration capability.
這兩種哲學都沒有絕對正確的答案。哪種適合你,要看你的應用是否符合該協定的功能、你是否更重視標準化還是靈活度、喜歡整合的簡易性還是控制具體實現,以及你是偏好可預期的成本還是快速迭代的能力。
Market Reaction: Enthusiasm Meets Skepticism
市場反應:熱烈期待與懷疑並存
The announcement and activation of MPT produced reactions that split along predictable fault lines in the blockchain community.
MPT 的宣布與啟用,在區塊鏈社群內引發了預期中的分歧回響。
XRP advocates celebrated the launch as validation of XRPL's institutional focus. The multi-year development process, the formal amendment voting, and the immediate availability of compliance features demonstrated that XRPL was evolving specifically to meet enterprise needs. Community members highlighted use cases like FortStock's warehouse receipt tokenization pilot, which uses MPT to represent physical commodities as on-chain collateral, as proof that real institutions were already building on the standard.
XRP 支持者將這次上線視為 XRPL 企業導向的證明。多年開發過程、正式的修正案投票、即時提供合規功能,都展現XRPL 正是在為企業需求而演進。社群成員特別點出像 FortStock 倉儲憑證代幣化試點這樣的應用案例,利用 MPT 將實體商品作為鏈上抵押品,證明標準已被真正的機構採用。
The speed of development impressed observers familiar with blockchain governance challenges. From initial proposal to mainnet activation took approximately eighteen months, a relatively fast timeline for introducing major protocol changes. The amendment received strong validator support, passing the required eighty percent threshold and activating on October 1, 2025, without controversy.
熟悉區塊鏈治理困難的觀察者,對開發速度留下深刻印象。從最初提案到主網啟用,僅花約十八個月,這對於引入重大協定變更而言相當快速。該修正案得到了多數驗證者的強力支持,通過所需的 80% 門檻,並於 2025 年 10 月 1 日毫無爭議地上線。
Ethereum maximalists and DeFi advocates raised concerns about centralization. The clawback and freeze capabilities particularly drew criticism. Commentators noted that giving issuers unilateral power to seize tokens fundamentally contradicts cryptocurrency's goal of creating censorship-resistant money. If issuers can freeze accounts or reverse transactions, tokens become similar to traditional bank accounts rather than bearer instruments.
以太坊至上主義者以及 DeFi 擁護者對中央集權問題表達擔憂。特別是回收與凍結功能,引發不少批評。評論指出,賦予發行方單方面沒收代幣的權力,根本違反加密貨幣設計去審查機制的初衷。如果發行方能凍結帳戶或回溯交易,那這些代幣就與傳統銀行帳戶無異,而非真正的持有人資產。
This criticism reflects a philosophical divide. To some, blockchain's value proposition is permissionlessness and resistance to arbitrary control. Features that enable issuers to override user control undermine this value. To others, compliance with legal requirements and institutional needs justifies capabilities that would be unacceptable for base-layer cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ether.
這些批評反映出哲學上的分歧:有人認為區塊鏈的價值主張在於無需授權和抗拒胡亂控制;允許發行方取代用戶掌控的功能,會削弱這一價值。但對另一部分人來說,符合法規以及機構需求,則合理化了這些在比特幣或以太幣等基礎層加密貨幣中難以接受的功能。
Bitcoin purists, who often dismiss all other blockchain projects as insufficiently decentralized, used MPT as further evidence that XRP serves institutional interests over user freedom. Critics like Pierre Rochard, VP of Research at Riot Platforms, argue that Ripple's influence over XRPL validator selection and the amendment process means the network cannot provide credible neutrality. If Ripple effectively controls which validators are trusted, they contend, Ripple could push through amendments that serve their business interests rather than users' needs.
比特幣純粹主義者時常將其他區塊鏈項目說成去中心化不足,這次也以 MPT 作為 XRP 服務於機構利益而非用戶自由的佐證。像是Riot Platforms研究副總裁 Pierre Rochard 就批評,Ripple 對 XRPL 驗證者選擇權及修正提案流程有很大影響,使網路無法真正保持中立。如果 Ripple 能實質控制哪些驗證者獲得信任,就能促使對自家利益有利的修正案過關,而非以用戶需求為優先。
Ripple's CTO David Schwartz has repeatedly countered these centralization claims. He notes that XRPL has over 190 active validators, with only 35 in the default Unique Node List. Validators must reach consensus on transactions every three to five seconds, and no single party controls enough validators to unilaterally determine outcomes. The amendment process requires supermajority support for two weeks, preventing any entity from forcing protocol changes.
Ripple 技術長 David Schwartz 多次反駁這些集中化的指控。他指出 XRPL 擁有超過 190 個活躍驗證者,在預設的唯一本節點列表中僅佔35個。驗證者每三到五秒就要對交易達成共識,沒有任何單一方能獨立決定結果。修正程序必須連續兩週獲得超過八成贊成,杜絕任何實體強行修改協定。
The empirical question is whether XRPL's consensus mechanism provides sufficient decentralization for institutional use cases, not whether it matches Bitcoin's decentralization model. Banks and asset managers comparing blockchain options care whether the network is reliable, whether their transactions will process as expected, and whether governance is transparent, not whether it is maximally resistant to nation-state attacks.
最實際的問題,是 XRPL 的共識機制是否對機構級應用有足夠的去中心化,而不是是否達到比特幣的極致分散。銀行及資產管理者在選擇區塊鏈時,更在意網路是否可靠、交易會否如期處理、治理是否透明,而不是抗國家級攻擊是否最大化。
Security token professionals and compliance experts responded more positively. Multiple firms noted that MPT could significantly reduce legal and audit costs compared to deploying custom smart contracts on Ethereum. The protocol-level implementation means one security audit of the XRPL code covers all MPT tokens, rather than requiring per-issuer contract audits. For institutions issuing multiple securities, this could mean hundreds of thousands of dollars in cost savings.
安全型代幣與合規專家則給予較多正面回應。多家業者指出,與以太坊自訂智慧合約相比,MPT 可大幅降低法律及審計成本。在協定層實作,代表一次性審計 XRPL 代碼即可涵蓋所有 MPT 代幣,不必為每個發行方另行審查合約。對同時發行多種證券的機構來說,這可能意謂數十萬美元的成本節省。
The simplicity of MPT deployment also garnered praise. Creating an MPT requires submitting a single transaction with the desired configuration parameters. No Solidity code to write, no contracts to deploy, no gas optimization required. For financial institutions whose developers have limited blockchain experience, this ease of use lowers the barrier to experimentation.
MPT 部署的簡易性也受到讚賞。發行 MPT 只需提交一筆帶有所需參數的交易,無需撰寫 Solidity 代碼、佈署合約或進行 gas 優化。對開發經驗有限的金融機構來說,這種易用性大大降低了嘗試門檻。
Criticism emerged around MPT's limitations. Developers accustomed to Ethereum's flexibility noted that MPT lacks programmability. Complex securities with conditional logic, dynamic behaviors, or intricate governance cannot be represented purely through MPT's fixed feature set. Use cases requiring those capabilities would still need smart contract solutions, potentially on XRPL's EVM-compatible sidechain or on other platforms.
不過也有針對 MPT 侷限性的批評。習慣以太坊彈性的開發者認為,MPT 缺乏可編程性。具條件判斷、動態機制或複雜治理設計的證券,無法純粹靠 MPT 的固有功能來實現。有這方面需求者,還是得用智慧合約方案,可能是在 XRPL 的 EVM 兼容側鏈,或其他平台上實作。
The immutability of MPT configurations also drew concern. If an issuer creates a token with specific settings and later discovers they need different capabilities, they must issue a new token and migrate holders. With smart contracts, upgradeable patterns allow changing logic without changing the token contract address. The proposed Dynamic MPT extension would address this, but it remains under development.
MPT 設定值不可改變的性質同樣引發疑慮。若發行人在設計後發現需要差異化功能,必須重新發行新代幣並遷移持有者。智慧合約常用可升級模式,無需變動合約位址即可逐步修改邏輯。目前已有動態 MPT 擴充方案的提案,但還在研發階段。
Competitors in the tokenization space acknowledged MPT as a serious offering while defending their own approaches. Ethereum-focused platforms emphasized their established ecosystems, the thousands of developers familiar with Solidity, and the availability of audited contract templates that reduce deployment risk. They argued that protocol ossification is a bug, not a feature - markets evolve quickly, and smart contract flexibility enables keeping pace.
同領域競爭者承認 MPT 具有高度實力,同時也維護自家解決方案。以太坊生態平台強調其現有的龐大生態系、海量熟悉 Solidity 的開發者,以及眾多審計過的合約範本降低部署風險。他們認為協定僵化不是優點,而是缺陷——市場變化迅速,智慧合約的彈性才跟得上市場步伐。
Stellar, which competes directly with XRPL in the payment and settlement space, highlighted its own asset tokenization capabilities and questioned whether a separate MPT standard was necessary when trust line tokens already existed on XRPL. The response from Ripple engineers was that trust lines, while powerful, lack the compliance controls that regulated institutions require, making MPT a necessary evolution rather than redundant functionality.
在支付與結算領域與 XRPL 直接競爭的 Stellar,也強調自己資產代幣化能力,並質疑:既然 XRPL 早有 trust line 代幣,是否真的還需要新的 MPT 標準?Ripple 工程師則回應,雖然 trust line 很強大,但缺乏合規管控,無法滿足受監管機構需求,MPT 屬於必要升級,而非重複冗餘機能。
Early adopters provided the most tangible reaction. FortStock's warehouse receipt pilot demonstrated real-world usage. The company is tokenizing inventory held in warehouses across emerging markets, allowing that inventory to serve as collateral for short-term credit. Using MPT, they can embed metadata about the commodity type, storage location, expiration dates, and audit trails directly in the token. The protocol-level transfer restrictions let them ensure only approved creditors receive tokens as collateral.
早期採用者給出了最具體的回饋。FortStock 倉儲憑證試點展現了真實世界應用。該公司正將新興市場中的倉儲存貨代幣化,讓這些存貨能作為短期信貸抵押品。運用 MPT,可在代幣裡直接嵌入商品類型、倉儲位置、到期日及審計紀錄的元資料。透過協定層級的轉帳限制,確保只有核准的債權人可獲取代幣作為擔保。
Financial institutions remained cautiously observant. While several banks and asset managers acknowledged exploring XRPL for institutional use cases, most were waiting to see whether liquidity and market infrastructure would develop before committing to production deployments. The chicken-and-egg problem persists: institutions want established ecosystems before committing, but ecosystems develop only when institutions commit.
金融機構依然採取審慎觀望態度。雖然有數家銀行和資產管理業者承認正在研究 XRPL 的機構用例,但大多在觀察市場流動性和基礎設施是否成熟後,才決定是否進入正式部署。這是一個「雞生蛋、蛋生雞」的問題:機構想等生態系成熟再加入,但只有機構加入,生態系才會發展。
The market's ultimate judgment will emerge over the next eighteen to twenty-four months as institutions decide whether to launch tokenized securities using MPT, Ethereum-based standards, or alternative platforms like Avalanche or Polygon. Early mover advantages in tokenization go to platforms that attract major issuers, creating network effects that make those platforms the default choice for subsequent issuers.
市場最後的評價將在未來十八到二十四個月內浮現——機構將決定要用 MPT、以太坊標準,還是像 Avalanche、Polygon 這類替代平台來發行通證化證券。誰能吸引主要發行方,創造網路效應,誰就能在初期搶得先機,成為後續發行人的預設選擇。
Ripple's Institutional DeFi Vision and XRPL 3.0
Ripple 的機構級 DeFi 願景與 XRPL 3.0
MPT exists not as a standalone feature but as a foundational component of Ripple's broader institutional DeFi strategy. The September 2025 roadmap announcement positioned MPT alongside several other protocol upgrades designed to make XRPL a comprehensive platform for regulated on-chain finance.
MPT 並非單獨的功能,而是 Ripple 更廣泛機構級 DeFi 策略中的基石組件。2025 年 9 月公佈的路線圖,將 MPT 與多項協定升級列為 XRPL 朝向合規鏈上金融綜合平台發展的關鍵。
The centerpiece is a native lending protocol, currently under development and scheduled for inclusion in XRPL Version 3.0.0. This protocol would enable pooled lending and borrowing directly at the ledger level without requiring smart contracts.
核心項目是一套原生借貸協定,目前仍在開發,預計納入 XRPL 3.0.0 版本。該協定將能讓用戶直接在帳本層進行資金池借貸,無需依賴智慧合約。
The lending design uses "Single-Asset Vaults" that aggregate liquidity from multiple providers. If several institutions want to lend RLUSD, Ripple's upcoming stablecoin, they deposit their RLUSD into a vault. The protocol issues transferable vault shares representing each lender's proportional claim on the pool. Borrowers can request loans from the vault if they provide acceptable collateral, with the protocol enforcing loan-to-value ratios and managing repayment schedules automatically.
其借貸設計採用「單一資產金庫」模式,集合多方流動性。若多家機構願意出借 Ripple 即將發行的穩定幣 RLUSD,只要將 RLUSD 存入金庫,協定就會發放可轉讓的金庫股份,分別代表每位出借方對資金池的持分比例。借款方若能提供被接受的抵押品,即可向金庫申請借款,由協定自動管理擔保率與還款行程。
The connection to MPT is that vault shares themselves could be represented as MPT tokens. If a lending vault issues shares as MPTs with appropriate compliance controls, those shares become tradeable, usable as collateral in other protocols, or redeemable through the vault's automated mechanism. The protocol understands MPT properties like freeze status or transfer restrictions, letting itmake safe lending decisions based on collateral quality.
根據抵押品品質做出安全的放貸決策。
This integration enables institutional credit markets at the protocol level. A money market fund represented as an MPT could serve as collateral for short-term loans. A tokenized bond could be borrowed against. Real-world assets held in MPT form could unlock liquidity without requiring centralized intermediaries to warehouse collateral and manage lending operations.
此整合讓機構信貸市場能在協議層面運作。以 MPT 形式表示的貨幣市場基金可被用作短期貸款的抵押品。亦可將代幣化債券用作借貸標的。以 MPT 形式持有的現實世界資產,無需中心化中介機構來倉儲抵押品及管理放貸作業,就能釋放流動性。
The "MPT DEX" concept extends XRPL's existing decentralized exchange to handle MPT trading. Currently, XRPL's native order book supports trading XRP and trust line tokens. Extending this to MPTs enables secondary market trading of tokenized securities, stablecoins, and real-world assets with the same low fees and high performance that XRPL provides for other assets.
「MPT DEX」概念將 XRPL 現有的去中心化交易所擴展到支援 MPT 交易。目前,XRPL 的原生訂單簿支援 XRP 與信任線代幣交易。將其擴展到 MPT,可用同樣低費用且高效能的方式,支援代幣化證券、穩定幣和現實世界資產的二級市場交易。
The challenge is regulatory compliance. Securities trading must occur on registered exchanges or through broker-dealers in most jurisdictions. A fully permissionless order book where anyone can place orders for security tokens would violate these requirements. The solution involves "permissioned DEX" functionality where issuers can restrict who can place orders for their tokens.
挑戰來自於法規遵循。在多數司法管轄區,證券交易必須在註冊交易所或券商平台進行。若訂單簿完全無需許可,任何人皆可為證券型代幣下單,會違反這些規定。解決方案是「受限許可的 DEX」功能,讓發行人可以限制誰能為其代幣下單。
If a tokenized bond issuer enables the "Can Trade" flag on their MPT, then only authorized addresses can participate in order book trading. The protocol enforces this restriction, ensuring that even if someone tries to place an order, it will fail unless they are on the issuer's approved list. This lets security tokens trade on decentralized infrastructure while maintaining compliance with trading restrictions.
若代幣化債券發行人啟用其 MPT 的「可交易」標記,則只有授權的地址方可參與訂單簿交易。協議會強制執行此限制,即使有人嘗試下單,只要不在發行人核准名單上就會失敗。如此可使證券型代幣在去中心化基礎設施上交易,同時保持對交易限制之合規性。
The roadmap also includes confidential MPTs, scheduled for early 2026. These would use zero-knowledge proof technology to enable privacy-preserving transfers while maintaining the compliance and audit capabilities that regulators require.
發展路線圖亦包含了機密型 MPT,預計於 2026 年初推出。這將採用零知識證明技術,在保護隱私的同時,也滿足監管機構要求的合規性和稽核能力。
The concept is to prove facts about transactions without revealing the facts themselves. A confidential MPT transfer could prove that the sender is authorized to hold the token, that the receiver is authorized, that the transfer amount does not exceed the sender's balance, and that all compliance rules are satisfied, all without revealing which accounts participated in the transfer or how many tokens moved.
這一概念目的是在不揭露具體事實的情況下,證明某些交易事實。機密型 MPT 轉帳可證明發送方擁有代幣的權限、接收方也被授權、轉帳金額未超過發送方餘額,並且所有合規規則都被遵守,卻無需透露涉及的帳戶或具體移動了多少代幣。
For institutions, this addresses a critical need. Privacy is not just a preference but a requirement for many financial transactions. A corporation taking out a loan does not want competitors seeing the loan amount on a public ledger. An asset manager purchasing securities for a fund does not want their trading strategy exposed to front-runners. Traditional financial markets provide transaction privacy through opacity - information stays in private databases at centralized intermediaries.
對機構來說,這解決了一個關鍵需求。隱私不僅是偏好,更是許多金融交易的必要條件。企業辦理貸款時,不希望競爭對手在公鏈上看到借款金額。資產管理人在為基金購買證券時,也不願交易策略被搶先交易者獲知。傳統金融市場透過不透明機制確保交易隱私——資訊只留在中心化中介機構的私有資料庫中。
Blockchain's transparency creates accountability but eliminates privacy. Confidential MPTs aim to restore privacy while retaining blockchain's advantages: cryptographic auditability, elimination of reconciliation, and reduced intermediary costs. Regulators and auditors could still verify that transactions followed rules and that balances are accurate, but market participants could not surveil each other's activities.
區塊鏈的透明性帶來了問責性,卻犧牲了隱私。機密型 MPT 旨在於保留區塊鏈優勢(如密碼學稽核、免調對、降低中介成本)的同時,恢復隱私。監管者和稽核人員仍可驗證交易是否合規、餘額是否正確,但市場參與者之間將無法監視彼此的活動。
The technical implementation likely involves proving systems like zkSNARKs or zkSTARKs that generate cryptographic proofs of transaction validity. These proofs can be verified by validators without revealing transaction details. The sender and receiver know what they transacted, regulators with appropriate permissions could view transaction details for oversight, but the general public sees only that valid transactions occurred.
技術實現很可能會採用 zkSNARKs 或 zkSTARKs 等證明系統,用以產生交易有效性的加密證明。這些證明可由驗證者檢查,而不需要披露交易細節。發送方與接收方知道自己的交易內容,具適當許可的監管者能檢視交易詳情進行監督,而大眾僅能看到有有效交易發生。
Zero-knowledge technology remains relatively early and carries performance costs. Proof generation is computationally intensive, potentially adding seconds of latency to transaction processing. Proof size affects blockchain throughput, as larger proofs consume more space in ledgers. These constraints are improving as the technology matures, but confidential transactions will likely remain more expensive and slower than transparent ones for some time.
零知識技術仍處於較早期階段,並且帶有效能成本。證明生成運算密集,可能會讓交易處理延遲數秒。證明文件大小影響區塊鏈的處理量,越大的證明佔用帳本空間越多。隨著技術成熟,這些限制正在改善,但在一段時間內,機密型交易仍會比透明交易昂貴且更慢。
Ripple's adoption strategy acknowledges this reality by making confidentiality optional. Standard MPTs remain fully transparent, suitable for use cases where privacy is unnecessary or where regulation requires transparency. Confidential MPTs opt into privacy features where that privacy is valuable enough to justify additional costs.
Ripple 的推廣策略考量了這一現實,將隱私設定為可選功能。標準型 MPT 完全透明,適用於不需要隱私或法規要求透明的場合。機密型 MPT 則可選用隱私功能,僅當隱私價值足以抵償額外成本時才啟用。
The Credentials system, which activated in September 2025, provides an identity layer that MPT and other XRPL features can leverage. Credentials are on-chain attestations about accounts, issued by trusted entities. A credential might attest that an account completed KYC with a specific provider, that the account holder is an accredited investor, or that the account belongs to a regulated financial institution.
2025 年 9 月啟用的憑證系統,為 MPT 及其他 XRPL 功能提供了身份層。憑證是由可信任機構發佈、託管於鏈上的帳戶證明。憑證可能證明某帳戶已完成特定機構的 KYC、帳戶持有人是合格投資人,或該帳戶屬於受監管金融機構。
Issuers can reference credentials in their authorization decisions. Rather than maintaining their own lists of approved addresses, an issuer could specify that their MPT requires holders to possess a specific credential. The protocol then checks credential presence during transfers. This decentralizes identity management - multiple credential issuers can provide attestations that many token issuers accept, rather than each token issuer building their own identity infrastructure.
發行人可在授權決策時引用憑證。不必自行維護核准地址名單,而是可指定其 MPT 必須持有特定憑證。協議會於轉帳時檢查憑證存在與否。如此一來,身份管理自動實現去中心化——多個憑證發行者可提供多數代幣發行人都能接受的認證,而無需每家代幣發行人各自建立身份基礎建設。
The Deep Freeze feature, also recently activated, extends issuer control to decentralized exchange activity. A traditional freeze prevents an account from sending tokens through payment transactions. But on XRPL, accounts can also trade frozen tokens by placing offers on the decentralized exchange or providing liquidity to automated market makers. Deep Freeze closes these loopholes by preventing frozen tokens from being involved in any on-ledger activity, even DEX trading.
新啟用的 Deep Freeze 功能,更進一步將發行人的控制權延伸至去中心化交易。傳統的凍結只阻止帳戶經付款交易發送代幣。但在 XRPL 上,帳戶仍可在 DEX 下單或給自動化做市商提供流動性來交易已凍結的代幣。Deep Freeze 封堵了這些漏洞,防止被凍結的代幣參與任一帳本活動,甚至包括 DEX 交易。
For compliance purposes, this ensures that freezes are comprehensive. If an account is flagged as suspicious and its token balances are frozen, the account cannot simply trade those tokens for XRP or other assets on the DEX. This level of control matches what regulators expect from traditional financial platforms.
就合規目的而言,這確保凍結的範圍是全方位的。如果帳戶被標記為可疑且代幣餘額遭凍結,則無法僅靠 DEX 交易將這些代幣兌換為 XRP 或其他資產。這種控制力正符合監管機構對傳統金融平台的要求。
The EVM-compatible sidechain, operational since early 2025, provides developers familiar with Ethereum a pathway to build on XRPL infrastructure while using Solidity and standard Ethereum tools. The sidechain connects to XRPL mainnet through a bridge, allowing assets to move between environments.
與 EVM 相容的側鏈自 2025 年初啟用,讓熟悉以太坊開發的團隊能以 Solidity 與乙太坊標準工具於 XRPL 架構上開發。該側鏈透過橋接連接 XRPL 主鏈,資產得以在環境間移動。
This hybrid approach acknowledges that some applications require smart contract flexibility that XRPL's native protocol does not provide. A complex DeFi protocol with novel logic could launch on the sidechain, while leveraging XRPL mainnet for settlement and custody. Tokenized assets on mainnet could be bridged to the sidechain for use in smart contract applications, then brought back to mainnet.
這種混合模式認可部分應用需要 XRPL 原生協議尚不提供的智能合約彈性。一個有創新邏輯的複雜 DeFi 協議可以在側鏈上執行,並以 XRPL 主網作為結算和託管。主鏈上的代幣化資產可以橋接到側鏈進行智能合約應用,再回流至主鏈。
The architectural vision positions XRPL mainnet as a settlement layer optimized for security, compliance, and efficiency, while sidechains and layer-two solutions provide programmability for applications requiring it. This separation of concerns lets Ripple avoid compromising mainnet's design to accommodate every possible use case.
架構藍圖將 XRPL 主網定位為,針對安全、合規與效率最佳化的結算層,而側鏈與第二層解決方案則提供給需要可編程性的應用。這種職責分離,讓 Ripple 不必為支應所有潛在應用而犧牲主網設計。
Competition and Ecosystem Effects in the Tokenization Landscape
代幣化格局下的競爭與生態效應
MPT arrives in a crowded market where multiple blockchain platforms compete for institutional tokenization business. Understanding how MPT fits into this competitive landscape requires examining what each platform offers and where their strengths lie.
MPT 進入了一個競爭激烈的市場,多個區塊鏈平台爭奪機構級代幣化業務。要了解 MPT 如何融入這個競爭格局,須檢視各平台提供什麼服務,以及其優勢所在。
Ethereum remains the dominant platform for tokenized securities, with billions of dollars in assets represented through ERC-20, ERC-1400, and ERC-3643 standards. The ecosystem's depth - thousands of developers, extensive tooling, multiple auditing firms familiar with the technology, and institutional-grade infrastructure like Fireblocks and Anchorage - creates powerful network effects. Institutions considering tokenization often default to Ethereum simply because it is where the infrastructure and expertise already exist.
以太坊仍是代幣化證券的主導平台,數十億美元資產透過 ERC-20、ERC-1400 與 ERC-3643 標準展現。生態體系深厚,包含數千位開發人員、完善工具、多家熟悉該技術的稽核公司,以及如 Fireblocks、Anchorage 這類機構級基礎設施,強化了網絡效應。考慮導入代幣化的機構往往預設選擇以太坊,因其基礎設施與專業能力已經到位。
Layer-two solutions like Polygon and Optimism extend Ethereum's reach by providing lower transaction costs while inheriting Ethereum mainnet's security. A tokenized security could be issued on Polygon as an ERC-3643 token, benefiting from Ethereum's established standards and tooling while paying fraction-of-cent transaction fees. For high-frequency trading or retail-facing applications where Ethereum mainnet gas costs are prohibitive, these layer-twos present compelling alternatives.
Polygon、Optimism 等第二層解決方案,讓以太坊擴展到低手續費領域,卻繼承主網的安全性。可於 Polygon 發行 ERC-3643 代幣化證券,在享受以太坊成熟標準及工具同時,僅需支付幾分之一美分的交易費。對高頻交易或面向零售的應用而言,主網高昂的 gas 成本過於負擔,這些 L2 方案成為具競爭力的選擇。
Avalanche positions itself as an institutional blockchain platform with permissioned subnets that can enforce regulatory requirements while connecting to the public Avalanche network for settlement. An institution could launch a private subnet for tokenized securities trading, restricting access to approved participants, while still benefiting from Avalanche's architecture and tooling. Several institutions have explored this model for trade finance and private market securities.
Avalanche 主打機構級區塊鏈平台,提供具許可控制的子網,可執行監管需求並與公共主網結算。機構可設立專屬子網進行代幣化證券交易,只允許核准參與者進入,同時享有 Avalanche 架構與工具帶來的好處。已有數家機構將此模式探索於貿易融資與私人市場證券。
Stellar, XRPL's closest competitor in the payment-focused blockchain space, has emphasized simplicity and regulatory friendliness for years. Its asset tokenization model uses native ledger capabilities similar to XRPL's approach, rather than relying on smart contracts. Stellar has particularly strong adoption in emerging market payment corridors and has positioned itself for both stablecoin issuance and remittances.
Stellar 作為 XRPL 在支付導向區塊鏈領域的最接近競爭對手,長期強調簡約與合規友好。其資產代幣化採用與 XRPL 類似的原生帳本機制,而非依賴智能合約。Stellar 在新興市場支付渠道擁有極高採用度,並積極佈局穩定幣發行及國際匯款。
Traditional financial infrastructure providers present a different kind of competition. The Digital Asset Modeling Language platform, used by Australian Securities Exchange's upcoming settlement system replacement, keeps tokenization entirely within permissioned networks managed by traditional intermediaries. Canton, which powers post-trade settlement for multiple securities markets, provides blockchain benefits like synchronized state and cryptographic auditability without creating public tokens at all.
傳統金融基礎設施業者則帶來完全不同的競爭類型。澳洲證交所正採用的 Digital Asset Modeling Language 平台,使代幣化操作僅發生於受許可且由傳統中介管理的網路。Canton 系統則支援多個證券市場的清算交割,帶來區塊鏈之即時同步、加密稽核等優勢,卻完全不需發行公有型代幣。
These permissioned approaches arguably address institutional needs more directly by avoiding public blockchain
這些受許可的作法,或許更直接地回應了機構的需求,因其避免了公有區塊鏈...constraints entirely. Institutions can implement tokenization, programmable settlement, and cryptographic auditability without worrying about gas costs, public transparency, or integrating with cryptocurrency ecosystems. The trade-off is that they sacrifice blockchain's core innovation: shared infrastructure that eliminates reconciliation by giving all parties access to a common, verifiable state.
機構可以完全不用擔心 gas 費用、公開透明度,或是與加密貨幣生態系整合等問題,就能實現代幣化、可編程結算以及密碼學可稽核性。但這樣做的交換條件就是會犧牲區塊鏈最核心的創新:共享基礎設施,也就是讓所有參與方都能存取同一個、可驗證的共同狀態,從而消除對帳需求。
MPT's competitive advantage lies primarily in cost efficiency and integration simplicity. Transaction fees orders of magnitude lower than Ethereum enable use cases that are economically impractical elsewhere. Representing thousands of microtransactions, high-frequency trading scenarios, or retail payment tokens becomes viable when each transaction costs fractions of cents rather than dollars.
MPT 的競爭優勢主要在於成本效益與整合簡單。其交易費遠低於以太坊,讓在其他平台經濟上不可行的應用案例成為可能。當每筆交易只需幾分之一美分,而非以美元計算時,處理數千筆微支付、高頻交易或零售支付型代幣等情境都變得有可行性。
The protocol-level implementation reduces technical complexity for institutions. Banks and asset managers can use MPT without learning Solidity, hiring smart contract developers, or conducting extensive security audits of contract code. This lower barrier to entry could accelerate institutional experimentation, particularly among traditional financial institutions whose technical staff lack blockchain expertise.
協議層級實作則降低了機構面臨的技術複雜度。銀行和資產管理公司可以直接使用 MPT,而無需學習 Solidity、雇用智慧合約開發人員,或進行大規模合約程式碼安全稽核。這項較低的進入門檻有望加速傳統金融機構的區塊鏈實驗,尤其對缺乏區塊鏈技術人力的單位更為有利。
Network effects favor incumbents, which poses MPT's biggest challenge. An institution issuing a tokenized bond on Ethereum can immediately access liquidity through established platforms like OpenEden, Ondo Finance, or Backed Finance. Secondary market makers, custodians, and trading venues understand Ethereum-based securities. Launching on a less established platform means building this infrastructure from scratch or convincing existing providers to add platform support.
網路效應有利於現有主導者,這對 MPT 是一大挑戰。機構若在以太坊發行代幣化債券,可以即時透過像 OpenEden、Ondo Finance、Backed Finance 等成熟平台取得流動性。二級造市商、託管機構和交易場所都了解以太坊型證券。相較之下,在尚未成熟的平台發行即意味著要從零建立整個基礎建設,或說服現有服務供應商加入新平台支持。
Ripple's strategy appears to be building this infrastructure themselves where necessary. The upcoming native lending protocol, MPT DEX, and partnerships with stablecoin providers aim to create a vertically integrated stack where institutions can issue, trade, and use tokenized assets entirely within the XRPL ecosystem. If successful, this could bootstrap network effects without depending on third-party infrastructure that might never materialize.
Ripple 的策略似乎是必要時由自己建立相關基礎建設。即將推出的原生借貸協議、MPT DEX,以及與穩定幣業者的合作,都是要打造一套垂直整合的技術棧,讓機構能完全在 XRPL 生態內發行、交易並運用代幣化資產。若能成功,將可不必依賴第三方基礎建設(因其未必出現),而自力培養網路效應。
The regulatory arbitrage potential presents another consideration. If MPT's protocol-level compliance proves more acceptable to regulators than smart contract-based approaches, institutions might prefer it specifically to reduce regulatory risk. A bank considering tokenized deposit receipts might choose MPT because the built-in freeze and clawback capabilities clearly demonstrate regulatory compliance, whereas proving the same properties about a complex smart contract requires extensive legal analysis.
監管套利潛力是另一個考量點。如果 MPT 在協議層級上的合規性更容易獲得監管單位認可,機構就可能傾向於採用,以降低監管風險。例如銀行若考慮發行代幣化存款憑證,可能會選擇 MPT,因其內建的凍結和追繳(clawback)功能明確展現合規性,而複雜智慧合約的同樣特性則需大量法律分析才能驗證。
Cross-chain bridges and interoperability protocols potentially reduce the importance of platform choice. If assets can move freely between blockchains through trustless bridges, institutions could issue on the platform best suited for their compliance needs then bridge to platforms with better liquidity or infrastructure. Projects like LayerZero and Axelar aim to enable this cross-chain future, though trustless bridge security remains an active research area.
跨鏈橋與可互操作協議有望降低平台選擇的重要性。如果資產能夠透過無信任橋樑在多個區塊鏈間自由流轉,機構便可以選擇最符合法規要求的平台發行產品,再橋接到流動性或基礎建設更佳的平台。像 LayerZero 和 Axelar 等專案正朝這種跨鏈未來發展,儘管無信任橋的安全性仍是積極研究領域。
The realistic outcome is likely ecosystem specialization rather than winner-takes-all dominance. Ethereum and its layer-twos will continue serving applications requiring maximum smart contract flexibility and where existing infrastructure integration is critical. XRPL and MPT will attract use cases prioritizing compliance, cost efficiency, and simplicity over programmability. Permissioned platforms will serve institutions that want blockchain benefits without public infrastructure.
較為現實的結果,可能是各區塊鏈生態專精,而非單一平台全面勝出。以太坊及其二層網路將持續服務那些需要最高智慧合約靈活性與現有基礎建設整合的應用。XRPL 和 MPT 則會吸引更重視合規性、成本效益與簡易性的用戶,而非著重可編程性的需求。至於許可制平臺,則會鎖定只想要區塊鏈好處卻不要公共基礎設施干擾的機構。
Different institutions will make different choices based on their specific requirements, risk tolerances, and existing technology relationships. A cryptocurrency-native firm might naturally choose Ethereum because their developers already know Solidity and their infrastructure integrates with Ethereum tooling. A traditional bank exploring tokenization for the first time might prefer MPT's simplicity and lower technical complexity.
不同機構會根據自己的需求、風險承受度與現有技術關係做出不同選擇。例如加密貨幣原生企業可能自然而然傾向以太坊,因為他們的開發人員已熟悉 Solidity,所用基礎設施也與以太坊工具鏈相容;而初次探索代幣化的傳統銀行則可能偏好 MPT 的簡易性與較低技術門檻。
Market momentum will ultimately determine platform success. The first platform to host billions of dollars in actively traded tokenized securities from multiple issuers creates a gravitational pull that attracts additional issuers seeking liquidity and infrastructure that already exists. Whether MPT can achieve this momentum against Ethereum's substantial head start remains the key question for XRPL's institutional ambitions.
市場動能最終將影響平台成敗。第一個託管來自多發行人、真正有在流通交易的數十億美元等級代幣化證券的平台,會產生吸引後來加入者的「重力」,讓渴望流動性與現成基礎建設的發行人自動聚集。MPT 能否在以太坊巨大的先發優勢下取得突破,則是 XRPL 推動機構布局的關鍵未解之題。
Technical Challenges and Implementation Roadblocks
技術挑戰與實作障礙
Despite MPT's thoughtful design, several technical challenges could impede adoption or limit what the standard can achieve.
儘管 MPT 設計考慮周詳,仍有數項技術挑戰可能阻礙其普及,或限制其標準化可達到的目標。
Validator Upgrade Coordination required for MPT activation highlighted governance challenges that will recur with future amendments. The MPT amendment needed eighty percent of trusted validators to vote for activation over a two-week period. While the amendment successfully activated on schedule, future protocol changes will face similar coordination requirements.
MPT 上線所需的 驗證者升級協調 暗示未來所有協議修改都會重複面臨治理挑戰。MPT 修正案必須在兩週內獲得 80% 信任驗證者同意才能啟用。雖然修正案這次如期生效,但日後的協議更新同樣會碰到協調調整的要求。
If an amendment proves controversial or validators disagree about technical implementation choices, achieving consensus could take significantly longer. Ethereum experienced this with its transition from proof-of-work to proof-of-stake, where years of discussion and multiple testnet iterations preceded mainnet deployment. XRPL's simpler amendment process might avoid such lengthy delays, but it also provides fewer opportunities for stakeholder input before changes become permanent.
如果協議修正方向存在爭議,或驗證者對實作細節有歧見,協議共識可能會拖延甚久。以太坊在從工作量證明(PoW)切換到權益證明(PoS)時,就歷經多年討論與多次測試網演練,才上線主網。XRPL 修改流程雖較簡單,或許可避免冗長延宕,但也意味著重大改動在落實前,持份者能參與討論、給意見的機會較少。
The amendment mechanism's supermajority requirement prevents any single entity from forcing protocol changes, which protects against centralized control. But it also means necessary improvements might be delayed if validator consensus proves difficult to achieve. Balancing agility with decentralized governance remains an ongoing challenge for all blockchain platforms.
修正機制的超高門檻設計,確保單一實體無法強行修改協議,降低中心化風險。但這也意味著如果難以取得足夠驗證者共識,必要改進就會被拖延。如何在變革敏捷度與去中心化治理之間取得平衡,是所有區塊鏈平台長期共同的挑戰。
Privacy and Transparency Tradeoffs become more complex with confidential MPTs. Zero-knowledge proof systems that prove transaction validity without revealing details are powerful but introduce new trust assumptions and technical requirements.
隱私與透明權衡 在機密型 MPT 現身後更加複雜。零知識證明(ZKP)可以不透露細節就證明交易有效性,相當強大,但也引入了新的信任前提與技術門檻。
The proof generation must happen somewhere. If users generate proofs on their own devices, they need sufficient computational power and must trust the proving key material. If a third-party service generates proofs, that service becomes a centralizing point of control and a potential target for coercion. If validators generate proofs collectively through secure multi-party computation, consensus latency increases significantly.
產生證明必須在某處執行:如由使用者端裝置產生,則需用戶端具備足夠算力並且信任證明金鑰;若由第三方服務產生,則該服務成為潛在的中心化控制節點與被脅迫目標;若由多方驗證者透過安全多方運算集體產生,又會大幅增加共識延遲。
Regulatory acceptance of zero-knowledge privacy remains uncertain. Regulators want the ability to audit transactions for compliance, investigate suspicious activity, and enforce legal requirements. Confidential transactions make these tasks harder. While cryptographic protocols exist for selective disclosure - where regulators with proper authorization can view transaction details that remain hidden from the public - implementing these systems without compromising security is technically challenging.
監管單位對零知識隱私的接受度仍屬未知。監管者希望能查核交易以確保合規、調查可疑活動並執行法律,但機密交易讓這些任務更困難。雖然已經有選擇性揭露(selective disclosure)密碼協議,能讓有授權的監管人員看到對外隱藏的交易細節,但要確保落實這種機制同時不犧牲安全,仍然頗具挑戰。
The balance between privacy and accountability will likely require ongoing negotiation between technology designers, institutions seeking privacy for legitimate business reasons, and regulators ensuring they can fulfill oversight responsibilities.
未來隱私與問責的平衡,勢必須在技術設計者、以正當業務理由尋求隱私的機構,以及具有監督任務的監管者三者間,持續討論、協商。
Composability with Existing XRPL Features presents integration challenges. MPT must interact correctly with XRPL's decentralized exchange, automated market makers, escrow system, and other protocol features. Each interaction creates potential edge cases that require careful consideration.
與現有 XRPL 功能的可組合性 也帶來整合挑戰。MPT 必須與 XRPL 的去中心化交易所(DEX)、自動做市商(AMM)、託管(Escrow)及其他協議功能正確互動。每種互動都存在潛在邊界案例,需仔細考慮。
For instance, what happens if someone places an offer to trade MPTs on the DEX but those MPTs get frozen before the offer executes? The protocol must either reject the offer creation, cancel the offer when the freeze occurs, or fail the trade attempt. Each choice has different implications for users and platform integrators.
例如,若有人在 DEX 上掛單交易 MPT,卻在成交前該 MPT 被凍結,那會發生什麼事?協議可能必須要拒絕掛單、在凍結時自動撤單或執行失敗,每種選項對用戶與整合方都有不同影響。
Escrow functionality with MPTs introduces similar complexity. If tokens are escrowed with a time-based release condition but the issuer claws them back while escrowed, which operation takes precedence? If supply caps are configured, do escrowed tokens count toward circulating supply or not?
MPT 結合託管功能時,也會產生類似複雜度。例如:若某筆代幣以時間條件託管,但在託管期間發行人行使追繳權,究竟哪一操作優先?又若有流通量上限,託管中的代幣是否算入流通?
These edge cases might seem minor but become critical for institutional use. Financial systems depend on predictable, deterministic behavior in all circumstances. Ambiguity or unexpected behavior in corner cases creates operational risk and potential financial losses.
這類邊界情境看似瑣碎,卻對機構級應用至關重要。金融體系講究各種情境下的可預期與確定性。邊界情況若有歧義或未預期行為,會帶來營運風險與財務損失。
Thorough specification and testing can address these issues, but the combination of MPT with every other XRPL feature creates a large state space to explore. Bug bounties and testnet deployments help, but production systems inevitably discover edge cases that testing missed.
完整規格書和廣泛測試能協助減緩這類問題,但 MPT 與所有其他 XRPL 功能的交互組合,會產生大量狀態空間需要探索。漏洞獎勵、測試網佈署雖有幫助,但實務系統最終還是會碰上測試遺漏的邊界條件。
Interoperability with Other Blockchains matters as the industry moves toward multi-chain ecosystems. An institution might want to issue a tokenized security as an MPT on XRPL but enable trading on Ethereum's deeper liquidity pools, or vice versa. This requires bridge protocols that can safely move MPT tokens between chains while preserving their compliance properties.
隨著產業邁向多鏈生態,與其他區塊鏈的互操作性 也顯得重要。機構可能希望在 XRPL 上以 MPT 發行代幣化證券,但又能在以太坊的高流動性市場上交易,或反過來。這就需有能確保 MPT 於不同鏈間安全轉移,同時保留其合規特性的橋接協議。
Building such bridges is technically complex. The bridge must understand MPT semantics like authorization requirements, freeze status, and clawback capabilities. It must potentially replicate these features on the destination chain, or determine how to represent MPT properties using that chain's token standards.
搭建這類橋樑技術難度高,因為橋接協議必須讀懂 MPT 的授權、凍結狀態與追繳等語義,還得在目標鏈複製這些功能,或用該鏈的代幣標準重新詮釋這些特性。
Cross-chain bridges have historically been major security vulnerabilities, with billions of dollars lost to bridge exploits. Adding compliance requirements to bridge designs increases complexity and expands the attack surface. A bridge vulnerability that allows unauthorized addresses to receive MPTs would completely undermine the authorization system's security guarantees.
過去跨鏈橋常是主要安全漏洞來源,已發生過數十億美元損失。橋接協議若還要納入合規層設計,其複雜度和攻擊面都會擴大。只要有漏洞可讓未授權地址收取 MPT,等同徹底破壞授權系統的安全保障。
The alternative is keeping MPTs entirely within XRPL's ecosystem, which limits liquidity and market reach but eliminates cross-chain security
另一路徑,則是讓 MPT 完全只在 XRPL 生態內流通,如此雖會犧牲流動性和市場規模,但能完全避開跨鏈安全風險。concerns. 這種權衡將影響機構是否選擇 MPT,或寧願使用像 Ethereum 這類已經擁有最完整代幣化基礎建設的平台。
可擴展性限制隨著採用率上升而浮現。雖然 XRPL 每秒可處理超過 1,500 筆交易,遠高於目前 Ethereum 主網的吞吐量,但這依然屬於有限的上限。如果 MPT 的採用大幅加速,交易需求可能會超過容量。
協議目前的架構是將驗證者的工作負載,橫跨所有交易分配給所有驗證者。隨著帳號、MPT 及其他對象的增加,帳本狀態成長,驗證者需要儲存與處理愈來愈多的資料。倘若 XRPL 上有數千件 MPT 發行、數百萬名持有者,儲存擴展性與狀態成長管理就會成為關注焦點。
第二層擴展方案或側鏈可以藉由將活動移到主網之外、定期還原至主網來解決擴展限制。但這將導入額外複雜性,可能會削弱 MPT 原本因簡單而具吸引力的優勢。如果機構必須了解第二層結構與跨層橋接,MPT 的易用性優勢將大打折扣。
網絡吞吐量與狀態成長的限制意味著 MPT 很可能定位於高價值、相對低頻率之證券,而不適合一般民眾支付代幣或極高頻交易用途。每隔一段時間僅幾千名持有人進行操作的公司債,協議上限內輕鬆容納。若是上百萬名用戶每天都要交易的消費型支付代幣,可能需要完全不同的基礎設施。
案例研究:使用 MPT 與 ERC-1400 發行公司債
為了說明 MPT 和 Ethereum 為基礎的做法在實務上的差異,請考慮一個情境假設:某家公司向合格機構投資人發行一筆為期五年的 1 億美元公司債。
Ethereum 上的 ERC-1400: 發行人或其平台提供者需部署客製化的 ERC-1400 智能合約。此合約必須實作分割邏輯,例如劃分不同條件的分期(tranches)、用於連結債券說明書及條款的文件管理,以及確保僅限合格買方持有代幣的轉帳限制。
部署過程需撰寫 Solidity 程式碼,無論是自創或基於現有範本客製化。合約必須交由可靠公司進行安全審計,驗證代碼是否正確實現預期邏輯且無漏洞。這種審計費用通常需 5 萬至 20 萬美元,數週完成。
部屬後,發行人還需負擔啟動狀態、鑄造初始代幣的 Gas 費。Ethereum 主網上的 Gas 費依部屬時網路壅塞程度,總額可能需數千美元。合約位址即成為該債券的鏈上永久識別碼。
投資人必須經過白名單審核,需將他們的 Ethereum 地址新增到合約的核准持有者名單。每次白名單新增都需一筆 Gas 費交易。如果初期有 100 位合格買家,發行人得為 100 筆白名單交易支付相當於數千美元的 Gas 費用。
合格買家之間的轉讓同樣會產生 Gas 費。如果投資人將部分債券賣給另一合格投資人,該筆轉讓交易成本約 10-50 美元,端看 Ethereum 網路壅塞情況。這種浮動收費模式導致部分轉讓經濟上不合理——若小金額轉讓的 Gas 費高於標的價值,便毫無意義。
發行人須設定分割屬性以處理利息支付或贖回。半年一次利息支付時,發行人得按比例將支付型代幣或穩定幣發給全部債券持有人。必須逐一遍歷持有人地址個別發送交易,或使用批次處理的合約,但同樣產生隨持有人數成正比的 Gas 費。
到期日,債券須進行贖回。發行人將本金(穩定幣或法幣掛鉤代幣)發給所有債券持有人,然後銷毀債券代幣。這贖回流程同樣產生每位持有者獨立的 Gas 費交易。
法律結構上也需要製作詳細文件,說明智能合約如何實現債券條款、在合約漏洞時風險誰負責、投資人如何驗證合約實際運作。針對智能合約的法律審查,發行成本又得再加上數萬美元。
XRPL 上的 MPT: 發行人透過提交一筆 MPTCreate 交易創建 MPT,填入債券各屬性。該交易設置供應上限 100,000(即每枚面額 1,000 美元,總計 1 億美元),啟用 "Require Auth" 限制僅合格買家持有,啟用 "Can Lock" 以符合法規要求,並在欄位中嵌入到期日、票面利率、文件哈希等相關資料。
這筆交易成本約 0.0002 XRP,目前匯率下不到一分錢的五十分之一。不需部署智能合約、不用寫 Solidity、不用單獨針對合約行為做安全審計。規範控管由協議本身實作、也已納入 XRPL 核心程式碼的審計範圍。
投資人通過送出 MPTAuthorize 交易將其地址加入可持有該代幣的白名單。每筆授權僅花費 0.0002 XRP。若有 100 位合格買家,總授權成本約兩分錢台幣。這些交易三到五秒即可最終確認。
合格投資人間的轉帳無論金額,一律只需 0.0002 XRP。無論出售 10 萬美元或 100 美元面值債券,手續費全都一樣低。這種平價、可預測且低廉的收費模式,讓所有金額的轉讓都具有經濟合理性。
利息支付時,發行人需按持有比例支付穩定幣給所有債券持有人。這流程與 Ethereum 類似,但成本大幅降低。若向一百位債券持有人支付利息,總交易費僅約兩分錢 XRP,對比 Ethereum 則需數千美元的 Gas 費用。
到期時,贖回操作流程一致。發行人支付本金穩定幣給持有人,然後銷毀所持該債券之 MPT。總成本相比 Ethereum Gas 可忽略不計。
法律架構更單純,因核心合規控管由協議功能直接落實,而非合約程式碼客製。法律文件釐清 MPT 的設定屬性及 XRPL 協議如何強制執行。由於都是標準化協議功能,邊界行為較少出現法律模糊地帶——協議規範本身就是最終依據。
比較分析: ERC-1400 方法彈性較高。若債券條件特殊需客製化邏輯,智能合約可充分應對,支援專屬分期結構、複雜利息計算公式、或特殊贖回條件。
MPT 方法則成本較低、部署較簡單。若是條件單純僅需標準合規控管的債券,MPT 可讓發行人節省數十萬美元並縮短數週開發與審計時間。日後營運成本因手續費超低而大幅下降。
關鍵在於發行需求是否落在 MPT 的功能組範圍內——若能適用,MPT 具備壓倒性優勢。倘若有必須靠自訂邏輯才能表現出的需求,則只能選用 Ethereum 的彈性,儘管成本較高。
對多數機構型證券來說,條件其實相當標準。債券有息票、有到期日。股票有多種股份類別及特定權利。貨幣市場基金有規範化的股份結構。這類標準化金融商品正好符合 MPT 的模型,因此協議等級的作法,或將滿足機構代幣化的大宗需求。
產業大環境:全球監管正加速明朗化
MPT 正是在全球數位資產監管日益明朗的背景之下問世。多個司法管轄區已經實施或即將完成落地框架,讓機構型代幣發行得以合法合規。
歐盟於 2024 年 12 月 30 日全面生效的《加密資產市場監管條例》(Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation, MiCA),針對所有歐盟成員國內的加密資產發行方與服務提供者訂定完善準則。對已被歸類為證券代幣,MiCA 採取現有金融服務法規監管,視其為金融工具。但對穩定幣與效用型代幣,MiCA 則創設全新類型,明定授權條件。
資產掛鉤型代幣與電子貨幣代幣必須由合格持牌機構、依一對一持有準備金發行。發行人必須公開揭露風險與代幣屬性的白皮書。持有人享有贖回權利,可依面值換回實體資產。有上述要求,對穩定幣發行商帶來法律確定性,也保障消費者安全。
美國則於 2025 年 7 月通過 GENIUS Act,為穩定幣監管提供聯邦級完整法律框架。此立法准許銀行與非銀行均可在聯邦監理下發行支付型穩定幣,需全額準備金支持並定期接受審計。各州監管機構可發給少於 100 億美元發行量以下的執照,大額則由聯邦主管。
MiCA 與 GENIUS Act 的監管接軌程度很高。兩者皆需完全準備金支持,並強制賦予贖回權---- and implement tiered oversight based on issuance size. This transatlantic regulatory alignment makes it feasible for firms to issue compliant stablecoins that operate in both the EU and US markets under similar requirements.
並根據發行規模實施分級監管。這種跨大西洋的監管一致性,讓企業有可能發行在歐盟及美國兩地市場,都能合規運作的穩定幣,並遵守類似的要求。
United Kingdom regulators have proposed similar stablecoin frameworks while emphasizing that tokenized securities will be regulated as securities under existing Financial Services and Markets Act authorities. The Financial Conduct Authority's Digital Securities Sandbox provides a controlled environment for experimentation with tokenization while regulators develop appropriate rules.
英國的監管機構也提出了類似的穩定幣框架,同時強調「代幣化證券」將依現有的《金融服務與市場法》權責,作為證券來監管。金融行為監管局(FCA)的數位證券沙盒,則為代幣化實驗提供一個受控環境,讓監管單位在發展適切規則的同時推動創新。
Singapore's Project Guardian has convened major financial institutions to pilot tokenization use cases and develop regulatory recommendations. The Monetary Authority of Singapore has indicated openness to authorizing tokenized fund structures and digital security trading platforms under adapted versions of existing securities regulation.
新加坡的「Guardian計畫」已集結主要金融機構,進行代幣化應用案例的試點,並制定監管建議。新加坡金融管理局(MAS)也表示,願意根據調整後的現有證券規範,授權代幣化基金結構和數位證券交易平台。
Hong Kong similarly launched tokenization initiatives, with the Hong Kong Monetary Authority enabling banks to participate in tokenized deposit trials. The Securities and Futures Commission approved the first tokenized securities under existing securities law, demonstrating that tokenization can proceed within current regulatory frameworks if structured appropriately.
香港同樣啟動了多項代幣化措施,當中由香港金融管理局允許銀行參與「代幣化存款」試驗。證券及期貨事務監察委員會(SFC)則根據現有證券法,通過了首宗代幣化證券,證明在適當設計下,代幣化可於現行監管架構下推行。
This global regulatory activity creates both opportunities and constraints for platforms like XRPL. The opportunity is that regulatory clarity removes a major barrier to institutional adoption. When firms know what legal requirements apply to tokenized assets, they can confidently launch products. Uncertainty about whether regulators would permit tokenization at all has held back many pilots from becoming production systems.
這些全球性的監管動態,對於像XRPL這類平台而言,同時帶來機會與限制。機會在於監管明確可消除機構採用的一大障礙。當企業明確知道代幣化資產適用哪些法律要求時,就能有信心地推出產品。過去,多起試驗案因不確定主管機關是否允許代幣化,無法進展到實際商業化階段。
The constraint is that regulation demands specific technical capabilities. If regulations require issuer controls over token transfers, platforms without freeze or clawback capabilities become unsuitable. If regulations mandate redemption mechanisms, platforms must provide ways for issuers to burn tokens and return underlying value. If KYC requirements apply, platforms need identity systems or integration points for off-chain verification.
限制則在於監管要求具備特定技術能力。如果法規要求發行方能控制代幣轉移,缺乏凍結或追徵(clawback)能力的平台即不合適。如果規定必須有贖回機制,平台就得提供讓發行者註銷代幣並返還基礎價值的方式。若有KYC(身份驗證)要求,平台需具備身份系統或可串接鏈下驗證的接點。
MPT's design anticipated many of these regulatory requirements. The protocol-level freeze, clawback, authorization, and metadata capabilities directly address concerns that regulators have repeatedly raised in guidance documents. This alignment suggests that XRPL designers studied regulatory frameworks carefully when building MPT.
MPT的設計本身就預見並考慮多項監管需求。協定層級的凍結、追徵、授權、以及中繼資料等功能,直接回應了監管單位多次於指引文件中提出的疑慮。這種一致性,顯示XRPL設計團隊在打造MPT時,對監管架構做過謹慎研究。
Whether this regulatory-friendly design becomes an advantage depends on how comfortable institutions become with blockchain technology. If institutions remain cautious, a platform that clearly demonstrates regulatory compliance might gain adoption more quickly. If institutions embrace permissionless innovation, Ethereum's flexibility and established ecosystem might matter more than explicit compliance features.
這類利於監管的設計能否成為優勢,還取決於機構對區塊鏈技術的接受程度。如果機構仍然謹慎,能明確展現符合法規的平台可能更快獲得採納;若機構願意擁抱無需許可的創新,那以太坊的彈性和既有生態系,也許會比高度合規的特性更具吸引力。
The tension between innovation and compliance remains unresolved in blockchain design. Cryptocurrency advocates often view regulation as constraining freedom and undermining blockchain's value proposition. Institutional advocates counter that regulation enables larger-scale adoption by providing legal certainty and protecting investors from fraud.
「創新」與「合規」之間的矛盾,在區塊鏈設計上始終無法完全化解。加密貨幣倡議者通常認為監管限制了自由、削弱區塊鏈的核心價值;而機構支持者則主張,監管帶來法律明確性,避免詐欺,從而推動更大規模的應用。
MPT clearly targets the institutional perspective. Its feature set is designed for compliance, not for permissionless finance. This positioning will attract some users and repel others, depending on their priorities and beliefs about what blockchain technology should enable.
MPT明顯以機構需求為導向。其功能設定以合規為目標,而非追求無許可式金融。這樣的定位,會吸引某些用戶、排斥另一些用戶,取決於其對區塊鏈應具備哪些能力的期望與看法。
Final thoughts
結語
The MPT roadmap extends significantly beyond the initial October 2025 launch. Several major developments could expand the standard's capabilities and adoption over the next two years.
MPT的發展藍圖遠不只侷限於2025年10月首次發行。未來兩年內,還有多項重大發展可望進一步拓展這套標準的功能性與實際應用範疇。
Confidential MPTs scheduled for early 2026 represent the most significant technical enhancement. Using zero-knowledge proof technology, confidential MPTs would enable private transfers while maintaining compliance verification. Regulators or auditors with appropriate credentials could verify that transactions followed all rules and that parties were authorized, but the transaction details would remain hidden from public observation.
預計於2026年初推出的「機密型MPT」(Confidential MPTs),將是最具突破性的技術升級。運用零知識證明,機密型MPT可在維持合規驗證的同時,實現私密性轉帳。持有適當憑證的監管者或稽核人員,可以查證交易是否符合法規、雙方是否有授權,但交易詳細內容則對公眾隱藏。
This capability addresses a critical institutional need. Financial privacy is not just desirable but essential for many use cases. A corporation refinancing debt does not want competitors analyzing their capital structure through public blockchain records. An investment fund accumulating a position does not want to signal its strategy to the market through visible on-chain purchases.
這項能力回應了機構的重大需求。金融隱私不只是加分而是許多應用場景的必要條件。例如,一家公司進行債務再融資時,肯定不希望競爭對手可以透過公有區塊鏈資料來分析其資本結構;投資基金建倉時,也不樂見交易策略因鏈上可見而外洩。
Traditional finance provides privacy through opacity - transactions happen in private databases at centralized intermediaries. Blockchain's transparency provides accountability at the cost of privacy. Confidential transactions aim to restore privacy through cryptography rather than centralized control.
傳統金融藉由不透明(opacity)達到隱私保障──所有交易皆於集中機構內部資料庫進行。區塊鏈的透明性則是以隱私為代價換取問責性。機密型交易的目標,是透過密碼學而非中央控管,來回復隱私。
The implementation challenges are substantial. Zero-knowledge proof systems are computationally intensive. Generating proofs might add latency to transaction processing. The proof verification that validators must perform could impact network throughput. And the cryptographic assumptions underlying proof systems must remain secure - a breakthrough in cryptanalysis that breaks the proof system's security could compromise all confidential transactions.
但實現這項功能所面臨的技術挑戰相當巨大。零知識證明極為耗費運算資源,產生證明會讓交易處理延遲;驗證者需進行證明驗證,會影響網路吞吐量。而且支撐證明系統的密碼學假設必須維持安全,一旦密碼分析(cryptanalysis)有突破,導致證明系統失守,所有機密交易都可能被破解。
Despite these challenges, the technology is maturing. Multiple blockchain projects have deployed zero-knowledge proofs in production. Zcash pioneered private transactions. Ethereum developers are incorporating zkSNARKs into layer-two scaling solutions. The Monero network has processed billions of dollars in confidential transactions. The technology works; the question is optimizing it for institutional compliance requirements.
雖然挑戰不少,這項技術正逐步成熟。已有多個區塊鏈專案應用零知識證明於實際環境。Zcash率先落實私密交易;以太坊開發者也積極將zkSNARKs整合至第二層擴容方案。Monero網路已處理數十億美元的機密交易。這技術行得通,只是如何針對機構合規需求進一步最佳化,仍是課題。
Secondary Trading Infrastructure through the MPT DEX could unlock liquidity for tokenized securities. One of the biggest challenges in security token adoption has been the lack of secondary markets. If investors cannot sell their tokens after purchase, illiquidity makes tokenization unattractive compared to traditional securities.
針對代幣化證券,MPT的去中心化交易所(DEX)能夠提供「二級市場」基礎建設,為其流動性帶來突破。一直以來,證券型代幣推廣的最大困難,就是欠缺活絡的二級市場。如果投資人買進代幣後無法脫手,比起傳統證券,代幣化就會缺乏誘因。
Building compliant secondary trading infrastructure requires solving both technical and regulatory problems. Technically, the order book must enforce compliance checks on every trade. If a token requires authorization, both parties to a trade must be authorized. If a token is frozen, no trades can occur. If transfer fees apply, they must be calculated and burned correctly.
打造合規的二級交易基礎建設,必須同時攻克技術與監管挑戰。技術上,訂單簿系統要能對每一筆交易落實合規檢查。如果代幣需授權,雙方都必須獲得許可;代幣被凍結則不得交易;有轉讓手續費須即時計算並銷毀等。
Regulators in most jurisdictions require securities trading to occur on registered exchanges or through licensed broker-dealers. A fully decentralized order book where anyone can place trades would violate these requirements. The solution involves permissioned trading where only authorized market participants can access the order book for particular securities.
多數司法管轄區規定,證券交易必須在登記交易所或受許經紀商體系內進行。完全開放、去中心化的訂單簿,允許任何人掛單交易,這將違反這些規定。解決方案是採用有限度開放(permissioned)的交易模式,僅授權市場參與者可進入特定證券的訂單簿。
XRPL's native DEX provides a technical foundation, but extending it to support permissioned access per asset requires protocol changes. These changes are under development but not yet available. Once deployed, institutions could tokenize securities using MPT and immediately list them for trading on compliant infrastructure native to the protocol.
XRPL原生DEX雖提供技術基礎,但若要做到資產層級的權限定存取,則需修改協定。目前這些改動尚在開發階段,尚未上線。一旦落地,機構就可直接用MPT發行證券型代幣,並在具合規性的原生基礎架構上即時掛牌交易。
Integration with Traditional Financial Systems remains essential for institutional adoption. No matter how sophisticated blockchain technology becomes, financial institutions need bridges to existing payment systems, custody infrastructure, and reporting frameworks.
與「傳統金融體系」的接軌,始終是機構採用的關鍵。不論區塊鏈技術再怎麼先進,金融機構都需要與現有支付系統、託管架構、報表體系等順利串接。
RLUSD, Ripple's upcoming stablecoin, provides one such bridge. If RLUSD becomes widely available as an MPT-based stablecoin with full regulatory compliance, it creates a stable-value asset that can denominate securities, serve as collateral, and facilitate settlement entirely on XRPL. Institutions can move dollar-denominated value on-chain without exposure to cryptocurrency volatility.
Ripple即將推出的穩定幣RLUSD,就是其中一種橋接方案。若RLUSD以MPT型態,並具備完整合規性在市場普及,將成為一種穩定價值資產,可以用來標價證券、充當抵押品,或全程於XRPL上進行結算。機構得以將美元計價資產移上鏈,同時避開加密貨幣波動性的風險。
Custody integration matters for institutional comfort. Major custodians like Anchorage, BitGo, Fireblocks, and traditional banks offering digital asset custody need to support XRPL and MPTs. Without trusted custody solutions, institutions cannot safely hold tokenized assets on-chain. Ripple has announced partnerships with several custody providers, but broad ecosystem support takes time to develop.
託管機制的整合,對機構用戶安全感十分重要。主流數位資產託管商如Anchorage、BitGo、Fireblocks,以及傳統銀行的數位資產託管服務,都須支援XRPL與MPT。缺乏可信託管方案,機構難以安全持有鏈上的代幣化資產。Ripple雖已宣布與多家託管業者合作,但整個生態系的廣泛支援,仍需一段時間逐步建立。
Reporting and tax systems must understand tokenized assets. When an institution holds a tokenized bond represented as an MPT, their accounting systems need to record it correctly, calculate accrued interest, track cost basis for tax reporting, and integrate with portfolio management platforms. Building these integrations across the financial services ecosystem requires years of effort.
報表及稅務系統也必須能識別、處理代幣化資產。舉例來說,當機構持有MPT格式的代幣化債券時,其會計系統要能正確記錄、計算累計利息、追蹤稅務成本基礎,並與投資組合管理系統對接。這種全金融服務生態的整合,需要多年努力。
Standards Evolution and Potential for Cross-Platform Adoption presents a longer-term question. Could MPT become a standard that other blockchains adopt, similar to how ERC-20 spread beyond Ethereum to nearly every EVM-compatible chain?
「標準演化」及「跨平台採用的潛力」,也是長線觀察焦點。MPT有可能像ERC-20一樣,成為其他區塊鏈紛紛採用的標準嗎?ERC-20從以太坊擴展至幾乎所有EVM相容鏈。
The architectural differences make this challenging. MPT is tightly integrated with XRPL's consensus protocol and ledger structure. Other blockchains would need to implement similar protocol-level features rather than simply adopting a smart contract interface. This deeper integration makes cross-platform standardization harder to achieve.
受限於架構差異,此路不無挑戰。MPT深度整合於XRPL的共識協議和帳本結構,其他區塊鏈若欲採用,得實作協定層級的功能,而非僅新增智能合約介面。這種深度整合,也讓跨平台標準化變得相對困難。
A more likely outcome is convergence on common patterns rather than identical implementations. If MPT proves successful, other platforms might add protocol-level tokenization features with similar capabilities, even if the technical details differ. The broader pattern of embedding compliance controls at the protocol layer rather than in smart contracts could spread, even if the specific implementations remain platform-specific.
更可能的情境是,走向共同模式的收斂,而非完全一致的部署實現。如果MPT證明有成效,其他平台也可能在協議層增設類似能力的代幣化功能,儘管技術細節各異。合規控制內嵌於協議層、而非僅靠智能合約,這種廣泛趨勢有望延伸開來,即使每個平台仍採專屬實作。
International standards bodies could eventually weigh in. The International Organization for Standardization has working groups examining blockchain and distributed ledger technology standards. If institutional tokenization becomes widespread, ISO or similar bodies might develop standards
國際標準組織最終也可能介入。國際標準化組織(ISO)已設有工作小組,專門研究區塊鏈和分散式帳本的技術標準。若未來機構代幣化普及,則ISO或類似機構有可能制定相關標準。for tokenized securities that platforms could voluntarily adopt. Such standards would likely focus on functional requirements and interoperability rather than prescribing specific technical implementations.
對於平台可以自願採用的代幣化證券,這類標準很可能會著重於功能性需求和互通性,而非規定特定的技術實現方式。
Competition and Market Evolution will ultimately determine MPT's significance. If major financial institutions launch production tokenized securities using MPT over the next two years, it validates the protocol-level approach and establishes XRPL as a credible institutional platform. If institutions continue defaulting to Ethereum despite MPT's advantages, network effects and ecosystem inertia prove more powerful than technical merits.
競爭與市場演化最終將決定MPT的重要性。如果主要金融機構在未來兩年內以MPT發行量產級的代幣化證券,這將證明協議層級方案的可行性,並確立XRPL作為可信機構平台的地位。如果機構即使面對MPT的優勢,仍習慣預設選用Ethereum,那麼網絡效應和生態系統的慣性將比技術優點更具影響力。
The most likely scenario is diversification. Different institutions will choose different platforms based on their specific needs, risk tolerances, and technical capabilities. A cryptocurrency-native firm building decentralized finance applications will naturally choose Ethereum's programmability. A traditional bank piloting tokenization for the first time might prefer MPT's simplicity and explicit compliance features. Both approaches can succeed in their respective niches.
最可能的情境是多元化。不同的機構會根據自身需求、風險承受度與技術能力,選擇不同的平台。傾向原生加密貨幣生態的公司,打造去中心化金融應用時,自然會偏好Ethereum的可編程性;而剛開始嘗試資產代幣化的傳統銀行,則或許會青睞MPT的簡單設計及明確的合規功能。兩種路線都能在各自領域取得成功。
The tokenization market is large enough to support multiple platforms. Trillions of dollars in real-world assets could potentially be tokenized. Current on-chain tokenization represents perhaps one percent of this potential. As the market grows, multiple platforms can achieve scale without any single platform dominating entirely.
代幣化市場的規模,足以支撐多個平台並存。兆計美元的現實世界資產皆有機會被代幣化。目前鏈上代幣化規模甚至可能僅佔這一潛力的百分之一。隨著市場發展,多個平台都有機會擴張至規模化,而不會被單一平台完全壟斷。
The key question for XRPL is whether it can capture sufficient institutional mind-share to build self-sustaining network effects. If early MPT adopters achieve success, attract attention, and inspire imitators, momentum builds. If early projects struggle or fail to demonstrate clear advantages over alternatives, the opportunity window closes.
對XRPL而言,關鍵在於是否能取得足夠機構層面的認知,進而打造自我強化的網絡效應。如果MPT的早期使用者取得成功、成為業界話題並引發跟進者,則正面循環會逐步形成。若早期專案難以展現明顯優勢或進展不順利,機會窗口則會迅速關閉。
Redefining Tokenization Infrastructure
重新定義代幣化基礎設施
The Multi-Purpose Token standard represents a genuine architectural innovation in blockchain token design. By embedding compliance controls, transfer restrictions, and regulatory capabilities directly into the protocol layer, MPT challenges the prevailing assumption that tokenization must be implemented through smart contracts.
多用途代幣(MPT)標準在區塊鏈代幣設計上,是一項真正的架構創新。將合規控管、轉帳限制及監管功能直接納入協議層,MPT挑戰了當前「代幣化必須依賴智能合約實現」的普遍觀念。
For financial institutions exploring blockchain, MPT offers a compelling value proposition. The dramatically lower costs compared to Ethereum - both in issuance complexity and ongoing transaction fees - remove significant barriers to experimentation. The protocol-level implementation eliminates smart contract security risk and audit requirements that have historically consumed hundreds of thousands of dollars per issuance. The explicit compliance controls like authorization, freeze, and clawback provide clear mechanisms for meeting regulatory requirements.
對於正在探索區塊鏈的金融機構而言,MPT提供了極具吸引力的價值主張:相較Ethereum,其發行的複雜度與持續性交易費用都大幅降低,讓創新試驗不再高門檻。協議層級實現消除了智能合約的安全風險和審計成本——這些通常為每次發行增加數十萬美元的花費。授權、凍結、回收等明確的合規控管,則提供了直接因應監管要求的手段。
These advantages come with trade-offs. MPT sacrifices the flexibility that smart contracts provide. Institutions requiring complex logic, unusual security structures, or innovative financial products may find MPT's fixed feature set constraining. The architecture's simplicity is both its strength and its limitation.
這些優勢是有取捨的。MPT不如智能合約靈活。若機構需要複雜邏輯、特殊安全架構,或極具創新性的金融產品,便可能覺得MPT的固定功能組合受限。這種簡潔的架構既是優點,也是其侷限。
The broader significance lies in reopening debate about where complexity should live in blockchain systems. Ethereum demonstrated that general-purpose computation on blockchains is possible and powerful. Developers can implement nearly any logic they can imagine. But this power comes at costs - gas fees, security risk, integration complexity, and the learning curve of mastering smart contract development.
更廣泛的意義在於,再次喚起業界對於「區塊鏈複雜度應該落在哪一層」的討論。Ethereum證明了區塊鏈承載通用運算的可行與強大,開發者幾乎可以實現任何想像得到的邏輯——但這種彈性帶來高昂代價,包括:gas手續費、安全風險、整合難度,以及學習智能合約開發的門檻。
XRPL's approach suggests an alternative. Rather than providing unlimited flexibility, identify the most common institutional needs and implement them as optimized, standardized protocol features. This reduces flexibility but also reduces costs and complexity. Not every use case fits the standardized model, but many do.
XRPL則提供另一種思路——不是強調無限彈性,而是聚焦於最常見的機構需求,將其優化並標準化為協議層功能。這種設計減少了彈性,同時也降低了成本和複雜度。雖然並非所有情境都適用標準化模型,但許多需求已可被涵蓋。
If MPT succeeds in attracting institutional adoption, it validates protocol-level tokenization as a viable alternative to smart contracts. Other platforms might adopt similar approaches, adding native token capabilities rather than relying on contract-layer implementation. This could fragment the tokenization landscape further as platforms differentiate on which features they provide natively.
如果MPT成功吸引機構採用,便證實協議層級的代幣化,可作為智能合約以外的可行選擇。其他平台也可能仿效,將核心代幣功能納入協議層,而非僅靠智能合約實現。這將讓代幣化生態更加多元,平台間會依原生功能做出差異化。
If MPT struggles to gain traction despite its technical merits, it demonstrates that network effects and ecosystem momentum matter more than architectural elegance. Ethereum's first-mover advantage, massive developer community, and established infrastructure might prove insurmountable regardless of alternative platforms' theoretical benefits.
若MPT即使有技術優勢仍推廣不易,說明網絡效應與生態系動能,比架構設計的優雅更具決定性。Ethereum的先行優勢、龐大開發社群與成熟基礎設施,可能讓其它平台即使理論上優越仍難以超越。
The next eighteen to twenty-four months will determine MPT's trajectory. Institutional pilot projects launching in 2025 and 2026 will either validate the approach and attract more issuers, or fail to demonstrate clear advantages and fade into the long list of promising blockchain features that never achieved adoption.
接下來十八到二十四個月,將決定MPT的發展路徑。若2025至2026年推出的機構試點專案證實此方法有效,將吸引更多發行人加入;若未能展現優勢,則可能逐漸被邊緣化,成為眾多未能落地的區塊鏈創新之一。
For the blockchain industry broadly, MPT serves as a reminder that design choices matter. The decision to implement features at the protocol layer versus the application layer, to prioritize standardization versus flexibility, and to optimize for institutional compliance versus permissionless innovation shapes what is possible and who adopts the technology.
對整個區塊鏈產業而言,MPT再次提醒設計選擇的重要性。決定某功能該被實現在協議層或應用層、該優先考慮標準化或彈性,以及要優化機構合規還是無許可創新,這些抉擇會直接塑造技術的可能性與採用者。
Ultimately, tokenization represents too large an opportunity for any single platform to capture entirely. Traditional finance assets worth hundreds of trillions of dollars could potentially gain efficiency, transparency, and new capabilities through blockchain representation. Multiple approaches will likely coexist, each serving different segments of this enormous market.
終究,資產代幣化是一個巨大的機會,沒有單一平台可以完全壟斷。傳統金融資產總規模數百兆美元,若經區塊鏈表徵,將有機會提升效率、透明度及提供新功能。多種模式很可能共存,各自服務這個龐大市場的不同客層。
The Multi-Purpose Token standard carved out a specific niche: protocol-level, compliance-focused tokenization optimized for cost efficiency and simplicity. Whether that niche grows into a major platform or remains a specialized tool depends on execution, timing, institutional receptiveness, and perhaps luck. But the architectural vision MPT embodies - that blockchains can standardize compliance rather than leaving it to thousands of application developers - deserves attention regardless of the specific platform's ultimate success.
多用途代幣標準開闢出一個專屬領域:協議層、重視合規、並以成本效益與架構簡單化為優先考量的代幣化方案。這個利基最終會壯大為主流平台,還是維持為特殊工具,取決於執行力、時機、機構接受度,甚至運氣。但MPT所體現的架構藍圖——「合規可以標準化於區塊鏈協議層,而不是交由數千應用開發者各自實現」——不論最終平台成敗,都值得產業關注。
In the end, MPT answers a question the blockchain industry has debated for a decade: should specialized capabilities be protocol features or application-layer implementations? XRPL's answer is clear - put compliance in the protocol. Time will reveal whether institutions agree.
最終,MPT為區塊鏈產業十年來的一大爭議做了回答:某些專業功能應該是協議功能,還是應用層實現?XRPL的答案很明確——合規應納入協議層。但是否能獲得機構認同,仍待時間檢驗。





