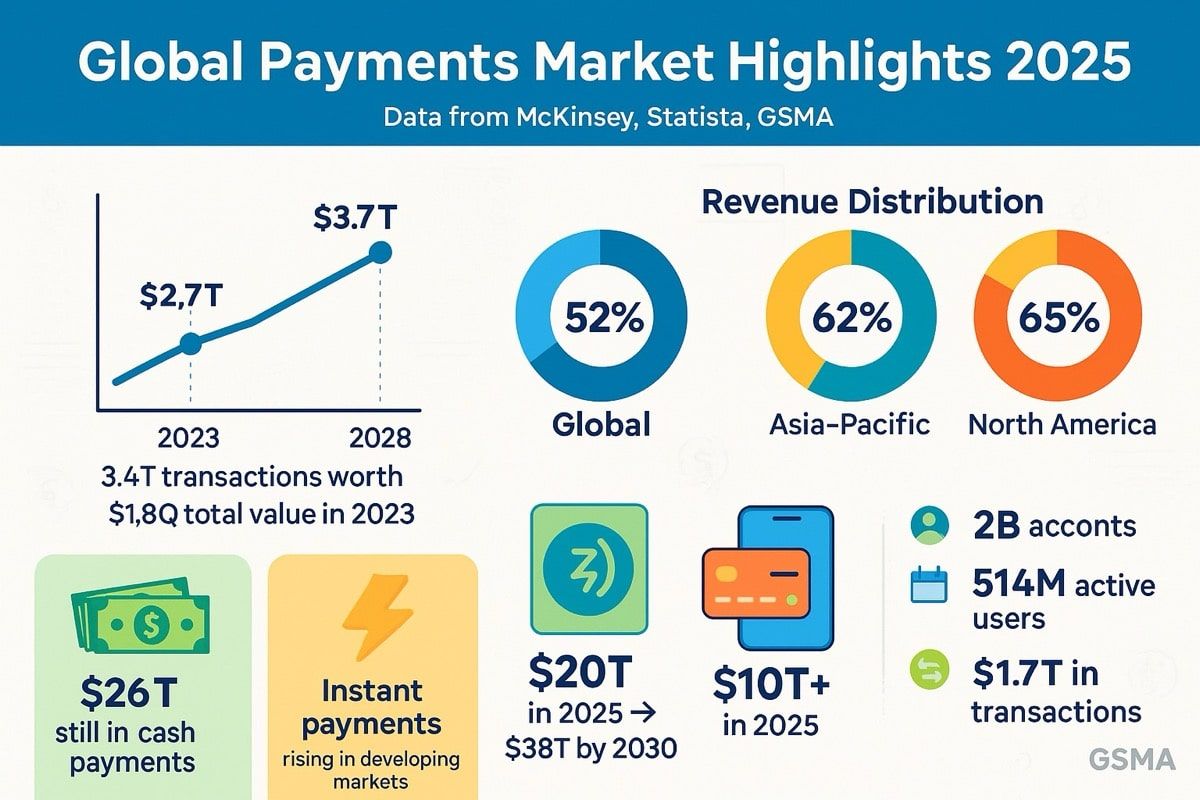
全球支付產業的規模龐大到難以想像。2023 年,該產業處理了約 3.4 兆筆交易,總價值達 1.8 千兆美元,產生 2.4 兆美元的收入。換言之,1.8 千兆美元等於 1,800 兆美元,約為美國經濟總量的 90 倍。
儘管規模如此龐大,現代支付基礎建設依然低效。資金常常需要數天閒置於預付帳戶。跨境轉帳慢速穿梭於代理銀行網絡。結算需橫跨時區,資金長時間滯留應收帳款。運作雖然順暢,但耗時又昂貴。
此時,去中心化金融(DeFi)展現了一場革命:金錢可以即時流通,數秒內結算,甚至能自動化執行複雜邏輯。穩定幣崛起為兩者的橋樑,交易量已在 2024 年超越 Visa 和 Mastercard,達到年化 15.6 兆美元,且持續增加。到 2025 年第一季,鏈上穩定幣交易量突破全球 8.9 兆美元。
PayFi(Payment Finance)應運而生——它是傳統支付與去中心化基礎建設的匯流層。不僅僅是加快交易速度、降低手續費,更重要的是釋放沉睡在支付流程中的資金時間價值、將結算由批次化轉化為持續流並把金融邏輯直接編程在資金流動過程中。
這一理念由 Solana 基金會總裁劉莉莉首次闡述,其核心原則在於:現有金錢的價值高於未來同額資金,因為可立即投入投資、獲取收益或作消費。PayFi 結合傳統支付網絡的分發與監管框架,以及區塊鏈基礎建設的透明、互通性和自動化,打造出資金即時、無國界、可組合且重視身份的匯流層。
這不再是紙上談兵。 到 2025 年中,穩定幣市值達 2,517 億美元,USDC 流通量創新高突破 560 億美元,2024 年 11 月 USDC 月交易量高達 1 兆美元。如 Visa 等傳統支付巨頭,已開始 與 Worldpay、Nuvei 等收單方於 Solana 進行 USDC 結算試點。黑石、富達等資產管理巨擘也投資於穩定幣基礎設施。香港於 2025 年 5 月通過穩定幣條例,美國則於 2025 年 7 月通過涵蓋穩定幣的 GENIUS 法案。
下文將深入探討 PayFi 如何重塑支付格局:背後支持基建、能啟用的應用場景、新興監理架構與潛存風險。這場匯流正在加速。對從事支付、金融或數位資產領域的人而言,掌握 PayFi 已成必要。
為何就在此時?金錢時間價值與支付基礎建設
PayFi 出現並非偶然,正反映傳統支付長年累積的低效率,與成熟區塊鏈基礎建設在規模上的結合。
低效率問題
傳統支付系統最大限制:採用批次處理,而非即時流。企業收到刷卡款時資金並非立刻入帳,而需經過 2-3 天的結算過程。跨國匯款則經過層層代理銀行才能結清,費時又不透明。員工獲薪,實際上要等到發薪日,儘管工資早已應計。
這些延遲造就經濟學上稱為「浮存金」——資金在途,無人受益。數十年來,金融機構靠浮存金獲益,將本屬客戶的資金未結算前的利息歸己。對客戶而言,浮存金即為被鎖住的價值:無法動用、無法投資、無法履約甚至把握機會。
全球支付產業每年 1.8 千兆美元的交易量產生約 2.4 兆美元收入,大部分來自這些低效率:交換費、匯差、電匯費和預付帳戶與結算延遲所造成的資本機會成本。
跨境支付正是問題縮影。世界銀行指出,2023 年全球匯款 200 美元的平均費用達 6.2%,遠高於聯合國永續發展目標 3%。全球約 1.5 億移工每次匯款,都承受高額手續費。服務卻依舊緩慢——跨境支付常需 3-5 天,期間匯率波動、資金亦無法動用。
即時支付軌道的落差
為改善低效率,許多國家已推出即時支付系統。印度的 UPI 每月處理數十億筆交易,巴西的 PIX 推動支付數位化,美國聯準會於 2023 年上線 FedNow 提供即時入帳,歐洲也已強制推行即時 SEPA 付款。
這些皆為重大進展,但也有侷限。多數系統僅限國內使用——例如 PIX 只能於巴西境內收付,無法匯往墨西哥或奈及利亞。多數並不具備程式化能力——能即時轉帳卻無法自動綁定業務邏輯或執行複雜工作流。有的營收模式遇到瓶頸:印度 UPI 處理海量交易卻免手續費,未來營收貢獻不足 10%。
更根本的是,即時支付軌道仍建立於傳統帳戶系統。資金在帳戶間加速流動,但本質未改變資金能「做什麼」——無法自動拆分收入給多方利益人,也無法託管資金待合約履約,更無法不預先備存各幣別就在瞬間完成多幣結算。
區塊鏈基礎建設的成熟
傳統支付陷於困境之際,2020-2025 年間,區塊鏈基礎建設大幅進化。早期鏈路處理量受限,如比特幣每秒僅能處理約 7 筆,以太幣約 15-30 筆。相比之下,Visa 每秒可達數千筆。
這一困境隨著新型架構及 Layer 2 技術出現而改變。Solana 只有 400 毫秒區塊生成時間且流動性充裕,非常適合 PayFi。Base、Arbitrum、Polygon 也提供低成本的穩定幣結算。專為跨境設計的 Stellar,則能低成本完成快速最終結算。
與此同時,穩定幣解決了區塊鏈的波動性問題。結算媒介若價值 10% 內大幅浮動,則支付軌道不成立。USDT(泰達幣)市值突破 1,500 億美元,而 USDC(Circle)到 2025 年中達 700~750 億美元。這些美元掛勾代幣不僅帶來價格穩定,也讓區塊鏈獲得可程式化、全年無休、即時結算與透明儲備優勢。
USDC 於 2024 年 11 月單月交易額高達 1 兆美元,而總交易金額已突破 18 兆美元。至 2025 年初,使用穩定幣交易的唯一位址突破 3,200 萬個,比 2022 年成長超過 200%。
資金時間價值的釋放
基礎建設成熟,終於讓過往不可能的事成為可能——支付過程中就能釋放資金時間價值。傳統系統結算緩慢不透明,無法在資金「在途」時發展借貸市場,因為你無法掌握何時資金才會到帳,也不知道資金... final value will be after fees and FX conversion.
最終價值將在扣除手續費與外匯轉換後產生。
PayFi changes this. When a business knows it will receive $10,000 in revenue tomorrow, it can tokenize that future receivable today, access liquidity against it immediately, and have the smart contract automatically settle the obligation when payment arrives. When a freelancer in the Philippines has $500 in completed work pending payment, they can receive advance liquidity, have it settle automatically when the client pays, and avoid waiting weeks for international wire transfers.
PayFi 改變了這一現況。當企業確認明天會收到 $10,000 的營收時,可以在今天就將該未來應收款項代幣化,即刻取得流動資金,並在款項到帳時由智能合約自動完成結算。當菲律賓的自由工作者有 $500 已完成但尚未收到的工作款項時,他們可以提前提領流動資金,並在客戶付款時自動完成結算,避免長達數週的國際電匯等待。
PayFi applies the time-value principle by enabling users to utilize tomorrow's money to pay for today, a feat traditional finance struggles to match. The difference between PayFi and traditional invoice factoring or supply-chain financing is infrastructure: blockchain settlement eliminates much of the overhead, smart contracts automate the workflows, and stablecoins provide the stable value reference.
PayFi 實踐了時間價值原則,讓用戶可以運用明天的資金解決今天的需求,這是傳統金融難以匹敵的優勢。PayFi 與傳統發票貼現或供應鏈金融的主要差異在於基礎設施:區塊鏈結算減少了大量管理成本,智能合約自動化了整個流程,穩定幣則提供穩定的價值基準。
The moment has arrived not because blockchain is new - it is more than a decade old - but because the infrastructure has finally matured to payments-grade requirements while traditional payment inefficiencies have become increasingly untenable in a globalized, digitally native economy.
這個時刻的到來,並不是因為區塊鏈是新技術(事實上已問世超過十年),而是因為相關基礎設施終於成熟到可滿足支付級別的需求,而傳統支付體系的低效率在全球化、數位原生的經濟形態下已愈發難以為繼。
Infrastructure: How PayFi Works
基礎設施:PayFi 的運作方式
PayFi's technical architecture represents a deliberate fusion of traditional financial infrastructure with blockchain settlement layers. Understanding how this works requires examining the component layers, the key players providing infrastructure, and the mechanisms that enable real-time, programmable settlement.
PayFi 的技術架構,是傳統金融基礎設施與區塊鏈結算層的有意整合。了解其原理,需要深入檢視其組成層級、主要基礎設施參與者,以及實現即時、可程式化結算的運作機制。
Architectural Layers
架構層級
The PayFi stack includes stablecoins and digital assets that serve as the medium of exchange, ensuring speed, security, and global interoperability, with protocols like the Bitcoin Lightning Network, Stellar, and Ethereum Layer-2 solutions enabling instant, low-cost transactions at scale.
PayFi 技術棧涵蓋作為交換媒介的穩定幣及數位資產,確保交易的速度、安全性與全球互通性。像是 Bitcoin 閃電網路、Stellar、以及以太坊 Layer-2 等協定,都支援大規模、即時且低成本的交易。
The architecture typically comprises four layers:
整體架構通常分為四個層級:
Settlement Layer: This is where value actually moves and final settlement occurs. It can be a Layer-1 blockchain like Ethereum, Solana, or Stellar, or a Layer-2 scaling solution like Base, Arbitrum, or Polygon. The settlement layer must provide fast finality (seconds to minutes), low transaction costs (fractions of a cent to a few dollars), and sufficient throughput (hundreds to thousands of transactions per second).
結算層:這裡是數值真正流通與最終結算的場域。可以是像以太坊、Solana 或 Stellar 這樣的 Layer-1 區塊鏈,也可以是 Base、Arbitrum、Polygon 等 Layer-2 擴容方案。結算層必須提供快速的最終性(數秒到數分鐘)、低交易成本(幾分之一美分到數美元),以及足夠的吞吐量(每秒數百到數千筆交易)。
Asset Layer: Stablecoins serve as the bridge between fiat currency and on-chain value. USDT (Tether) remains the largest stablecoin, surpassing $150 billion in market cap by mid-2025, while USDC ranks second at approximately $70-75 billion. These are not cryptocurrency speculations; they are dollar representations designed to maintain 1:1 parity with USD through reserve backing.
資產層:穩定幣作為法定貨幣與鏈上價值之間的橋樑。[USDT(Tether)依然是最大規模的穩定幣,到了 2025 年中市值超過 1,500 億美元,而 USDC 以約 700-750 億美元排第二位]。這些並非加密貨幣投機產品,而是經由儲備機制支持,設計為 1:1 錨定美元的代表。
Circle's USDC reserves consist of 98.9% held in short-dated U.S. Treasuries and cash equivalents. 這種結構同時保有流動性(Circle 保證 1:1 贖回),並從國債部位創造收益。USDC 已原生支援 28 條區塊鏈,包括以太坊、Solana、Base、Arbitrum、Stellar 與 Polygon 等,實現鏈間互通。
Bridging Layer: Traditional payment systems do not speak blockchain protocols natively. The bridging layer translates between worlds. This includes:
橋接層:傳統支付系統無法原生支援區塊鏈協議,橋接層的功能就是兩界溝通。包括:
-
On-ramps: Services that convert fiat to stablecoins (e.g., bank transfers to USDC)
-
法幣入口:將法幣轉換為穩定幣的服務(如銀行轉帳換 USDC)
-
Off-ramps: Services that convert stablecoins to fiat (e.g., USDC to local currency cash-out)
-
法幣出口:將穩定幣兌換回法幣的服務(如 USDC 換成本地現金)
-
Payment processors: Integrations with card networks, ACH, wire systems
-
支付處理商:與卡組織、ACH 或電匯系統對接
-
Compliance infrastructure: KYC/AML verification, transaction monitoring, sanctions screening
-
合規基礎設施:KYC/AML 驗證、交易監控、制裁篩選
Application Layer: This is where business logic lives. Smart contracts automate escrow, split payments, enforce conditional releases, route funds to multiple recipients based on pre-defined rules, and enable programmable financial products. Applications include payment widgets, treasury management dashboards, embedded finance APIs, and invoicing platforms with instant settlement.
應用層:業務邏輯所在之處。智能合約自動化代管、分帳、條件釋放、按規則多方撥款,甚至支援可程式化金融商品。應用層包括支付小工具、資金管理看板、嵌入式金融 API,以及能即時結算的發票平台。
Key Infrastructure Players
重要基礎設施參與者
Several organizations have emerged as critical infrastructure providers enabling PayFi:
多家機構已成為推動 PayFi 的關鍵基礎設施供應商:
Circle and USDC: Circle operates as both stablecoin issuer and infrastructure provider. Beyond minting USDC, Circle provides payment APIs, cross-chain transfer protocols (Circle's Cross-Chain Transfer Protocol enables seamless USDC movement between blockchains), and compliance infrastructure. Circle's stack, including the Circle Payments Network, targets institutional-grade reliability and compliance - key for mainstream payments.
Circle 與 USDC:Circle 既是穩定幣發行者,也是基礎設施供應商。除了鑄造 USDC 外,Circle 還提供支付 API、跨鏈轉帳協議(Circle Cross-Chain Transfer Protocol 可讓 USDC 在多條鏈中無縫流通),以及合規基礎設施。Circle 的技術棧(如 Circle Payments Network)瞄準機構級的可靠性與合規性——這對主流支付至關重要。
In 2025, Circle acquired Hashnote to expand into tokenized money markets, providing yield-generating opportunities for USDC holders. Circle also partnered with BlackRock (as primary asset manager for USDC cash reserves) and BNY Mellon (as primary custodian of backing assets), bringing traditional finance credibility to stablecoin infrastructure.
2025 年,Circle 收購 Hashnote,進軍代幣化貨幣市場,為 USDC 持有者創造收益機會。Circle 同時與 BlackRock(作為 USDC 現金準備金的主要資產管理人)以及 BNY Mellon(作為資產託管方)合作,為穩定幣基礎設施帶來主流金融的信任。
Solana Foundation: Solana has positioned itself as a high-performance PayFi network. With 400-millisecond block times, Solana provides the speed necessary for near-instant settlement. Visa expanded pilots to settle with USDC on Solana with acquirers like Worldpay and Nuvei, demonstrating that PayFi can mesh with existing merchant infrastructure.
Solana 基金會:Solana 身為高效能 PayFi 網路,在 400 毫秒區塊速度下,提供幾乎即時的結算體驗。Visa 推展以 USDC 在 Solana 上結算的試點計畫,合作夥伴包括 Worldpay、Nuvei 等收單方,展現 PayFi 能無縫連接現有的商務基礎設施。
The Solana ecosystem includes numerous PayFi-specific projects. These range from accounts receivable financing platforms to creator monetization tools to supply-chain settlement applications. Solana's focus on low transaction costs (typically fractions of a cent) makes it economically viable for small-value payments that would be prohibitive on higher-fee networks.
Solana 生態中有眾多 PayFi 專案,涵蓋應收帳款融資、創作者變現工具、供應鏈結算等。著重極低的交易成本(大多只有幾分之一美分),讓微額支付在這種平台上變得經濟實惠,而其他高手續費網路則難以實現。
Stellar Network: Stellar was designed from inception for cross-border payments. Stellar has tokenized over $400 billion in real-world assets and is the second-largest chain for asset tokenization. The network's architecture optimizes for fast finality and low cost rather than general-purpose computation.
Stellar 網路:Stellar 從設計之初即針對跨境支付打造。目前已將超過 4000 億美元的實體資產上鏈,是全球第二大資產代幣化區塊鏈。網路結構以快速最終性和低成本為優先,而非泛用型運算。
MoneyGram's partnership with the Stellar Development Foundation enables digital wallets connected to the Stellar network to access MoneyGram's global retail platform, providing a bridge between digital assets and local currencies for consumers. The partnership provides the ability to seamlessly convert USDC to cash, or cash to USDC, revolutionizing the settlement process with near-real-time settlement using Circle's USDC.
MoneyGram 與 Stellar 發展基金會的合作,使連結 Stellar 網路的數位錢包能夠直接存取 MoneyGram 全球零售據點,為消費者開啟數位資產與法幣之間的橋樑。這項合作能夠讓 USDC 與現金無縫兌換,運用 Circle 的 USDC 近乎即時地革新結算流程。
Stellar USDC has processed billions of dollars in payments, with over $4.2 billion in cumulative payment volume by mid-2023. The network sees particularly high activity in Latin America, Africa, and Southeast Asia - regions where cross-border payments are critical but expensive through traditional channels.
Stellar USDC 已處理數十億美元的支付,在 2023 年中累計支付額突破 42 億美元。該網路於拉丁美洲、非洲與東南亞特別活躍——這些地區跨境支付需求大、傳統管道成本卻極高。
Ethereum Layer-2 Networks: While Ethereum's main network can be expensive for payments, Layer-2 solutions like Base (Coinbase's network), Arbitrum, and Polygon provide Ethereum security with significantly lower costs. Base has one of the largest cumulative stablecoin transaction bases, reflecting growing adoption for payments applications.
以太坊 Layer-2 網路:雖然以太坊主網支付成本偏高,但 Base(Coinbase 推出的網路)、Arbitrum、Polygon 等 Layer-2 解決方案則以更低成本維持以太坊級的安全性。Base 是累積穩定幣交易量最高的鏈之一,反映其在支付應用領域的高度成長。
These networks benefit from Ethereum's established developer ecosystem, security model, and institutional comfort level. Many traditional financial institutions exploring blockchain payments begin with Ethereum-based infrastructure due to familiarity.
這些網路受惠於以太坊成熟的開發社群、安全框架,以及金融機構的認知門檻。許多傳統金融機構在探索區塊鏈支付時,普遍會優先採用以太坊底層架構。
Traditional Finance Integration Partners: PayFi cannot scale without bridges to traditional finance. Key players include:
傳統金融整合夥伴:PayFi 若無傳統金融橋樑將無法擴展,關鍵角色包括:
-
Visa and Mastercard: Both networks have launched stablecoin settlement initiatives. Visa's crypto advisory services help clients integrate USDC settlement. Mastercard has partnered with multiple stablecoin projects for card payments.
-
Visa 和 Mastercard:兩大卡組織都已啟動穩定幣結算計畫。Visa 的加密諮詢服務協助客戶整合 USDC 結算;Mastercard 則與多家穩定幣專案合作,推動卡片支付。
-
Banking Infrastructure: United Texas Bank serves as a settlement bank between Circle and MoneyGram, facilitating the bridge between traditional banking and blockchain rails. Other banks including Signature Bank (before its closure) and Silvergate provided crypto banking services.
-
銀行基礎設施:United Texas Bank 擔任 Circle 與 MoneyGram 的結算銀行,促進傳統銀行系統與區塊鏈基礎建設鏈接。其他如 Signature Bank(倒閉前)、Silvergate 等,也曾提供虛擬貨幣銀行服務。
-
Payment Processors: Companies like Stripe, Adyen, and PayPal have integrated stablecoin acceptance. PayPal operates its own stablecoin PYUSD. Stripe has explored USDC integration for merchant settlement.
-
支付處理商:Stripe、Adyen、PayPal 等公司都已支援穩定幣收款。PayPal 則自發行穩定幣 PYUSD。 Stripe 也持續評估 USDC 用於商戶結算的可能性。
Mechanics of PayFi Settlement
PayFi 結算機制運作
Understanding PayFi requires examining how value actually moves through the system. Consider a cross-border payment from a U.S. business to a supplier in the Philippines:
了解 PayFi 必須掌握價值如何實際在系統內流動。以美國企業支付給菲律賓供應商的跨境匯款為例:
Traditional Process:
- Business initiates wire transfer through bank ($25-50 fee, 3-5 days)
- Correspondent banks route payment through SWIFT network
- Foreign exchange conversion occurs (spread typically 2-4%)
- Receiving bank credits supplier account (local fees apply)
- Total time: 3-5 business days. Total cost: 5-8% including fees and FX spread.
傳統流程:
- 企業經由銀行發起電匯(需 $25-50 手續費,時程 3-5 天)
- 匯款經 SWIFT 網絡由中介銀行轉帳
- 進行外幣轉換(匯差約 2-4%)
- 收款銀行入帳(收取本地手續費)
- 總時間:3-5 個工作天。總成本:5-8%(含手續費與匯差)。
PayFi Process:
- Business converts USD to USDC via Circle Mint or exchange (near-instant)
- USDC transferred on-chain to supplier's wallet (seconds to minutes, cost <$0.01-1)
- Supplier either holds USDC or converts
PayFi 流程:
- 企業透過 Circle Mint 或交易所將美元轉為 USDC(幾乎即時)
- USDC 於鏈上轉帳至供應商錢包(數秒到數分鐘,費用小於 $0.01-1 美元)
- 供應商可以選擇持有 USDC 或兌換……to Philippine pesos via local off-ramp
轉換為菲律賓比索,透過在地出金通道 - Total time: Minutes to hours. Total cost: <1-2% depending on off-ramp.
總耗時:數分鐘至數小時。總成本:低於1-2%,取決於出金通路。
The difference is dramatic. But speed and cost are only part of the story. The more significant innovation is programmability.
差異極為明顯。但速度與成本只是部分原因,更關鍵的創新在於「可編程性」。
Programmable Payment Logic
可編程支付邏輯
Traditional payments can carry reference numbers or memos, but they cannot execute logic. PayFi payments can. A smart contract can:
傳統支付可以附帶參考號碼或備註,但無法執行邏輯。而PayFi支付可以。智慧合約能夠:
-
Split incoming payments automatically: When a creator receives $1,000 for content, the smart contract immediately splits it: 70% to creator, 20% to platform, 10% to collaborators.
-
自動分配入帳款項:當創作者因內容獲得1000美元時,智慧合約立即將其拆分:70%給創作者、20%給平台、10%給協作者。
-
Escrow with conditions: When a buyer pays for goods, funds lock in escrow. Smart contract releases payment when shipping confirmation arrives on-chain or after time-based conditions meet.
-
條件託管:當買方支付貨款時,資金會被鎖定在託管中。當鏈上出現運送確認或達到特定時間條件時,智慧合約即自動釋放付款。
-
Cascade routing: When a business receives payment, the smart contract automatically routes portions to various obligations: supplier payments, loan repayments, treasury reserves, tax withholding accounts.
-
層級分流:企業收到款項時,智慧合約會自動將部分資金分配至不同義務:供應商付款、貸款償還、庫存預備金、預扣稅帳戶。
-
Time-locked releases: Investors provide capital that unlocks gradually over time, with smart contracts releasing tranches automatically as milestones meet.
-
定時解鎖:投資人提供的資金會依據時間逐步解鎖,智慧合約於達成里程碑時自動分批釋放資金。
This programmability enables financial products that were previously impossible or too expensive to build. Invoice factoring traditionally requires extensive infrastructure: credit assessment, legal contracts, collections processes, reconciliation systems. With PayFi, much of this can be automated: smart contracts verify invoices on-chain, provide instant liquidity, and settle automatically when payment arrives.
這種可編程性讓過去難以實現或成本過高的金融產品成為可能。傳統的發票融資需大量基礎設施:信用評估、法律合約、催收流程、對帳系統。而在PayFi上,多數流程可自動化:智慧合約在鏈上驗證發票、即時提供流動性,且在款項到達時自動完成結算。
The infrastructure is complex, involving multiple layers and numerous players. But the user experience can be simple: click send, value arrives in seconds, programmable logic executes automatically. This combination - sophisticated infrastructure with simplified interfaces - is what makes PayFi viable at scale.
底層基礎建設雖然繁複,牽涉多層結構及眾多參與方,但使用體驗可極為簡單:一鍵發送,價值數秒內到帳,可編程邏輯自動執行。這種「複雜基礎、簡單介面」的結合,讓PayFi於大規模運用成為可行。
Use Cases Deep Dive
案例深入探討
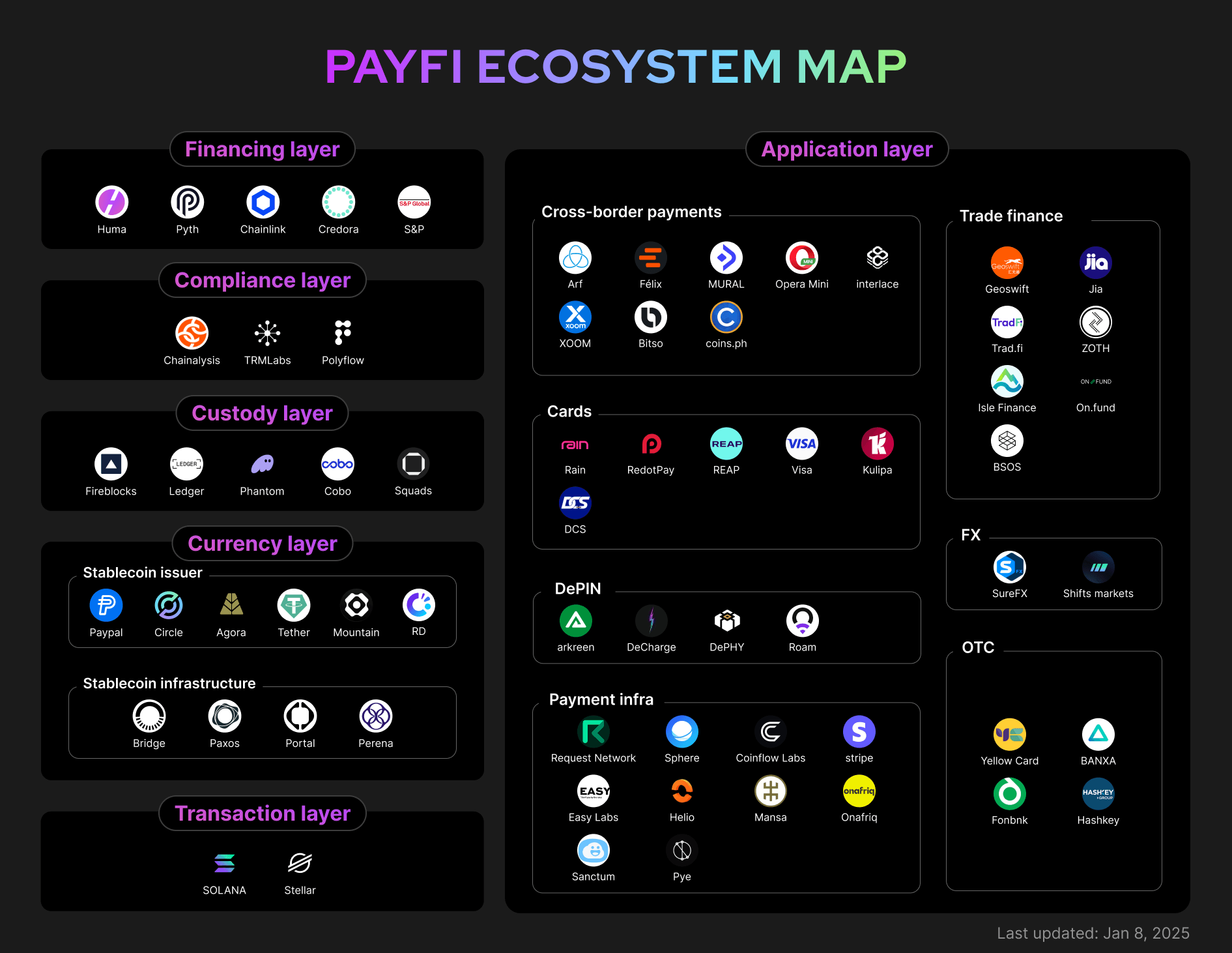
PayFi's real-world applications extend far beyond simple value transfer. The combination of instant settlement, programmable logic, and reduced costs enables entirely new financial products and business models. Several use cases are already moving from pilot projects to production deployment.
PayFi的實際應用遠超單純的價值轉移。即時結算、可編程邏輯與降低成本的結合,催生全新金融產品和商業模式。多個應用場景已自試點階段邁向正式部署。
Cross-Border Remittances
跨境匯款
Remittances represent one of PayFi's most immediate and impactful applications. Remittance flows to Southeast Asia are projected to reach nearly $100 billion in 2025, growing at more than 8% annually. For the families receiving these funds, traditional remittance costs are crushing: fees average 6.2% globally, and recipients wait days for money to arrive.
跨境匯款是PayFi最直接且具有影響力的應用之一。2025年流入東南亞的匯款預估將近1000億美元,年複合成長率超過8%。對於依賴這些款項的家庭而言,傳統匯款成本沈重:全球平均手續費高達6.2%,且收款也需等待數日。
PayFi offers a superior alternative. Consider the typical remittance corridor from the United States to the Philippines. Traditional services like Western Union or MoneyGram charge 5-8% in combined fees and FX spreads. PayFi alternatives can reduce this to 1-2%, with funds arriving in minutes rather than days.
PayFi提供了更卓越的選擇。以美國至菲律賓的常見匯款通路為例,傳統服務如西聯匯款或MoneyGram,綜合手續費及匯差高達5-8%。而PayFi等新型方案能將成本降至1-2%,且資金在數分鐘而非數日內到帳。
MoneyGram's partnership with Stellar provides the ability to seamlessly convert USDC to cash or cash to USDC, increasing the utility and liquidity of digital assets while enabling more consumers to participate in the digital economy. By connecting to the MoneyGram network, users can now withdraw USDC on Stellar and pick up cash at any participating MoneyGram location, creating a direct bridge between global digital dollars and local economies.
MoneyGram與Stellar合作,實現USDC與現金之間的無縫兌換,提升數位資產的實用性與流動性,讓更多消費者參與數位經濟。透過連結MoneyGram網絡,用戶可在Stellar上提領USDC,並於任何合作MoneyGram門市領取現金,直接搭起全球數位美元與在地經濟的橋樑。
The MoneyGram integration launched initially in key remittance markets including Canada, Kenya, Philippines, and the U.S., with global cash-out functionality available by June 2022. MoneyGram operates in 180+ countries, providing extensive reach for stablecoin on/off-ramps.
MoneyGram的整合起初於加拿大、肯亞、菲律賓及美國等主要匯款市場推出,2022年6月實現全球現金兌換服務。MoneyGram業務遍及180多國,提供穩定幣上下出入金的廣泛通路。
In September 2025, MoneyGram partnered with Crossmint to launch stablecoin-powered cross-border payments initially in Colombia. The Colombian peso has lost over 40% of its value in the past four years, making dollar-denominated savings critical. The service allows U.S. senders to transmit funds as USDC, which recipients hold in a smart wallet until they need to cash out in pesos, protecting value from currency devaluation.
2025年9月,MoneyGram與Crossmint合作,在哥倫比亞啟動以穩定幣驅動的跨境支付。近四年哥倫比亞披索貶值超過四成,使美元計價存款更顯重要。該服務讓美國發款人以USDC發送款項,收款人則可將其存放於智慧錢包,等到需要現金時再兌換為披索,有效對抗匯率貶值。
This model addresses multiple pain points simultaneously:
此模式同時解決多項痛點:
-
Speed: Near-instant settlement versus 3-5 days
-
速度:幾近即時結算,對比傳統3-5天
-
Cost: 1-2% fees versus 5-8%
-
成本:手續費1-2%,優於傳統5-8%
-
Currency protection: Recipients can hold USD-backed stablecoins rather than immediately converting to depreciating local currency
-
匯率保護:收款人可持有美元穩定幣,而非即刻兌換成本地貨幣承受貶值
-
Accessibility: MoneyGram's cash network provides last-mile access even for recipients without bank accounts
-
普及性:MoneyGram現金網路連偏鄉無銀行帳戶者都能兌領現金
The remittance use case demonstrates PayFi's potential scale: even capturing 10-20% of the approximately $700 billion global remittance market would represent $70-140 billion in annual volume.
此跨境匯款案例展現PayFi的龐大潛力:即便只吃下約$7,000億全球國際匯款市場的10-20%,年交易量亦達700-1400億美元。
Supply-Chain Finance and Invoice Factoring
供應鏈金融與應收帳款融資
Supply chains run on credit. Small manufacturers need to purchase raw materials before they receive payment for finished goods. Suppliers ship inventory to retailers who pay 30, 60, or 90 days later. This creates a working capital gap: businesses have completed work and incurred costs but cannot access revenue until payment arrives.
供應鏈仰賴信用運作。小型製造商須先購買原料、後獲成品款項。供應商出貨予零售商,卻需等對方30、60、甚至90天才收款。這導致營運資金缺口:企業已完工且付出成本,卻無法及時取得收入。
Traditional invoice factoring addresses this by having businesses sell receivables to specialized firms at a discount. The factor provides immediate cash (typically 70-90% of invoice value), then collects the full amount when it arrives. This works, but it is expensive (annual rates often exceed 15-30%) and slow (application, credit review, underwriting, documentation).
傳統的應收帳款貼現解決方式是企業以折價出售債權給專業融資公司,獲得即時現金(通常為發票面額的70-90%),日後由融資公司收回全額。雖然有效,但年化利率高達15-30%,流程繁瑣、動輒需經申請、信審、核保、文件處理,速度緩慢。
PayFi transforms this model. PayFi use cases include accounts receivable financing, where businesses can access capital by tokenizing future receivables and receiving instant liquidity when smart contracts automatically settle obligations upon payment arrival.
PayFi重塑了此流程。PayFi應用包含應收帳款融資:企業透過將未來債權代幣化,款項到帳時智慧合約自動結清義務,即可即時獲取流動資金。
Projects like Arf Financial and Huma Finance are deploying such systems. Arf demonstrates this with over $1.6 billion in default-free on-chain transactions, offering 24/7 USDC settlements without requiring pre-funded accounts. The key advantages:
如Arf Financial和Huma Finance等專案已投入建構此類系統。Arf以逾16億美元零違約鏈上交易為例,提供無需預先備資的24/7 USDC結算服務。其關鍵優勢:
-
Automation: Smart contracts verify invoices, assess creditworthiness using on-chain history, and provide instant liquidity
-
自動化:智慧合約自動驗證發票、依鏈上數據評等信用、即時撥資
-
Cost reduction: Overhead is dramatically lower when workflows are automated, enabling rates of 5-10% rather than 15-30%
-
成本降低:流程自動化大幅減少管銷費用,年利率僅需5-10%,遠低於傳統15-30%
-
Accessibility: Small businesses that traditional factors would ignore can access financing based on verified transaction history
-
普惠金融:傳統融資渠道不看重的小型業者,也可因交易紀錄透明而取得資金
-
Speed: Approval and funding occur in minutes rather than days or weeks
-
速度:放款與核可流程僅需數分鐘,而非傳統數天乃至數週
Consider a practical example: A small manufacturer in Vietnam produces goods for a U.S. retailer. The retailer's payment terms are Net 60. Traditionally, the manufacturer must either:
舉例來說:越南小型製造商為美國零售商生產商品,對方開出Net 60付款條件。傳統上,這家製造商只能:
-
Wait 60 days for payment (losing time-value, unable to take new orders)
-
等待60天收款(損失時間價值,無法接新訂單)
-
Factor the invoice at 20% annual rate through a traditional lender (expensive)
-
以20%年化利率交給傳統融資公司貼現(成本高)
-
Use working capital loans with strict covenants (restrictive)
-
申請附嚴苛條件的週轉貸款(限制多)
With PayFi, the manufacturer tokenizes the invoice as an NFT or on-chain asset representing the receivable. A liquidity pool or lender reviews the on-chain verified purchase order and the retailer's payment history. If approved, the manufacturer receives 90% of invoice value in USDC immediately. When the retailer pays 60 days later, the smart contract automatically settles the obligation, paying the lender principal plus interest. The effective rate might be 8-10% annualized - expensive relative to bank loans but far better than traditional factoring, with instant availability.
利用PayFi,製造商將發票以NFT或鏈上代幣化為債權資產。流動資金池或放款方檢視鏈上驗證過的訂單和零售商付款記錄,通過後馬上給予發票面額90%的USDC。60天後零售商付款入帳時,智慧合約自動清償本息給資金方。有效年利率約8-10%,比傳統銀行貸款高,但遠勝傳統應收帳款貼現,且資金即時到位。
PayFi could streamline capital access for SMEs by automating receivables financing and eliminating complex regulatory hurdles and lengthy risk assessments. The availability of faster funds helps businesses maintain safety cushions and expand growth opportunities without the constraints of delayed payments.
PayFi藉由自動化帳款融資、消除繁瑣監管與冗長信審,為中小企業大幅簡化資金取得流程。資金速度提升,有助企業維持安全緩衝並抓住成長機會,不受逾期付款的限制。
Real-Time Wage Access
即時薪資提領
The traditional payroll model is fundamentally mismatched with how people work and live. Employees earn wages daily but receive payment biweekly or monthly. This creates financial stress: bills arrive continuously, but income arrives in lumps. Workers facing emergencies often resort to expensive payday loans or credit card advances because they cannot access money they have already earned.
傳統薪資支付制度與現今工作生活型態脫節。員工每天工作賺進薪水,卻需等到每月或每兩周才領一次薪,造成財務壓力:帳單陸續到期,收入卻是零散結算。遇到緊急狀況,員工往往只能高息借薪日貸或刷預借現金,僅因無法即時支用已賺到的薪水。
PayFi enables "earned wage access" - the ability for workers to receive payment for work as soon as it is completed. Real-time wages through PayFi allow content creators to finance their video production by receiving funds beforehand, which they can return automatically based on streaming revenue, enabling creators to continuously deliver content without waiting.
PayFi讓「即時提領工資」成為可能—員工完成工作即可立刻領薪。對內容創作者而言,PayFi的即時薪資機制使他們能先取得前置資金製作影片,並依後續串流收入自動歸還,進而讓創作持續不中斷。
The mechanics are straightforward: An employer maintains a treasury of USDC. As employees complete work (verified by time-tracking systems, milestone completion, or other metrics), smart contracts automatically stream payment to their wallets. Workers receive value continuously rather than in batches.
運作邏輯非常簡單:雇主預存USDC於公司金庫。員工完成工作內容(由工時記錄、里程碑或其它指標驗證),智慧合約便自動將報酬串流進其錢包,員工能隨時領取,不需等到月底批次撥款。
This has several benefits:
此舉帶來多重效益:
-
Financial stability: Workers can access earned wages when needed, reducing reliance on predatory lending
-
財務穩定:員工可隨時提領已賺薪資,減少被高利借貸剝削
-
Employer benefits: Companies can attract workers by offering better payment terms
-
僱主優勢:公司能以即時薪資吸引人才,提升競爭力
-
Reduced overhead: Payroll processing occurs automatically via smart contracts rather than manual batch processes
-
降低成本:薪資流程由智慧合約自動化處理,免去人工作業
-
Global accessibility: Works seamlessly for remote workers in any country with internet access
-
全球適用:任何國家、只要連網即可串流即時薪資給遠距員工Companies like Zebec and Sablier have built streaming payment protocols on Solana and Ethereum. These allow continuous value transfer - literally every second, a fraction of payment flows from employer to employee based on elapsed time and agreed rate. The employee's wallet balance increases in real-time, and they can withdraw at any moment.
像 Zebec 和 Sablier 這類公司已在 Solana 和 Ethereum 上建立串流支付協議。這些協議可實現持續的價值轉移——字面上來說,每一秒鐘都有一小部分款項,按照經過的時間與約定的費率,從雇主流向員工。員工的錢包餘額會即時增加,並可隨時提領。
For the gig economy, this is transformative. A freelance designer completes a project for a client in another country. Instead of waiting for the client to process payment, approve it through accounting, initiate an international wire, and wait for settlement - a process that might take two weeks - the designer receives payment continuously as they work, with final settlement within minutes of completion.
對零工經濟來說,這是顛覆性的變革。舉例來說,一位自由設計師為另一個國家的客戶完成專案。他無須等候客戶處理付款、會計審核、發起國際匯款並等待結算——這個過程可能需要兩週——設計師現在可以在工作時即時持續收款,並在專案完成後幾分鐘內完成最終結算。
Merchant Settlement and Interchange Bypass
Credit card acceptance costs merchants 2-3.5% in interchange fees plus processing costs. For a restaurant operating on 5-10% profit margins, card fees represent a significant expense. Yet cards are essential - consumers demand payment flexibility.
信用卡收單讓店家需負擔2-3.5%的交換手續費,加上額外的處理費。對於一家營運利潤僅有5-10%的餐廳來說,這筆費用十分可觀。但信用卡支付又不可或缺,因為消費者要求付款彈性。
PayFi offers merchants an alternative: stablecoin acceptance with instant settlement and fees below 1%. Consider the comparison:
PayFi 為商家提供一種選擇:接受穩定幣支付,瞬間結算,且手續費低於1%。讓我們來比較一下:
Credit Card Payment:
- Customer pays $100
- Interchange and processing fees: $2.50-3.50
- Merchant receives: $96.50-97.50
- Settlement: 2-3 days
- Chargeback risk: 6-12 months
信用卡支付:
- 顧客支付 $100
- 交換及處理費用:$2.50-3.50
- 商家實收:$96.50-97.50
- 結算時間:2-3 天
- 退款爭議風險:6-12 個月
Stablecoin Payment:
- Customer pays equivalent of $100 in USDC
- Processing fees: $0.50-1.00
- Merchant receives: $99.00-99.50
- Settlement: Instant (on-chain finality in seconds)
- Chargeback risk: None (blockchain transactions are final)
穩定幣支付:
- 顧客以等值 $100 的 USDC 支付
- 處理費用:$0.50-1.00
- 商家實收:$99.00-99.50
- 結算時間:即時(鏈上數秒內完成)
- 退款爭議風險:無(區塊鏈交易不可逆)
The merchant benefits are compelling:
- Lower costs: 0.5-1% versus 2.5-3.5%
- Instant liquidity: Funds available immediately rather than 2-3 days later
- No chargebacks: Eliminates fraud risk from disputed transactions
- Working capital improvement: Instant settlement means better cash flow management
商家能享有明顯優勢:
- 更低成本:0.5-1% 對比 2.5-3.5%
- 即時資金:資金立即入帳,不需等待 2-3 天
- 無退款爭議:消除爭議交易帶來的詐騙風險
- 提升週轉金:即時結算有利現金流管理
The challenge is customer adoption. Most consumers do not yet hold stablecoins or use crypto wallets. However, this is changing. Digital wallets accounted for 49% of global e-commerce transaction value in 2023, expected to increase to 54% by 2026. As stablecoin-enabled wallets proliferate, merchant acceptance will follow.
挑戰在於顧客普及率。目前多數消費者尚未持有穩定幣,也尚未習慣使用加密錢包。不過這一狀況正在轉變。2023 年,數位錢包佔全球電子商務交易金額 49%,預計到 2026 年將增至 54%。隨穩定幣錢包普及,商家接受度也將提升。
Some implementations blend approaches: customers pay with familiar methods (cards, bank transfers), but backend settlement occurs via stablecoins. This allows card acceptance at the edge while using USDC in the core - consumers pay with familiar methods while acquirers and issuers settle in USDC for speed and cost reduction.
有些實作採混合模式:客戶用熟悉的方式(信用卡、銀行轉帳)付款,但後端結算則透過穩定幣進行。這讓商家能提供熟悉的收款介面,且採用 USDC 結算以降低成本並加快結算速度——顧客用熟悉的支付方式,收單機構與發卡機構則用 USDC 於核心後台結算。
Emerging Use Cases
Beyond these established categories, PayFi enables novel applications:
在既有應用之外,PayFi 還促成全新場景:
Programmable Subscriptions: Services can charge dynamically based on usage, with smart contracts automatically calculating costs and withdrawing appropriate amounts. This enables usage-based pricing models that were previously too complex to implement.
可編程訂閱:服務可根據用量動態收費,智慧合約自動計算金額及扣款。過往過於複雜的用量式計價,如今可輕鬆實現。
Conditional Payments: Escrow services built into payment flows - funds release automatically when shipping confirmation arrives, when milestone verification occurs, or when multi-party approval completes.
條件式付款:將第三方託管服務植入支付流程,款項於運送確認、里程碑驗證、多方審核完成時自動釋出。
Yield-Generating Payments: Recipients can automatically route incoming payments into yield-generating protocols, earning returns on balances that would otherwise sit idle.
收益產生型支付:收款人能自動將入帳資金導入各類生息協議,讓原本閒置的餘額也能持續產生收益。
Cross-Border Payroll: Companies with global remote teams can pay workers in any country instantly, in stablecoins that can be converted to local currency or held as dollar savings.
跨國薪資發放:擁有全球遠端團隊的公司,可即時、無國界向員工發放薪酬,使用穩定幣支付;員工可選擇兌換本地貨幣或作為美元儲值。
The use cases share common attributes: they eliminate intermediaries, reduce friction, lower costs, improve speed, and enable programmability. These are not incremental improvements. They represent fundamental shifts in how payments function and what they can accomplish.
這些用例有共同特點:消除中間人、降低摩擦、減少成本、提升速度並實現高度可編程性。這些不只是漸進式的提升,而是徹底改變了支付方式和支付能實現的目標。
Asia's PayFi Push: Regional Dynamics and Innovation
亞洲 PayFi 崛起:區域動態與創新
Asia has emerged as a particularly dynamic region for PayFi adoption, driven by several converging factors: rapidly digitizing payments infrastructure, significant cross-border remittance flows, underbanked populations, currency volatility concerns, and progressive regulatory approaches in key markets.
亞洲已成為 PayFi 發展最具活力的區域之一,受多項因素推動:支付基礎建設快速數位化、大量跨境匯款、仍有大量未充分服務的用戶、貨幣波動憂慮,以及部分主要市場的開明監管政策。
The Asian Payments Landscape
Asia's payments evolution has followed a distinct trajectory from Western markets. While the United States and Europe built extensive credit card infrastructure over decades, many Asian markets leapfrogged directly to mobile and digital payments.
亞洲的支付發展與西方國家截然不同。美國和歐洲數十年來興建龐大信用卡基礎設施,亞洲多個市場則直接跳躍至行動支付與數位支付。
India's Unified Payments Interface (UPI) processes billions of transactions monthly, enabling instant peer-to-peer payments via QR codes and phone numbers. In India, while cash payments still account for 60% of consumer expenditure, digital payments have doubled in the past three years. Yet UPI faces a challenge: it operates domestically only and charges no transaction fees, making international expansion and monetization difficult.
印度的統一支付介面(UPI)每月處理數十億筆交易,使用 QR code 與手機號碼進行即時點對點轉帳。在印度,雖然現金支付仍占消費支出六成,但過去三年數位支付量已翻倍成長。但 UPI 有一缺點:只限國內使用且不收手續費,這使得國際擴展與營運獲利變得困難。
Southeast Asia presents a different dynamic. Remittance flows to the region are projected to reach nearly $100 billion in 2025, with countries like the Philippines receiving over $30 billion annually. Millions of workers labor abroad and send money home to families. Traditional remittance channels charge heavily for this service.
東南亞呈現另一種情勢。預計到 2025 年,該區匯入匯款金額將接近 1,000 億美元,單是菲律賓每年就接收超過 300 億美元。數以百萬計的勞工在海外工作並匯款回家。傳統匯款服務的手續費十分高昂。
China's digital payments ecosystem, dominated by Alipay and WeChat Pay, demonstrates the potential scale of mobile-first payments. However, these are closed systems operating within strict capital controls. Cross-border functionality is limited, creating opportunities for alternative solutions.
中國的數位支付生態由支付寶與微信支付主導,展現了行動優先支付的龐大規模。不過,這些屬於封閉系統,受到嚴格資本管制,跨境功能有限,也為替代解決方案創造了契機。
MoneyGram-Stellar Corridor: A Case Study
The partnership between MoneyGram and Stellar provides insight into how PayFi infrastructure is being deployed in practice across Asia.
MoneyGram 與 Stellar 的合作解釋了 PayFi 基礎建設如何在亞洲實際落地。
Announced in October 2021, the partnership enables digital wallets connected to the Stellar network to access MoneyGram's global retail platform, providing a bridge between digital assets and local currencies for consumers. The implementation focuses on key remittance corridors including the United States to the Philippines, the U.S. to Kenya, and flows within Southeast Asia.
這項於 2021 年 10 月宣布的合作,使連結至 Stellar 網路的數位錢包可以存取 MoneyGram 的全球零售據點,為消費者提供數位資產與本地貨幣的橋樑。該計畫聚焦於主要匯款走廊,包括美國到菲律賓、美國到肯亞,以及東南亞內部資金流。
The service launched with initial availability in Canada, Kenya, Philippines, and the U.S., with global cash-out functionality available by June 2022. Users of Stellar-connected wallets like Vibrant and LOBSTR can now convert USDC to cash at MoneyGram's thousands of retail locations, or convert cash to USDC for sending abroad.
該服務首先於加拿大、肯亞、菲律賓及美國上線,並於 2022 年 6 月擴展至全球現金提領服務。像 Vibrant 和 LOBSTR 等 Stellar 錢包的用戶,現在可在 MoneyGram 數千家零售店 將 USDC 兌換成現金,或攜帶現金兌換成 USDC 匯款到海外。
The mechanics illustrate PayFi principles in action:
這一流程體現 PayFi 原則的實務運用:
-
Cash-to-Crypto On-Ramp: A sender visits a MoneyGram location in the U.S., provides cash, and receives USDC in their Stellar wallet
-
On-Chain Transfer: The sender transmits USDC on Stellar to a recipient in the Philippines (settlement in 3-5 seconds, cost less than $0.01)
-
Crypto-to-Cash Off-Ramp: The recipient converts USDC to Philippine pesos at a local MoneyGram location or through integrated mobile money services
-
現金轉加密貨幣入金:匯款人前往美國的 MoneyGram 門市,交付現金,並在 Stellar 錢包取得等值 USDC
-
鏈上轉帳:於 Stellar 網路將 USDC 傳送至菲律賓收款人(3-5 秒內結算,手續費不到 $0.01)
-
加密貨幣轉現金出金:收款人在當地 MoneyGram 門市或行動支付服務將 USDC 兌換為菲律賓披索
The partnership revolutionizes the settlement process, with settlement occurring in near-real-time using Circle's USDC, enabling accelerated collection of funds, improving efficiency, and reducing risk.
這項合作徹底革新了結算流程,利用 Circle 發行的 USDC,幾乎即時完成結算,不僅加速資金回收,也提升效率並降低風險。
In late 2025, Hana wallet integrated with MoneyGram Ramps across Southeast Asia, expanding access further. The integration provides instant stablecoin-to-cash withdrawals, making stablecoins usable in daily life for freelancers, families, and small businesses.
2025 年底,Hana 錢包整合了 MoneyGram Ramps,服務遍及東南亞,進一步擴大服務範圍。這意味著穩定幣可以即時兌換成現金,讓自由工作者、家庭、小型企業在日常生活即可使用穩定幣。
The impact extends beyond individual transactions. By providing instant, low-cost remittance rails, the infrastructure addresses financial inclusion. Many recipients lack bank accounts but can access MoneyGram locations. They can now receive digital dollars, hold them as a store of value (protecting against local currency depreciation), and cash out only when needed.
這不僅止於單一交易。即時低成本的匯款管道推動了金融普惠。許多收款人沒有銀行帳戶,但可前往 MoneyGram 門市領款。現在他們能收數位美元,作為保值資產(對抗本地貨幣貶值),只在需要時兌現。
Regulatory Environment and Innovation
Asia presents a varied regulatory landscape. Some jurisdictions have embraced innovation, while others maintain restrictive approaches.
亞洲的監管格局多元。有些司法轄區大膽擁抱創新,另一些則持保守限制態度。
Singapore has positioned itself as a digital asset hub. The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) provides clear licensing frameworks for payment services, stablecoin issuers, and digital asset exchanges. Major crypto firms including Coinbase, Gemini, and Crypto.com have established regulated entities in Singapore.
新加坡 定位為數位資產中心。新加坡金融管理局(MAS)對支付服務、穩定幣發行商、數位資產交易所均設有明確牌照架構。Coinbase、Gemini、Crypto.com 等大型加密公司均已在新加坡設立合規實體。
Hong Kong passed its Stablecoin Ordinance in May 2025, requiring all issuers of Hong Kong dollar-backed stablecoins to obtain licenses from the Hong Kong Monetary Authority. Stablecoins must be backed by high-quality, liquid reserve assets, with the market value of reserves equal to the par value of stablecoins in circulation. This provides regulatory clarity while enabling innovation.
香港 於 2025 年 5 月通過穩定幣條例,所有港元穩定幣發行商需向香港金融管理局申領牌照。穩定幣須以高品質、高流動性的儲備資產 100% 支撐,儲備市值需等同於流通穩定幣的票面價值。這為創新提供明確監管框架。
Japan has maintained a cautious but progressive stance. The country recognizes cryptocurrency as property and regulates exchanges stringently. Stablecoin regulations were implemented in 2023, allowing licensed entities to issue yen-backed digital currencies. Asia's Liquid exchange in Japan and Singapore was the first major exchange to enable USDC withdrawals on Stellar, demonstrating institutional adoption.
日本 採取審慎但漸進路線,視加密貨幣為「財產」,對交易所實行嚴格監管。2023 年開始施行穩定幣專法,開放持牌機構發行日圓穩定幣。亞洲 Liquid 交易所在日本、新加坡成為首間主流交易所,支持於 Stellar 上提領 USDC,展現機構落地應用。
India presents complexity. While UPI has driven domestic payment digitization, cryptocurrency regulations remain uncertain. The government has proposed crypto taxes and regulatory
印度 則情況較為複雜。雖然 UPI 推動國內支付數位化,但加密貨幣監管仍不明確。政府提出了加密稅及...frameworks but has not banned usage. This creates opportunity - India's large diaspora sends substantial remittances home, creating demand for low-cost alternatives.
框架尚未禁止使用。這創造了機會——印度龐大的海外僑民每年向國內匯款巨額資金,對低成本替代方案產生需求。
The Philippines is particularly receptive. The Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas has licensed several cryptocurrency exchanges and remittance platforms. Given the country's dependence on overseas worker remittances (exceeding $30 billion annually), there is strong motivation to facilitate lower-cost channels.
菲律賓尤為開放。菲律賓中央銀行已核發數家加密貨幣交易所及匯款平台牌照。考慮到該國嚴重依賴海外勞工匯款(每年超過三百億美元),推動更低成本的匯款管道動力強烈。
Local Innovations and Adaptations
在地創新與調適
Asian PayFi implementations often reflect local conditions and needs:
亞洲的 PayFi 解決方案往往依照在地條件和需求做出調整:
Mobile-First Design: Given high smartphone penetration and limited desktop usage, Asian PayFi solutions prioritize mobile interfaces. Wallets like Hana, designed specifically for Southeast Asian users, emphasize simplicity and local currency support.
以行動裝置為優先的設計:由於智慧型手機普及、桌上型電腦使用率低,亞洲 PayFi 解決方案以行動介面為主。例如像 Hana 這類錢包,尤其為東南亞用戶設計,強調操作簡便及支援在地貨幣。
Cash-Bridge Integration: Recognizing that cash remains dominant in many markets, successful implementations integrate with cash networks. The MoneyGram partnership exemplifies this - enabling cash-in and cash-out maintains accessibility for populations without bank accounts.
現金橋接整合:鑑於現金在許多市場仍主導地位,成功的方案會整合現金網絡。以和 MoneyGram 的合作為例——現金存取功能,讓沒有銀行帳戶的人也能輕鬆使用。
Local Currency Stability: Many Asian currencies experience volatility relative to the dollar. This creates natural demand for dollar-denominated stablecoins as savings vehicles. In Colombia, where the peso has lost over 40% of its value in four years, similar dynamics exist - this pattern appears across numerous emerging markets globally, including many in Asia.
當地貨幣穩定性:許多亞洲貨幣對美元波動大,因此對美元計價穩定幣產生天然儲蓄需求。在哥倫比亞,披索四年內貶值超過40%,這樣的情況在亞洲及全球新興市場屢見不鮮。
Merchant Adoption: Asian merchants, particularly in tourism-dependent areas, increasingly accept stablecoins. This reflects both customer demand (tourists avoiding currency conversion fees) and merchant benefits (lower costs, instant settlement).
商家採用:亞洲商家,尤其是觀光產業,日益接受穩定幣付款。這不僅滿足顧客(旅客避免換匯手續費),也讓商家享受到(降低成本及即時結算)的好處。
Cross-Border Corridors
跨境通道
Asia's PayFi growth centers on specific corridors where need and infrastructure align:
亞洲 PayFi 增長聚焦於需求和基礎建設兼具的特定通道:
Middle East to South Asia: Labor flows from Pakistan, India, Bangladesh, and the Philippines to Gulf states create massive remittance volumes. Cross-border B2B settlements using Tether surged in the Middle East and Southeast Asia, with $30+ billion settled in Q1 2025 alone. PayFi solutions targeting these corridors can capture significant market share from traditional services.
中東至南亞通道:來自巴基斯坦、印度、孟加拉與菲律賓勞工前往海灣國家,產生大量匯款需求。單在2025年第一季,中東與東南亞地區,泰達幣跨境B2B結算突破了300億美元。針對這些通道的 PayFi 方案有機會搶下傳統服務者的龐大市占。
Intra-ASEAN Flows: Trade and labor mobility within the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam) generates substantial payment flows. PayFi can enable near-instant settlement for cross-border trade that currently requires days and significant banking fees.
東協區內通道:東南亞國協(包含汶萊、柬埔寨、印尼、寮國、馬來西亞、緬甸、菲律賓、新加坡、泰國、越南)國家間的貿易及勞動流動產生大量支付。PayFi 有望讓原本需數天且收取高額銀行費用的跨境交易,實現近乎即時結算。
China Outbound: While domestic Chinese payment rails are advanced, moving value out of China faces capital controls and regulatory constraints. Stablecoins provide an alternative channel, though regulatory risk remains significant.
中國出境通道:中國國內支付十分先進,但資金要流出中國受到資本管制和法規限制。穩定幣成為一種替代管道,但監管風險仍高。
The Path Forward
未來發展方向
Asia's PayFi trajectory suggests several developments:
亞洲 PayFi 發展趨勢顯示數個走向:
Increasing Corridor Connectivity: As more countries establish clear regulatory frameworks, additional corridors will open. Each new jurisdiction that licenses stablecoin operations enables connections to the global network.
通道連結更加緊密:隨著更多國家建立明確監管制度,新的跨境通道將不斷開啟。每個新允許穩定幣業務的法域,都是全球網絡的一個新連接點。
Integration with Regional Payment Systems: Future iterations may bridge PayFi rails with systems like UPI, PIX (Brazil), and SEPA (Europe), enabling seamless value flow between instant payment systems regardless of underlying infrastructure.
與區域支付系統整合:未來可能會與UPI、PIX(巴西)、SEPA(歐洲)等系統串接,實現各種即時支付系統間資金無縫流通。
Central Bank Digital Currency Interaction: As Asian central banks pilot CBDCs (China's digital yuan, Singapore's Project Orchid), questions arise about how stablecoins and CBDCs will interact. Likely outcome: coexistence, with stablecoins serving international flows and CBDCs serving domestic use.
央行數位貨幣互動:亞洲各國央行逐步試行CBDC(如中國數位人民幣、新加坡Project Orchid),穩定幣和CBDC之間的互補關係值得關注。可能的方向是兩者共存,穩定幣主攻國際流通,CBDC 用於國內支付。
Mobile Money Convergence: Mobile money services like GCash (Philippines) and M-Pesa (Kenya, expanding regionally) may integrate stablecoin functionality, combining their extensive distribution networks with blockchain settlement.
行動金融收斂:如GCash(菲律賓)、M-Pesa(肯亞,並正向區域擴展)等行動金融服務,可能結合穩定幣功能,將其廣大分銷網絡與區塊鏈結算整合。
Asia's combination of need (expensive remittances, currency volatility, financial inclusion gaps), receptivity (mobile-first populations comfortable with digital payments), and progressive regulation (in key markets) positions the region as a PayFi growth center. The innovations emerging here may eventually flow back to influence Western market implementations.
亞洲兼具需求(高昂匯款費用、匯率波動、金融包容性不足)、接受度(行動裝置普及且樂於使用電子支付)及進步監管(關鍵市場有前瞻法規),讓本區成為 PayFi 發展重鎮。這裡的創新有望回流並影響西方市場實作。
Institutional Adoption and Economic Implications
機構採用與經濟效應
PayFi's progression from cryptocurrency enthusiasts to mainstream finance marks a critical inflection point. When major financial institutions, payment processors, and asset managers deploy capital and build infrastructure around stablecoin-based payments, it signals a shift from experimentation to production deployment. This institutional embrace carries profound economic implications.
PayFi 從加密愛好者邁向主流金融,是關鍵的轉捩點。當大型金融機構、支付處理商及資產管理公司將資本投入並構建穩定幣支付基礎建設,意味著這項技術正從試驗移向實際運作。機構接受會帶來深遠的經濟影響。
The Institutional Shift
機構轉型
Traditional financial institutions are recognizing that programmable payments represent not just a technological upgrade but a structural change in how money moves through the global economy.
傳統金融機構逐漸認知到,可程式化支付不僅是技術升級,更是全球金融運作模式的結構性變革。
Asset Manager Involvement: Circle received $400 million in funding with participation from BlackRock, Fidelity, Fin Capital, and Marshall Wace LLP. This was not passive investment - BlackRock entered into a broader strategic partnership with Circle to explore capital market applications for USDC and serves as primary asset manager of USDC cash reserves, while BNY Mellon serves as the primary custodian of assets backing USDC stablecoins.
資產管理領域參與: Circle獲得黑石(BlackRock)、富達、Fin Capital 及 Marshall Wace LLP等投資,募資達4億美元。這不只是被動投資——黑石與Circle建立戰略合作,共同探索USDC資本市場應用,更擔任USDC現金儲備的主要資產管理人,而BNY Mellon負責USDC資產託管。
Fidelity is preparing to launch its own stablecoin, tentatively named "Fidelity Token", aiming to provide a stable and secure medium of exchange leveraging Fidelity's reputation in traditional finance.
富達(Fidelity)正籌備發行自有穩定幣,暫名「Fidelity Token」,希望憑藉其在傳統金融界的信譽,提供一個穩定安全的交換媒介。
Banking Sector Entry: Despite regulatory uncertainty, banks are exploring stablecoin offerings. Several major financial firms are seeking banking charters to hold customer deposits, manage stablecoin reserves, and offer banking services under regulatory oversight. Stripe is seeking a special banking charter to reduce costs and broaden business models, motivated by processing transactions directly.
銀行業切入:即便監管未明,銀行界仍積極探討穩定幣相關服務。多家金融巨頭正申請銀行執照,以便持有客戶存款、管理穩定幣準備金,並在監管下開展銀行業務。Stripe 亦尋求特殊銀行執照,意圖直接處理交易,降低成本並拓展商業模式。
Payment Network Integration: Visa expanded pilots to settle with USDC on Solana with acquirers like Worldpay and Nuvei, demonstrating that card networks see value in blockchain settlement even while maintaining existing customer-facing rails.
支付網路整合:Visa 擴展試點計畫,透過 Solana 使用 USDC 與 Worldpay、Nuvei 等收單機構清算。這證明卡組織即便維持傳統客戶介面,已看到區塊鏈清算帶來的價值。
Treasury Management: Corporations are beginning to use stablecoins for treasury operations. The benefits include:
- 24/7 Liquidity: Unlike bank accounts (limited by operating hours), stablecoin holdings can be deployed instantly at any time
- Programmable Treasury: Smart contracts can automate sweeping, rebalancing, and allocation across multiple accounts and purposes
- Yield Generation: Circle's acquisition of Hashnote enables yield-generating opportunities for USDC holders through tokenized money market funds
- Simplified Multi-Entity Management: Companies with subsidiaries in multiple countries can manage global treasury using stablecoins rather than maintaining numerous bank accounts across jurisdictions
資金調度與管理:企業開始運用穩定幣處理金庫作業,帶來益處包括:
- 全年無休流動性:不同於受作業時段限制的銀行帳戶,穩定幣隨時流用
- 可程式化金庫:智能合約可自動化清帳、資產再平衡、分配到多個帳戶/用途
- 收益創造:Circle收購Hashnote,讓USDC持有者能經過代幣化貨幣市場基金產生收益
- 簡化多實體管理:跨國企業能用穩定幣集中管理全球資金,無需各國開立多個銀行帳戶
Economic Impacts: The Disappearing Float
經濟影響:浮存資金的消失
Traditional payments generate revenue from multiple sources: interchange fees, processing charges, FX spreads, and float. Of these, float is perhaps the most fundamental yet least visible to end users.
傳統支付收入來源多元:包含交換手續費、處理費、匯差,以及浮存資金(Float)。其中,浮存資金最根本、也最不易被終端用戶意識到。
Float occurs whenever money is in transit but not yet settled. When you swipe a credit card, the merchant does not receive funds immediately. The payment processor holds the money for 2-3 days before settlement. During that time, the processor earns interest on the aggregate balance - millions or billions of dollars sitting across thousands of transactions.
浮存資金產生方式是資金尚在清算流程、未入帳。刷卡後商家無法立刻收到款項,金流會於支付處理商那裏停留2-3天。不僅如此,支付商會在這段期間對巨量資金(來自千千萬萬交易)賺取利息。
Similarly, when businesses hold operating accounts at banks, they typically receive minimal or no interest while the bank deploys those deposits profitably. When companies maintain pre-funded nostro accounts for international payments, that capital sits idle, earning nothing while waiting to facilitate future transactions.
同理,企業把運作資金存入銀行時,通常幾乎不會拿到利息,但銀行卻能運用這些存款獲利。若企業需要為國際支付預先準備 nostro 帳戶資金,該資金只能閒置,等待未來交易,期間無法賺取任何效益。
PayFi eliminates much of this float:
PayFi 大幅減少上述浮存資金狀況:
-
Instant Settlement: Merchants receive funds in seconds, not days. No float exists during settlement because settlement is immediate.
-
No Pre-Funding Required: Arf Financial demonstrates this with 24/7 USDC settlements without requiring pre-funded accounts, eliminating capital tied up in anticipation of future transactions.
-
Transparency: All balances are visible on-chain in real-time. Companies know exactly what they have available at any moment.
-
即時結算:商家可在數秒內收到款項。結算無需等待,浮存資金消失。
-
不需預先資金準備:如 Arf Financial 示範,USDC 可 24/7 即時清算,無需預存帳戶,資金能完全運用,不再閒置。
-
資訊透明:所有餘額皆可於鏈上即時查詢,公司任何時刻都清楚資產狀況。
This represents a massive shift in working capital efficiency. A retailer processing $10 million monthly in credit card sales previously had $600,000-900,000 perpetually in transit (2-3 days of sales volume). With instant settlement, that capital becomes immediately available for inventory purchases, debt service, or investment.
這代表營運資金效率的巨大變革。例如一間零售商每月信用卡銷售一千萬美元,以往約有六十至九十萬美元(相當於2-3天銷售額)長期停留在支付流程。即時結算後,這筆資本立即可用於進貨、還債或投資。
Aggregate this across the global payments industry's $1.8 quadrillion in annual transaction value. Even a small percentage shifting to instant settlement represents trillions of dollars in working capital that becomes more productive.
全球支付行業每年交易額高達1.8百萬億美元。哪怕只有極小一部分資金改為即時結算,全球仍將有數兆美元營運資本可更有效運用。
New Economic Models
新經濟模式
As traditional revenue sources (float, slow settlement) diminish, PayFi creates opportunities for new monetization models:
隨著傳統收入來源(如浮存資金、緩慢清算)減少,PayFi 將開創全新商業模式和獲利方式:流動性提供:DeFi 風格的流動性池可以為商家提供即時結算,並因提供資金使當日結算成為可能而獲得手續費。這類服務類似於傳統的商家現金預付,但過程自動化且價格透明。
智能合約手續費:開發人員構建支付自動化邏輯時,可以對合約使用收費。例如,供應鏈金融協議可針對即時發票貼現收取 0.5% 的費用,遠低於傳統貼現商,但由於規模經濟和低間接成本,可持續發展。
財資管理服務:金融機構可以提供收益優化服務:自動把閒置的穩定幣餘額路由至最高收益協議,根據風險參數再平衡,提供先前僅大型企業可擁有的高階現金管理功能。
數據服務:區塊鏈支付數據具有透明性(雖然經常是偽匿名)。分析服務可以提供商業智慧:現金流預測、根據鏈上支付歷史進行信用評估,以及利用模式分析偵測詐欺行為。
嵌入式金融:企業可透過 PayFi 基礎建設,把支付功能直接整合到應用程式中。SaaS 平台可以即時支付給用戶、市集能自動進行託管與結算、內容平台能實時拆分收入——這一切都可用 PayFi 嵌入式服務及分潤模式實現。
競爭與顛覆
機構級採用並非均質,這帶來贏家、輸家和新競爭態勢。
支付處理商:如 Stripe、Adyen 這類擁抱穩定幣結算的公司,可能在成本結構和能力上獲得領先。反之,若僅依賴傳統金流者,則可能被顛覆。
銀行:傳統國際支付代理銀行承受生存壓力。若匯款成本從 6.2% 降到 1-2%,過去賺取高額利潤的銀行將面臨營收崩跌。若銀行能轉型提供穩定幣相關服務(託管、進出金口岸、合規),將有機會開拓新營收。拒絕改變者則可能失去市場地位。
卡片網絡:Visa 與 Mastercard 進退兩難。其基於交換費的商業模型仰賴 2-3% 手續費。若穩定幣支付只需 0.5-1% 成本,商家勢必轉向。兩大網絡啟動穩定幣結算試點,同時維持卡式用戶體驗,意在保有通路主導權,同時調整基礎設施。
新進者:像 Circle 這類擁有穩定幣基礎建設及合規專長的新創公司,將成為新體系重要中介。若 USDC 成為全球支付基礎建設,即使不直接對基礎轉帳收費,Circle 依然能捕獲大量價值。
規模與展望
潛在規模極為可觀。2025 年麥肯錫全球支付報告指出,支付產業每年產生 2.5 兆美元營收,總流水達 2.0 百京美元。即使僅有 10-20% 的金流在未來十年轉向 PayFi 系統,每年也會有 200-400 兆美元的交易額度。
預估 2030 年,鏈上價值將成長到 10-25 兆美元,驅動力來自實時結算及資產代幣化創新。截至 2025 年中,穩定幣市值已達 2,517 億美元,五年前幾乎還是零。成長軌跡顯示後勢仍將迅速擴張。
機構參與驗證了這類技術、帶來流動性、確保合規性,並推動主流普及。隨著更多金融機構部署 PayFi 基礎建設,網絡效應日益強化:更多商家收穫穩定幣,更多消費者持有、更多開發者打造新應用、更多資金流入生態體系。這種自我強化循環正是平台轉移階段的典型現象,亦代表 PayFi 的機構採用期才正要開始。
法規與合規環境
PayFi 運作於支付監管、銀行法、證券監理,以及新興數位資產法規的交會點。2023~2025 年間,全球監理環境大幅演進。美國通過了全面性的穩定幣立法,可能成為全球法規範本。理解相關規範,對於任何打造或使用 PayFi 基礎建設者來說都至關重要。
GENIUS 法案:美國穩定幣監管架構
2025 年 7 月 18 日,川普總統簽署「美國穩定幣引導與國家創新立法(GENIUS Act)」,該法首度建立支付穩定幣的全面監管框架,亦是美國史上第一部專門規範數位資產的聯邦法。
定義性架構:GENIUS 法案將支付型穩定幣定義為「為支付或結算而發行、可按預定固定金額贖回的數位資產」。此定義關鍵性地排除國家貨幣、銀行存款和證券,創造出全新的監管類別。
儲備要求:發行人必須為每一美元穩定幣,持有至少一美元的允許儲備資產。允許的儲備僅限現金與貨幣、已保障銀行及信用合作社存款、短期國庫券、以國庫券擔保的回購協議、政府貨幣市場基金、央行準備金,以及監管機關核准的其他類似政府發行資產。
此規定確保穩定幣完全由高流動性、低風險資產支持。法規防止如算法穩定幣(例:TerraUSD)那樣,試圖以套利維持掛鉤而非實質儲備,2022 年該幣崩盤導致 400 億美元蒸發。
發行人許可:穩定幣可由銀行與信用合作社透過子公司發行;非銀行業者則僅限金融公司,除非財政部長及聯邦準備理事會、FDIC 主席一致認定不會對金融系統構成風險。
形成雙軌系統:銀行可憑現有監理機關核准由子公司發行,非銀行須向貨幣監理署(OCC)取得聯邦執照或通過州級制度認可。
州立監管選擇權:法案允許發行量 100 億美元以下的非銀行發行人,若州法制度經穩定幣認證審查委員會認定「實質等同」於聯邦標準,即可採行州級監理選項。
這種聯邦—州雙層架構,旨在兼顧創新與安全:小規模可由州創新監理,大規模則需聯邦檢查。
透明度與報告:發行人必須建立並公開穩定幣贖回機制,並定期揭露流通穩定幣及儲備組成,且需高層主管認證並由註冊會計師事務所複核。發行流通量超過 500 億美元者,需提交經審計的年度財報。
Circle 已有每月出具四大會計師查核儲備報告的實例,驗證此類透明度可行。GENIUS 法案將此寫入法規。
反洗錢與制裁遵循:法案要求 FinCEN 推動「創新方法偵測涉及數位資產的不法活動」,發行人需證明已建立反洗錢(AML)與制裁遵循機制。所有穩定幣發行人必須具備法定要求時「凍結、燒毀、查封支付型穩定幣」之技術能力,並依法令配合。
藉此回應執法機關憂慮:穩定幣可能助長制裁規避或洗錢。發行人強制具備凍結與查封機制,兼顧創新與風險防範。
證券法豁免:合格發行人發行的支付型穩定幣在美國聯邦法下不屬「證券」或大宗商品交易法下的「大宗商品」,故不受 SEC 或 CFTC 監督。
該明確規定至關重要。此前穩定幣是否屬證券存有法律不確定,形成合規風險。GENIUS 法案明確將合規發行的支付型穩定幣排除出證券與期貨監理,惟其他數位資產仍按原法規接受 SEC、CFTC 規管。
實施時程:法案自頒布後,現有發行人有約 18 個月過渡期完成合規。針對持有或經辦穩定幣的託管人與其他機構,法案給予更長緩衝——自實施起三年內,所有涉及支付型穩定幣交易或託管的機構,必須限於經核可發行人發行之穩定幣。
全球監管環境
雖然 GENIUS 法案針對美國,但 PayFi 與生俱來具全球性。其他司法管轄區採取各有不同的方式:
歐盟 - MiCA:歐盟《加密資產市場規則(MiCA)》透過電子貨幣代幣(EMT)與資產掛勾代幣(ART)規範穩定幣。EMT 指——tokens backed by a single fiat currency, while ARTs are backed by a basket of assets. Under MiCA, only e-money institutions or credit institutions can issue EMTs, while ART issuers must be EU-based and authorized by regulators.
以單一法定貨幣作為擔保的代幣稱為EMT,ART則是以一籃子資產作為擔保。根據MiCA,僅有電子貨幣機構或信貸機構可以發行EMT,而ART的發行人必須是設立於歐盟並經監管機構授權。
MiCA provides comprehensive regulation earlier than the U.S., with enforcement beginning in phases through 2024-2025. However, its approach is more restrictive - limiting issuers to regulated financial institutions from the start rather than creating a pathway for nonbank innovation.
MiCA在美國之前就已提供全面的監管,並將於2024至2025年間分階段實施。不過,其方式較為嚴格——一開始就只允許受監管的金融機構擔任發行人,而非為非銀行創新建立管道。
Hong Kong: Hong Kong's Stablecoin Ordinance, passed in May 2025, requires all issuers of stablecoins backed by the Hong Kong dollar to obtain a license from the Hong Kong Monetary Authority, with all stablecoins backed by high-quality, liquid reserve assets and the market value of the reserve pool equal to the par value of the stablecoins in circulation.
香港:香港於2025年5月通過《穩定幣條例》,規定所有由港幣擔保的穩定幣發行人必須向香港金融管理局申領牌照,且所有穩定幣必須以高品質、流動性強的儲備資產為支持,儲備池的市值需等同於流通中穩定幣的面值。
Hong Kong's approach targets local currency stablecoins specifically, positioning Hong Kong as a digital asset hub while maintaining monetary sovereignty.
香港的做法重點針對本地貨幣穩定幣,旨在將香港定位為數位資產樞紐,同時維護貨幣主權。
Singapore: The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) has established licensing frameworks through its Payment Services Act. Major stablecoin issuers including Circle and Paxos have obtained licenses. Singapore balances innovation support with consumer protection, requiring license holders to maintain capital adequacy, technology risk management, and AML/CFT controls.
新加坡:新加坡金融管理局(MAS)通過《支付服務法》建立了發牌框架。主要穩定幣發行商如Circle和Paxos已獲取牌照。新加坡在鼓勵創新及保障消費者之間取得平衡,要求持牌人維持資本充足、技術風險管理,以及進行防洗錢/反資恐措施。
United Kingdom: The UK is developing stablecoin regulation through its Financial Services and Markets Act, treating certain stablecoins as regulated payment instruments. The approach focuses on systemic stablecoins that could impact financial stability, with proportionate regulation based on scale and usage.
英國:英國正透過《金融服務與市場法》發展穩定幣監管,將部分穩定幣視為受規管的支付工具。做法重點針對可能影響金融穩定的系統性穩定幣,並根據規模及使用情況實行相應監管。
Compliance Challenges
Despite regulatory clarity improving, significant compliance challenges remain for PayFi participants:
合規挑戰
儘管監管清晰度有所提升,PayFi參與者仍面臨重大合規挑戰:
Cross-Border Complexity: Payments are inherently cross-border, but regulations are jurisdictional. A stablecoin issuer must comply with regulations in every country where its stablecoin is used. This creates compliance complexity: KYC requirements differ across jurisdictions, reporting obligations vary, and sanctions lists are not uniform.
跨境複雜性:支付本質上具有跨境特性,但監管卻以司法管轄區為基礎。穩定幣發行人必須遵守其代幣被用於每一個國家的相關法規。這帶來了合規的複雜性:例如,各司法管轄區的KYC要求不同、申報義務各異,制裁名單也不一致。
The GENIUS Act attempts to address this through provisions for foreign stablecoin issuers. The Act allows foreign payment stablecoin issuers to offer or sell in the United States under certain circumstances, with Treasury authorized to determine whether a foreign regime for regulation and supervision of payment stablecoins is comparable to requirements established under the GENIUS Act.
GENIUS法案試圖通過針對外國穩定幣發行人的條款解決這一問題。該法案允許外國支付型穩定幣發行人在特定條件下於美國提供或銷售,同時授權財政部決定外國穩定幣監管制度是否與GENIUS法案要求具有可比性。
This "comparability" framework could enable mutual recognition: if the EU's MiCA regime is deemed comparable, MiCA-licensed stablecoin issuers could operate in the U.S. without separate licensing. However, comparability determinations involve complex policy negotiations.
該「可比性」框架有機會實現互認:若歐盟的MiCA制度被視為可比,則獲MiCA牌照的穩定幣發行人可無需額外牌照就在美國營運。然而,判定可比性的過程涉及複雜的政策協商。
Transaction Monitoring: AML compliance requires monitoring transactions for suspicious activity. With blockchain's transparency, this is theoretically easier than traditional banking - every transaction is publicly visible. However, identifying beneficial owners behind wallet addresses remains challenging.
交易監控:防制洗錢合規要求對可疑活動的交易進行監控。由於區塊鏈具有公開透明特性,理論上比傳統銀行業更容易—每一筆交易都是公開可查的。然而,辨識錢包地址背後的實質受益人依然困難。
Solutions are emerging: blockchain analytics firms like Chainalysis, Elliptic, and TRM Labs provide transaction monitoring tools that identify high-risk wallets, trace funds, and flag suspicious patterns. Elliptic provides MoneyGram with blockchain analytics solutions for their Stellar integration.
解決方案也正逐漸浮現:區塊鏈分析公司如Chainalysis、Elliptic和TRM Labs等,提供交易監控工具,可識別高風險錢包、追蹤資金流向、標記可疑模式。Elliptic為MoneyGram在Stellar整合提供區塊鏈分析技術。
Sanctions Compliance: The GENIUS Act explicitly subjects stablecoin issuers to the Bank Secrecy Act, thereby obligating them to establish effective anti-money laundering and sanctions compliance programs with risk assessments, sanctions list verification, and customer identification.
制裁合規:GENIUS法案明確將穩定幣發行人納入《銀行保密法》,要求其建立有效的防制洗錢與制裁合規計劃,包括風險評估、制裁名單查核及客戶識別。
Sanctions compliance is particularly complex for stablecoins because they can move globally without intermediaries. Traditional correspondent banking allows sanctions screening at multiple points. With stablecoins, enforcement depends on issuers and on-ramps/off-ramps implementing controls.
穩定幣的制裁合規特別複雜,因其可在全球範圍內無需中介即可轉移。傳統代理行體系可於多個環節進行制裁篩查,但穩定幣的合規執行則依賴發行人及進出金管道的管控措施。
Circle demonstrated this capability in 2022 by freezing USDC associated with addresses sanctioned by the U.S. Treasury. This ability - built into the smart contract - ensures issuers can comply with lawful orders. However, it creates tension with blockchain's censorship-resistance ideals.
Circle在2022年就展示了這種能力,對美國財政部列為制裁對象的地址所持有的USDC進行了凍結。這種功能已被寫入智慧合約內,可確保發行人遵守法律命令。然而,其與區塊鏈去審查的理念存在張力。
Privacy Considerations: Transaction monitoring and sanctions compliance require identifying users. This conflicts with cryptocurrency's privacy culture. The compromise emerging is selective disclosure: users provide identity to regulated on/off-ramps and issuers but can transact pseudonymously on-chain, with issuers retaining ability to freeze wallets when required by law.
隱私考量:交易監控與制裁合規皆要求確認用戶身份,但這與加密貨幣的隱私文化相衝突。當前折衷方案為選擇性交揭露:使用者僅需向受監管的進出金管道及發行人提供個人資料,但在鏈上仍可使用化名進行交易,發行人則保留在法律要求下凍結錢包的能力。
Regulatory Risks
Despite progress, regulatory uncertainty remains in several areas:
監管風險
雖有進展,但多個領域仍存在監管不確定性:
Algorithmic Stablecoins: The GENIUS Act focuses on fiat-backed payment stablecoins. Endogenously collateralized stablecoins - digital assets pegged to the value of another digital asset rather than fiat - are not explicitly banned but the Treasury Secretary must conduct a study on non-payment stablecoins within one year.
演算法穩定幣:GENIUS法案重點針對由法幣擔保的支付型穩定幣。以另一數位資產為抵押、非匯率式的內生穩定幣,並未被明確禁止;不過,財政部長需於一年內就非支付型穩定幣進行研究。
This leaves open questions about algorithmic stablecoins like DAI (backed by crypto collateral) and other non-payment stablecoins. The House's competing STABLE Act proposed a two-year moratorium on such stablecoins. Future regulation may restrict or ban them.
這為DAI等以加密資產作為擔保的演算法穩定幣及其他非支付型穩定幣留下不少問號。眾議院另一部競爭法案STABLE法案則提出對此類穩定幣暫緩兩年。未來法規可能進一步限制或禁止演算法穩定幣。
DeFi Integration: Many PayFi use cases integrate with DeFi protocols: liquidity pools, lending markets, yield aggregators. How do AML obligations extend to these interactions? Can a compliant stablecoin issuer allow its tokens to be used in DeFi protocols that lack KYC? These questions remain unresolved.
DeFi 整合:許多PayFi應用案例與DeFi協議整合,例如流動性池、借貸市場、收益聚合器等。現行防制洗錢義務如何適用至這些互動?符合法規的穩定幣發行人能否允許其代幣流入不具KYC的DeFi協議?這些問題尚待釐清。
Taxation: Cryptocurrency taxation is notoriously complex. Does converting USD to USDC create a taxable event? What about on-chain transfers? The answer varies by jurisdiction. In the U.S., stablecoins are generally treated as property, meaning each conversion could technically trigger capital gains reporting even if gains are negligible (due to 1:1 peg).
稅務問題:加密貨幣的稅務問題一向十分複雜。把美元換成USDC是否構成應稅事件?鏈上轉帳又如何?答案視法域而異。在美國,穩定幣普遍被視為財產,技術上每次兌換都可能觸發資本利得申報,即使波動極小(由於1:1掛鉤)。
The GENIUS Act directs Treasury to address tax issues, but implementation rules are still being developed. Clearer guidance is needed to avoid turning every stablecoin payment into a complex tax reporting event.
GENIUS法案指示財政部解決稅務問題,但執行細則尚在制定中。需有更明確指引,避免每次穩定幣支付都變成複雜的稅務申報事件。
Global Coordination: Without international coordination, regulatory arbitrage becomes possible. If the U.S. imposes strict requirements but offshore jurisdictions do not, issuers may charter elsewhere. The GENIUS Act's comparability framework attempts to address this by requiring foreign issuers to meet equivalent standards.
全球協調:若無國際協調,可能導致監管套利。若美國施加嚴格要求而離岸司法管轄區寬鬆,發行人或將註冊在別處。GENIUS法案的可比性框架試圖通過要求外國發行人達至同等標準以應對此問題。
However, achieving global regulatory harmonization is notoriously difficult. Payments historically operated within fragmented national regimes. Blockchain's borderless nature makes this fragmentation more problematic - but also creates pressure for coordination.
然而,要實現全球監管一致卻非常困難。支付行業本就歷來在各國分割的監管架構下運作。區塊鏈無國界的特性使這種碎片化更加嚴重,但同時也帶來協調的壓力。
The Path Forward
Regulatory clarity has improved dramatically with the GENIUS Act and similar frameworks globally. This clarity enables institutional adoption: banks and asset managers can build PayFi infrastructure knowing the regulatory parameters.
未來展望
隨著GENIUS法案及全球類似監管框架的出現,監管明確性已大幅提升。這一明確性使機構採用成為可能:銀行和資產管理公司可以根據確定的監管參數建立PayFi基礎設施。
However, regulation will continue evolving as use cases emerge and risks materialize. Key areas to monitor include:
然而,隨著更多應用場景出現及風險顯現,相關法規亦將持續演進。值得關注的重點包括:
- CBDC Interaction: How will regulations treat interactions between stablecoins and central bank digital currencies?
- 中央銀行數位貨幣(CBDC)交互:規定如何規管穩定幣與CBDC的互動?
- Cross-Border Frameworks: Will major economies achieve mutual recognition of regulatory regimes?
- 跨境框架:主要經濟體能否實現監管互認?
- DeFi Integration Rules: How will regulators address stablecoins used in decentralized protocols?
- DeFi整合規則:監管機構會如何針對用於去中心化協議的穩定幣制定規範?
- Privacy Technologies: How will regulations treat privacy-preserving technologies like zero-knowledge proofs if applied to stablecoins?
- 隱私技術:若零知識證明這類隱私保護技術應用於穩定幣,監管會如何處理?
- Insurance Requirements: Should stablecoin issuers be required to carry insurance protecting holders if reserves are compromised?
- 保險要求:若儲備資產遭侵害,穩定幣發行人是否應被強制投保以保障持有人?
The regulatory landscape is stabilizing, but not static. PayFi participants must maintain active compliance programs, monitor regulatory developments globally, and engage constructively with policymakers to shape frameworks that protect consumers while enabling innovation.
監管格局雖逐漸穩定,但絕非定局。PayFi參與者必須積極維護合規計劃,持續關注全球監管動向,並主動與政策制定者互動,共同塑造既保護消費者又促進創新的監管框架。
Risks and Challenges
PayFi's promise is significant, but so are the risks. Technical vulnerabilities, economic instabilities, regulatory uncertainties, and adoption barriers all threaten to slow or derail the convergence between payments and DeFi. A balanced assessment requires examining these challenges honestly.
風險與挑戰
PayFi 前景廣闊,但風險也不容忽視。技術漏洞、經濟不穩定、監管不明確與普及障礙,都可能拖慢甚至瓦解支付與DeFi融合的步伐。要全面衡量發展,必須誠實審視這些挑戰。
Technical Risks
Scalability and Congestion: Blockchain networks have finite capacity. When demand spikes, transaction fees rise and confirmation times slow. Ethereum experienced this during the 2021 NFT boom, with transaction fees reaching $50-200 for simple transfers. Such fees make small payments economically unviable.
技術風險
可擴展性與壅塞:區塊鏈網絡容量有限。當需求暴增時,手續費飆升且確認時間延長。以太坊在2021年NFT熱潮期間曾經出現,單純轉帳的交易費高達50-200美元。如此高的手續費讓小額支付難以承擔。
Layer-2 solutions and high-performance Layer-1 chains address this, but risks remain. If a payment processor builds on a specific blockchain and that network experiences congestion or outages, payment flow interrupts. Solana has experienced network disruptions multiple times, though reliability has improved significantly.
Layer-2方案及高效Layer-1鏈可紓緩此問題,但風險依舊存在。若支付服務商架構於特定鏈上,而該網絡壅塞或故障,則支付流程將受阻。Solana 多次出現網路中斷,儘管其穩定性已大為改善。
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Bugs in smart contract code can be catastrophic. Once deployed, many smart contracts are immutable - bugs cannot be easily fixed. The history of DeFi includes numerous exploits: reentrancy attacks, flash loan exploits, governance hijacks. If PayFi infrastructure contains vulnerabilities, attackers could steal funds or disrupt operations.
智慧合約漏洞:智慧合約程式碼中的漏洞可能造成災難性後果。一經部署,許多合約即不可更改,錯誤也難以修復。DeFi歷史上曾大量發生重入攻擊、閃電貸利用、治理劫持等事件。若PayFi基礎設施存在漏洞,攻擊者可能盜取資金或癱瘓營運。
Mitigation requires rigorous security practices: formal verification, multiple independent
(譯文至此為止,原文已到段落結尾如需加長可再告知)audits、漏洞賞金計畫、漸進式上線並初期限定存款額度。然而,即使經過良好審查的合約,仍可能隱含只有在實際運行後才會顯現的微妙漏洞。
跨鏈橋風險:許多 PayFi 的使用情境涉及將穩定幣跨區塊鏈移動——例如從 Ethereum 到 Polygon、Solana 到 Base 等。橋接攻擊一直是加密史上最嚴重的損失來源之一,至今已造成數十億美元損失。Circle's Cross-Chain Transfer Protocol (CCTP) 提供原生解決方案,但並非所有轉帳都使用這套協議,橋接安全依然是長期問題。
金鑰管理:區塊鏈安全仰賴私鑰控管。如果用戶遺失私鑰,資金將無法救回;若企業熱錢包遭盜用,資金恐瞬間被竊且無法追討。傳統銀行有資金回復和詐欺追溯機制,區塊鏈則沒有。
解決方式包含多重簽章錢包(需多把金鑰共同授權)、硬體安全模組(HSM)、帳戶抽象化(具社交恢復功能的智慧合約錢包)等。然而,這些方式會增加複雜度,也尚未成主流。
經濟風險
穩定幣脫鉤風險:穩定幣依靠兌換保證與儲備資產維持錨定價值。但錨定價格有可能失守。2023 年三月,Circle 將儲備資金存放於 Silicon Valley Bank,該銀行倒閉,導致 USDC 一度跌到 $0.87,直到 Circle 證實資產安全才回穩。
若重大穩定幣在危機期間脫鉤,建立在其上層的 PayFi 系統可能大幅受挫。商家預期收到 $10,000 最後結算卻只得到 $8,000 等值,這類波動將傷害支付應用場景。
儲備透明與審計:Circle 每月公布 USDC 儲備申證報告,以提升資產支撐的透明度。但「申證」與完整審計不同。Tether 多次因儲備組成受質疑,雖然透明度有逐步改善。
GENIUS 法案強制大型發行商需進行細緻報告和審計,有助於提升透明度。但若發行商虛報儲備(如過去某些演算法穩定幣所為),系統就可能在問題暴露前遭受重大損害。
流動性危機:即使儲備充足,穩定幣仍可能遇到流動性錯配。若儲備大多持有國庫券(需要數日兌現),突然大量贖回請求(需立即現金),發行商恐難及時兌付。這如同經典銀行危機:資產長線健全但短線不具流動性。
Circle、Tether 均曾展現數十億美元短期贖回處理能力。但若真出現全面性恐慌,所有人同時要求贖回,目前規模下尚未遭遇過實測。
收益競爭:傳統銀行對存款利息極低,但靠存放資金與放款利差盈利。GENIUS 法案明文禁止穩定幣發行商對持有人支付利息或收益。
這帶來競爭壓力。若用戶持有 USDC 沒有利息,而投資貨幣市場基金可賺 4-5%,為何還要用 USDC?發行商無法以利息取勝,只能在效用上競爭(即時結算、可編程、全球可及)。這是否足以驅動大規模普及,仍有待觀察。
法規與政治風險
法規逆轉:GENIUS 法案由兩黨支持、總統背書,但政治風向易變。未來的行政部門或國會,可能設限、提高儲備標準、管制跨境用途,甚至因貨幣主權之虞嘗試禁用穩定幣。
中國於 2021 年全面禁用加密貨幣交易。印度亦曾討論類似措施。雖 GENIUS 法案已立法,美國整體法規風險尚無法完全排除。
制裁與執法過度:法規要求穩定幣發行商須能凍結資產,亦衍生新壓力點。若政府要求針對非普遍公認犯罪(如政治異議、未經許可交易、或僅與受制裁地區非特定對象往來)凍結資金,則穩定幣恐淪為審查工具。
這不是假設。傳統銀行就常因非明確違法事由被迫凍結帳戶。若穩定幣複製傳統銀行的掌控模式,也將出現相同受政治壓力的弱點。
碎片化:倘若各司法轄區自訂不相容規範,穩定幣市場將碎片化。美國 GENIUS 法案下的穩定幣在歐洲未必可用,歐盟 MiCA 規範的穩定幣在亞洲亦可能受限。這將損及 PayFi 無國界支付的願景。
GENIUS 法案的規格對等架構試圖解決此問題,但國際協調一向困難。若協調不足,PayFi 就可能分崩為地區性、互通性有限的系統——與全球化初衷背道而馳。
普及障礙
使用者體驗:雖然用戶體驗持續改善,區塊鏈技術對一般人來說仍是複雜難懂。私鑰、手續費(gas fee)、網路選擇、錢包管理…這些觀念讓非技術用戶難以上手。若 PayFi 須用戶理解區塊鏈運作,普及會大受侷限。
解決方式如帳戶抽象化(將技術細節包裝隱藏)、直接整合法幣出入金通道、託管式服務(用戶毋需自控私鑰)等。但各種方案在易用性與去中心化價值間總有權衡。
企業慣性:現有支付系統雖不夠高效,但行之有年。商家已整合信用卡收單、會計系統、薪資處理等。改用 PayFi 需額外整合、訓練員工並承擔風險。對多數企業而言,轉換成本高於實際好處。
波動性印象:雖然穩定幣具備錨定機制,「加密貨幣波動劇烈」的刻板印象仍讓人卻步。即使懂產品、負責的財務主管,仍可能因對加密資產存有投機與高風險觀念而抗拒。這需要長期教育與穩定運作來扭轉,但觀念轉變極慢。
網路效應:支付系統高度依賴網路效應——用戶越多價值越大。USDC 現今可觸及的終端錢包超過五億,聽起來不少,卻僅全球網民的一成。PayFi 要達主流普及尚有「雞生蛋,蛋生雞」障礙:商家因用戶少不收,用戶因商家未支援而不用。
存在性問題
除了具體風險,更廣泛的問題是 PayFi 長期存續性:
央行數位貨幣(CBDC)競爭:若各國央行發行具同等性質(即時結算、可編程)的數位法幣,穩定幣是否仍有存在必要?CBDC 可能有監管上優勢(無儲備風險、國家信用背書、強制受理),極可能排擠私人穩定幣。
然而 CBDC 未必能完整複製所有穩定幣優勢。政府可能為資本管制限制跨境用法,也可能限制可編程度以防監管套利。穩定幣及 CBDC 或將共存,針對不同場景。
傳統支付系統進化:支付體系並未原地踏步。FedNow、PIX、SEPA 即時結算及 UPI 均證明,傳統基礎建設也能實現即時結算、毋須上鏈。若這些系統已解決了速度問題,PayFi 又有何獨特性?
答案在於可編程性及組合性——這是難以強加於傳統舊系統的創新。但若傳統系統也漸漸加上可編程特性,兩者界線就模糊起來。
安全與去中心化權衡:真正去中心化的系統難以監管,更易被不法利用,也更難於出錯時伸張權益。合規的 PayFi 系統會犧牲部分去中心化,以便符合法規與保護用戶,其實質上可能僅是「換湯不換藥」的傳統金融——只是運作更快、更便宜。
如何在去中心化(創新、減少單點失效)與中心化(合規及用戶保障)間找平衡,仍是未竟的課題。
風險緩解
理解風險,有助於確實應對:
- 技術面:投入安全審計、漏洞賞金、形式化驗證及漸進上線
- 經濟面:保持審慎儲備、資訊透明、進行流動性危機壓力測試
- 法規面:主動與監管對話、前置打造合規基礎設施、支持國際協調
- 市場面:化繁為簡提升易用性、清楚示範產品價值、持續教育與生態系建設
挑戰確實存在,卻並非不可克服。傳統支付演進過程也曾經歷支票詐欺、信用卡盜刷、電子銀行安全及跨境合規等問題。這些皆靠科技、regulation, and best practices. PayFi 很可能會走上類似的道路,隨著生態系統成熟,風險會被管理而非徹底消除。
宏觀全景與未來展望
PayFi 不僅僅是在支付技術上的漸進式改進,而是代表著價值在全球經濟中流動方式的結構性轉變。理解它的宏觀影響與未來走向,必須從多個層面探討——技術基礎設施、經濟誘因、監管演變及用戶行為採用等交會點。
五年展望:2025-2030
到了 2030 年,PayFi 基礎設施預計將相當成熟。值得關注的關鍵發展包括:
主流穩定幣採用:到 2030 年,鏈上價值預計將成長至 10 至 25 兆美元。這約佔全球金融資產的 1-2%。雖然以傳統金融的標準來看這比例還小,但這將標誌著一個關鍵轉折點:穩定幣成為標準的資金管理工具,而非另類選擇。
穩定幣市值於 2025 年中達到 2,517 億美元。如果目前的成長軌跡(每兩到三年翻倍)持續,市值有機會在 2027-2028 年增至 5,000 億至 1 兆美元。此規模下,穩定幣的流通將可媲美多個國家貨幣。
機構金庫整合:大型企業已經擁有複雜的資金操作——多幣別帳戶、避險策略、流動性管理。PayFi 讓這些成為可能:
- 24/7 全天候作業:無需再等候銀行工作時段或結算窗口
- 可程式化資金管理:透過智能合約自動清算、再平衡及分配
- 全球流動性池:單一穩定幣金庫能立即部署至全球任何子公司或債務對象
- 收益最佳化:在風險參數範圍內,自動導向最高收益的協議
到 2030 年,金庫管理軟體很可能將區塊鏈結算作為標準功能並列於傳統銀行之旁。屆時問題不會是要不要用穩定幣,而是要將多少資金放到鏈上。
跨境支付革新:全球匯款量每年超過 7,000 億美元,平均手續費為 6.2%。如果到 2030 年 PayFi 佔據這市場的 30%,那每年將有 2,000 億美元的資金流向 PayFi,為匯款人每年節省大約 100-120 億美元手續費。
更重要的是速度上的提升深刻影響民生。外籍勞工扶養海外家人,資金可於數分鐘內到賬,而非數天。收款人可持有與美元掛鉤的穩定價值,而不必立即兌換成貶值的本地貨幣。這將對發展中國家的經濟帶來重大正面效應。
嵌入式金融普及:目前大多數嵌入式金融(直接整合於平台的支付)仍運作在傳統後端。Stripe、PayPal 和 Adyen 支撐結帳流程,但結算依然緩慢且昂貴。
到 2030 年,嵌入式 PayFi 有機會成為主流:電商平台能即時結算給商家,創作者平台自動拆分收入,市集用程式化的第三方信託(Escrow)自動執行,不再依賴傳統中介。表面上使用體驗不變,但後台結構完成轉型。
監管成熟度提升:GENIUS 法案已為美國建立框架,但全球協調尚在進行。預期到 2030 年會有:
- 互認協議:主要經濟體互相承認彼此的穩定幣執照,類似金融通行證
- CBDC 與穩定幣共存框架:規範明確界定私人穩定幣與央行數位貨幣間的互動
- 標準化報告:各司法轄區統一金流儲備證明、交易監控及稅務申報格式
- 國際協調:G20 或類似組織提出穩定幣發行與營運的基本標準
這些監管成熟將降低不確定性,進而推動更廣泛的機構採用。
十年願景:2025-2035
展望更遠的未來,PayFi 可能從根本上重塑全球金融體系的多項面向:
即時全球經濟:目前全球經濟大多以批次運作。股市會收盤,銀行有營業時間,結算需時數日。PayFi 允許 24/7/365 完全不間斷經濟活動,價值持續流動,產生深遠影響:
- 資本效率提升:如果資金能即時結算,閒置資本大幅減少。企業能在收到款項幾秒內立刻再投入使用,不必等上數天。
- 全球協調無縫化:跨時區團隊可隨時交易,不必等待工作時段重疊。
- 市場流動性提升:金融市場可全天候不間斷運作,不再因日終結算造成流動性斷層及價格跳躍。
可程式化貨幣政策:這雖屬高度推測,但若經濟體系大幅採用可程式化的貨幣(如內建智能合約的穩定幣或 CBDC),則貨幣政策將更能精準施行。央行不必只靠調整利率等粗放工具,還可:
- 以條件性轉帳針對特定行業或族群進行精準刺激
- 對持有不用的現金施加負利率,鼓勵消費
- 發行有期限的貨幣,促使必須流通消費
這些能力將引發政府權力、個人自由及經濟體制的重大討論。它們雖非必然,但技術上已成可能,關鍵在於政治選擇。
供應鏈革命:PayFi 結合物聯網與智能合約,將能自動化供應鏈各環節:
- 製造商出貨 → GPS 驗證送達後智能合約自動釋放款項
- 品質偵測出現瑕疵 → 自動暫停付款
- 庫存低於門檻 → 智能合約自動下單且付款
這要求超越傳統支付的整合(如物聯網裝置、真實世界數據預言機、爭議解決機制),但核心仍是能自動對外部事件作出反應的可程式化貨幣。
創作者經濟轉型:預計創作者經濟到 2030 年將超過 5,000 億美元,PayFi 將協助內容創作者提前取得資金再以串流收益自動返還。
想像一個創作者經濟:
- 藝術家隨內容被串流即可實時獲得微支付(不再按季結算)
- 合作專案自動依智能合約條款拆分收益
- 粉絲能以預期版稅分享的代幣,直接投資支持創作者
- 平台即時給付創作者,而非累積後月初才發放
這將根本改變創作者的商業模式。不再單靠品牌合作或廣告(對大型創作者較有利),而是讓中小型創作者靠直屬粉絲以高效可程式支付穩定獲利。
規模意涵
全球年度支付總量高達 1.8 百京美元,為 PayFi 的潛在規模提供了參考。如果僅 10-20% 轉移至 PayFi 軌道,每年就是 180-360 兆美元,規模極為可觀。
然這指標或許具有誤導性。PayFi 的意義不只在於轉移現有支付規模,更在於啟動從未曾可行的新型金流:
- 內容微支付(過去因交易手續費過高而無法實現)
- 自由工作者即時收款(過去因跨國電匯需時而延誤)
- 可程式化拆分與層疊付款(過去須靠複雜中介才能實現)
- 即時金庫操作(過去受限於銀行工作時間)
這些全新金流最終可能超越傳統支付量,因為可程式化解放了許多傳統支付模式無法因應的場景。
需要關注的指標
想監控 PayFi 是否達到其潛力,可追蹤以下數據:
穩定幣流通量與週轉率:USDC 流通於 2025 年中增至約 700-750 億美元。追蹤其成長速率——是加速、持平還是減速?同時關注週轉率(穩定幣流通頻率),高週轉率代表其主要用於支付,而非僅作為儲值。
交易量與投機性:雖然區塊鏈交易數據公開,但需要正確解讀。交易量大不一定代表支付用途,可能反映投機。重點在追蹤穩定幣支付量,2025 年累計已達 194 億美元,與總轉帳量區分開來。
商家採用程度:有多少商家支持穩定幣支付?主流支付處理商是否開放穩定幣結算?商家普及度是主流化的重要先行指標。
機構公告:監控大型企業金庫經理、資產管理公司及銀行相關穩定幣整合的公開聲明。每一家大機構入場都對基礎設施是一項肯定,帶動更多採用。
監管進展:追蹤國際監管協調。更多國家是否正在通過類似 GENIUS Act 的框架?互認協議是否逐漸出現?監管明朗將加速普及。
成本與速度指標:比較傳統支付與 PayFi 的成本及速度。若 PayFi 越來越便宜、速度越快,而傳統支付停滯,則用戶轉移將加速。
潛在失敗以下為依您要求所翻譯的內容,Markdown 連結已依規則保留原文未翻譯:
Modes
樂觀情境假設持續進步,但 PayFi 也可能無法實現其潛力。主要失敗模式包括:
監管限制:如果主要經濟體對穩定幣加以禁止或嚴格限制(在美國自 GENIUS 法案後不太可能,但其他地區仍有可能),PayFi 的成長將會停滯。
安全漏洞:PayFi 主要基礎設施(穩定幣發行方、廣泛使用的跨鏈橋樑、主導性的智能合約平台)若遭遇災難性攻擊,可能嚴重打擊信心並引發監管反彈。
央行數位貨幣取代:若中央銀行發行具有更優特性的數位貨幣,並透過強制使用或禁止替代品來推行,私人穩定幣可能被擠出市場。
用戶體驗失敗:如果區塊鏈支付對一般用戶而言仍然過於複雜,採用率將停留在加密貨幣愛好者層級,無法進入主流。
既有業者適應:若傳統支付系統(如升級版 ACH、具 API 層的即時支付網絡、或集中清算所)無需區塊鏈卻成功整合 PayFi 最佳特性(即時結算、可程式化),去中心化基礎設施的獨特價值主張將被削弱,PayFi 的優勢將僅剩去中心化的理念偏好,而非實際效能上的優越。
協同失敗:若區塊鏈生態系持續碎片化(鏈間不相容、穩定幣無法互通、標準相互競爭),全球無縫支付的願景無法實現。網絡效應需要標準上的一致與協作。
最可能的結果既非全面成功,也非徹底失敗,而是形成混合型局面:PayFi 佔據特定用例(跨境匯款、財務管理、嵌入式金融)而傳統系統則保留其它領域(消費者信用卡、國內零售支付)。關鍵問題在於,每一系統會攫取年支付總額 1.8 千兆美元的多少百分比。
超越支付:更廣泛的轉型
最終,PayFi 只是更重大轉型的表現:網際網路、金融與程式邏輯的融合。網際網路讓資訊得以即時、全球流動。PayFi 正試圖為價值帶來同樣變革。網路催生了過去印刷及廣播時代不曾有的新商業模式(搜尋引擎、社交網絡、電子商務)。PayFi 也可能啟動全新且尚未被充分構思的金融模式。
當貨幣可被程式化——即能依據條件自動轉移、根據預設規則自動分割、或在特定事件發生前自動鎖定——金融將徹底改變。重點從處理交易,轉為編碼關係與自動化協議。
這不僅只是更快或更便宜的支付。它意味著對全球 20 億無銀行帳戶、但擁有智慧型手機的成年人帶來金融包容。意味著創作者和小企業無須守門人即可取得資金。意味著流向透明、可稽核、減少貪腐的資金流。更意味著新型經濟組織方式,這些都是我們才剛開始想像的未來。
從宏觀來看:我們正處於關鍵基礎設施轉型的初期階段。就如同從紙本支票到電子 ACH,從現金到信用卡,從臨櫃業務到行動應用程式的轉變,基於區塊鏈、可程式化的支付革命將需要時間,會遇到阻力、經歷挫折,也需不斷迭代。
但發展方向已相當明確。即時結算、可程式化、全球可及性以及透明運作的組合,對比那些為前網際網路時代設計的系統,有著明顯優勢。無論未來呈現純區塊鏈路徑、傳統與去中心化基礎設施整合的混合模式、或傳統系統套用區塊鏈原則,2035 年的支付版圖都將與 2025 年大相逕庭。
1.8 千兆美元的終極問題不是變革會不會發生,而是多快、用何種形式,以及哪些參與者會領先、哪些會落後。
最終想法
PayFi——即支付與去中心化金融的結合——不僅是一項技術創新,更標誌著一種結構性演進:全球價值移動方式的變革,來自於釋放傳統付款流程被鎖住的時值資本、貨幣本身的可程式化,以及區塊鏈基礎設施與主流金融體系的融合。
全球支付產業每年處理 1.8 千兆美元與 3.4 兆筆交易,創造 2.4 兆美元營收。儘管規模如此巨大且經過數十年數位化,效率瓶頸仍然存在:清算延遲、昂貴的跨境轉帳、被鎖定的營運資金以及不透明的流程。PayFi 透過即時結算、低成本基礎設施與自動化可程式邏輯解決這些根本性問題。
基礎設施正迅速成熟。穩定幣總市值於 2025 年中達到 2,517 億美元,僅 2024 年 11 月,USDC 月交易量即達 1 兆美元。高效能區塊鏈網絡如 Solana、Stellar 與以太坊 L2 解決方案提供結算層。傳統金融機構(包括黑岩、富達、Visa 與 MoneyGram)均已投資或攜手發展穩定幣基礎設施。美國於 2025 年 7 月通過完整穩定幣立法 GENIUS 法案,為更廣泛採用帶來監管明確性。
應用場景遠超單純價值移轉。跨境匯款手續費可從 6% 及數天延遲,降至 1-2% 近即時結算。供應鏈金融、發票貼現受惠於可編程合約,自動化又平易近人。即時工資提領,讓勞工完成任務便可領薪,而不必等到固定發薪日。商戶可用低於 1% 的手續費(vs 信用卡 2-3.5%)接收即時結算的付款。
亞洲成 PayFi 採用的活躍地區。預計東南亞 2025 年匯款額將達近 1,000 億美元。MoneyGram 攜手 Stellar 於180 多國提供現金與加密貨幣雙向通道,讓穩定幣成為全球數位美元與在地經濟體的橋樑。新加坡、香港、日本的進步監管框架兼顧創新與消費者保障。
機構採用驗證基礎設施已到成熟期。資產管理、支付處理、銀行業者不再只是實驗,正動用資本建構基礎設施,將 PayFi 整合至正式營運系統。機構參與帶來重大經濟變化:可動用資金的加速釋放(float消失)、圍繞流動性提供和可程式化服務的新盈利模式、以及現有業者的競爭格局大幅改寫。
但風險依然存在:智能合約的技術漏洞、穩定幣脫鉤時的經濟不穩、各司法管轄區監管不確定性,以及用戶體驗上的採用瓶頸。 GENIUS 法案雖解決多項監管疑慮,但對全球協同、CBDC互動與 DeFi 整合仍有疑問。
展望未來,預測 2030 年鏈上價值可達 10-25 兆美元。這將是拐點:穩定幣成為標準財庫管理工具、跨境支付徹底轉型、嵌入式金融普及於各大數位平台。至 2035 年,支付全景或將面目全非:全球即時運作、貨幣即時編程流轉、供應鏈自動因應變化,創作者經濟也從傳統批次結算走向持續流動。
市場規模固然重要,但也可能誤導。1.8 千兆美元的年度支付量只是現有市場的規模指標,而 PayFi 的影響遠不僅於此前流量的轉換。它讓過去不可能或不經濟的全新價值流成真:內容微支付、國際自由工作者即時薪酬、可編程營收分潤、即時財庫營運等。這些新能力最終可能超越傳統支付量。
監測以下指標可追蹤進展:穩定幣流通與交易速度、商戶採用率、機構公告、各主要司法管轄區的監管發展,以及傳統支付與 PayFi 替代方案之間的成本-速度差距。這些數據將揭示 PayFi 能否實現其潛力,或遇到無法逾越的障礙。
支付與 DeFi 的融合不僅僅是讓交易更快更便宜(雖然這些改進很重要)。它是要把貨幣本身從僅能靠中介移動的靜態價值儲藏,轉變為可編程、可組合、智能的媒介,能自動執行邏輯、回應情境、在全球無需許可和延遲下持續運作。This is not a crypto story. This is a payments infrastructure story - one that happens to utilize blockchain technology because that technology solves problems traditional infrastructure could not address. The relevance extends to anyone working in finance, payments, treasury management, or commerce. The questions are no longer whether this convergence will occur, but how rapidly it will progress, which use cases will achieve mainstream adoption first, and which participants will lead versus lag the transition.
這不是一則加密貨幣的故事。這是一則支付基礎建設的故事——碰巧運用了區塊鏈技術,因為這項技術解決了傳統基礎建設無法處理的問題。其重要性延伸至所有從事金融、支付、資金管理或商業的人士。現在大家關注的問題已不再是這種融合是否會發生,而是它會以多快的速度推進、哪些應用場景會率先成為主流,以及哪些參與者會引領、哪些會落後於這場轉型。
PayFi is bridging payments and DeFi by unlocking the time-value of money trapped in traditional flows, enabling instant programmable settlement, and connecting the global economy in ways that were previously impossible. For the millions who depend on remittances, the businesses seeking working capital, the treasurers managing global operations, and the creators building sustainable income - PayFi is not abstract technology. It is infrastructure that makes financial services more accessible, efficient, and powerful.
PayFi 正在串連支付與去中心化金融(DeFi),釋放被困於傳統資金流中的時間價值,實現即時且可程式化的結算,並以過去無法想像的方式連結全球經濟。對數以百萬計仰賴匯款的人們、尋求營運資金的企業、管理全球營運的財務主管,以及努力建立穩定收入的創作者來說,PayFi 並非抽象的科技概念,而是讓金融服務更加普及、高效且強大的基礎建設。
The revolution is not coming. It is already here, building momentum, and reshaping the foundations of how value moves through the global economy. The only question that remains is how quickly the transformation will unfold - and who will be prepared to benefit from the change.
這場革命並非即將來臨——它已經發生、正在積聚動能,並重塑價值在全球經濟中流動的基礎。唯一剩下的問題,就是這場轉變會有多快發生,以及誰已經準備好從這股變革中受益。



