Binance — 全球最大的加密貨幣交易所 — 於週一宣布,已全面開放比特幣「選擇權寫入」權限給所有用戶。實際上,這代表 Binance 上的日常交易者,現在除了買入選擇權外,也能賣出比特幣的買權(Call)和賣權(Put)。以往這類進階策略,僅限於機構或高階用戶。Binance 此舉正逢散戶對複雜交易工具的需求顯著升溫,已不再只追求單純的買進持有策略。
「加速加密貨幣普及會帶動對更多高階流動性能工具的需求,我們致力於建構更完整的衍生品產品線支援用戶,」Binance 產品副總裁 Jeff Li 就此擴展表示。
寫入(出售)選擇權,等於交易者成為選擇權買方的對手方——本質上是為他人提供價格波動「保險」。寫權者收取買方預付的權利金,但必須承擔極端市場波動的風險。如 Binance 所述,賣出買權或賣權,即如同為比特幣價格多空擺盪售出保險。如果市場未超過選擇權履約價(Strike Price),寫權者可將權利金作為利潤;反之,若行情超出,寫權者則需依契約補足差額(或交割標的資產)。
風險管理:考量賣出選擇權的風險不小,Binance 採取多重嚴謹措施。用戶需通過適合度評估以確認其充分理解選擇權交易,並需提供保證金作為潛在損失擔保。這些措施能防止用戶過度槓桿或承擔無法負荷的風險。據官方說法,平台所有選擇權合約皆完全保證金(以穩定幣結算),且具備明確到期日(每日、每週、每月及每季,皆於 UTC 08:00 結算)。
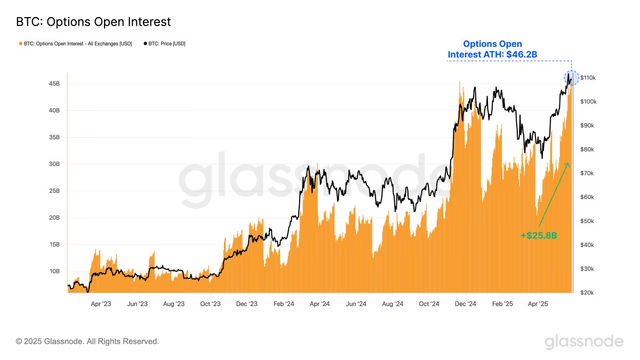
Binance 此舉正值加密選擇權市場爆發性成長階段。根據 Binance 的新聞稿,比特幣選擇權總交易量從 2020 年的 41.1 億美元,激增至 2025 年 6 月約 1,387.6 億美元,五年暴漲超過 3200%。機構與散戶參與帶動衍生品市場的高度發展,只做買方以外,「寫權」讓更多投資人可「表達市場觀點、控管風險、賺取權利金、執行複合策略」。
為激勵參與,Binance 針對新選擇權合約(BTC、ETH、BNB、SOL)推出 20% 手續費折扣,降低早鳥用戶交易成本。針對機構與大額交易者,平台同步升級選擇權增強計畫,降低參與門檻並提供更具吸引力的費率。這些激勵措施展現 Binance 以親民與高性價比搶佔加密選擇權市場版圖的雄心。
總結來說,Binance 全面開放比特幣選擇權寫權功能,對加密交易生態為一大進展,讓進階選擇權策略不再只是專業人士的遊戲,也彰顯了加密衍生品的成熟與成長。但什麼是比特幣選擇權?交易者又如何運用這類工具?本文將進一步拆解比特幣選擇權的基礎原理、運作方式,以及相關交易與控管風險與追求獲利的關鍵策略。
什麼是比特幣選擇權?
比特幣選擇權是一種衍生性契約,賦予持有人於特定日期前,有權但無義務以預定價格買進或賣出指定數量的比特幣。簡言之,選擇權是與比特幣價格(標的資產)掛鉤的金融合約,提供投資人極大彈性:
-
買權(Call Option):買權讓持有人得以在到期日或之前,依指定履約價買入比特幣。當交易者看好未來走勢時會購買買權,行情上漲、超過履約價時,買權價值提升。舉例,如果你持有一個履約價 $30,000、期限一個月的買權,即使市價升到 $35,000,你也可用 $30,000 買進 1 枚比特幣,立刻賺取 $5,000(扣除權利金);若到期時低於 $30,000,選擇權作廢,損失僅限於已付權利金。
-
賣權(Put Option):賣權讓持有人於到期日前以預設價格賣出比特幣。購買賣權為防禦或看跌策略—若比特幣價格跌破履約價時,賣權價值增長。投資人可用作避險需求,例如持有履約價 $25,000、下月到期的賣權,即便市價跌到 $20,000,也可用 $25,000 售出 1 BTC,相當於設下底價。若結算時高於 $25,000,賣權失效,最壞損失為權利金。
上述兩種情形,持有人可選擇是否行使權利;如市況有利,可執行或出售該選擇權合約獲利;否則讓其到期失效,最大損失僅為已付權利金。這種「下檔有限(僅損失權利金)、上檔無限」的非對稱風險誘因,也是眾多交易者青睞選擇權的主因。
重要名詞解釋:討論選擇權時,以下基本術語常被提及:
- 履約價(Strike Price):持有人可買入(買權)或賣出(賣權)標的資產(BTC)的固定價格。例如 $30,000 買權,代表你可用 $30,000 買進 1 枚比特幣。
- 到期日(Expiration Date):選擇權合約的截止日期。持有人需於到期前決定行使與否。比特幣選擇權到期日多元,有每日、每週、每月、每季等。到期後合約結束,失效作廢。
- 權利金(Premium):指選擇權的價格,即買方需先付給賣方的金額。其價值取決於現行比特幣價格、履約價、距到期天數及波動度等市場條件。它即為買權的「成本」,例如一個月的比特幣買權價格為 $500,若合約到期作廢,即損失 $500(賣方則即為利潤)。
可獲取性:選擇權在股票與大宗商品市場盛行數十年,比特幣選擇權則約從 2020 年 1 月普及。日後迅速成長為熱門加密衍生品。主流機構如芝加哥商業交易所(CME)2020 年推出監管版 BTC 選擇權,原生平台如 Deribit、OKX、Binance 亦活躍參與。交易者現可於傳統券商(如 CME 現金交割選擇權、比特幣 ETF 選擇權)或加密交易所交易選擇權。
比特幣選擇權為交易者及投資人帶來靈活工具。其主要優勢在於能在劇烈行情中,透過有限成本(權利金)進行避險或賺取可觀利潤。不同於直接買進或放空比特幣(需大量資金,空頭則潛在虧損無上限),選擇權讓你能以小額資金、定額承擔風險表達多空觀點。若靈活使用,將有機會提升回報或保護資產組合,下文詳述。
比特幣選擇權如何運作?

為深入了解比特幣選擇權實際運作機制,以下分解購買或賣出台權後的關鍵流程:
- 選擇權價值與價內/價外:一份選擇權價值主要取決於比特幣現價與選擇權履約價之間的距離,以及剩餘有效期。常見的「價內/價外」術語如下:
-
價內(ITM, In-the-Money):若現價高於買權履約價,買權即屬於價內(因可便宜買入市場價格),若現價低於賣權履約價,賣權即價內(可高價售出)。價內選擇權具有內含價值。例如你持有 $30,000 履約價買權,現價 $32,000,你每枚比特幣相當於賺 $2,000(扣掉權利金);如持有 $30,000 賣權,現價 $25,000,則獲利為 $5,000。
-
價外(OTM, Out-of-the-Money):如比特幣現價低於買權履約價,該買權屬價外(無人願意用比現價更高的價格買),賣權則相反。價外選擇權不存在內含價值,只能期待到期前行情有利反轉。此類合約費用較低,但若市場未越履約價,最終將成為無價值選擇權。例如一張 $30K... call when BTC is at $25K is $5K out-of-the-money; unless BTC rallies above $30K, that call won’t pay off.
(當比特幣現價為 $25,000 時,行使價 $30,000 的買權(call)為價外 $5,000;除非比特幣價格漲超過 $30,000,否則該買權不會有利潤。) -
At-the-Money (ATM): When Bitcoin’s price is approximately equal to the strike price. An ATM option is right on the cusp – it has little intrinsic value, mostly time value. Traders often favor ATM options for their balance of cost and likelihood of expiring profitable.
-
平價(At-the-Money,ATM):當比特幣現價接近或等於履約價時,即為平價選擇權。此時選擇權幾乎沒有內在價值,主要由時間價值構成。交易者常選擇平價選擇權,因為它在成本與有望獲利之間取得平衡。
The distinction matters because it affects exercise decisions and pricing. An ITM option is likely to be exercised if held to expiration (since it gives a profitable trade at the strike). OTM options will expire unused (worthless) unless the market moves beyond the strike.
這種區分非常重要,因為會影響是否行使以及定價方式。價內選擇權(ITM)到期時通常會被行使(因為可以以履約價進行有利可圖的交易)。而價外選擇權(OTM)若標的價格未超過履約價則將自動失效(變得一文不值)。
-
European vs. American Style: Bitcoin options offered on most crypto exchanges are typically European-style, meaning they can only be exercised at the moment of expiration (on the expiry date). In contrast, American-style options (common in equity markets) allow the holder to exercise at any time before expiry. European options simplify things for exchanges and traders – you don’t have to worry about early exercises. However, it means as a holder you must wait until expiration to capture the option’s value by exercise (though you can still sell the option contract to someone else earlier). Notably, CME’s Bitcoin options and many crypto platforms use European-style contracts, so exercise happens only on expiry. This is important for planning: if you have a profitable European option, you’ll usually sell it on the market before expiry if you want to lock in gains, rather than exercising early.
-
歐式與美式選擇權:大部分加密貨幣交易所提供的比特幣選擇權都是歐式選擇權(European Style),即只能在到期的那一天才能行使。相對地,美式選擇權(常見於股票市場)允許持有人在到期日前的任何時刻行使。歐式選擇權對於交易所與交易者來說較為簡化——你不必擔心提前行使的風險。但這也代表身為持有人,你必須等到到期時才能透過行使來獲得選擇權的價值(儘管你可以提前賣出該合約)。值得注意的是,CME(芝加哥商品交易所)的比特幣選擇權與多數加密貨幣平台都是採用歐式合約,因此僅在到期日行使。這對於交易計畫很重要:如果你持有有利潤的歐式選擇權,通常會選擇在到期前於市場上賣出鎖定獲利,而非提前行使。
-
Settlement: Bitcoin options may be physically settled or cash settled. Physically settled means if the option is exercised, actual bitcoin changes hands (the call buyer buys BTC, the put buyer sells BTC). Cash-settled means the payout is done in cash (or stablecoin) equivalent to the profit of the option, without transferring actual BTC. For example, Binance’s options are USDT-settled: profits or losses are paid in the tether (USDT) stablecoin, and you don’t have to deliver or receive actual BTC. CME’s options on futures are cash-settled in dollars. It’s important to know which type you’re trading, especially if you write options – physical settlement means you should be prepared to deliver BTC (for a call seller) or purchase BTC (for a put seller) if the option ends ITM.
-
結算方式:比特幣選擇權有實物交割或現金交割兩種方式。實物交割代表選擇權被行使時,實際的比特幣會轉移(買權買方買入BTC、賣權買方賣出BTC)。現金交割則是以現金(或穩定幣)依獲利金額支付,不用實際轉移BTC。例如,幣安(Binance)的選擇權為USDT結算:盈虧以泰達幣(USDT)支付,你不需交付或收取實體比特幣。CME期貨選擇權則以美元現金結算。這點對於交易尤其是在寫(賣出)選擇權時特別重要——如果是實物交割,賣方必須準備好交割BTC(賣買權)或購入BTC(賣賣權),若選擇權最後為價內。
-
Pricing Factors: The premium of an option is determined by several factors, often explained by the Black-Scholes model or simply supply and demand in the market. Key factors include: the current spot price of BTC, the strike price relative to spot, time to expiration, volatility of BTC’s price, and interest rates. One can think of an option’s price as having two components: intrinsic value (if any, based on moneyness) and time value (the extra value from the possibility that the option could become profitable before expiry). Generally, the more volatile Bitcoin is expected to be, or the more time until expiry, the higher the premium for a given strike – because there’s a greater chance the option ends up valuable. As time passes, the time value portion decays (this is known as theta decay), which is bad for option buyers but beneficial for option sellers (writers) who earn that decay as profit if the option expires worthless.
-
定價因素:選擇權的權利金受到多種因素影響,常以Black-Scholes模型解釋,也會受到市場供需決定。主要因素包括:比特幣現貨價、履約價與現價的相對關係、到期時間、比特幣價格波動率以及利率。選擇權價格由兩個部份組成:內在價值(如有,取決於價內/價外狀態)、時間價值(選擇權到期前有機會獲利的額外價值)。一般來說,比特幣預期越波動、距到期時間越長,特定履約價的權利金會越高——因為選擇權有成為價值選擇權的更大機會。隨著時間推移,時間價值會逐漸流失(稱為Theta衰減),對買方不利,但對賣出選擇權(寫手)有利—後者可藉由選擇權過期而賺取時間價值。
-
At Expiration: On the expiration date, the option will either be exercised (if it’s in the money and the owner chooses to exercise) or expire worthless (if out of the money). Many crypto exchanges automatically handle exercise: if you are holding a bitcoin call that’s ITM at expiry, the platform may automatically exercise it for you and either credit you the profit or deliver the BTC per the contract terms. If it’s OTM, it simply expires and stops trading. Before expiry, an option’s market price will fluctuate – you don’t have to wait until the expiration; you can close your position by selling the option (if you bought it) or buying it back (if you wrote it) at the market price any time. This allows traders to realize profits or cut losses before the deadline.
-
到期時處理:到期日時,選擇權若為價內且持有人選擇行使,將被行使;若為價外則自動失效。一些加密貨幣交易所會自動處理行使:如果你持有到期時為價內的比特幣買權,平台可能會自動為你行使,將利潤計入帳戶或依合約條款交付比特幣。若為價外則自動失效且停止交易。到期前,選擇權價格會隨市場波動——你不必等到到期才處理,可以隨時賣出(如你是買方)或回補(如你是賣方)來平倉,提早實現利潤或止損。
Example Scenario: To illustrate how a bitcoin option works, consider this example adapted from a recent market scenario:
範例情境:為說明比特幣選擇權運作方式,以下舉一個近期市場範例:
-
Ellen buys a BTC call option with a strike of $55,000, expiring 3 months from now, and pays a $1,200 premium for it. This contract gives Ellen the right to purchase 1 BTC at $55K even if the market price is higher. Suppose within those 3 months, Bitcoin’s price surges to $70,000. Ellen’s call option is now deep in-the-money – she can exercise and buy at $55K, then immediately sell that BTC at market $70K. Her profit would be roughly $70,000 – $55,000 = $15,000 minus the $1,200 premium paid, netting $13,800 gain. If she didn’t have the funds to buy the full BTC, she could alternatively sell the call option itself for about $14K (its intrinsic value) to another trader and take profits that way. Conversely, if BTC’s price had stayed at $50,000 (below the strike) by expiry, Ellen’s call would end out-of-the-money and expire worthless. She’d lose the $1,200 premium – that’s her maximum loss, which was known upfront.
-
艾倫購買一份比特幣買權,履約價 $55,000,到期日為三個月後,支付了 $1,200 權利金。這份合約讓艾倫有權利以 $55,000 購買 1 BTC,即使當時市價更高。假設三個月內,比特幣價格暴漲到 $70,000,艾倫的買權現在為深度價內——她可以以 $55,000 行使買入,並立即以市場價 $70,000 賣出。她的獲利約為 $70,000 – $55,000 = $15,000 減去 $1,200 權利金,淨賺 $13,800。如果她沒足夠資金買整枚比特幣,也可將這份買權(其內在價值約 $14,000)賣給其他交易者來實現獲利。相反地,若到期時比特幣價格僅 $50,000(低於履約價),艾倫的買權會成為價外並失效。她只會損失 $1,200 權利金——這是她事前就已知的最大風險。
-
Paul buys a BTC put option with a strike of $50,000, expiring in 90 days, as a hedge in case of a market drop. He pays, say, a $1,000 premium. If Bitcoin indeed plunges to $40,000 before expiry, Paul’s put becomes valuable. It gives him the right to sell BTC at $50K while the market is at $40K. By exercising, he could essentially get $10,000 more for his bitcoin than the market would otherwise offer. If Paul didn’t actually own BTC, he could still profit by selling the put option contract (which would be worth up to $10K intrinsic value) to someone else. On the other hand, if BTC stays above $50K, the put isn’t needed and expires worthless, limiting Paul’s loss to the $1,000 premium (the cost of insurance).
-
保羅為了防範市場下跌,買入一份履約價 $50,000、90天後到期的比特幣賣權,支付了 $1,000 權利金。如果比特幣真的在到期前跌到 $40,000,保羅的賣權就變得有價值,可以在市場價僅 $40,000 時用 $50,000 售出比特幣。行使賣權,他可比市價多賣 $10,000。即使保羅手中沒有比特幣,他也可以將這份賣權(內在價值高達 $10,000)賣給其他人實現利潤。反之,若比特幣價格始終高於 $50,000,該賣權就沒必要並失效,保羅最大損失就是已支付的 $1,000 權利金(就像保險的成本)。
Bottom Line: Bitcoin options work as powerful tools that can be used to either speculate on price movements with defined risk or to hedge against adverse moves. They introduce concepts like time decay and volatility into crypto trading, which are new considerations beyond just the price of the coin. Traders should familiarize themselves with how option pricing behaves – for instance, an out-of-the-money option can suddenly become profitable if BTC makes a big move in the right direction, and vice versa, an in-the-money option will lose value rapidly as it approaches expiration if it looks unlikely to stay ITM.
總結:比特幣選擇權是強大的工具,可作為有明確可控風險的投機,也能對沖市場不利波動。選擇權為加密貨幣市場引入了時間價值消逝與波動度等全新考量,不再只有單純的現貨價格。交易者應熟悉選擇權定價行為——舉例來說,價外選擇權若比特幣大幅朝有利方向波動即可迅速變為有價值,反之,價內選擇權若接近到期時無法維持價內狀態會迅速失去價值。
Next, we will discuss why traders use bitcoin options and what benefits they offer over simply trading bitcoin itself, before diving into how you can start trading options and some popular strategies.
接下來,將會探討為何交易者會使用比特幣選擇權,以及選擇權相較於單純交易比特幣擁有哪些優勢,然後再深入介紹如何開始交易選擇權及一些常見策略。
Why Trade Bitcoin Options?
Bitcoin options have rapidly grown in popularity because they offer several strategic advantages and use cases that regular spot trading of bitcoin cannot. Here are some key reasons traders and investors turn to options:
為何要交易比特幣選擇權?
比特幣選擇權之所以快速普及,是因為它們帶來許多現貨交易比特幣無法替代的策略優勢與用途。以下為主要理由:
-
Risk Management and Hedging: One of the most common motivations is hedging against unfavorable price movements. If you hold a significant amount of BTC, you might worry about a short-term drop. Instead of selling your bitcoin (and potentially missing an upside rebound), you can buy put options as insurance. A put option will increase in value if BTC’s price falls, offsetting some of your losses on the holdings. Professional miners and long-term holders also use options to lock in prices or protect against downturns. In essence, options allow you to insure your crypto portfolio – much like buying insurance on a house – limiting downside without necessarily liquidating your assets.
-
風險管理與避險:其中一個最常見的動機是對沖不利價格變動。如果你持有大量比特幣,可能會擔心短期內價格下跌。與其賣出比特幣(冒著錯失後續反彈的風險),不如買入賣權作為保險。當比特幣價格下跌時,賣權會升值,可以抵消部分帳面損失。專業礦工與長線持有者也會利用選擇權鎖定價格或避免回跌。簡單來說,選擇權就像給你的加密貨幣資產買保險——在不必完全賣出資產的情況下,限定下檔損失。
-
Leverage and Capital Efficiency: Options provide a form of built-in leverage. By paying a relatively small premium, an options trader can control a larger notional amount of bitcoin than if they bought the coin outright. For example, instead of spending $30,000 to buy 1 BTC, a trader might spend $1,500 on a call option that gives exposure to 1 BTC’s upside. If BTC’s price rallies, the percentage returns on that $1,500 could far exceed the percentage gains of holding BTC – yielding a high return on investment. This ability to amplify gains with limited capital is attractive to speculators. (Of course, if BTC doesn’t rise, the call can expire worthless and the premium is lost, so leverage cuts both ways.) The key point is that options let you take meaningful positions with less capital outlay.
-
槓桿與資本效率:選擇權內建槓桿功能,支付相對較小的權利金,就能掌控比實際買入更多名義價值的比特幣部位。例如,不需花 $30,000 購買 1 枚比特幣,只需花 $1,500 買入帶有 1 BTC上漲收益權的買權。若比特幣價格上漲,這 $1,500 可以帶來遠大於直接持有比特幣的報酬率,投資報酬率極高。這種以小博大的特性很受投機者歡迎。(當然,若比特幣不上漲,買權將失效,權利金損失,槓桿效應也會放大損失。)關鍵在於,選擇權讓你用較少的資本配置就能參與有意義的市場部位。
-
Limited Risk (for Buyers): When you buy options (calls or puts), your maximum risk is capped at the premium paid. This is a crucial difference from margin trading or futures, where losses can exceed your initial investment. For instance, going long BTC futures could lead to large losses if price drops significantly, potentially even liquidation. But buying a BTC call option will never lose more than the upfront cost, no matter how badly the market moves against you. This limited downside, unlimited upside profile appeals to many traders – you can seek upside exposure to bitcoin, but know exactly how much you’d lose in a worst-case scenario. In a notoriously volatile market like crypto, such clarity on risk is valuable.
-
風險受限(針對買方):買進買權或賣權時,最大損失就是所支付的權利金。這與保證金交易或期貨最大的不同——後者損失可能超過本金甚至被強平。而買比特幣買權,最壞情況下頂多損失權利金,無論市場如何反向劇烈波動。這種“有限虧損,無限獲利”的結構對無數交易者極具吸引力——你能掌握比特幣上漲潛力,同時明確了解最壞損失多少。在波動劇烈的加密市場,風險可視化極其重要。
-
Flexibility and Strategic Diversity: Options enable complex strategies that can profit from any market condition – up, down, or even sideways. You are not limited to simply betting on price going up (long) or down (short). With options, you can profit from volatility itself (regardless of direction), set target price ranges, or earn yield if the market stays relatively stable. For example, if you expect Bitcoin to trade in a tight range for a month, you could use an options strategy (like selling both calls and puts – an iron condor or strangle) to collect premiums that profit if indeed the price remains range-bound. Conversely, if you expect a major move but aren’t sure of the direction (say, around an important regulatory decision or economic event), you could buy a combination of calls and puts (a straddle strategy) to gain if a
-
彈性與多元策略:選擇權允許複雜策略,無論行情漲跌甚至橫盤,都有獲利空間。不再只能單靠多頭或空頭下注方向。運用選擇權,可直接針對波動度(不論方向)獲利、設計區間套牢或賺取時間價值收益。例如,預期比特幣未來一個月區間盤整,可採用同時賣出買權與賣權(如鐵兀鷹或勒式策略)來賺取權利金,只要價格真的維持區間就能獲利。反過來,若預期市場將大幅波動但不確定方向(如重要監管消息、經濟事件),可以同時買進買權與賣權(勒式或跨式策略)來布局。big swing occurs either way. This flexibility to design custom payoff profiles is a huge benefit of options. Traders can fine-tune how they want to express a market view, far beyond just “buy or sell”.
-
Income Generation (Yield): As hinted in the Binance news, writing options can generate extra income on your holdings. If you own bitcoin (or another crypto), you can sell call options against your position (a covered call strategy, which we explain later) to earn premiums. Many crypto holders use this as a way to earn yield – essentially “renting out” their coins for income. As long as BTC stays below the strike price, the options expire worthless and you keep the premium, boosting your overall returns. This is similar to how stock investors sell covered calls on shares to earn yield in flat markets. With interest rates on fiat relatively low and many DeFi yields declining, option premiums can be an attractive source of return on crypto assets. (Note: While income strategies like covered calls are popular, they do cap your upside if the asset rallies strongly, so there’s a trade-off of limiting potential future gains in exchange for immediate income.)
大幅波動無論往哪一邊發生,選擇權擁有設計專屬報酬結構的彈性,這是選擇權的一大優勢。交易者可以微調想要表達的市場觀點,遠超出單純的「買或賣」。
-
收益產生(收益率):如同在幣安新聞中提到,賣出選擇權可以為您的資產持倉帶來額外收益。如果您持有比特幣(或其他加密貨幣),可以針對您的持倉賣出買權(Covered Call 策略,稍後會解釋)來賺取權利金。許多加密貨幣持有者會用這個方法賺取收益——本質上就是將你的幣「出租」來賺錢。只要BTC價格維持在履約價以下,這些選擇權最後就會變得一文不值,您就能保留所有權利金,提升總體報酬。這其實類似股票投資人在盤整行情時,賣出覆蓋型買權來賺取收益。當法幣的利率較低、加上多數DeFi的收益也在下滑時,選擇權的權利金獲利,對加密資產來說就變成有吸引力的回報來源。(註:儘管像覆蓋型買權等收益策略很受歡迎,但如果標的價格大幅上漲,這會限制你的上行空間,也就是你必須用一部分潛在未來獲利來換取即時的收益。)
-
Access for Institutional Players: The advent of regulated bitcoin options (e.g. CME options) has provided institutions a way to get exposure or hedge exposure to crypto in a familiar format, often without holding the underlying asset directly. Some large funds or traditional financial institutions that have mandates against holding actual crypto can use options and futures to participate indirectly. The growth in options open interest to record highs (nearly $50+ billion by mid-2025 across exchanges) suggests rising institutional involvement. Options allow these players to structure positions that align with risk management rules – for instance, an institution can buy protective puts on their bitcoin investments to limit downside risk to a known amount, which might be required by their risk committees.
-
機構玩家的參與:受到監管的比特幣選擇權(如CME選擇權)問世,讓機構能用熟悉的金融工具取得加密貨幣曝險或進行避險,而且往往無需直接持有標的資產本身。部分大型基金或傳統金融機構,若有政策規定不能持有加密實體資產,也能透過選擇權或期貨間接參與。2025年中,各交易所總未平倉口數已創新高(接近或超過500億美元),顯示機構參與度持續升溫。對這些法人來說,選擇權允許它們按照自身風控規則設計部位——例如,機構可以對其持有的比特幣買進保護性賣權,這樣能將最大下行風險鎖定在固定範圍內,有時甚至是風控委員會的強制要求。
-
Price Discovery and Market Sentiment: Options markets can also be insightful for gauging sentiment. The relative demand for calls vs. puts (often measured by metrics like the put/call ratio or the “skew” in implied volatility) gives clues about whether investors as a whole are leaning bullish or bearish. For example, if far more traders are buying puts (downside protection) than calls, it might signal caution or bearish sentiment. Conversely, heavy call buying might indicate bullish speculation is rampant. Additionally, large open interest at certain strike prices can act as magnets or resistance levels for the spot price as expiry approaches (a phenomenon traders watch known as “max pain” theory). In summary, options trading is not only a way to trade, but also provides data that reflect what the market expects about future volatility and price movements.
-
價格發現與市場情緒:選擇權市場也非常適合用來觀察市場情緒。買權與賣權的相對需求(通常用買賣權比率put/call ratio、或隱含波動率的歪斜度skew來衡量),能給你提示市場整體是偏多還是偏空。例如,如果市場上買進賣權(下跌保護)的人遠多於買權,這可能代表投資人偏向謹慎或看空。反之,如果市場大幅買入買權,則可能說明多頭氣氛高漲。此外,某些履約價附近如果有大量未平倉口數,在到期前會像磁鐵或壓力點一樣吸引現貨價格靠攏(這就是所謂的「最大痛點 max pain」現象)。總之,選擇權交易不只是交易工具,同時也揭示反映出市場對未來波動和價格方向的預期。
In essence, bitcoin options add a toolbox for crypto market participants: hedgers use them to protect against adverse moves; speculators use them to bet on moves with defined risk; and yield seekers use them to generate income. All of this contributes to a more mature market ecosystem. As crypto adoption accelerates, demand for such sophisticated tools is likely to continue growing – a trend Binance’s latest offering clearly aims to capitalize on.
總結來說,比特幣選擇權為加密貨幣參與者帶來一套工具箱:避險者用來防範不利行情,投機者可利用其有限風險特性表達方向觀點,收益追求者則可用來創造現金流。所有這些都將促進市場生態更加成熟。隨著加密貨幣採用加速,這類專業工具的需求勢必只增不減——幣安最近的產品顯然正是看好這波趨勢。
How to Trade Bitcoin Options (Step-by-Step)
Trading bitcoin options might sound complex, but getting started can be straightforward if you follow a step-by-step process. Here’s a guide for beginners on how to begin trading BTC options, from choosing a platform to executing your first trade:
比特幣選擇權交易乍聽之下好像很複雜,其實只要按部就班學習,就可以輕鬆入門。以下是初學者如何從挑選平台到下單進行BTC選擇權交易的操作指南:
-
Pick a Reputable Options Trading Platform: The first step is to find an exchange or brokerage that offers bitcoin options. Not all crypto platforms have options trading, so you’ll need to seek out those that do. Major crypto exchanges known for BTC options include Deribit (a popular platform specializing in crypto options), Binance (for non-U.S. users), OKX, Bybit, and others. In the U.S., regulated options on bitcoin are available via the CME (through futures brokers) or on Bitcoin ETFs (like options on the BITO ETF), since direct crypto platforms are limited for U.S. residents. When choosing a platform, consider factors like security record, liquidity (trading volume and open interest in options), user interface, fees, and whether you can meet any eligibility requirements. For example, some exchanges might require you to pass a quiz or demonstrate understanding of derivatives before enabling options trading (Binance now does this for writing options) to ensure you know the risks.
-
選擇有信譽的選擇權交易平台:第一步是找出有提供比特幣選擇權的交易所或券商。不是所有加密平台都有選擇權功能,所以你必須主動尋找支援此功能的平台。國際主流BTC選擇權交易所有Deribit(專門做加密選擇權的平台)、Binance(非美用戶)、OKX、Bybit等。在美國,監管選擇權可經由CME(透過期貨券商),或比特幣ETF(例如BITO ETF選擇權)進行,因為直接加密平台功能受限於美國居民。選擇平台時,建議考量安全記錄、流動性(選擇權成交量及未平倉量)、介面、手續費,以及自己是否能符合資格門檻。例如,有些交易所會要求你先通過測驗或證明對衍生品有基本認識,才開放選擇權交易權限(幣安現在要求寫選擇權前需測驗),以確保你了解風險。
-
Sign Up and Verify Your Account: Once you’ve chosen a platform, create an account. This usually involves providing an email and password, and then completing any required KYC (Know Your Customer) verification if applicable. Many regulated exchanges will require identity verification (ID upload, proof of address) before you can trade derivatives, in compliance with anti-money laundering rules. Make sure to secure your account with strong 2FA (two-factor authentication) since you’ll be trading valuable assets.
-
註冊並驗證帳戶:選好平台後就可以註冊帳戶,通常只需提供Email和密碼,然後依規定完成KYC(實名制)身分驗證。很多合規交易所有衍生品時,都會要求用戶上傳身分證件與地址證明,這是為了遵循防洗錢(AML)規範。由於選擇權部位資金量大,請務必啟用強密碼和雙重驗證(2FA)來保障帳戶安全。
-
Fund Your Trading Account: After your account is set up, you need to deposit funds. Depending on the platform, you may deposit cryptocurrency (like USDT, USDC, BTC, etc.) or fiat currency (USD, EUR) to act as collateral for trading. Many crypto exchanges operate in crypto terms – for example, Deribit uses USD-denominated contracts but requires Bitcoin or Ethereum as collateral; Binance might allow USDT as collateral for options. Ensure you understand what currency your account needs. If you’re using a platform like CME via a broker, you’d deposit cash to your brokerage which then allows you to trade BTC options. On retail crypto platforms, often stablecoins like USDT are convenient to fund your account for options trading (as they’re used for settlement).
-
充值資金:帳戶設立後需入金。平台不同,可能允許用戶充值加密貨幣(如USDT, USDC, BTC等)或法幣(美元、歐元),用於充當交易保證金。許多加密交易所交易結算以加密幣為主,例如Deribit合約以美元計價但用BTC或ETH當保證金,幣安則可以USDT作為選擇權保證金。建議在交易前搞清楚平台要求的帳戶幣種。如果在CME這類傳統券商下單,則要先存入現金才能交易比特幣選擇權。對於零售型用戶,USDT這類穩定幣經常用於選擇權結算和入金,非常方便。
-
Navigate to the Options Trading Section: Inside the exchange’s interface, find the derivatives or options section. This might be under a separate tab or menu (sometimes labeled “Options” or under “Derivatives”). On Binance, for example, you’d navigate to the Options trading screen. On Deribit, you’d go to the Options order book for BTC. Familiarize yourself with the layout: you should see a list of available option contracts organized by expiry date and strike price. There’s usually an order book or pricing interface showing premiums for various strikes, often separated into Calls and Puts. Take a moment to understand how to read the option quotes – typically you’ll see the premium (price) and possibly implied volatility for each option.
-
進入選擇權交易專區:在交易所介面中,找到衍生品或選擇權板塊(有時會在「Options」或「Derivatives」選項下)。以Binance為例,進入選擇權交易畫面即可。Deribit則選擇BTC的Options訂單簿。熟悉一下版面,你應該會看到各種依到期日和履約價分類的選擇權合約清單,分為買權和賣權兩個欄位,並有即時報價和訂單簿。花點時間學會看懂各種報價:通常會標示權利金(價格),有些會另外顯示隱含波動率。
-
Choose Your Option Contract: Decide on the specific option you want to trade, based on your strategy or market outlook. You’ll need to pick the expiration date, the strike price, and whether it’s a call or put. For example, you might choose a call option expiring in one month with a strike price of $35,000. Or a put option expiring this Friday with a strike of $28,000. Most trading interfaces have filters to narrow down by date and strike. A key consideration is your market view: if you’re bullish, you might buy calls (or sell puts); if bearish or seeking protection, you might buy puts; if aiming for income, you might sell calls against holdings, etc. Ensure you also consider the strike relative to current price – in the money, at the money, or out of the money – depending on how aggressive or conservative you want to be.
-
選擇合適的選擇權合約:根據自己的策略與市場觀點,挑選具體想要交易的選擇權。你需要決定到期日、履約價、以及要買權還是賣權。舉例來說,你可以選一個下個月到期、履約價$35,000的買權,或本週五到期、履約價$28,000的賣權。大部分介面都有篩選功能讓你按日期與履約價挑選。最重要的是根據盤勢決定部位:看多就可以買進買權(或賣出賣權);看空或希望保護部位則可買賣權;想賺收益則對現有持倉賣出買權等。要特別注意選擇的履約價和現價的關係——價內(in the money),平價(at the money),價外(out of the money)——這會影響你部位的風險報酬結構。
-
Examine the Premium and Greeks: Before executing, check how much premium you’ll pay or receive for that option. The platform will show a premium quote (often in BTC or in USD terms). This is the price per unit of the underlying (many exchanges use 1 BTC as the contract unit for simplicity). For instance, a quote might show a premium of 0.010 BTC for a certain option, meaning it costs 0.01 BTC (about 1% of BTC price) to buy one contract. Also be aware of contract size – some platforms use 1 BTC as one option contract, others might use e.g. 0.1 BTC per contract. Additionally, advanced traders will examine the “Greeks” (Delta, Theta, etc.) provided, which measure the option’s sensitivity to various factors. Delta tells you roughly how much the option’s price moves for a $1 move in BTC; Theta tells you how much value the option loses per day from time decay, etc. Beginners need not master these immediately, but it’s useful to note that a near ATM call might have a delta around 0.5 (behaving like half a BTC position) whereas a far OTM call might have a small delta (low probability of paying off).
-
檢查權利金與希臘字母:下單前先確認你要支付或收取多少權利金。平台都會直接顯示權利金報價(通常以BTC或美元表示),這是每一單位標的的價格(很多平台規定1BTC為1口合約)。舉例,如果某選擇權的權利金標為0.01 BTC,表示買1張要支付0.01 BTC(約等於BTC市價的1%)。也要注意每張合約的單位,有的平台1口=1BTC,也有些用0.1BTC。進階玩家還會看「希臘值」(Greeks)指標,例如Delta、Theta等。Delta反應標的每漲跌1美元時此權證價格的預期變化,Theta則是反應每日因時間衰退損耗的價值。初學者不必馬上精通,但要知道像近平價(ATM)的買權,Delta約0.5(等於持有半顆BTC部位的風險貢獻),而遠價外買權的Delta就很小(低機會獲利)。
-
Place Your Trade (Buy or Sell the Option): Now you’re ready to execute. If you’re buying an option (long call or long put), you will pay the premium (make sure you have enough balance). If you’re selling (writing) an option, you will receive the premium, but you must have sufficient collateral/margin to cover the position. Enter the order details: number of contracts, and the price. You can often choose a limit order (setting the premium you’re willing to pay/receive) or execute at the market price for immediate fill. Double-check everything – for a buy, confirm you’re buying the correct call or put, strike, expiry, and that the premium is acceptable. For a sell, ensure you understand the margin impact and have the asset to cover if it’s a covered call (or enough margin if it’s uncovered/naked). Submit the order and wait for it to fill. Once executed, you’ll see the open position in your account.
-
下單(買入或賣出選擇權):準備好就可下單。如你是買方(做多買權或賣權),要支付權利金(確認帳戶餘額充足)。若是賣方(寫選擇權),你會收錢,但必須有足夠保證金或對應資產來承擔部位。填寫下單明細,包括口數和價格。一般可用限價單(指定自己要的權利金價格,也就是你想付或想收多少)或選擇市價單立即成交。下單前仔細檢查明細:買方要確認是正確的買權/賣權、履約價、到期日及權利金是否合理;賣方務必了解保證金占用,若是賣Covered Call則要有現貨資產覆蓋,否則須準備足夠保證金(裸賣Uncovered/Naked)。送出下單後等成交,部位就會顯示在帳戶中。
-
Monitor Your Position: After the trade, keep an eye on how your option is performing. Option prices will change as Bitcoin’s price moves, and as time to expiry counts down. Your exchange interface should show real-time unrealized P&L (profit or loss) for your option positions. Be aware of key moments like
-
監控你的部位:下單之後,要持續留意選擇權部位表現。選擇權價格會隨比特幣價格波動、時間遞減而改變,交易所介面通常都會有實時損益(未實現盈虧)。請特別留意關鍵時刻,例如——approaching expiration (options lose time value rapidly in the final week or days) and any major events (earnings in stock world, but in Bitcoin maybe macro events or ETF decisions) that could cause big volatility swings. Monitoring also means watching your margin if you sold options – if the market moves against a short option, you may need to add collateral to maintain the position.
臨近到期日(選擇權在最後一週或最後幾天會迅速失去時間價值)以及任何可能導致大幅波動的重大事件(股票世界有財報,對比特幣來說則可能是宏觀事件或 ETF 決策)。監控也意味著如果你賣出選擇權,要留意自己的保證金——如果市場往不利於你賣方部位的方向走,你可能需要追加保證金來維持部位。
-
Closing or Exercising the Option: Before or at expiry, you’ll choose how to conclude the trade. If you bought the option and it’s in profit, you have a few choices:
-
平倉或行使選擇權:在到期前或到期時,你需要選擇如何結束這筆交易。如果你是買方且已經有獲利,通常有以下幾種選擇:
-
Sell the option back to the market to lock in gains (most common).
-
Hold to expiration and (for an ITM option) either exercise it to acquire/deliver BTC or take the cash settlement. Many retail traders simply sell the option before expiry to realize profit instead of dealing with exercise.
-
If the option is out-of-the-money and likely to expire worthless, you may just let it expire (your loss is limited to premium already paid).
-
將你的選擇權賣回市場獲利了結(最常見)。
-
持有到到期(若為價內選擇權),可選擇行使權利以取得/交割 BTC,或選擇現金結算。許多散戶會在到期前直接賣出選擇權來實現獲利,避免處理行權程序。
-
如果選擇權已經價外、很可能變成廢紙失效,你可以直接讓它到期(此時損失只限於你當初付的權利金)。
If you sold the option initially (wrote it), you can:
- Buy back the option to close your short position (for instance, if you sold at 0.01 BTC and now it’s 0.005 BTC, you could buy it back cheaper and pocket the difference as profit).
- Hold to expiry:
如果你一開始是賣方(寫出選擇權),你可以:
-
回補選擇權部位(例如你以 0.01 BTC 賣出,現在市價變成 0.005 BTC,直接回補平倉就能賺取中間差額)。
-
持有至到期日:
-
If it expires out of the money, it expires worthless and you keep the full premium – best outcome for a writer.
-
If it expires in the money, you will be assigned. That means if you sold a call, you’ll have to deliver BTC at the strike (or cash equivalent) to the option buyer; if you sold a put, you’ll have to buy BTC at the strike from the buyer. On many platforms, this is handled via your collateral (they’ll use your posted margin or holdings to settle). Make sure you’re prepared for that scenario.
-
如果最後變成價外選擇權、到期作廢,你就保留全部權利金 —— 這是賣方最希望的情況。
-
如果最後變成價內選擇權,你必須履行交割義務。例如,你賣出的是 call,你要依履約價賣出 BTC(或現金等值)給買方;你賣出的是 put,你要依履約價向買方買入 BTC。很多平台會用你的保證金或已質押資產直接自動結算,所以你要確保自己已做好因應。
-
Many traders new to options start by paper trading (using a testnet or demo account if available) or trading very small position sizes to learn the mechanics. This is highly recommended, as options have more variables to consider than spot trading, and the interface may seem complex at first.
許多選擇權新手會透過模擬交易(使用 testnet 或模擬帳戶)或極小倉位來學習操作流程。這是非常建議的做法,因為選擇權比現貨有更多變數需要考量,剛接觸時介面也可能讓人一時無法適應。
Popular Bitcoin Options Trading Strategies
常見比特幣選擇權交易策略
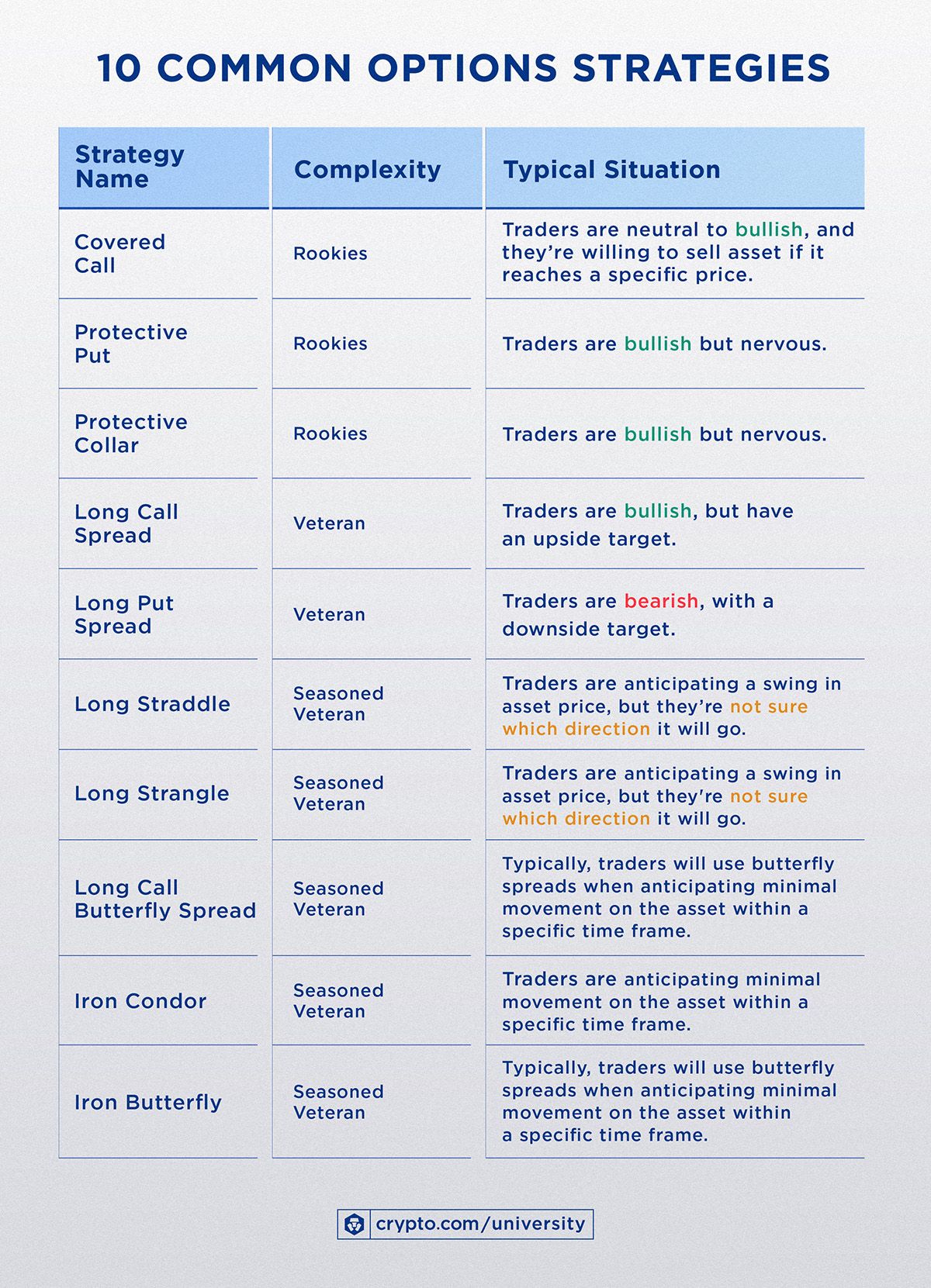
With an understanding of the basics, we can explore some popular strategies involving bitcoin options. Different strategies serve different goals – some aim to maximize profit under certain market conditions, others to protect investments or generate income. Below are a few of the most widely used and useful strategies for bitcoin options, along with how they work:
在理解基本概念後,我們可以來看看幾種常見的比特幣選擇權交易策略。這些策略各有用途——有的在特定市況下追求最大化獲利,有的則用來保護投資或創造現金流。以下介紹幾個最廣泛且實用的比特幣選擇權策略,並說明它們的運作方式:
1. Covered Call (Writing Covered Calls on Bitcoin)
1. 有擔保賣出買權(Covered Call,比特幣賣出有擔保買權)
Goal: Generate income (premium) from your BTC holdings in neutral-to-moderately bullish market conditions.
目標:在中性或溫和偏多的市場環境下,利用你的 BTC 持倉獲取額外權利金收益。
Strategy Outline: In a covered call, you hold the underlying asset (Bitcoin) and simultaneously sell call options against those holdings. Because you own the BTC, your call option is “covered” – you can deliver the bitcoin if the call buyer exercises. This strategy lets you earn the call option premium as income, but in exchange, you agree to sell your BTC at the strike price if it rises beyond that.
策略概要:在有擔保賣出買權策略中,你先持有標的(比特幣),再賣出等量的 call 選擇權。由於你已持有 BTC,這個賣出買權就屬於「有擔保」,即若買方行使權利時你能履行交割。這個策略讓你能獲取賣出買權的權利金,但同時你必須同意如果市價漲破履約價時,以履約價賣出你的 BTC。
How it works: Suppose you own 1 BTC currently worth $30,000. You think BTC will stay relatively flat or only rise modestly in the next month – say, under $35,000. You sell a one-month call option with a strike price of $35,000 for a premium of $500. Here are the possible outcomes:
運作方式:假設你持有 1 BTC(現價 $30,000),你預估下個月 BTC 大致持平或只會小漲(不超過 $35,000)。你賣出一張履約價 $35,000、到期日一個月後的 call 選擇權,收到 $500 權利金。可能的情境如下:
-
If by expiration BTC stays at $30K or only rises to (but not above) $35K, the call will expire out-of-the-money (since market ≤ strike). The buyer won’t exercise, and you keep your 1 BTC. You also keep the $500 premium as profit (minus any fees). Essentially, you earned $500 yield on your asset for that month, boosting your return.
-
If BTC rallies above $35K – say to $38,000 – by expiration, the call will be in-the-money and the buyer will likely exercise. You are “called away” to sell your 1 BTC at $35,000 (below market price). You still keep the $500 premium, but you miss out on any upside beyond $35K. In this scenario, you effectively sold your BTC for an effective price of $35,500 (strike + premium) instead of $38,000 market, meaning $2,500 of “missed” upside. This is the trade-off: your profit was capped at the strike price (plus premium).
-
如果到期時 BTC 還在 $30,000 附近,或漲到 $35,000 但沒有超越,這張 call 是價外的,買方不會行使,你保留 1 顆 BTC,同時留住 $500 權利金作為本月被動收益(扣除手續費后)。等於你本月靠這個資產額外賺到 $500。
-
如果 BTC 最後大漲,超過 $35,000,比如漲到 $38,000,到期時 call 就會變成價內,買方很可能執行權利。你被「call away」:必須以 $35,000 賣出 1 顆 BTC(低於現價)。你仍保留 $500 權利金,但錯過了 $35,000 以上的漲幅。換算等於你實際賣出 BTC 的價格是 $35,500(履約價 + 權利金),而不是 $38,000,等於少賺 $2,500。這就是這個策略的取捨:你的利潤被封頂在履約價(加上權利金)。
The covered call is considered a conservative strategy for holders. You only risk losing potential upside beyond the strike; you won’t lose on the BTC you already own unless its price falls (in which case the call premium at least gives a small buffer). It’s most effective when you expect sideways or slow-rising prices – you earn income and don’t think you’ll regret selling at the strike price. It’s not a good strategy if you expect a sharp rally (because then you’d rather not cap your gains). Many long-term investors systematically sell calls on a portion of their crypto to generate yield, especially in range-bound markets. Tools and platforms (like certain DeFi vaults or ETFs) have even emerged to automate covered call strategies on Bitcoin, highlighting its popularity. For example, early 2024 saw filings for a Bitcoin Covered Call ETF, signaling mainstream interest in this income strategy.
有擔保賣出買權普遍被認為是持有者的保守策略。你唯一的損失風險是錯失履約價以上的潛在漲幅;至於已持有的 BTC 就算沒漲甚至下跌,你也不會因此多損失(反而權利金還能提供一點點緩衝)。這策略最適用於判斷市價橫盤或緩漲的情況,不但能賺權利金,也不會後悔市價沒突破履約價。如果你預期大漲,這就不合適(因為會封頂盈利)。許多長期投資人會把幣的一部分固定賣出買權來賺取收益,特別是盤整時期。近年還出現可以自動執行這種策略的工具或平台(如某些 DeFi Vault、ETF 等),顯示其受歡迎。例如 2024 年初就有比特幣有擔保賣權 ETF 的申請案,反映主流對這現金流策略的興趣。
Risk: The main risk is opportunity cost – if Bitcoin shoots up past your strike, you’ll have to sell your coins at the strike price, sacrificing some gains. Also, if BTC plunges, the premium earned only slightly offsets your spot losses (you still keep the BTC, which is now worth less). So it doesn’t fully protect against downside; it just gives a small cushion (premium) and income when flat.
風險:主要是所謂機會成本——若比特幣大漲超過你的履約價,你只能以履約價賣掉,損失額外漲幅。而若 BTC 崩跌,你賺到的權利金只會稍微抵銷現貨損失(BTC 仍然變便宜,你還是持有著)。所以這個策略並無法全面防守下跌,只是多了小小的緩衝墊——適合盤整市、不甘現貨「叫價無法賺收益」的人。
2. Protective Put (Buying Downside Protection)
2. 保護性賣權(買入賣權避險)
Goal: Protect your BTC holdings from a significant drop in price (like an insurance policy), while retaining upside potential.
目標:為你的 BTC 現貨部位設下價格下限(類似保險),在不放棄上漲潛力的情況下防止重挫。
Strategy Outline: A protective put involves buying put options while holding the underlying BTC. If you own Bitcoin, you purchase a put option with a strike price near or below the current price, which gives you the right to sell your BTC at that strike. This acts as a floor – no matter how low the market goes, you can still sell at the strike (via the put). It’s essentially insurance against a crash.
策略概要:所謂的保護性賣權,就是你持有 BTC 的同時,買入賣權(put)當保險。選擇權履約價設在現價附近或略低,這讓你擁有在市價暴跌時,依履約價賣出 BTC 的權利,底價有保障。即使市場崩跌,你也能在 put 履約價脫身,等同避開暴跌損失——就像保了一張保險單。
How it works: Suppose BTC is $30,000 and you are worried about a short-term downside (perhaps due to an upcoming regulatory decision or bearish technical signals), but you don’t want to sell your BTC holdings. You buy a one-month put option with a strike of $28,000, paying a premium of, say, $500. Now consider outcomes by month-end:
運作方式:假設 BTC 現價 $30,000,你擔心短期有利空或技術面走跌,但又不想賣掉現貨。你可以買一張 1 個月到期、履約價 $28,000 的賣權(put),權利金假設是 $500。月底結果有幾種可能:
-
If BTC plummets to $20,000, your put option becomes very valuable. You have the right to still sell BTC at $28K. In practice, you could exercise the put and sell your 1 BTC for $28,000, far above the market price (or just sell the put contract itself for roughly $8,000 intrinsic value). This means your effective worst-case price for your BTC was $28K, protecting you from deeper losses – minus the $500 cost of the option. Instead of losing $10k (from $30K to $20K) on your holding, you only effectively lost $2k (from $30K down to the $28K insurance level, plus the $500 premium) because the put hedge compensated the rest. This illustrates how a protective put can hedge against crashes.
-
If BTC’s price instead rises or stays flat (say ends at $32,000 or $30,000), the put expires worthless (it’s OTM since market > $28K). You wouldn’t use it, since you wouldn’t sell below market price. Your loss in that case is just the premium paid ($500), but your BTC is fine and even gained value if it went to $32K. So you participate fully in the upside (minus the small cost of the put).
-
若 BTC 崩跌到 $20,000,你這張賣權變超有價值,因你有權以 $28,000 卖出 BTC(遠高於現價),實際上你可以選擇行使、或用大約 $8,000 內在價值直接賣掉這張賣權合約。這表示你這顆 BTC 最差價格就是 $28,000,劃出下跌保護線(扣除 $500 成本)。比起直接虧掉 $10,000,實際只虧 $2,000(即 $30,000 → $28,000,再加 $500 權利金成本),避險效果明顯。
-
若 BTC 反而上漲或橫盤(結算價 $32,000 或 $30,000),賣權就變成價外、直接歸零作廢。你也不會用這張賣權去賣(沒人笨到低於市價賣)。此時你的損失就只剩 $500 權利金的成本,而現貨仍可參與上漲獲利。
In essence, a protective put locks in a worst-case selling price for your BTC, providing peace of mind. Many investors will buy puts ahead of potentially volatile events, akin to buying insurance ahead of a storm. This strategy is common in equities (investors hedging stock portfolios with index puts) and is gaining traction in crypto especially for institutions that need to limit downside risk.
總結來說,保護性賣權等於為你的 BTC 設定一個「最壞賣價」,獲得心理保障。很多投資人會在重大不確定事件之前買 put,等同預先買保險。這策略是股票市場中常見的避險手法,在加密圈(尤其是大型機構須風控者)也越來越流行。
Cost Consideration: Insurance is not free – the premium paid for protective puts can be significant if volatility is high. In very choppy markets, put options get expensive. Traders must decide if the cost is worth the protection. Sometimes they might buy slightly OTM puts (a bit below current price) as a compromise to reduce premium cost while still guarding against tail risk. Another approach to reduce cost is to implement a collar, described next.
成本考慮:保險都是要花錢的——當市況動盪時,避險用 put 權利金會變很貴。交易者必須評估保成本與避險效益是否划算。有時候大家會選擇買價格稍微低於現價的 OTM put,花比較少錢但仍能對付極端下跌風險。另一種降低成本的方法則是下一種策略——collar。
3. Collar Strategy (Downside Protection with Upside Trade-off)
3. 項圈策略(Collar,下檔保護+封頂上檔收益)
Goal: Hedge against a significant price drop at low or zero net cost, by giving up some potential upside beyond a chosen level.
目標:以低成本或零淨成本抵禦重大下跌風險,條件是放棄部份高位漲幅收益。
Strategy Outline: A collar combines a protective put and a covered call: you buy a put option for downside protection and simultaneously sell a call option to finance that put. The call premium received helps offset the cost of the put. In effect, you create a band or “collar” around the current price – you’re protected below a certain price (the put strike) and you cap your gains above a certain price (the call strike).
策略概要:項圈策略=買保護性賣權(put 避險)+ 賣出覆蓋式買權(收權利金)。賣 call 收到的權利金可以抵消部分/全額 put 賣權成本,讓你在現價上下打造一個價格帶——下檔受保護(put 履約價),上檔有封頂(call 履約價),綁定一個屬於自己的「項圈」。
How it works: Continuing the previous example, BTC at $30,000 – you want to insure below $28K but you don’t want to spend much on puts. You decide to sell a call at an upper strike to pay for it. For instance, you buy a $28,000 put (pay $500 premium) and simultaneously sell a $35,000 call (collect $500 premium) with the same expiration. The premiums roughly cancel, making it a zero-cost collar (or low-cost if not exact). Now:
運作方式:延續剛才例子,BTC $30,000,你想在 $28,000 下方躲避暴跌風險,又不想花太多錢買 put,所以選擇同時「賣一張」高一點履約價的 call 把成本抵消掉。例如:買一張 $28,000 put(付 $500),再賣一張 $35,000 call(收 $500),到期日相同。權利金幾乎互抵,等同零成本項圈(或極低成本)。然後可能會發生:
-
If BTC crashes to $20K, your put kicks in and protects you at $28K (you can sell at $28K). The call you sold will expire worthless (since market well below $35K), so you keep that premium. You effectively hedged the downside very cheaply. This is great – you largely sidestepped the crash, aside from any small net premium difference.
-
If BTC stays in a middle range (between $28K and $35K) until expiry, both options expire worthless. You keep your BTC (which
-
若 BTC 崩跌到 $20,000,你的 put 生效,能以 $28,000 脫身;賣出的 call 變成廢紙,權利金你也拿著。你等於非常便宜就完成強力下檔避險,幾乎不花錢度過崩盤事件。
-
若 BTC 到期在 $28,000~$35,000 間,兩張選擇權都落空作廢,你既沒損失保費,也未被迫交割,上下都有保障。你可以一直持有 BTC...might be roughly same value) and likely paid very little for the collar. No harm, no foul – aside from opportunity cost if BTC did go up a bit and you had no upside cap because it didn’t breach $35K anyway.
(可能兩者價值大致相同),而且你很可能幾乎沒花什麼錢買這個領口策略。這樣做沒有損失也沒有壞處——除了機會成本:如果 BTC 漲了一點,而你沒有設上限(因為價格無法突破 $35K),那麼你就錯過了上漲機會。 -
If BTC rallies above $35K, say to $40K, the call you sold is ITM. You’ll be obligated to sell your BTC at $35,000 (or settle the difference) due to the call, even though market is $40K. So you miss out on the gain above $35K. Essentially, you locked your max selling price at $35K. However, remember you had the downside put, so what the collar achieved was: you gave up upside beyond $35K in order to have protection below $28K. You’ve defined an acceptable range for your returns: you will sell no lower than $28K (floor) and no higher than $35K (ceiling), at least for that time period. The trade was “free” in terms of premium outlay, since call and put premiums offset.
-
若 BTC 價格衝破 $35K,例如漲到 $40K,之前賣出的 call 就會成為價內期權。你必須按照 $35,000 售出 BTC(或結算差額),即使市價是 $40K。所以你錯過了 $35K 以上的收益。基本上,你把最高賣出價格鎖在 $35K。不過,請記得你有下方的 put 作保護,因此這個領口策略的作用其實是:犧牲了 $35K 以上的上漲空間,來換取 $28K 以下的保護。換言之,你為你的報酬設定了一個可接受範圍:這段時間內,賣出價格不會低於 $28K(底線),也不會高於 $35K(天花板)。這個交易在權利金支出上是「免費」的,因為 call 和 put 的權利金大致相互抵銷。
A collar is a cautiously bullish strategy – you’re bullish enough to hold the asset (you expect some upside), but you want to guard against a crash, and you’re willing to cap extreme upside in exchange for that protection. Investors who “want to sleep at night” employ collars, knowing they have a worst-case and best-case defined. Jack Ablin, a $65B fund CIO, recently highlighted the collar as a way to “tiptoe into bitcoin without...getting your head handed to you” – i.e., you can get exposure to BTC’s upside while drastically limiting downside risk. 領口是一種謹慎樂觀的策略——你看多到願意持有資產(預期還會漲),但也擔心大跌,因此願意犧牲極端上漲空間,以換取下檔保護。想要「晚上可以安心睡覺」的投資人常常會運用領口策略,因為這樣可以提前鎖定最壞與最好的情境。65 億美元基金的投資長 Jack Ablin 最近特別強調,領口是「不冒著被割頭的風險下小步踏入比特幣」的方法——你可以參與 BTC 的上漲潛力,同時大幅限制下跌風險。
This strategy tends to be popular when volatility is high (making protective puts costly) but there’s also optimism (investors willing to sacrifice some upside). Note that you can adjust the strikes as needed – a tighter collar (closer strikes) might even yield a net credit, or a looser one might cost a bit. It’s all about trade-offs between insurance cost and giving away gains. 這種策略通常在波動大(避險 put 很貴)但市場也存在樂觀氣氛(投資人願意放棄部分上漲)時特別受歡迎。你可以根據需要調整履約價——窄一點的領口(履約價接近)甚至還能收到淨權利金,若是寬一點的領口則可能需要額外付一些錢。本質上,是在保費支出與犧牲收益之間做權衡。
4. Long Straddle (Betting on Volatility)
Goal: Profit from a large price move in either direction (high volatility play), when you expect big movement but are unsure of direction.
策略目標:從價格大幅波動(無論上漲或下跌)中獲利,適合預期走勢劇烈但無法判斷方向時使用。
Strategy Outline: A long straddle involves buying a call and a put at the same strike price and expiration, typically at-the-money. Because you hold both a call and put, a significant move either up or down can make one of them very profitable, ideally enough to cover the cost of both premiums and then some. This strategy is direction-neutral but volatility-positive: you want a big swing. 策略說明:Long straddle 是同時買入一組履約價及到期日相同的 call 和 put,通常會選擇平價(at-the-money)。因為你同時擁有 call 和 put,所以只要價格劇烈變動(不論方向),其中一邊會產生可觀利潤,理想狀況下能超過總權利金成本。這個策略不押注方向,只押注波動性,就是你希望出現大行情。
How it works: Say BTC is around $30,000 and a major event (for example, a SEC decision on a Bitcoin ETF or a macroeconomic announcement) is coming up that you expect will jolt the market, but you aren’t sure if it’ll break bullish or bearish. You buy a 1-month $30,000 call and a $30,000 put. Imagine each costs $1,000 in premium. Your total outlay is $2,000. Now: 操作方式:假設 BTC 現在約 $30,000,而且即將有重大事件(例如 SEC Bitcoin ETF 決策或宏觀經濟數據公佈)可能震盪市場,但你不確定會漲會跌。你買進一組 1 個月期、履約價 $30,000 的 call 及同履約價的 put。假設每個期權權利金為 $1,000,總支出 $2,000。接下來:
-
If BTC rockets to $40,000 well before or by expiration (+33% move), the call option goes deep in the money. It would be worth about $10,000 intrinsic (since it gives right to buy at $30K when market is $40K). The put would expire worthless, but that’s fine – your call’s value far exceeds the combined premium cost. You could sell the call for a big profit. So a strong rally yields gains.
-
假如 BTC 在到期前大漲到 $40,000(+33%),你的 call 會深度價內,理論價值大約 $10,000(可以 3 萬買進,4 萬市場賣)。Put 過期歸零沒關係,因為 call 的利潤遠高於你付的總權利金。你隨時可以把 call 拋售獲利。因此行情劇烈上漲時可賺錢。
-
If BTC instead plunges to $20,000 (–33%), the put option becomes valuable (worth about $10,000 intrinsic, right to sell at $30K vs market $20K). The call expires worthless. Again, the gain on the put minus the initial cost leads to a healthy profit.
-
若 BTC 反而暴跌至 $20,000(–33%),put 則變得有價值(約 $10,000,因為 3 萬賣出比市價高),call 歸零沒關係,put 的利潤減去成本後一樣有不錯的淨利。
-
If BTC barely moves, say ends around $31K or $29K (small +/-), both call and put will lose value (the call slightly ITM or OTM, the put slightly OTM or ITM but by tiny amount). Likely both might expire near worthless if the move is minimal. Then you lose most of the $2,000 combined premium. That’s the risk – if volatility turns out lower than expected, a straddle loses money on both legs.
-
若 BTC 幾乎沒波動,收在 $31K 或 $29K(小幅區間),call、put 兩邊都只小幅價內或價外,最終可能雙雙歸零或近乎歸零。你就會虧掉大部分的 $2,000 權利金。這就是風險——如果最終波動度比預期小,straddle 兩邊都會虧損。
The straddle is an attractive strategy before known binary events or when implied volatility is perceived as underpriced relative to future reality. Crypto markets often see big moves on news (e.g., ETF approvals, halving events, regulatory crackdowns), so traders sometimes position with straddles to profit from the anticipated volatility. It is important, however, to consider the cost: you need a move big enough to cover the premiums. In the example, any final price outside the range $28K–$32K (roughly) by expiry would start yielding profit beyond cost. Inside that band, the strategy loses money. Straddle 在已知的「二元事件」前特別受到青睞,或當預期未來波動比期權定價更大時更有吸引力。加密市場常常因消息(如 ETF 审批、減半事件、監管打擊)出現劇烈波動,因此有些交易者會用 straddle 搶先布局賺波動利潤。但一定要注意成本:你需要行情足夠大才能覆蓋權利金支出。以本例來說,到期時只要價格落在 $28K–$32K 區間外,才有可能超過成本而獲利;反之則會虧損。
Variations include the strangle, where you buy an out-of-the-money call and an out-of-the-money put (different strikes, e.g. a $32K call and $28K put). That reduces cost since OTM options are cheaper, but requires an even larger move to hit payoff (because the options start out OTM). Traders choose based on how large a move they expect and how much they want to spend. 相關變化型有 strangle——買進價外(out-of-the-money)call 和 put(履約價不同,例如 $32K call 與 $28K put)。這樣權利金較便宜,但需要更劇烈的波動才能有利可圖(因為期初兩邊都是價外)。交易者可根據自己對波動幅度的預期及可接受成本來決定選哪一種。
5. Bull Call Spread (Moderate Bullish Spread)
Goal: Benefit from a modest rise in BTC’s price with limited risk and limited upside, making the trade cheaper than a straight call.
策略目標:看好 BTC 會有適度上漲,希望用有限風險和有限收益來降低建倉成本。
Strategy Outline: A bull call spread involves buying a call option at a lower strike and selling another call at a higher strike (same expiration). Both are calls, so it’s a net bullish position, but selling the higher strike call caps your maximum gain while reducing the net cost of the strategy. This is a vertical spread commonly used to express a bullish view in a cost-efficient way. 策略說明:Bull call spread 是買入較低履約價的 call,同時賣出較高履約價(到期日相同)的 call。兩個都是 call,因此方向是做多;賣出高價 call 限制了最大收益,但可以抵銷部分建倉成本。這是一種常用於表達看多但節省成本的垂直價差策略。
How it works: Suppose BTC is $30K and you think it could rise to around $35K in the next month, but probably not beyond $40K. A straightforward call option at $30K might be expensive, so you set up a bull call spread. You buy a 1-month $30,000 call for $1,200 and simultaneously sell a $35,000 call for $400 (just as an example prices). The net cost is $800. The payoff scenario at expiration: 操作方式:假設 BTC 現價 $30K,你預期一個月內可能漲到 $35K 左右,應該不會超過 $40K。直接買 $30K call 期權可能很貴,所以你做 bull call spread:買 1 個月期 $30,000 call(權利金 $1,200),同時賣出 $35,000 call(權利金 $400,假設值)。淨成本 $800。到期時有幾種情境:
-
If BTC indeed rises into your target range, say finishes at $36K, what happens? Your long $30K call is worth $6,000 intrinsic (right to buy at 30K and sell at 36K), and your short $35K call is worth $1,000 intrinsic (because the buyer of that call can buy from you at 35K and it’s 36K market). Net payoff = $5,000 (6k – 1k). Subtract the $800 cost, you have $4,200 profit.
-
若 BTC 果然漲到你預期區間,例如收在 $36K,你的 $30K call 內含價值為 $6,000($36K – $30K),而你賣出的 $35K call 則有 $1,000 內含價值(人家可 $35K 向你買,市價 $36K)。淨收益 $5,000($6K – $1K),扣掉成本 $800,賺 $4,200。
-
The max profit occurs if BTC is at or above the higher strike ($35K) at expiry. In that case, your $30K call is fully ITM and your $35K call is also ITM and will be exercised. Effectively, you bought at $30K and have to sell at $35K due to the short call, netting $5,000 gain per BTC. So $5,000 is the maximum spread between strikes you can capture. In our example, $5k minus $800 cost = $4,200 max profit. This happens at any final price $35K or above – beyond $35K, you don’t gain more because any extra profit on the long call is exactly offset by losses on the short call.
-
當 BTC 到期價等於或高於 $35K(高履約價)時,就是最大獲利的情境。這時 $30K call 完全價內,而 $35K call 也價內且會被執行。你等於用 $30K 進、$35K 出,每 BTC 固定賺 $5,000。本例 $5K 減掉 $800 成本,最大純利 $4,200。只要到期價超過 $35K,這策略再也不會多賺:因為 $30K call 的額外利潤都被 $35K call 的損失抵銷了。
-
If BTC instead fails to rally and stays below $30K, both calls expire worthless. You lose the $800 net premium – that’s your max loss, considerably less than if you had just bought a call for $1,200 outright.
-
如果 BTC 沒上漲,收盤在 $30K 以下,兩邊的 call 都會歸零。你最終只虧掉 $800 權利金。這比單純買 call($1,200)要小得多。
-
If BTC goes up modestly, e.g., to $33K, the $30K call has $3K value, the $35K call expires worthless (OTM). You could profit: $3k – $0 minus $800 cost = $2,200 gain.
-
若 BTC 小漲到 $33K,你的 $30K call 有 $3,000 內含價值,$35K call 價外歸零。這樣你可賺 $3K – $0 – $800 = $2,200。
-
The breakeven point here would be somewhere around $30,800 (lower strike + net cost) in price at expiration.
-
損益兩平點約 $30,800(低履約價 + 淨成本)。
The bull call spread is thus a risk-managed bullish play. You’re trading off unlimited upside for a higher probability of a decent return at lower cost. This strategy is popular if you have a specific target price or range in mind. It’s also useful when implied volatility is high (making outright calls pricey) – by selling one call, you offset some cost. A similar concept on the bearish side is the bear put spread: buy a higher-strike put, sell a lower-strike put to bet on a moderate decline with limited risk. Bull call spread 是風險控管型的看多策略,你用放棄無限上檔的條件,換取較大機率賺到一筆還不錯的收益,且總成本較低。這方法很適合你有明確目標價或區間時。當隱含波動率高(單買 call 很貴)時也很實用,因為賣掉一邊可以省點錢。看空時有類似概念:bear put spread,即買高履約價 put、賣低履約價 put,壓注適度回檔且最大損失可控。
6. Iron Condor (Advanced Range-Bound Strategy)
Goal: Earn income by selling volatility when you expect Bitcoin’s price to stay within a certain range, with limited risk on both sides. 策略目標:當你預期比特幣價格會維持區間整理時,透過賣波動性來賺取權利金收益,且同時限定上下行風險。
Strategy Outline: An iron condor is a combination of two spreads: you sell an out-of-the-money call and an out-of-the-money put (forming a short strangle), and simultaneously buy a further OTM call and put for protection. It consists of four legs: sell 1 OTM call, buy 1 higher strike call (to cap risk), sell 1 OTM put, buy 1 lower strike put (to cap risk). The result is you receive net premium upfront, and you have defined maximum loss. You profit most if Bitcoin’s price remains between the short strikes (so both the short put and short call expire worthless), letting you keep the premiums. 策略說明:Iron condor 結合兩組 vertical spread:賣出價外 call 與價外 put(形成 short strangle),同時分別買更遠價外的 call 和 put 作保險。總共有四條腿:賣價外 call、買更高價 call(限定風險)、賣價外 put、買更低價 put(限定風險)。這種結構可以讓你先收一筆權利金,且最大損失已鎖定。只要比特幣價格維持在兩個賣出履約價之間(即 short 端),call 與 put 都不會被執行,你就能全收權利金,收益最大。
How it works: Suppose BTC is around $30K, and you believe in the next month it will trade sideways between $25K and $35K (no major breakout). You construct an iron condor:
- Sell a $35K call, buy a $40K call (this is a short call spread).
- Sell a $25K put, buy a $20K put (this is a short put spread). Assume you collect $300 for the short call, $200 for the short put, and pay $100 each for the long call and long put for insurance. Net credit = $300+$200–$100–$100 = $300 received.
操作方法:假設 BTC 現價 $30K,你預期未來一個月會橫盤在 $25K~$35K(不會有大行情)。你可以這樣設計 iron condor:
- 賣 $35K call,買 $40K call(構成 short call spread)。
- 賣 $25K put,買 $20K put(構成 short put spread)。 假設賣 call 收 $300、賣 put 收 $200,買入保險各花 $100。總淨收入 $300+$200-$100-$100 = $300。
Now your critical zones:
-
Profit zone: roughly between $25K and $35K at expiration (the short strikes). If BTC stays in this range, both the short put and short call expire out-of-the-money. You keep the $300 premium entirely as profit, and the long options you bought expire worthless (which is fine, they were just insurance).
-
利潤區間:到期時若價格落在 $25K~$35K(兩賣盤履約價之間),兩個賣出的 put/call 都歸零,你全收 $300 權利金,買的保險部分作廢沒關係,那只是保護。
-
If BTC crashes below $25K: The short put becomes in-the-money. But thanks to the long $20K put you bought, your downside loss is limited. Essentially below $20K, both puts are ITM but the difference is capped. Your maximum loss on the put side is the difference between strikes (25K–20K = $5K) minus the net premium received. Using smaller numbers relative to premium: say you had a structure so max loss is $500, minus the $300 credit = $200 net max loss on that side. Similarly on the upside…
-
如果 BTC 跌破 $25K,賣的 put 變成價內,但你有買 $20K 的 long put 保險,最大損失受限。本質上,$20K 以下,兩個 put 都價內,但損失被價差限制。最大損失等於履約價差($25K–$20K = $5K),減掉收的權利金。舉例如果單位縮小,設計上最大損失 $500,扣掉 $300 收益,等於這側最大純損 $200;上面(call)一側也一樣有相同邏輯。 minus the premium. Again limited.
-
最壞情境:在到期時,若比特幣價格超過任一長倉價位(這裡假設為低於 $20,000 或高於 $40,000),你的其中一組價差會全額進價(ITM)。此時最大損失就是該價差間距減去你一開始收到的權利金。作為承擔這種風險的回報,你將會先收到 $300。
總結來說,鐵兀鷹價差策略在市場處於一個「舒適區間」時,可以帶來穩定(但相對有限)的收益,同時也自帶保險機制,避免市場劇烈波動時造成災難性的損失。交易者通常在低波動、盤整行情時選用「鐵兀鷹」策略來有系統地賺取權利金。由於此策略涉及四個選擇權倉位且需要謹慎的風險控管,因此被認為是進階策略。加密貨幣波動很大,若判斷失誤,「鐵兀鷹」可能非常危險——突發行情可能會同時打穿兩邊。不過,這種有限風險(本質上是兩組有對沖的價差單),其實比「裸賣」跨價策略(未對沖的買權賣權賣出,風險無上限)安全得多。
比特幣選擇權交易的風險與注意事項
雖然比特幣選擇權帶來許多機會,但同時也具備顯著風險。謹慎且具備知識地參與選擇權交易非常重要。以下是幾點主要風險與注意事項:
-
風險高於現貨交易:與單純做比特幣現貨交易相比,選擇權交易通常風險更高、機制更複雜。現貨比特幣若下跌,你頂多損失原始投入,可以選擇長抱期待反彈。但在選擇權交易(特別是你賣出選擇權或使用槓桿)時,若行情逆向,可能瞬間產生巨額損失。例如:你賣出的未對沖買權(uncovered call),若比特幣價格不停上漲,理論上損失無上限。即使選擇權買方損失有限,但如果到不到履約價,損失全部權利金的機會也不小。永遠不要用你無法承擔的資金來交易選擇權,因為這些合約可能毫無價值到期。
-
選擇權可能毫無價值到期:比特幣現貨沒有到期日,但選擇權有。如果你的行情預測未在到期日內實現,該選擇權可能一夜之間變得毫無價值。時機非常關鍵——你或許判斷「比特幣會上漲」沒錯,但若是在選擇權到期後才發生,上述交易依然會失敗。這種「時間風險」是現貨交易沒有的。許多新手低估了打平所需的價格跳動,因為要扣掉權利金成本。永遠計算「損益兩平點」(履約價±權利金)及剩餘時間。
-
複雜的定價與Greeks:選擇權價格除了標的資產變動外,還會受到許多關鍵因素(即「希臘字母」Greeks)影響:時間耗損(Theta)、波動率(Vega)、Delta(標的價格敏感度)、Gamma(Delta曲度)等等。例如:即使比特幣價格朝你預期移動,如果速度太慢,時間耗損(Theta)會吞噬掉權利金,或波動率下降導致價值縮水,選擇權仍可能貶值。這使得選擇權的損益(P&L)不像現貨那麼直觀。你至少要概念上理解以下幾點:
- Theta(時間耗損): 每天如果其他因素不變,選擇權會損失一些價值,尤其臨近到期日。選擇權屬於「遞減資產」。買方會和時間賽跑。
- Vega(波動率):購買選擇權後若市場波動下降,即便比特幣價格未動,權利金可能縮水,因為市場變平淡。反之,高波動會抬高權利金。
- Delta:深價外(OTM)選擇權Delta很低(對標的價格變動不敏感)、價內(ITM)Delta很高(近似持有現貨),平價(ATM)約為0.5。
- Gamma:賣方最怕Gamma,當標的移動,Delta會劇變,可能放大賣方損失。大幅急速行情可能把表面安全的賣方部位打穿變為大量義務。
你不需要當數學家,但必須理解選擇權的價值變動不會完全跟標的走,有時候會讓只關心現貨價格的新手大吃一驚。
-
流動性與市場結構:比特幣選擇權市場比幾年前大幅成長,但相較傳統市場,依舊年輕且沒那麼流動。大部分交易集中在少數平台(如Deribit歷史悠久,目前CME、OKX、Binance等也成長中)。這代表買賣價差可能較寬、深度不足,特別是長天期或遠價外選擇權。流動性不足將使進出場成本增加。滑價(成交價格偏差)是一項風險。另外,若非熱門月份或價格區間,可能難以找對手方。剛開始建議選擇流動性較好的到期日(月度、季度)與常見價位。
-
交易所與對手風險:在加密貨幣交易所交易時,意味著你多數情況需將資金託付於平台(除非用去中心化選擇權協議)。存在交易所遭駭、破產、技術故障等風險。例如市場劇烈波動時,有些衍生品平台曾因系統過載導致用戶不能及時操作,非常可怕。選擇有良好信譽、安全紀錄與保險基金的交易所至關重要。不論如何,切忌將所有資本放在單一平台。
-
保證金與強制平倉風險:如果你是「賣方」,交易所會要求保證金。倉位若逆風,保證金要求會動態調整。比特幣大幅波動時,賣方損失快速擴大,平台就會要求補充保證金;資金不足時,部位可能會被強制平倉(以極不利價格砍倉),造成慘重損失。務必了解交易所的選擇權保證金制度,有些採用「投資組合保證金」(會考慮避險部位),有些則較粗糙。請預留額外保證金並設好停損,避免強平。裸賣選擇權(無避險的賣方)風險極高,處理不好猶如在鐵路上撿硬幣。
-
法規與稅賦考量:根據你所在地不同,選擇權等衍生品可能有限制或資格要求。加密選擇權的法規環境正持續演進。例如Binance等平台會因地區不同設有限制;美國用戶基本無法合法使用離岸選擇權平台,只能用CME等合規渠道。一定要確認自己符合當地法規。此外,選擇權交易也有可能產生複雜的稅務結果(有些地方行使或到期時點就要課稅)。務必留存所有交易紀錄以便申報。
-
教育與策略:最後,不懂本身就是風險。選擇權常被稱為「非線性工具」,新手容易不知所措。投入大筆資金前,建議多學習。有大量相關資源(書籍、文章、測試網等)可供練習。建議先從最基本策略(買進買權或賣權、或簡單的covered call)開始,熟悉後再嘗試多腿組合或賣方策略。正所謂「別想一口氣吃成胖子」。好消息是資源越來越多——例如Binance就強制用戶在寫選擇權前需通過適合度測驗。
總結來說,比特幣選擇權提供強大的操作武器,但必須敬畏伴隨而來的風險。每次建倉請用你整體資產可承受的比例(選擇權波動極大,盈虧可能都很驚人)。善用工具——例如為單邊方向做單設停損、追蹤Greeks敏感度、與多腿組合理論上有助風險控管,避免單邊裸倉。隨著經驗增加,可逐步提升操作規模及複雜度。選擇權交易對懂行的投資人可能回報豐厚,對草率者則極為嚴酷。
結語
比特幣選擇權已從小眾產品發展為加密貨幣市場的重要一環——為交易員與投資人提供新的投機、避險及賺取收益工具。像Binance這樣的平台對所有用戶開放寫賣選擇權功能,就是市場成熟化的指標:這些原屬華爾街或老手的工具,如今一般用戶都能接觸。近年交易量激增數十倍,選擇權無疑已成為加密貨幣交易生態的核心。
本指南已涵蓋比特幣選擇權的要點及運作方式,從最基礎的買權(Call)和賣權(Put)概念,到選擇權定價與到期的運作細節。我們也探討了使用選擇權的動機——不論是避險、加槓桿抑或是賺取收益——並且逐步介紹如何實際在平台上下單,還包含多種熱門策略:從簡單的covered call、protective puts,到多腿價差及波動策略,每種手法在交易員工具箱裡都有其角色。
對一般有加密貨幣基礎的讀者而言,最重要的啟示是:選擇權能大幅提升你管理與獲利於加密投資的能力,並賦予你很大的彈性:Sure! Here's your translation into zh-Hant-TW, with markdown links left untranslated as requested:
你不再只限於當價格上漲時才能獲利——你可以利用「賣權」(put) 從價格下跌中獲益,甚至可以利用「跨式」(straddle) 從單純的波動性中賺錢,或透過賣出權利金策略從市場停滯時獲利。此外,期權如果用於避險,還能帶來一定程度的安全性(雖然聽起來有點矛盾)——例如,設置得當的保護性賣權能在市場崩盤時讓你避免災難性損失。
然而,能力越大,責任也越大。期權本身具有的複雜性和槓桿效果,意味著教育與謹慎至關重要。如果你是期權新手,建議從小額、簡單入手。或許可以先買入一兩張期權,感受一下期權價格如何相對於比特幣現貨價格波動。賣出(寫出)期權——像幣安現在廣泛提供的功能——很容易讓人因其帶來的收益而心動,但請記住賣出期權會帶來義務,而且潛在風險無上限。務必要完整理解市場劇烈波動時可能發生的所有情況。
令人鼓舞的是,像幣安這樣的大型交易所現在都導入了風險控制措施(測驗、保證金防護等)——請善加利用這些資源並測試你的理解。期權世界有它自己的術語(call、put、行使價、希臘字母、飛鳥策略等等),起初可能會讓人不知所措。但許多交易者發現,一旦你突然領悟,期權就變成在加密市場航行時不可或缺的工具——無論市場平靜或風暴皆可獲利,並可在需要時提供防護。
隨著加密市場持續演變,我們或許會看到更先進的衍生性商品,以及更多監管面的明朗化,促使更廣泛的參與。到目前為止,趨勢非常明確:不論散戶或機構都在擁抱加密期權,推動未平倉量創新高,甚至出現了基於期權策略的新ETF。對於願意花時間學習的人來說,比特幣期權帶來了數位資產交易的新機會前沿。
總結來說,若能善用知識,比特幣期權能大幅提升獲利並管理風險。它賦予的策略層次遠超出單純的「HODL」或「低買高賣」。不論你是想鎖定未來價格、幫持有資產買保險、用有限風險押注直覺、或為你的加密資產賺取穩定收益——總有對應的期權策略適合你的需求。只要謹慎踏出每一步,尊重潛在風險,並持續精進你的理解。透過實踐和謹慎,比特幣期權有機會成為你加密交易之旅中強大的盟友,讓你在市場中能更加靈活、自信地航行。





