經過多年構建愈來愈龐大的單一式鏈,試圖讓一個系統負責所有功能,加密貨幣業界終於意識到:專業化優於全功能化。
正如 Celestia 的 共同創辦人 Mustafa Al-Bassam 所說,加密產業長期受制於一輪又一輪新的單一式智慧合約平台,大家為了更低交易手續費而犧牲去中心化和安全性。Web3 無法在單一式架構下實現大規模擴展。這種認知催生了模組化區塊鏈設計的興起,將核心功能拆分到各專業層,彼此協作,而非在同條鏈中競爭。
這一趨勢在 2023 到 2025 年劇烈加速。Celestia 於 2023 年 10 月上線主網,推出第一個生產可用、利用資料可用性抽樣的資料可用性層。EigenDA 於 2024 年跟進,借助以太坊再質押基礎設施,提供超大規模資料服務。
Avail 則於 2024 年 7 月從 Polygon 生態系誕生,以鏈無關的資料可用性解決方案自居。這些專案針對同一難題提出不同方案:如何為模組化區塊鏈生態系提供基礎設施,而無需每條鏈都從零打造共識、資料儲存和執行層。
其影響不僅限於技術架構。模組化區塊鏈動搖了現有的區塊鏈經濟模型,改變安全假設,並在帶來新機會的同時伴隨全新風險。要理解這一轉型,必須深入探討模組化系統如何運作、為何會出現、解決了哪些痛點,以及引入了哪些取捨。
若要真正理解這項革新,先得認識區塊鏈的發展歷程:從比特幣專注轉帳安全,到以太坊引入通用運算,再到揭示單一式設計極限的第二層擴容解決方案,最終發展到今日能大規模部署的模組化架構。每個階段都建立在上一步的經驗與洞察之上,逐步揭露模組化設計欲克服的侷限。
單一式區塊鏈解析
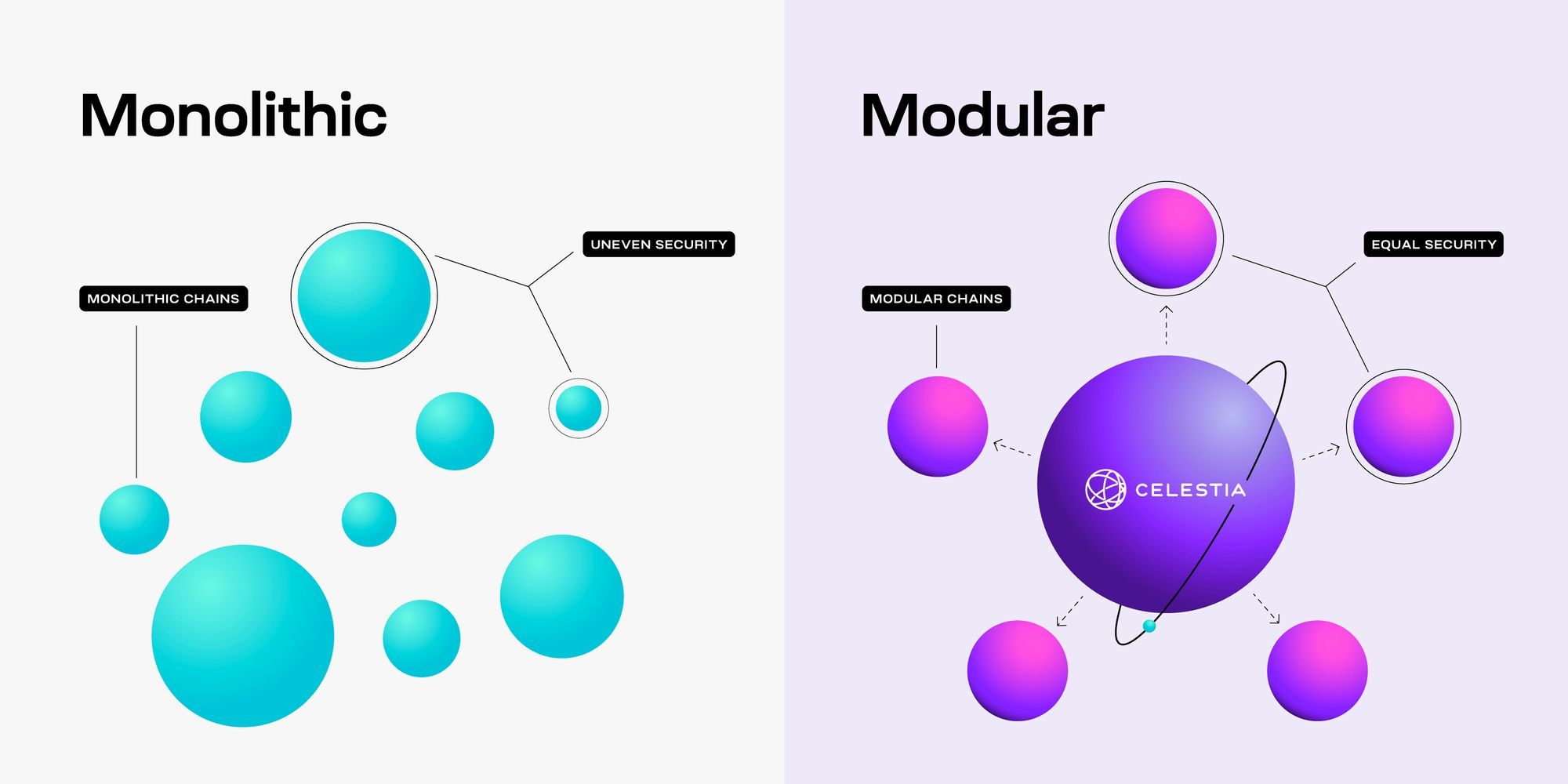
單一式區塊鏈將所有核心功能合而為一,包括執行交易與智慧合約、決定交易排序與有效性的共識、確保資料可用性以方便驗證,以及作為交易最終結算與爭議解決的平台。比特幣、早期以太坊、Solana 都是典型例子。
單一式設計有不少優勢,其中最大的是簡單。所有功能都在一個系統裡,開發者整合問題少,使用者也容易理解。安全性亦受惠於統一設計,同一組驗證者保護所有層,消弭不同元件各自信任機制的疑慮。單一式系統的原子性組合度高,應用和合約可無縫互動無需跨鏈橋接或消息傳遞協議。
比特幣最能展現單一式設計的純粹。它專注於轉帳安全,執行層僅提供簡單指令碼。每個全節點都要下載並驗證全部交易,確保最大化安全和去中心化,代價是效能有限。
比特幣每秒僅能處理約七筆交易,而每當有人嘗試提升這個能力時,就會陷入激烈爭論,因為碰動任何一環都會波及整體。
以太坊在轉向模組化之前,就是一條更複雜的單一式鏈。它負責智慧合約執行、透過權益證明進行共識、管理所有交易資料可用性,以及 L2 的結算地位。這樣才能爆發出眾多去中心化應用與 DeFi,但也出現龐大擴展難題。在需求高峰時期,Gas 費用每筆可飆升至數百美元,讓許多用戶被拒於門外。
Solana 則採取不同路線,優先追求高效能的單一式架構。它運用創新共識機制和平行交易處理,在理想狀況下可突破 50,000 TPS,但也因此提高驗證節點硬體要求,偶爾因過載導致網路中斷。
單一式區塊鏈的根本限制在於擴展性三難題:區塊鏈只能同時最優化去中心化、安全與擴展性其中兩項。將執行、共識、資料可用性全部置於同一系統,必然爭奪資源。要提升吞吐量就得擴大區塊大小,這又增加運營全節點成本、降低去中心化。若維持高度去中心化,就受限於區塊小、吞吐低。維持安全又需大量重複驗證,影響擴展性。
這些侷限隨著主流應用需求成長而越發明顯。2022 年 9 月以太坊轉 PoS 後,能源效率與安全提升,但未解決擴容關鍵。高需求時期,Gas 價仍偏高,吞吐很有限。第二層 Rollup 因此誕生,將交易移至鏈下處理,再將壓縮資料返回鏈上,但仍面臨資料可用性成本瓶頸。
單一式設計也束縛創新。單一鏈上的開發者只能被動接受鏈固有的程式語言、虛擬機、共識機制與費率結構設計。如要建立特定應用鏈,就得另起新鏈、設共識、招募驗證者,全盤自建安全,門檻極高,資金與流動性因此分散在眾多無法互通的體系。
到了 2023 年,單一式設計的限制已明顯無法忽視。Rollup 向以太坊支付的費用,有約 95% 是資料可用性相關。這份低效率提示解方:將原本綁一起的功能拆開,各自最佳化又能相互協作。
模組化區塊鏈:新的設計思維
模組化區塊鏈將傳統鏈的功能分解成獨立的專業層或元件。它不會將執行、共識、結算和資料可用性全部混在同一系統,而是分別授權給專業鏈或服務,各自優化某項功能,再合作實現完整的區塊鏈功能。
此概念靈感來自軟體工程和計算機科學中的模組化設計原則,就如現代程式將呈現層、業務邏輯、資料儲存分開,模組化區塊鏈也將功能切割為不同層級。這種分工讓每一層都能專攻本質,互不妥協。
模組化架構有四個關鍵功能,定位各自不同:執行層負責處理交易和運行智慧合約邏輯,根據用戶動作決定狀態轉換;共識層確保所有節點一致排序和打包交易,維護歷史一致性;資料可用性層則確保所有必需交易資料已公開、可供驗證,即使全節點不需處理所有內容;結算層則提供最終確認和爭議解決,是 Rollup 及其他執行環境的定錨地。
模組化設計並非四層必然分離,有的架構會結合共識和資料可用性,有的則合併結算與共識。重點在於專業分工,而非絕對切割;每個元件應聚焦於其專長,並與其他元件有明確介面協作。
Celestia 是模組化資料可用性層的先驅,2023 年 10 月啟動主網,針對 Rollup 與其他擴展方案亟需穩定、低成本發佈交易資料這一痛點提出解方。在以太坊這類昂貴執行層發佈資料會成為瓶頸,Celestia 以資料可用性抽樣自底重構架構,將執行與共識徹底分離,讓所有構建其上的專案不受執行與結算約束,專心擴展資料可用性。
Celestia 網路本身就是聚焦於共識及資料可用性的極簡區塊鏈。
It does not execute smart contracts or provide a virtual machine.
它不執行智慧合約或提供虛擬機器。
Instead, developers can deploy their own execution layers, whether rollups, application-specific chains, or entirely custom environments, and use Celestia purely for ordering transactions and ensuring their data remains available.
相反地,開發者可以部署自己的執行層,不論是 rollup、特定應用鏈,或是完全自訂的環境,並僅將 Celestia 用於交易排序與確保資料可用性。
Celestia's roadmap targets relentlessly scaling beyond 1 gigabyte per second data throughput, aiming to remove crypto's ultimate scaling bottleneck.
Celestia 的發展路線圖致力於將資料吞吐量規模提升至每秒超過 1 GB,目標是消除加密產業最終的擴充瓶頸。
The technical innovation enabling Celestia's scalability is data availability sampling.
Celestia 能實現高度擴充性的技術創新是資料可用性抽樣(Data Availability Sampling)。
Traditional blockchains require every full node to download all transaction data to verify availability.
傳統區塊鏈要求每個完整節點下載所有交易資料來驗證其可用性。
This creates a direct tradeoff between block size and decentralization.
這導致區塊大小與去中心化之間產生直接的權衡。
Data availability sampling changes this dynamic by allowing light nodes to verify data availability by randomly sampling small portions of each block.
資料可用性抽樣改變了這種狀況,讓輕節點可藉由隨機取樣每個區塊的一小部分來驗證資料的存在。
If the samples are available, nodes can be confident with high probability that all data is available, without downloading everything.
如果這些樣本可取得,節點就能以極高的機率確信所有資料皆可用,而無需下載全部內容。
This enables Celestia to scale data availability as more light nodes join the network, inverting the traditional scaling curve.
這讓 Celestia 能隨著越多輕節點加入網路而提升資料可用性,徹底扭轉傳統的擴充曲線。
Celestia also introduced the concept of sovereign rollups, which are execution layers that use Celestia for data availability and consensus but make their own decisions about execution rules, governance, and upgrades.
Celestia 也引入了「主權 Rollup」的概念,這些執行層利用 Celestia 進行資料可用性與共識,但能自行制定執行規則、治理模式與升級決策。
Unlike Ethereum rollups, which typically inherit security and settlement from Ethereum, sovereign rollups on Celestia operate more independently.
與通常繼承以太坊安全性及結算的以太坊 Rollup 不同,Celestia 上的主權 Rollup 運作更為獨立。
They post their data to Celestia to ensure availability, but they define their own validity conditions and do not rely on an external chain for final settlement.
他們僅將資料發布到 Celestia 以確保可用性,並自行定義有效性規則,不依賴外部鏈進行最終結算。
EigenDA emerged as a different approach to modular data availability, built on top of the EigenLayer restaking protocol.
EigenDA 則提出了另一種模組化資料可用性的方法,其建立於 EigenLayer restaking 協議之上。
EigenDA utilizes an elegant architecture that maintains optimality or near-optimality across the dimensions of performance, security, and cost through Reed Solomon encoding that is cryptographically verified by KZG polynomial opening proofs.
EigenDA 採用優雅的架構,藉由 Reed-Solomon 編碼及 KZG 多項式展開證明的加密驗證,在效能、安全性與成本三方面維持最佳或接近最佳狀態。
Rather than building an independent blockchain like Celestia, EigenDA operates as an actively validated service within the EigenLayer ecosystem, allowing Ethereum stakers to reuse their staked ETH to help secure the data availability layer.
EigenDA 並非像 Celestia 那樣建立獨立區塊鏈,而是在 EigenLayer 生態系中成為主動驗證的服務,讓以太坊質押者能重複利用已質押的 ETH 來協助維護資料可用性層的安全。
The EigenDA architecture separates roles among different participants.
EigenDA 架構將參與者分為不同角色。
Dispersers encode data and distribute it to validator nodes.
Disperser 負責編碼資料並分發給驗證者節點。
Validator nodes attest to data availability and store portions of each data blob.
驗證節點則負責證明資料可用性並儲存每個資料區塊的一部分。
Retrieval nodes collect data shards from validators and reconstruct the original data when needed.
回收節點則從驗證節點收集資料分片,並在需要時重建原始資料。
The network launched with an industry-leading 100 megabytes per second data availability throughput, with a roadmap to scale exponentially.
該網路一開始就達成業界領先的每秒 100MB 資料可用性吞吐量,並計劃持續以指數方式擴大。
This high throughput derives from EigenDA's design, which requires each operator to store only a fraction of the total data while maintaining the ability to reconstruct everything if needed.
如此高吞吐來自 EigenDA 的設計:每位運營者僅需儲存部分總資料,但在需要時仍能重建所有內容。
EigenDA's integration with Ethereum through EigenLayer creates unique security properties.
EigenDA 透過 EigenLayer 與以太坊整合,形成獨特的安全特性。
The protocol leverages billions of dollars in restaked ETH as economic security, inheriting Ethereum's robust validator set while providing specialized data availability services.
該協議利用數十億美金的再質押 ETH 來做為經濟安全性,既能繼承以太坊強大的驗證者機制,又能供應專業的資料可用性服務。
This shared security model reduces the capital cost of securing the data availability layer compared to bootstrapping an entirely independent blockchain.
這種共享安全模式,與自建一條獨立區塊鏈相比,大幅降低資料可用性層的資本成本。
EigenDA also natively uses Ethereum as a settlement layer for operator set management, ensuring enhanced security for layer-two networks that settle to Ethereum.
EigenDA 也將以太坊作為運營者管理的結算層,為需回到以太坊結算的二層網路帶來更高的安全保障。
Avail represents a third major approach to modular data availability, emphasizing chain-agnostic infrastructure and cross-chain interoperability.
Avail 則是第三種主要的模組化資料可用性方案,強調鏈無關基礎建設和跨鏈互通性。
The project's horizontally scalable, chain-agnostic and trust-minimized infrastructure aims to unify the fragmented blockchain ecosystem by providing unlimited blockspace, native interoperability, and modular security.
該項目橫向可擴充、鏈無關且最低信任的基礎設施,旨在提供無限區塊空間、原生跨鏈互通及模組化安全,來統整支離破碎的區塊鏈生態系。
Built using the Polkadot SDK, Avail operates as a specialized data availability blockchain that connects with multiple layer-one ecosystems including Ethereum, Solana, and BNB Chain.
Avail 採用 Polkadot SDK 打造,作為專門的資料可用性區塊鏈,並與多個一層生態 (如以太坊、Solana、BNB Chain)串接。
Avail's architecture consists of three components working together.
Avail 架構由三個協作組件組成。
The data availability layer stores transaction data using erasure coding and KZG polynomial commitments for efficient verification.
資料可用性層利用抹除編碼(Erasure Coding)和 KZG 多項式承諾來有效驗證並儲存交易資料。
The Nexus layer provides trust-minimized cross-chain interoperability, enabling seamless communication between rollups and sovereign chains built on different ecosystems.
Nexus 層提供最低信任度的跨鏈互操作性,使來自不同生態所建立的 rollup 及主權鏈可無縫溝通。
The Fusion layer offers multi-token economic security, allowing the network to be secured not just by Avail's native token but also by ETH, BTC, SOL, and other assets.
Fusion 層實現多代幣經濟安全性,讓網路不僅由 Avail 原生代幣守護,還能用 ETH、BTC、SOL 等資產保障安全。
Avail's data availability layer employs KZG polynomial commitments to cryptographically prove data availability without requiring full downloads, allowing chains like Polygon zkEVM Validium to reduce Ethereum costs by approximately 90 percent while maintaining security.
Avail 的資料可用性層使用 KZG 多項式承諾加密地證明資料存在,無須全部下載,使如 Polygon zkEVM Validium 等鏈可在維持安全的前提下,將以太坊成本降低約九成。
The protocol's emphasis on light client verification enables users to run lightweight nodes on devices like phones or browsers, verifying data availability in seconds without the resource requirements of full nodes.
協議極為重視輕客戶端驗證,用戶能直接在手機或瀏覽器等設備運作輕型節點,於數秒內驗證資料可用性,無須完整節點的高資源開銷。
Each of these projects represents a different philosophy about how modular blockchains should operate.
上述每個項目都展現出對模組化區塊鏈運作模式的不同哲學。
Celestia prioritizes neutrality and sovereignty, allowing any execution environment to build on top without imposing specific settlement or security assumptions.
Celestia 強調中立與主權,讓任何執行環境都可在其之上建構,而不附加特定結算和安全假設。
EigenDA emphasizes deep integration with Ethereum's ecosystem, leveraging restaking to create cost-efficient data availability backed by Ethereum's security.
EigenDA 著重於與以太坊生態的深度整合,利用 restaking 建立以以太坊安全性背書且成本有效的資料可用性服務。
Avail focuses on interoperability and unification, building bridges between different blockchain ecosystems through its Nexus layer.
Avail 則聚焦於互通和統合,透過 Nexus 層在不同區塊鏈生態系間搭起橋樑。
The modular approach has catalyzed rapid innovation in execution layers as well.
模組化方法同樣推動了執行層的高速創新。
Projects like Arbitrum Orbit, Optimism's OP Stack, and Polygon's Chain Development Kit enable developers to deploy custom rollups with minimal effort.
如 Arbitrum Orbit、Optimism 的 OP Stack 以及 Polygon 的 Chain Development Kit,讓開發者可以輕鬆布署自訂的 rollup。
These rollup-as-a-service platforms leverage modular data availability layers for publishing transaction data, allowing development teams to focus on application-specific execution environments rather than rebuilding consensus and data availability infrastructure from scratch.
這些「rollup 即服務」平台,皆運用模組化的資料可用性層來發布交易資料,開發團隊因此能專心於特定應用的執行環境,而不必從零打造共識與資料可用性基礎設施。
Data Availability Layers - The New Backbone
資料可用性層──區塊鏈的新中樞
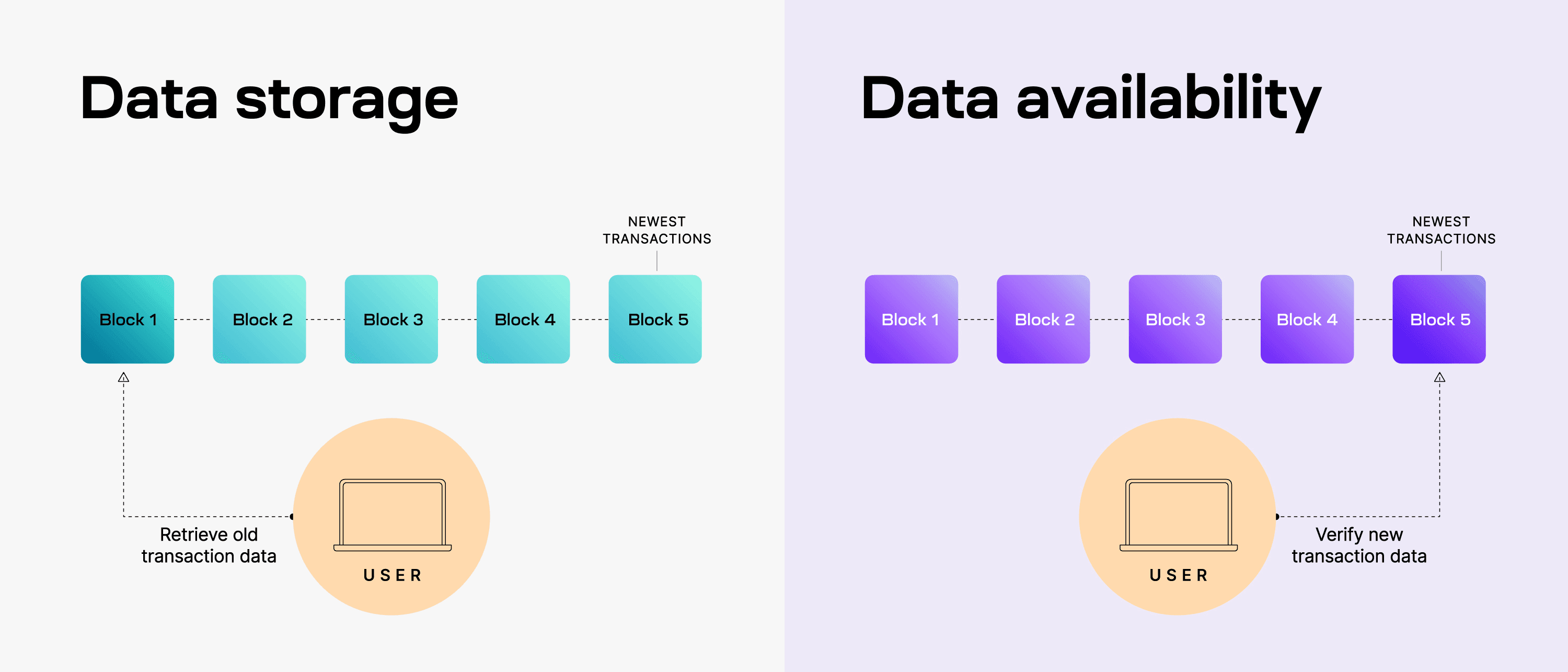
Data availability has emerged as the critical infrastructure bottleneck for blockchain scaling, and understanding why requires examining what data availability means and why it matters.
資料可用性已成為區塊鏈擴展的關鍵基礎設施瓶頸,想明白原因,需先理解什麼是資料可用性,以及它為何重要。
When a blockchain produces new blocks containing transactions, the data availability problem asks: how can the network ensure that all the transaction data in those blocks is actually available to anyone who needs it for verification, without requiring every participant to download and store everything?
當區塊鏈產生新區塊並包含眾多交易時,「資料可用性問題」即在於:網路如何確保這些區塊中的所有交易資料,能夠真正讓需要驗證的任何人取得,而無須每位參與者都下載並存儲全部資料?
In traditional monolithic blockchains, solving data availability is straightforward but expensive.
傳統單體式區塊鏈解決資料可用性的方法雖直接,卻極為昂貴。
Every full node downloads every block and stores all the data. If a node can download it, the data must be available.
每個完整節點都要下載每個區塊、存儲全部資料。若節點能成功下載,則可斷定資料確實存在。
This approach provides maximum security but creates significant scaling limitations.
這種做法帶來最高安全性,但也導致重大擴展限制。
As blocks get larger to accommodate more transactions, running a full node becomes more expensive, reducing decentralization.
若為容納更多交易而放大區塊,運行完整節點的成本會大增,進而削弱去中心化。
The cost of storing all this data on a high-security blockchain like Ethereum makes data availability the dominant expense for layer-two rollups.
像以太坊這樣高安全區塊鏈的資料儲存成本,讓資料可用性成為二層 Rollup 的主要資本支出。
The problem becomes more complex in modular architectures where execution happens in one place and data is stored in another.
在模組化架構下,執行層與資料儲存層分離,使問題更加複雜。
A rollup processes thousands of transactions off-chain, but it must publish the transaction data somewhere so that anyone can reconstruct the rollup's state and verify its correctness.
rollup 雖可在鏈外處理上千筆交易,但必須將交易資料發布於某處,使其他人能重新構造 rollup 狀態並驗證正確性。
If the rollup operator withholds data, users cannot detect invalid state transitions, creating a vulnerability.
若 rollup 操作方隱藏資料,使用者便無法發現無效的狀態變更,產生安全漏洞。
Data availability layers exist to solve this problem: providing a place to publish transaction data with cryptographic guarantees that the data is available, at a lower cost than posting everything to an execution layer.
資料可用性層正是為了解決此問題而生,提供一個具加密保證的資料發布場所,讓資料以比發布到執行層更低的成本確保可用。
Celestia's approach to data availability centers on data availability sampling, a technique that fundamentally changes the relationship between block size and verification cost.
Celestia 處理資料可用性的關鍵手段就是「資料可用性抽樣」,這一技術根本改變了區塊大小與驗證成本的關係。
In traditional blockchains, doubling the block size doubles the amount of data each full node must download.
傳統區塊鏈只要區塊大小倍增,每個完整節點的下載量也會倍增。
But with data availability sampling, light nodes can verify that data is available by sampling small random portions of each block.
有了資料可用性抽樣,輕節點僅針對每個區塊隨機抽取少量數據驗證資料是否可用即可。
Through erasure coding and clever cryptographic techniques, Celestia enables nodes to gain confidence in data availability without downloading everything.
透過抹除編碼與精妙的加密技巧,Celestia 讓節點無需全數下載便能對資料可用性建立高信心。
The process works through several steps.
這個流程包含數個步驟。
First, block producers take the transaction data and encode it using a two-dimensional Reed-Solomon encoding scheme.
首先,區塊生產者將交易資料用二維 Reed-Solomon 編碼處理。
This encoding adds redundancy to the data, expanding it beyond its original size but enabling reconstruction even if significant portions are missing.
這種編碼會將資料冗餘化,雖然資料量會增加,但即使有不少內容散失,也能重建。
The encoded data is organized into a matrix and committed to using KZG polynomial commitments, which provide succinct cryptographic proofs about the data's structure.
編碼後的資料會排列成矩陣,再用 KZG 多項式承諾做出簡要的密碼學證明,以確保資料結構。
Light nodes then randomly sample small portions of this extended data.
輕節點便可隨機取樣這組擴充後資料的一小部分。
Each sample includes a proof that the sampled data is part of the committed block.
每個樣本都附帶證明該資料確屬於已承諾的區塊。
By collecting multiple random samples, light nodes can become confident with high probability that the entire data matrix is available.
只要累積足夠隨機樣本,輕節點便能以極高機率確信整個資料矩陣皆可用。
The mathematics ensures that if the block producer withholds any significant portion of the data, light nodes will likely detect this through failed samples.
數學確保:若區塊生產者藏起資料一大部分,輕節點將很可能藉由驗證取樣失敗,即時察覺資料被扣留。
Importantly, the confidence level increases with more light nodes, as each performs independent random sampling.
重要的是,參與的輕節點越多,信心度越高,因每個節點都是獨立隨機取樣。
This creates a unique scaling property: Celestia becomes more secure as more participants join the network.
這帶來獨特的擴充特性:越多人參與,Celestia 就越安全。
Celestia's data availability layer costs approximately 64 percent less than Ethereum, with average costs of around $7.31 per megabyte compared to Ethereum's $20.56.
Celestia 的資料可用性層,成本比以太坊低約六成四,平均每 MB 約 $7.31,而以太坊則為 $20.56。
The project's SuperBlobs feature further reduces fees to approximately $0.81 per megabyte, enabling cost-effective high-volume
該項目的 SuperBlobs 功能更將費用降至每 MB 約 $0.81,大幅提升大量資料用途的經濟效益。
data processing for rollups. These economics make Celestia attractive for rollups and other scaling solutions that need to publish large amounts of data.
Skip translation for markdown links.
對於 Rollups 的資料處理。這些經濟模式讓 Celestia 對於需要發布大量數據的 Rollups 以及其他擴容解決方案極具吸引力。
技術實現上,Celestia 採用了命名空間 Merkle 樹(namespaced Merkle trees),能將資料依照不同應用分門別類到各自的命名空間。這使得每個利用 Celestia 的 Rollup 或區塊鏈,都可以在自己的命名空間中發布資料,而輕客戶端(light client)僅需下載並驗證與他們關心的鏈相關的資料。Rollup 監控自己的命名空間時,無需處理其他共享同一 Celestia 區塊的 Rollup 的資料,從而提升效率但仍維持共享安全性。
EigenDA 以不同的架構方式來處理資料可用性,強調極致的可擴展性,其特色是基於 operator 的架構。該協議設計為橫向擴展,意即網絡中運營者(operator)越多,整體吞吐量就越大。在 100 個節點的私有測試中,EigenDA 展現出每秒高達 10 兆字節(MB/s)的吞吐量,並計畫未來擴展至每秒 1 千兆字節(GB/s)。
EigenDA 系統通過糾刪碼(erasure coding)將資料分割成資料塊(chunks),再分散存放於大量 operator 之間。每個 operator 僅需存儲全部資料的一小部分,但透過編碼設計,只要有足夠的區塊子集就能重建出完整資料。這種分佈方式減輕了單一 operator 在儲存與頻寬上的負擔,同時藉由密碼學證明維持資料可用性的保障。
KZG 承諾(KZG commitments)在 EigenDA 的驗證系統中扮演關鍵角色,和 Celestia 一樣。這類多項式承諾技術讓證明資料屬性時無需透露全部內容。例如,在 disperser 編碼並分發資料區塊時,它會產生 KZG 承諾,使驗證者可以在不看到所有其他資料塊的情況下檢查自己區塊的正確性。這大幅提升驗證效率,並維持強大的安全性保證。
EigenDA 背後的經濟模型,則採用 EigenLayer 的再質押(restaking)機制。已在 Ethereum 上質押 ETH 的驗證者可以選擇額外執行 EigenDA 的軟體,以協助保護 EigenDA,從而賺取 Rollups 及其他資料可用性層用戶的報酬。這種再質押做法有幾個優勢:
它降低了保護網絡的資本成本,因為同一份質押同時保障 Ethereum 和 EigenDA 的安全性。EigenDA 可直接沿用以太坊的去中心化驗證者,而無需自行從零建立。也直接將 Ethereum 的安全經濟利益連結到 EigenDA 的可靠性上。
節點運營者必須至少質押 32 ETH 或 1 EIGEN 代幣,才能成為資料可用性網絡的成員。但由於像 EigenDA 這類積極驗證服務(AVS)需遷移到 operator 集合並指定具體slashing條件,所以協議的懲罰規則(slashing conditions)仍在持續開發中。這些懲罰機制的持續演進,展現了再質押安全模型帶來的創新與動態變化。
Avail 採取另外一種資料可用性路徑,強調維持強健安全性的同時,促進不同區塊鏈生態系的互操作性。該協議的資料可用性層同樣採用 KZG 承諾與糾刪碼,與 Celestia 和 EigenDA 類似,但更進一步地結合了跨鏈基礎設施的長遠藍圖。
Avail 網絡藉由基於 Polkadot SDK 構建的驗證者共識機制,來保障資料可用性。驗證者對包含多條 Rollup 或鏈交易資料的區塊達成共識,然後開放這些數據供驗證。輕客戶端可透過抽樣方式(sampling)驗證資料可用性,和 Celestia 的方式相近。Avail 的輕客戶端讓用戶端層級的交易驗證極為快速,預先確認可做到約 250 毫秒的交易驗證,速度是傳統方式的 15 倍。
Avail 的特殊之處在於其多代幣質押模型(multi-token staking)與 Nexus 跨鏈互通層。Avail 不僅限於使用原生代幣來保障安全,而是允許用戶用 ETH、BTC、SOL 等主要資產質押。這種多代幣設計致力於吸引更多不同公鏈社群的流動性與經濟安全性。Nexus 層則作為去信任化的跨鏈協調樞紐,讓建立於不同生態的 Rollups 與鏈,得以無需中心化橋樑展開互動。
這些資料可用性層的技術基礎,源自幾項共通的創新:糾刪碼透過冗餘擴展資料,即使部分丟失也能恢復;KZG 多項式承諾可提供資料屬性的簡潔證明;資料可用性抽樣(DAS, Data Availability Sampling)讓輕客戶端毋須下載全部數據也能驗證資料可用性。這些技術的結合實現了可擴展且可驗證的資料可用性。
但具體實作上仍有重要差異。Celestia 著重中立性與主權 Rollup,讓任意執行環境都能在其之上建構,無須對結算層有特定假設。EigenDA 注重與以太坊的深度整合和以再質押為主的安全模型。Avail 則側重跨鏈互操作和多生態支援。這些理念差異,影響了從經濟結構、治理模式到所吸引的應用類型等各個面向。
資料可用性層已成為推動模組化區塊鏈擴展的關鍵基礎設施。當資料可用性變得充足、可驗證且低廉,這些協議也釋放出更多執行層實驗創新設計的可能性,同時仍維持安全特性。現在的選擇題,已從「是否採用模組化資料可用性」轉為「哪種路徑最契合特定應用需求」。
執行層與結算層(Execution and Settlement Layers)
雖然資料可用性層是模組化區塊鏈的基石,但執行層與結算層才決定了交易如何被處理與最終確認。理解這些組件之間的關係,才能掌握模組化系統的完整架構,以及開發者在建構可擴展區塊鏈應用時所面臨的設計抉擇。
執行層負責處理交易與智能合約的運算。在模組化架構中,執行可發生於專為特定用途最佳化的運行環境中,而非傳統通用且單一的主鏈。Rollup 正是這種模式的代表,將交易脫鏈於各自專屬的執行環境處理,將壓縮後的資料發布至資料可用性層進行驗證。
目前主流的 Rollup 可分為兩大類:Optimistic Rollup(如 Arbitrum 與 Optimism),假設交易預設皆為有效,僅在有人提交欺詐證明時才進行檢查。這種模式提升效率,但也導入了一個挑戰期,通常長達七天,期間用戶提領資金需等待。Zero-knowledge Rollup(如 StarkWare 和 zkSync),則以密碼學證明保證交易正確執行。這類 Rollup 可立即完成結算,無需挑戰期,但需要更高階的密碼學運算和更複雜的證明生成。
這兩種 Rollup 都能藉由模組化資料可用性層降低成本。不需再以每 MB 20 美元甚至更高的費用將全量資料上鏈(如以太坊),可選擇將資料發佈到 Celestia 或 EigenDA,以極小成本達到同樣效果。由於資料仍可供驗證,Rollup 的安全屬性也得以維持,但經濟模型卻大幅變得更有利。2024 年 3 月以太坊實施 EIP-4844 的 Dencun 升級後,由於 Blob 交易降低了數據上鏈費用,layer-2 Rollup Base 交易量因此暴增 224%。
執行層的架構靈活性正是模組化區塊鏈的最大優勢之一。開發者可自行客製化程式語言、虛擬機器、Gas 價格結構與治理機制,無需自架通用型大型鏈。
舉例來說,遊戲類應用可能會追求高吞吐量與低延遲;去中心化金融協議則會重視安全與形式驗證;供應鏈應用可能會優化資料隱私與合規要求。每種應用都能部署專屬的執行環境,同時共用一致的共識與資料可用性基礎設施。
結算層則為 Rollup 與其他執行環境提供最終性以及來源真相。以太坊成為模組化區塊鏈生態中主流的結算層,特別是針對 Rollup。當 Rollup 完成一批交易處理時,會將壓縮資料提交至資料可用性層並向以太坊發出狀態更新。對 Optimistic Rollup 而言,這個狀態更新在挑戰期結束且無效欺詐證明後成為最終結果。對 Zero-knowledge Rollup,則會附帶有效性證明,經以太坊驗證即刻達到最終性。
將執行層與結算層分割帶來重要權衡。一方面,Rollup 能在各自的執行環境快速且低成本地處理大量交易;另一方面,最終結算於以太坊則確保了強大的安全與可組合性,用戶在 Rollup 及以太坊之間資產橋接時需待結算層最終性,與全程在單一鏈上的操作相比多了一些等待與摩擦。
有些模組化架構完全避免使用外部結算層。例如 Celestia 的主權 Rollup(sovereign rollups),會定義……(未完)their own validity conditions and settlement mechanisms. They use Celestia purely for data availability and consensus, handling settlement internally. This approach maximizes sovereignty and flexibility but requires each rollup to establish its own security properties and bridge mechanisms for interacting with other chains.
他們有自己的有效性條件和結算機制。這些 Rollup 僅將 Celestia 作為數據可用性和共識層使用,並在內部處理結算。這種做法最大化了主權和彈性,但也要求每個 Rollup 必須建立自身的安全屬性,以及跨鏈互動時的橋接機制。
The rise of rollups-as-a-service platforms has accelerated modular blockchain adoption by simplifying deployment. These platforms provide templates and tooling for launching custom execution environments without deep blockchain engineering expertise.
Rollups-as-a-service 平台的興起透過簡化布署流程加速了模組化區塊鏈的採用。這些平台提供範本與工具,無需深厚的區塊鏈工程知識即可啟動自定義執行環境。
Arbitrum Orbit allows developers to deploy layer-three rollups that use Arbitrum for settlement and can choose between multiple data availability options including Celestia and EigenDA. The Optimism OP Stack provides a modular framework where developers can swap out components like the execution environment, data availability layer, and sequencing mechanism while maintaining compatibility with the broader Optimism ecosystem.
Arbitrum Orbit 允許開發者部署以 Arbitrum 為結算層的第三層 Rollup,並能選擇包括 Celestia、EigenDA 在內的多種數據可用性選項。Optimism OP Stack 則提供一個模組化框架,讓開發者可替換執行環境、數據可用性層和序列機制等元件,同時維持與更廣泛 Optimism 生態系的相容性。
Conduit and AltLayer offer rollup-as-a-service solutions enabling deployment of fully-managed, production-grade rollups in just a few clicks, with integration options for EigenDA data availability. These platforms abstract much of the complexity involved in operating blockchain infrastructure, allowing developers to focus on application logic and user experience.
Conduit 和 AltLayer 提供 Rollup 即服務解決方案,開發者只需幾個步驟即可部署全託管、可用於生產環境的 Rollup,並支援整合 EigenDA 數據可用性。這些平台大幅抽象化了操作區塊鏈基礎設施的複雜度,使開發者能更專注於應用邏輯及使用者體驗。
Polygon's Chain Development Kit represents another approach, enabling developers to build customizable layer-two chains that can connect to Ethereum or operate more independently. The modular architecture supports various execution environments, data availability providers, and bridge mechanisms. Projects like Immutable X use these tools to build application-specific chains optimized for NFT trading and blockchain gaming.
Polygon 的 Chain Development Kit(CDK)則是另一種路線,讓開發者能打造可自訂的 Layer 2 鏈,可與以太坊連接,或較為獨立運行。模組化架構支援多元的執行環境、數據可用性供應商及橋梁機制。像 Immutable X 等專案就利用這些工具來構建針對 NFT 交易和鏈遊戲最佳化的應用專用鏈。
The proliferation of execution layers enabled by modular architecture creates both opportunities and challenges. On the positive side, developers gain unprecedented flexibility to optimize for specific use cases. Gaming applications can achieve sub-second block times. Privacy-focused applications can integrate zero-knowledge proofs deeply into their execution. Enterprise solutions can incorporate permissioned elements where needed. Each execution environment can experiment with novel approaches without requiring consensus from the broader blockchain community.
模組化架構帶來執行層的激增,這既帶來了機會,也帶來挑戰。優點是開發者可前所未有地針對特定用途進行最佳化。例如,遊戲應用能達到次秒級區塊時間;重視隱私的應用可將零知識證明深度整合進執行層;企業級解決方案可納入授權管理。每個執行環境都能嘗試創新做法,無需整體區塊鏈社群共識。
However, this flexibility also introduces fragmentation. Liquidity becomes divided across numerous execution layers. Users must bridge assets between chains, introducing friction and security risks. Applications that want to compose across multiple execution environments face increased complexity. The unified composability of monolithic blockchains gives way to a more fragmented landscape where interoperability becomes paramount.
然而,這種彈性也會帶來分散化。流動性分散在眾多執行層之間;使用者需跨鏈橋接資產,產生摩擦與安全風險;希望跨多個執行環境組合功能的應用將變得更加複雜。單體區塊鏈的統一組合性讓位於更分散化的版圖,鏈間互通性因而變得至關重要。
Cross-chain communication protocols have emerged to address these challenges. The Inter-Blockchain Communication protocol, originally developed for Cosmos, enables different chains to exchange messages and transfer assets trustlessly. Hyperlane and LayerZero provide similar functionality with different security models and tradeoffs. These protocols aim to create a world where applications can span multiple execution environments, accessing liquidity and users across the modular blockchain ecosystem.
跨鏈通訊協議因應這些挑戰而誕生。最初為 Cosmos 所開發的 IBC(跨區塊鏈通信協議),讓不同鏈可無信任地交換訊息和資產。Hyperlane 和 LayerZero 提供類似功能,但安全架構和權衡各異。這些協議目標是創造一個能跨多個執行環境運行的應用世界,讓其能存取整個模組化區塊鏈生態的流動性和用戶。
The relationship between execution and settlement layers also influences economic models. In monolithic chains, users pay fees directly to validators who secure the network. In modular systems, fees flow through multiple layers. A user executing a transaction on a rollup pays fees to the rollup's sequencer. The rollup pays fees to the data availability layer for posting data. The rollup also pays fees to the settlement layer for submitting state updates and storing commitments. This multi-layered fee structure creates complex economic dynamics and opportunities for optimization.
執行層與結算層之間的關係也會影響經濟模型。在單體鏈上,用戶直接向保護網路的驗證者支付手續費;在模組化系統中,費用會流經多個層級。例如,用戶在 Rollup 上發送交易需支付費用給該 Rollup 的排序器。Rollup 再將費用付給數據可用性層,用於數據上鏈;同時還要向結算層付費,用以提交狀態更新與儲存承諾。多層級的收費結構帶來複雜的經濟動態,也創造出優化空間。
Sequencers play a critical role in modular execution layers. These entities collect transactions from users, order them into blocks, and submit batches to data availability and settlement layers. Most rollups currently operate with centralized sequencers, introducing concerns about censorship resistance and single points of failure. The industry is actively developing decentralized sequencing mechanisms, including shared sequencing protocols that allow multiple rollups to coordinate block production and provide stronger ordering guarantees.
排序器在模組化執行層中扮演關鍵角色。這些實體從用戶收集交易、排序成區塊,並批次提交至數據可用性及結算層。多數 Rollup 目前仍採用中心化排序器,引發關於審查阻力和單點故障的疑慮。業界正積極研發去中心化排序機制,包括允許多個 Rollup 共同協作產生區塊並加強排序保證的共用排序協議。
The execution and settlement architecture continues evolving rapidly. Some projects experiment with asynchronous execution, where transactions process without immediately finalizing. Others explore parallel execution environments that can process non-conflicting transactions simultaneously. The separation of concerns in modular systems enables experimentation at the execution layer without requiring changes to underlying data availability or consensus mechanisms, accelerating the pace of innovation.
執行與結算架構仍在快速演進中。有些專案探索非同步執行,讓交易能在未即時最終定案的情況下處理;另有專案嘗試平行執行環境,以便同時處理不衝突的交易。模組化系統的職責分離,讓執行層可以不必更改底層數據可用性或共識機制,就能大膽實驗,大幅加快創新步伐。
Economic and Security Tradeoffs
Modular blockchain architectures introduce new economic models and security assumptions that differ fundamentally from monolithic chains. Understanding these tradeoffs is essential for evaluating the viability and risks of modular systems as they scale to support mainstream blockchain adoption.
模組化區塊鏈架構引入了全新、與單體鏈截然不同的經濟模型和安全假設。理解這些權衡對於評估模組化系統在擴展以支援主流區塊鏈應用時的可行性和風險至關重要。
The security model for modular blockchains depends on how components interact and where trust assumptions lie. In a monolithic chain, a single validator set secures all functions. If the validators are honest, the entire system remains secure. In modular systems, different layers may have different security mechanisms, creating a stack of trust assumptions that must be carefully analyzed.
模組化區塊鏈的安全模型取決於各元件如何互動,以及信任假設的落點。在單體鏈中,一組驗證者保護所有功能,只要驗證者誠實,整個系統就安全。而在模組化系統中,不同層級可能擁有不同的安全機制,導致信任假設層層堆疊,亟需審慎分析。
Consider a typical modular architecture: a rollup for execution, Celestia for data availability, and Ethereum for settlement. The security of this system depends on all three layers functioning correctly. If the rollup's sequencer acts maliciously, users must rely on fraud proofs or validity proofs submitted to the settlement layer. If Celestia withholds data, the rollup cannot prove what transactions occurred. If Ethereum's validator set gets corrupted, final settlement becomes unreliable.
以一個典型的模組化架構為例:執行層用 Rollup、數據可用性用 Celestia、結算層用以太坊。該系統的安全性取決於這三層都正常運作。若 Rollup 排序器惡意行為,用戶則得仰賴提交到結算層的欺詐證明或有效性證明。若 Celestia 扣留數據,Rollup 將無法證明發生哪些交易。若以太坊的驗證者組被攻破,最終結算也將變得不可靠。
Shared security models, like those implemented by EigenDA through restaking, aim to reduce these compounding trust assumptions. By allowing Ethereum validators to secure multiple services simultaneously, restaking creates stronger alignment between the settlement layer and other modular components. As of March 2025, EigenDA has 4.3 million ETH staked, representing billions of dollars of economic security backing the data availability layer. This substantial stake provides meaningful security guarantees, but it also introduces new risks around slashing conditions and the potential for cascading failures if vulnerabilities are discovered.
共用安全模型(如 EigenDA 所推行的再質押)旨在降低這些複雜的信任假設。透過讓以太坊驗證者同時保護多項服務,再質押可強化結算層與其他模組組件間的利益對齊。至 2025 年 3 月,EigenDA 已有 430 萬顆 ETH 質押,相當於數十億美元的經濟安全支撐其數據可用性層。如此鉅額質押帶來實質安全保障,同時也引入關於懲罰機制與漏洞導致連環失敗的全新風險。
The economic incentives in modular systems create interesting dynamics. Data availability layers compete on throughput and cost, with Celestia, EigenDA, and Avail each offering different price-performance tradeoffs. EigenDA cut its data availability service prices by 10 times and introduced a free tier in August 2024, while aiming to boost data availability on Ethereum by 1,000 times to enable use cases including fully onchain order books, real-time gaming, and decentralized artificial intelligence. This price competition benefits rollups and application developers but raises questions about the sustainability of data availability layer business models.
模組化系統的經濟誘因帶來了有趣的動態。數據可用性層彼此在吞吐量與成本上競爭,Celestia、EigenDA、Avail 各自有不同的價效組合。EigenDA 在 2024 年 8 月將其數據可用性服務費率降到原本十分之一並推出免費方案,同時力圖讓以太坊的數據可用性提升 1,000 倍,以支援全鏈訂單簿、即時遊戲和去中心化 AI 等應用。這場價格戰有利於 Rollup 與應用開發者,但也引發數據可用性層營運模式是否永續的疑問。
Revenue flows in modular systems differ significantly from monolithic chains. In Ethereum, users pay gas fees that go to validators and are partially burned, creating deflationary pressure on ETH. In a modular ecosystem, users pay fees to rollup sequencers, who pay fees to data availability layers and settlement layers. The distribution of value across these layers remains uncertain, and it is unclear which components will capture the most value long-term.
模組化系統的收益流向與單體鏈大不相同。在以太坊,用戶支付的 Gas 費用會流向驗證者,並有部分被銷毀,進而產生對 ETH 的通縮壓力。而在模組化生態中,用戶先向 Rollup 排序器支付費用,排序器再轉付給數據可用性層和結算層。至於價值在各層之間如何分配,以及哪些組件最終能抓住最大價值,目前都還不明朗。
The tokenomics of modular data availability layers reflect different approaches to value capture. Celestia's native TIA token is used to pay for data availability and to secure the network through staking. The token's value depends on demand for Celestia's data availability services and the security required to protect them.
模組化數據可用性層的通證經濟設計反映其不同的價值捕捉方式。Celestia 的原生 TIA 代幣用於支付數據可用性費用與網路質押安全,其價值直接受 Celestia 服務需求及安全門檻影響。
EigenDA operates within the EigenLayer ecosystem, where restakers earn rewards in various tokens for securing actively validated services. Avail's token model incorporates multi-asset staking, allowing participation with ETH, BTC, and other major cryptocurrencies alongside its native AVAIL token.
EigenDA 則運作於 EigenLayer 生態系中,讓再質押者因參與不同服務的驗證而獲得多元代幣獎勵。Avail 的代幣模型結合多資產質押,除了原生 AVAIL,還可用 ETH、BTC 等主流加密貨幣參與。
The cost efficiency of posting data to specialized data availability layers versus general-purpose execution layers represents one of modular blockchains' most compelling economic advantages. Ethereum's block space is expensive because it serves multiple purposes: executing smart contracts, securing the network, and storing data. Specialized data availability layers can optimize purely for data throughput and verification, achieving much higher throughput at lower cost.
將資料發布於專用數據可用性層相比於通用執行層的高成本,是模組化區塊鏈最吸引人的經濟優勢之一。以太坊區塊空間價格昂貴,因用途包含執行智能合約、網路安全與資料儲存。專用的數據可用性層則可專注最佳化資料吞吐與驗證,實現更高吞吐量與更低成本。
However, this cost advantage depends on maintaining sufficient demand for data availability services. If few rollups adopt modular data availability, the economies of scale that make these services cheap may not materialize. Network effects matter significantly in determining which data availability layers gain adoption and become economically viable.
但這項成本優勢前提是有足夠數量的 Rollup 採用模組化數據可用性。若採用者太少,難以形成規模經濟,服務也就難以持續便宜。網絡效應將極大影響哪些數據可用性層能被廣泛採納並成為有經濟價值的存在。
The security of data availability layers themselves raises important considerations. Celestia relies on its own proof-of-stake validator set, which must be sufficiently decentralized and economically secured to resist attacks. An attacker who controls enough stake could potentially withhold data or censor specific transactions. The protocol mitigates this through data availability sampling and economic incentives, but the security ultimately depends on the cost of attacking
數據可用性層本身的安全性也是一大考量。Celestia 依賴其自有權益證明驗證者組,須高度去中心化且經濟利益到位才能抵禦攻擊。攻擊者若擁有足夠質押,可能會扣留數據或審查特定交易。協議透過數據可用性抽樣與經濟誘因來降低風險,但最終安全性還是取決於攻擊成本。the network exceeding the potential gain.
網路超過潛在收益。
EigenDA inherits security from Ethereum's validator set through restaking but introduces new risks. If a vulnerability in EigenDA leads to slashing of restaked ETH, validators suffer losses that could cascade through the Ethereum ecosystem. The shared security model connects the fate of multiple systems, potentially amplifying failures.
EigenDA 透過再質押(restaking)從以太坊的驗證者集合(validator set)繼承安全性,但同時也帶來新的風險。如果 EigenDA 出現漏洞導致再質押的 ETH 被懲罰(slashing),驗證者將蒙受損失,而這些損失可能在以太坊生態系中產生連鎖效應。共享安全模型將多個系統的命運連結在一起,可能會放大失敗的影響。
While slashing is enabled at the EigenLayer protocol level, individual actively validated services like EigenDA must activate it by migrating to operator sets and defining slashing conditions. Currently, no slashing condition is in place for misbehaving EigenDA nodes. This ongoing development of slashing mechanisms reflects both the innovation and the unresolved challenges in restaking-based security.
雖然在 EigenLayer 協議層級啟用了懲罰(slashing)機制,但像 EigenDA 這類主動驗證的服務必須遷移至運營者集(operator set)並定義懲罰條件才能啟用 slashing。當前,對於行為不當的 EigenDA 節點,尚未實施任何懲罰條件。這項懲罰機制的持續發展,反映出再質押安全創新的同時也帶來尚未解決的挑戰。
Liveness guarantees represent another critical security consideration. A data availability layer must remain operational and responsive for rollups depending on it to function. If Celestia, EigenDA, or Avail experiences prolonged downtime or censorship, rollups using these services cannot post new data, effectively halting their operation. This creates single points of failure that differ from the distributed nature of monolithic chains, where consensus failure is less likely due to fewer dependencies.
活性(liveness)保證是另一個關鍵的安全考量。數據可用性層必須持續運作並保持回應,讓依賴它的 rollup 能正常運作。如果 Celestia、EigenDA 或 Avail 發生長時間停機或遭遇審查,使用這些服務的 rollup 就無法上傳新數據,實際上會被迫停止運作。這導致單點故障的風險,與單體區塊鏈分散架構相比,後者由於依賴較少,產生共識失敗的機率較低。
The relationship between execution layers and settlement layers introduces additional security considerations. Rollups that settle to Ethereum inherit aspects of Ethereum's security, particularly for finality and dispute resolution. Sovereign rollups that avoid external settlement gain more autonomy but must establish their own security guarantees and bridge mechanisms. Neither approach is strictly superior; the choice depends on the application's specific requirements and risk tolerance.
執行層與結算層之間的關係也帶來額外的安全議題。與以太坊結算的 rollup 可繼承以太坊的部分安全性,特別是在最終性和爭議解決方面。選擇自主(sovereign)但不對外結算的 rollup,則獲得更多自主權,但必須自行建立安全保證與跨鏈機制。兩者並無絕對優劣,適用方案端視應用的特定需求與風險承受度而定。
Fragmentation poses both economic and security challenges in modular ecosystems. When liquidity and users are distributed across numerous rollups and execution environments, each individual system may lack the network effects and security that concentrated activity provides. Cross-chain bridges connecting these fragmented systems introduce additional attack vectors and have been responsible for some of the largest hacks in blockchain history, with billions of dollars stolen from poorly secured bridge contracts.
碎片化在模組化生態系中帶來經濟與安全上的挑戰。當流動性與用戶分散到眾多 rollup 和執行環境,各個系統可能缺乏集中活動所帶來的網路效應與安全保障。將這些碎片化系統連結起來的跨鏈橋樑,會導入更多攻擊途徑,並且已釀成區塊鏈史上一些最大的駭客事件——數十億美元因安全措施不足的橋樑合約而遭竊。
Interoperability solutions like Avail's Nexus layer and protocols like the Inter-Blockchain Communication standard aim to reduce fragmentation risks by providing trust-minimized communication between chains.
像 Avail 的 Nexus 層這樣的互操作解決方案,以及像 Inter-Blockchain Communication(IBC)標準這類協議,目標都是透過去信任化的鏈間通訊來降低碎片化風險。
Avail's Nexus layer serves as a permissionless coordination hub enabling seamless cross-rollup and sovereign chain communication, addressing the growing need for unified infrastructure as blockchain ecosystems multiply. However, these solutions are relatively new and untested at scale, and their security properties require careful analysis.
Avail 的 Nexus 層是一個無需許可(permissionless)的協作樞紐,可實現跨 rollup 和主權鏈的無縫通訊,回應區塊鏈生態系日益增長的統一基礎設施需求。然而,這些解決方案相對新穎,尚未經過大規模驗證,其安全特性仍需仔細評估。
The economic sustainability of modular blockchain ecosystems depends on achieving sufficient adoption to justify the infrastructure costs. Data availability layers require large validator sets or operator networks to provide decentralization and redundancy. Settlement layers must maintain high security to serve as trusted arbitration points. If revenue from rollups and applications proves insufficient to sustain these infrastructure layers, the modular approach may fail to achieve its scaling potential.
模組化區塊鏈生態系的經濟可持續性,取決於能否獲得足夠採用來支撐基礎設施成本。數據可用性層需要龐大驗證者或運營者網路來提供去中心化與冗餘機制。結算層則必須維持高安全性,以作為值得信賴的仲裁基礎。若 rollup 與應用帶來的收益不足以支撐這些基礎設施層級,模組化方法將難以發揮其擴展潛力。
Market dynamics will ultimately determine value distribution across modular components. If data availability becomes commoditized with multiple providers offering similar services at razor-thin margins, these layers may capture little value despite being critical infrastructure. Alternatively, if network effects create winner-take-most dynamics, dominant data availability and settlement layers could accrue significant value while execution layers remain relatively undifferentiated.
市場動態最終將決定模組各組件的價值分佈。如果數據可用性成為商品化,多家供應商提供類似服務但利潤微薄,即便這些層是關鍵基礎設施,可能也難以捕捉大量價值。反之,若網路效應促成贏家通吃的局面,主導型的數據可用性與結算層將累積大量價值,而執行層則可能缺乏差異化。
The security and economic tradeoffs of modular blockchains require ongoing evaluation as the ecosystem matures. Early evidence suggests that specialization improves efficiency and reduces costs, but the long-term sustainability and security properties of highly modular systems remain open questions. The industry is essentially running a large-scale experiment in distributed system design, with billions of dollars at stake and the future architecture of Web3 infrastructure hanging in the balance.
模組化區塊鏈的安全與經濟權衡,隨著生態系成熟,必須持續評估。初步證據顯示,專業化能提升效率並降低成本,但高度模組化系統長期的可持續性與安全特性仍有待觀察。目前整個產業基本上正進行一場分散系統設計的大型實驗,數十億美元利害攸關,Web3 基礎設施的未來架構也將因此定調。
Impact on Existing Chains
對現有鏈的影響
The rise of modular blockchain architecture poses significant strategic challenges for established monolithic chains. Networks that built their value propositions around being complete, self-contained systems now face competition from specialized components that may perform individual functions more efficiently. The responses from major blockchain platforms reveal different philosophies about how blockchain infrastructure should evolve.
模組化區塊鏈架構的崛起,對現有單體鏈(monolithic chain)帶來了極大戰略挑戰。過去以「完整、自足系統」為價值主張的區塊鏈,如今面臨來自專業化組件之競爭,這些組件在單項功能上可能更為高效。主流區塊鏈平台的回應,展現出對基礎設施演進方向的各異哲學。
Ethereum's evolution toward a modular architecture represents perhaps the most significant validation of the modular thesis. The network that pioneered smart contract platforms has systematically restructured itself to serve as the settlement and security layer for an ecosystem of rollups rather than trying to handle all execution on layer one. This transformation was not inevitable; it emerged from pragmatic recognition that scaling execution on a single layer while maintaining decentralization proved infeasible.
以太坊轉向模組化架構,也許是對模組化論述最具說服力的實踐。這個率先創建智慧合約平台的網絡,已系統化調整改造自身,從原本要在第一層處理所有執行,轉型為服務 rollup 生態系的結算與安全層。這樣的變化並非必然,而是務實認知到在單一層級上維持去中心化的同時擴展執行能力,行不通。
The roadmap toward modular Ethereum accelerated with several key upgrades. The Merge to proof of stake in September 2022 improved energy efficiency and security but did not directly address scaling. The critical scaling upgrade came with the Dencun hard fork in March 2024, which implemented EIP-4844, also known as proto-danksharding. EIP-4844 introduces blob-carrying transactions, enabling rollups to post large, temporary data chunks to Ethereum's consensus layer at dramatically reduced cost compared to permanent calldata storage. The upgrade slashed layer-two transaction fees by 10 to 100 times, boosting scalability while preserving decentralization.
以太坊邁向模組化的路線因多次重大升級而加速。2022 年 9 月「The Merge」合併至權益證明(PoS)後,能源效率及安全性提升,但未直接解決擴容問題。2024 年 3 月的 Dencun 硬分叉,實現了 EIP-4844(即 proto-danksharding),帶來關鍵擴容。EIP-4844 引入可攜帶 blob 的交易,使 rollup 能以遠低於永久 calldata 儲存的成本,將大量臨時數據片段提交至以太坊共識層。這次升級讓 layer-2 交易費用降低 10 至 100 倍,提升可擴展性,同時保有去中心化。
Proto-danksharding represents an interim solution on the path toward full danksharding, which would expand data availability from six blobs per block to 64 blobs, enabling throughput approaching 100,000 transactions per second across the rollup ecosystem. The technical approach mirrors elements of Celestia's design, using KZG commitments and erasure coding to enable data availability sampling. Rather than compete with modular data availability layers, Ethereum is becoming one, providing native data availability services optimized for its rollup ecosystem.
Proto-danksharding 是邁向完整 danksharding 的過渡解法,最終目標是將每區塊的數據 blob 容量從 6 個提升到 64 個,使整個 rollup 生態系的吞吐量逼近每秒 100,000 筆交易。此技術方案類似 Celestia 的設計,運用了 KZG 承諾(commitment)和抹除編碼(erasure coding)來實現數據可用性抽樣。以太坊不僅不與模組化數據可用層競爭,而是成為其中一員,針對 rollup 生態系,提供原生的數據可用性服務。
This strategic pivot acknowledges that Ethereum's value lies not in executing every transaction on layer one, but in providing trusted settlement and coordination for a diverse ecosystem of execution environments. Rollups like Arbitrum, Optimism, StarkNet, and zkSync process the vast majority of transactions, while Ethereum layer one serves as the canonical source of truth and arbiter of disputes. The network's token economics are evolving to reflect this role, with fees from rollup settlements contributing to ETH burn and validator rewards.
這項戰略轉向,意識到以太坊的價值並非在第一層執行每一筆交易,而是作為一個多元執行環境生態系的信任結算層與協調中心。Arbitrum、Optimism、StarkNet、zkSync 等 rollup 處理絕大多數交易,而以太坊 L1 則扮演「真相唯一來源」及爭端裁決者的角色。其代幣經濟學也逐步調整,rollup 結算所產生的費用為 ETH 燒毀與驗證者獎勵貢獻收入。
Ethereum's modular transformation creates both opportunities and risks. On one hand, the network benefits from increased activity across its rollup ecosystem without the scaling constraints of processing everything on layer one. On the other hand, as execution moves to rollups and data availability potentially shifts to alternatives like Celestia or EigenDA, the question arises: what value does Ethereum layer one capture, and is it sufficient to sustain the network's security?
以太坊的模組化轉型帶來新機會,也帶來新風險。一方面,網絡可因 rollup 生態活動激增而受益,無需遭受 L1 全部執行的擴容限制。另一方面,隨著執行移至 rollup,數據可用性可能也轉向 Celestia、EigenDA 等替代方案,問題就出現了:以太坊 L1 還能捕捉多少價值?這些價值足以維繫整個網絡的安全性嗎?
The emergence of rollup-centric Ethereum has sparked debate about whether the network is becoming primarily a settlement layer or maintaining its role as the computational backbone of Web3. Some argue that Ethereum's value proposition strengthens as it focuses on what it does best: providing robust security and finality for a diverse ecosystem. Others worry that offloading too much activity to external layers could diminish Ethereum's centrality and value capture.
以 Rollup 為核心的以太坊興起,引發網路究竟是變成「主要的結算層」還是仍扮演 Web3 計算骨幹的爭論。有些人認為,專注於自己最擅長的——為多元生態系提供穩健安全性與最終性——以太坊的價值主張會更強。但也有人擔憂,若過多活動外包至外部層,恐削弱以太坊的核心地位與價值捕獲能力。
Solana represents a contrasting approach, doubling down on the monolithic high-performance model. The network prioritizes achieving maximum throughput on a single layer through aggressive optimization of consensus mechanisms, parallel transaction processing, and hardware requirements. Solana's perspective holds that the complexity and fragmentation of modular systems introduce friction that undermines user experience and composability.
Solana 則採取迥異策略,堅持單體高效能模式。此網絡致力於在單一層優化共識機制、平行處理交易和提升硬體要求,以追求極致吞吐。Solana 認為,模組化系統的複雜與碎片化會引入摩擦,損及用戶體驗和可組合性。
Solana's architecture achieves impressive throughput, regularly processing thousands of transactions per second with sub-second finality. The network's proponents argue that this performance, combined with the simplicity of a unified execution environment, provides a better foundation for applications than the fragmented landscape of modular blockchains. Gaming, high-frequency trading, and other latency-sensitive applications may indeed benefit from the tight integration and atomic composability that monolithic chains provide.
Solana 架構能達到驚人的吞吐量,常態處理每秒數千筆交易,並以次秒級實現最終性。網絡支持者主張,這種效能加上統一執行環境的簡單性,比模組化區塊鏈破碎的生態系更適合應用開發。遊戲、高頻交易和其他注重延遲的應用,的確可能從單體鏈的緊密整合與原子級可組合性中獲益。
However, Solana's approach comes with acknowledged tradeoffs. The network's hardware requirements for validators are significantly higher than Ethereum's, potentially limiting decentralization. The network has experienced several outages when transaction volume overwhelmed the system, raising questions about the practical limits of monolithic scaling. These challenges suggest that even high-performance monolithic chains face constraints that modular architectures might circumvent.
但 Solana 的做法也有缺點。其驗證者硬體需求遠高於以太坊,可能影響去中心化程度。該網絡在交易量激增時亦多次當機,讓人質疑單體擴展的實際極限。這些挑戰顯示,即使是高效能單體鏈,也難以避免模組化架構有望規避的樽頸。
The competitive dynamic between monolithic and modular approaches extends beyond technical considerations to ecosystem effects and developer mindshare. Ethereum's pivot toward modular infrastructure has catalyzed an explosion of rollup deployments and experimentation with novel execution environments. This proliferation of chains creates opportunities for innovation but also fragments liquidity and attention. Solana's unified environment provides
(原文到此處為止,未完待續。)Here’s the translation in zh-Hant-TW, following the requested formatting (skipping translation for markdown links):
簡單但客製化彈性較低。
Avalanche 以其子網(subnet)架構佔據了中間地帶,讓開發者能夠部署自訂區塊鏈,同時享有整個 Avalanche 生態系的安全性與互通性。子網可以自訂虛擬機、手續費結構,以及驗證人集合,並和其他 Avalanche 鏈保持相容。這種做法在緊密整合的生態系中融入模組化原則,試圖在彈性與整合間取得平衡。
子網模式在維持不同鏈之間強協調與共享安全的同時,也允許適當地方進行客製化,因此解決了一些純模組化系統的限制。不過,子網仍需擁有各自的驗證人集合與安全性,這點與直接從結算層繼承安全性的 rollups 有所區別。這種架構呈現於全單體整合與完全模組化分解的光譜間另一個選擇。
Cosmos 透過其跨鏈通訊協議(Inter-Blockchain Communication Protocol)及 Tendermint 共識機制,率先提出應用專屬區塊鏈的概念。Cosmos 生態向來擁抱模組化,讓專業化鏈可以透過標準化協議進行溝通。如今許多 Cosmos 鏈採用 Celestia 提供數據可用性,展現成熟生態如何融合模組化組件提升效率。
Cosmos 強調主權與互通性,而非共享安全。每條鏈都擁有自己專屬的驗證人組與安全模型,但透過標準通訊協議允許資產轉移與消息傳遞。這種理念和以 rollup 為核心的以太坊不同,後者的執行層繼承自結算層的安全,但兩者都共享模組化的專業化與協調原則。
Near Protocol 則透過其衍生專案 Nuffle Labs(以 1,300 萬美元資金啟動)進軍模組化數據可用性領域。Near 選擇不直接與自家 Layer-1 競爭,而是將定位轉為為更廣泛的模組化生態提供基礎設施。這個策略性的轉型反映出成熟平台已認識到,能夠提供專業化服務、而不是堅守單體架構,就能積極參與模組化浪潮。
模組化架構對現有鏈的影響,也延伸到代幣經濟學和價值捕獲。隨執行層和數據可用性移向專屬層,價值究竟累積在哪裡成為關鍵問題。在單體鏈裡,使用者直接向驗證人支付手續費,價值流動明確。而在模組化系統中,手續費會在多個層分配,長遠下來哪些組件能捕獲最多價值仍存變數。
像以太坊這類結算層,可能會因強網路效應受惠,因為 rollup 多會選擇在其他 rollup 已經結算的地方結算以實現可組合性。數據可用性層則更直接比拼價格及效能,可能導致商品化。執行層則可能透過應用專屬最佳化形成差異,但同時由於 rollup 即服務平台讓部署變簡單,也會面臨激烈競爭。
可見單體與模組化方法在可預見的未來會共存。不同應用有不同需求,沒有單一架構能兼顧所有使用場景。高吞吐量的遊戲應用可能偏好 Solana 的低延遲和簡單性。複雜的去中心化金融協議則可能重視以太坊 rollup 的安全和去中心化。企業用戶可能會偏好模組化基礎設施上應用專屬鏈的客製化彈性。
競爭格局最終很可能不會由純粹的技術優越決定,而是由生態效應、開發者體驗、流動性集中度與法規考量綜合影響。區塊鏈基礎設施目前仍處於早期階段,讓多種架構方式都有機會發展壯大,各自可於特定應用與社群中取得產品-市場契合。
區塊鏈設計的未來
區塊鏈架構的發展趨勢指向日益複雜的模組化系統,但多個未解決問題將影響這段演進過程。推動模組化區塊鏈的技術創新已相當成熟,但要讓模組化生態蓬勃發展,所需的經濟模型、治理結構與社會協作機制仍在建構中。
隨著專案開始實踐技術基礎,專業化、可組合區塊鏈相互連結的願景變得愈加清晰。開發者現在可以視需求選擇各種組件:從相容 EVM 的 rollup 到自訂虛擬機的執行環境,提供不同安全/成本取捨的數據可用性層,以及呈現不同終局性和可組合性的結算層。這種彈性造就了單體時代所沒有的創新與客製化機會。
所謂模組化堆疊的概念,更延伸至整體應用平台。部分專案正建立讓開發者能在數分鐘內啟動應用專屬鏈的開發框架,包括選擇數據可用性提供者、共識機制、虛擬機和橋接協議等標準選項。這種將複雜性抽象化的做法,有望降低進入門檻與加速區塊鏈普及。
然而,模組化的未來仍面臨數項重大挑戰。雖然像 IBC、Hyperlane 及 LayerZero 這類協議有所進展,但執行層間相容性仍不完美。這些系統雖然能夠實現跨鏈訊息傳遞與資產轉移,但用戶體驗仍有不少障礙,難以媲美單一體系。如何兼顧安全與去中心化,同時實現無縫互通,仍是一個持續的難題。
跨鏈通信也引入了安全風險,且這些風險已被攻擊者利用。連接不同鏈的橋接合約,曾成為區塊鏈史上一些最大駭客事件的目標。隨著模組化生態系下數十、上百條執行層湧現,跨鏈攻擊的攻擊面隨之擴大。推動跨鏈基礎設施的安全標準與最佳實踐,對於實踐模組化願景極為關鍵。
模組化組件之間的價值捕獲問題,也將大幅影響生態發展。如果數據可用性成為低利潤的商品服務,這些關鍵基礎設施的經濟可持續性可能受威脅。若結算層憑網路效應捕獲過多價值,模組化的紅利將集中在少數平台,而非廣泛分配。如何打造正確的經濟激勵機制,既推動創新又確保各組件持續發展,是不可迴避的課題。
治理則是模組化生態系的另一重大挑戰。單體鏈治理相對單純:同一社群能透過既定機制決策協議升級。但在模組化系統中,一個組件的變動可能影響他處,需要跨多個治理流程協調。例如,數據可用性層升級其共識機制會影響所有使用它的 rollup,結算層調整手續費結構也將波及所有結算之鏈。如何建立既能刺激創新,又能維持多組件間穩定協作的治理框架,是未解挑戰。
監管變因也讓模組化區塊鏈的未來更添不確定性。全球當局正在制定監管數位資產與區塊鏈的框架,但這些通常假設系統為單體鏈、且可明確識別受規對象。模組化系統由於應用橫跨多條鏈和基礎設施層,使合規更為複雜。管轄權、合規責任,以及故障時的法律責任等問題至今多未有定論。
根據目前發展路徑,模組化區塊鏈的擴展潛力看來極具規模。Celestia 路線圖瞄準每秒超過 1GB 數據吞吐量的擴充,EigenDA 也預計隨營運者數量成長可實現類似水平。以太坊全面開放 danksharding 後,目標讓其 rollup 生態能支撐每秒 10 萬筆交易。這些數字按理推測,長久以來作為瓶頸的數據可用性,或可於未來幾年內大致獲解決。
但光提升吞吐量僅是擴展的一部分。真正進入主流尚需無縫用戶體驗、明確監管、以及與現有金融及社交系統整合。模組化鏈必須證明其所帶來的複雜性,能為用戶和開發者帶來實質價值,而非僅止於架構上的理論改善。
也不排除模組化僅是區塊鏈設計的過渡階段。如單體鏈為解決擴展瓶頸而發展為模組化,未來創新可能帶來超越當前模組設計的新架構。例如零知識證明、新型共識機制、分散式系統的突破,也許會再定義區塊鏈的可能型態。
已有研究者探索如全同態加密等激進創意,該技術允許在加密資料上進行運算,或可徹底解決資料隱私與安全問題...
(翻譯至文末段落斷句處,如果需要接續後面內容,請再提供。)availability problems simultaneously. Others are investigating consensus mechanisms that achieve finality faster than current approaches, reducing the need for layered architectures. Quantum-resistant cryptography may eventually require redesigning core protocols. The pace of innovation in blockchain technology remains rapid enough that architectural paradigms could shift again in coming years.
同時,有人正在研究能夠比現有方式更快達到最終性(finality)的共識機制,這有助於減少對多層架構的需求。抗量子密碼學最終可能會要求核心協議重新設計。區塊鏈技術的創新速度依然迅速,未來幾年,架構範式可能會再一次發生轉變。
The relationship between decentralization and performance continues to evolve in ways that challenge assumptions underlying both monolithic and modular designs. Data availability sampling demonstrates that some traditional tradeoffs can be circumvented through clever cryptography and protocol design. Future innovations might reveal other ways to achieve seemingly incompatible properties, potentially enabling new architectural patterns.
去中心化與性能之間的關係,依然以挑戰單體與模組化設計基本假設的方式發展。資料可用性抽樣(data availability sampling)顯示,某些傳統上的權衡其實可以透過聰明的密碼學與協議設計來避免。未來的創新可能揭示更多達成看似不相容屬性的途徑,並可能催生全新的架構模式。
The vision of a modular blockchain internet - where diverse execution environments interoperate seamlessly over shared data availability and settlement infrastructure - represents a compelling possible future for Web3. Such an ecosystem would support tremendous diversity in application design while maintaining interoperability and shared security. Developers could build exactly the chain they need for their use case, users could move value and identity across chains without friction, and the ecosystem as a whole would benefit from specialization and optimization.
模組化區塊鏈網路的願景——不同的執行環境可以在共享的資料可用性與結算基礎設施上無縫互通——構成了Web3極具吸引力的未來可能性。這樣的生態系統能夠在維持互通性和共享安全性的同時,促進應用設計的高度多樣化。開發者可以建構最契合自身需求的鏈,使用者可以在不同鏈之間無縫轉移價值與身份,整個生態也會受益於專業化與最佳化。
Realizing this vision requires solving numerous technical, economic, and social challenges. But the progress in recent years suggests that the modular approach addresses real problems in ways that monolithic architectures cannot. The projects implementing modular infrastructure - Celestia, EigenDA, Avail, and others - have demonstrated technical viability and attracted significant adoption. The question shifts from whether modular blockchains can work to how they will be integrated into the broader blockchain landscape.
要實現這一願景,需要解決眾多技術、經濟與社會層面的挑戰。但近年來的進展顯示,模組化路線以單體架構難以做到的方式,實際解決了許多問題。像Celestia、EigenDA與Avail等模組化基礎設施專案,已證明其技術的可行性並吸引大量採用。因此,問題的焦點已不是「模組化區塊鏈可不可行」,而是「它們將以何種方式融入更廣闊的區塊鏈生態」。
The future likely involves a heterogeneous ecosystem where multiple architectural approaches coexist. Monolithic chains will continue serving use cases where their properties provide advantages. Modular systems will enable experimentation and customization at scales impossible in unified chains. Hybrid approaches will combine elements of both paradigms. The diversity of approaches reflects the reality that blockchain technology is still early enough that no single architecture has proven optimal for all purposes.
未來,很可能會出現多種架構路徑並存的異質生態系統。單體鏈依然會服務於其架構優勢明顯的場景;模組化系統則能讓開發者在規模與客製化上做出以往不可想像的嘗試。混合式架構則整合了兩大範式的元素。這種多元格局反映出——區塊鏈技術仍處於早期階段,目前尚未有單一架構能滿足所有用途。
Final thoughts
The emergence of modular blockchain architecture represents a fundamental reconceptualization of how decentralized systems should be built. After more than a decade of monolithic chains that bundle all functions into single systems, the industry has recognized that specialization and modularity unlock scaling potential impossible within unified architectures. The shift from monolithic to modular design is not merely a technical evolution but a philosophical transformation in how blockchain infrastructure is conceived.
模組化區塊鏈架構的出現,代表著對去中心化系統建構方式的根本再思考。經過超過十年的單體鏈嘗試——將所有功能綁定於單一系統——產業逐漸意識到,只有走向專業分工與模組化,才能釋放出單一架構無法實現的擴展潛力。從單體到模組化的轉變,不只是一項技術演進,而是在基礎設施理念層面的重大轉型。
Celestia, EigenDA, and Avail exemplify different approaches to modular data availability, each addressing the critical infrastructure bottleneck that has constrained blockchain scaling. By separating data availability from execution and settlement, these protocols enable rollups and application-specific chains to operate efficiently without bearing the full cost of running independent monolithic systems. The economics are compelling: data availability costs drop by orders of magnitude, throughput increases dramatically, and developers gain flexibility to customize execution environments for specific use cases.
Celestia、EigenDA與Avail各自以不同方式實現模組化資料可用性,針對限制區塊鏈擴展的關鍵基礎設施瓶頸提出解方。這些協議將資料可用性與執行、結算分離,使rollup及專用鏈能在無需負擔單體系統運營過高成本的情況下高效運作。其經濟效益極為顯著——資料可用性成本大幅下降、吞吐量劇增,開發者也獲得針對不同用途自訂執行環境的彈性。
The modular approach does not eliminate the scalability trilemma so much as it reframes the problem. Rather than forcing every blockchain to make identical tradeoffs between decentralization, security, and scalability, modular systems allow different layers to optimize for different properties. Data availability layers focus on throughput and verification efficiency. Settlement layers prioritize security and finality. Execution layers customize for specific application requirements. The combination achieves properties that no single layer could deliver alone.
模組化方法並非徹底解決了可擴展性三難問題,而是重新詮釋了這個難題。它不再強迫每條鏈都必須在去中心化、安全性與可擴展性之間做同樣的權衡,而是讓各層可針對特定屬性最佳化。資料可用性層專注於提升吞吐量與驗證效率,結算層則強調安全性與最終性,執行層能根據具體應用場景調整。這些組合出的系統性質,是單一層次難以達成的。
But modularization introduces new challenges. The security model becomes more complex when multiple components must work correctly for the system to remain safe. Economic incentives must align across layers to ensure sustainable operation. Interoperability between execution environments remains imperfect despite progress on cross-chain communication protocols. Governance becomes more complicated when changes to one component affect many others. These challenges are not insurmountable, but they require careful attention as the ecosystem matures.
然而,模組化也帶來新的挑戰。當系統安全性需仰賴多個組件協同正確運作時,整體安全模型變得更加複雜。經濟誘因必須跨層一致,以保證可持續營運。即使跨鏈通信協議已取得進展,執行環境間的互操作性仍不完美。管理模型也更複雜,單一模組的更動可能影響多個組件。這些挑戰雖非不可克服,卻需要隨著生態成長被審慎處理。
The question of whether modular blockchains represent the endgame for blockchain architecture or another transitional phase remains open. The technical innovations enabling modular systems - data availability sampling, zero-knowledge proofs, erasure coding, polynomial commitments - have proven powerful and robust. The economic models are still evolving, with uncertain value distribution across components and sustainability questions about commodity infrastructure layers.
模組化區塊鏈究竟是終極架構,還是又一過渡階段,這問題目前仍無定論。支撐模組化系統的技術創新——如資料可用性抽樣、零知識證明、消除編碼、函式承諾(polynomial commitments)——都已被證明強大穩健。經濟模型則仍在演進,組件間的價值分配以及基礎層可否可持續,仍有許多未知。
What appears certain is that modular design has permanently expanded the design space for blockchain systems. The experiments enabled by modular infrastructure - sovereign rollups, application-specific chains, novel virtual machines, customized consensus mechanisms - would be impossible or impractical within monolithic constraints. This flourishing of innovation, even if some experiments fail, benefits the broader ecosystem by exploring possibilities that pure monolithic approaches cannot access.
可以確定的是,模組化設計已經永久擴展區塊鏈系統的設計空間。模組化基礎設施所啟發的各種實驗——如主權型rollup、客製化專用鏈、新型虛擬機、特殊共識機制——在單體制約下根本不可能實現。此種創新百花齊放,即使有些實驗失敗,亦可助於整個生態探索單體體系難以觸及的可能性。
Established chains are adapting to the modular wave in different ways. Ethereum is restructuring itself as the settlement and security layer for a rollup ecosystem, implementing proto-danksharding to provide native data availability. Solana continues doubling down on monolithic performance, arguing that simplicity and composability outweigh modular flexibility. Cosmos and Avalanche incorporate modular principles within cohesive ecosystems, attempting to balance customization with integration. This diversity of approaches reflects genuine uncertainty about optimal architectures and suggests that multiple paradigms will coexist.
現有區塊鏈正以不同路徑回應這波模組化浪潮。以太坊將自身重塑為rollup系統的結算與安全層,推動proto-danksharding,以實現原生的資料可用性。Solana則持續強化單體效能,主張架構簡單與組合性比模組靈活性來得更重要。Cosmos與Avalanche則試圖在緊密生態內導入模組化原則,力求整合度與客製化兼顧。這些不同做法反映了目前對於最佳區塊鏈架構的真正不確定性,也預示多種範式將共存。
The impact of modular blockchains extends beyond technical architecture to economic models, governance structures, and the fundamental question of how value accrues in Web3 infrastructure. If data availability commoditizes, will the economic incentives suffice to maintain robust infrastructure? If settlement layers capture disproportionate value through network effects, will execution layers remain viable? How will governance coordinate across interconnected but independent components? These questions will shape the modular ecosystem's evolution in coming years.
模組化區塊鏈的影響不僅限於技術層面,也涵蓋經濟模型、治理架構,以及Web3基礎設施中價值如何流動這個根本議題。如果資料可用性趨於「商品化」,原有經濟誘因是否足以維持穩健的基礎設施?若結算層因網路效應而攫取過多價值,執行層還能持續發展嗎?要如何實現跨組件的治理協同?這些問題將牽動模組化生態在未來數年的走向。
The infrastructure being built today - data availability layers, settlement protocols, execution frameworks, interoperability solutions - forms the foundation for the next generation of blockchain applications. These modular components enable possibilities that were economically or technically infeasible in the monolithic era. Fully onchain gaming with complex state transitions. Decentralized social networks with high-throughput data posting. Sophisticated DeFi protocols spanning multiple execution environments. Real-time applications requiring sub-second finality. The technical capacity to support these use cases at scale is increasingly available.
如今正構建中的基礎設施——資料可用性層、結算協定、執行框架、互通解決方案——為下一代區塊鏈應用奠定了地基。這些模組化組件,使過去無法經濟或技術實現的應用成為可能:支援複雜狀態轉換的完全上鏈遊戲、支援高吞吐資料發佈的去中心化社群網路、跨多種執行環境的複雜DeFi協定,以及需要次秒級最終性的即時應用。大規模支撐這些應用的技術能力正在逐步到位。
Whether modular blockchains fulfill their promise of enabling mainstream Web3 adoption depends on more than technical capacity. User experience must improve to the point where the underlying complexity becomes invisible. Regulatory frameworks must evolve to accommodate distributed modular systems. Economic incentives must align to sustain critical infrastructure. Security must be proven robust against sophisticated attacks. Social coordination must scale to manage governance across interconnected components.
模組化區塊鏈能否真正兌現推動主流Web3採用的承諾,取決於的不只是技術能力。用戶體驗必須改善到足以隱藏底層複雜性;監管制度亦須進化以適應分布式模組化體系;經濟誘因要同步,才能維護關鍵基礎設施的運作;安全性需證明可承受複雜攻擊;而組織協調也要能隨生態擴大,妥善處理跨組件的治理問題。
The projects pioneering modular infrastructure are conducting a large-scale experiment in distributed system design. The outcome will determine not just which specific protocols succeed but what architectural patterns define blockchain infrastructure for decades. The early evidence suggests that modular designs address real constraints in ways monolithic architectures cannot, but the full implications will only become clear as the ecosystem matures and faces challenges that cannot be anticipated today.
這些開拓模組化基礎設施的專案,本質上是在進行分散式系統設計的大型實驗。這場實驗的結果,不只關係到哪些協議會勝出,更將決定未來數十年區塊鏈基礎設施會擁有哪些架構模式。目前的初步證據顯示,模組化設計確實以單體體系做不到的方式解決了許多實際瓶頸;但這場變革的全部意義,仍需隨著生態發展、面對更多新挑戰後,才能逐漸顯現。
Modular blockchains have moved from theoretical concept to production infrastructure supporting billions of dollars in value and millions of transactions daily. Celestia, EigenDA, Avail, and related projects provide the data availability backbone for an expanding ecosystem of execution layers. Ethereum's modular transformation validates the approach at the highest level of the industry. The question is no longer whether modular architectures are viable but how they will evolve and what role they will play in the broader blockchain landscape.
模組化區塊鏈已經從理論概念,成長為支撐每日數百萬筆交易、數十億美元價值流轉的生產級基礎設施。Celestia、EigenDA、Avail等計劃已成為不斷擴張的多執行層生態的資料可用性骨幹。以太坊的模組化轉型也從產業最高層證明此路線的可行性。如今,問題已不是模組化架構可不可行,而是它將如何演變、並在更廣大的區塊鏈體系內扮演什麼角色。
The transformation from monolithic to modular blockchains reflects maturation of the industry's understanding of distributed system design. Early blockchains necessarily bundled functions together, as the knowledge and tooling for modular architectures did not yet exist. As the technology advanced and scaling constraints became apparent, the possibility of separating concerns emerged. Now, with modular infrastructure deployed and operational, the industry can build the diverse, specialized, interconnected blockchain ecosystem that many have long envisioned.
從單體到模組化的轉型,反映了業界對分散式系統設計理解的成熟。早期區塊鏈因缺乏模組架構相關知識與工具,不得不將所有功能綑綁在一起。隨著技術進步,擴容瓶頸浮現,分層分工的可能性逐步展開。如今,模組化基礎設施已經落地,產業終於可以建構過去一直嚮往的多樣化、專業化、互聯互通的區塊鏈生態。
The future of blockchain design remains uncertain, but the direction is clear: toward greater specialization, more flexible architectures, and systems optimized for specific purposes rather than attempting to serve all functions equally. Modular blockchains embody this
區塊鏈設計的未來雖仍充滿變數,但發展方向明確:專業分工更明顯、架構更具彈性、各系統追求針對性最佳化,而非硬要兼顧所有功能。模組化區塊鏈正是這一方向的具體實踐。evolution, and their success or failure will shape Web3 infrastructure for years to come. The foundation has been built. The experiment is underway. 這些實驗的成敗將在未來數年內深刻影響 Web3 基礎設施的發展。基礎已經建立,實驗正在進行中。The implications will unfold as the ecosystem grows, faces challenges, and continues innovating toward the vision of a truly scalable, decentralized internet. 隨著生態系統的成長、面對挑戰,並持續創新邁向真正可擴展、去中心化的網際網路願景,其影響也將逐步展開。





