美國正處於加密貨幣監管關鍵時刻。多年來,數位資產產業始終處於監管灰色地帶,證券交易委員會(SEC)與商品期貨交易委員會(CFTC)的職權重疊,兩者皆未對加密貨幣廣大市場擁有明確權限。市場參與者——從大型交易所、代幣發行商到散戶投資人——只能在曖昧不明的監管環境下,透過謹慎合規與高額訴訟成本掙扎前行。
這一局面可能很快將徹底改變。2025年11月10日,參議院農業委員會主席John Boozman與參議員Cory Booker公布了一份跨黨派討論草案,準備根本性重塑美國加密貨幣監管。該法案提議將現貨數位商品交易的主要監督權從SEC轉交CFTC,將大多數加密貨幣歸類為數位商品(非證券),並建立美國第一套針對加密市場結構的聯邦監管框架。
這標誌著參議院迄今為止最嚴肅企圖與眾議院在相關立法上齊頭並進。2025年7月,眾議院以294票對134票通過「數位資產市場明確法案」,顯示出監管明確性獲得強烈的跨黨派支持。Boozman-Booker草案建立在該基礎上,汲取眾議院經驗,同時回應參議院對執法資源、消費者保護,以及CFTC監管新市場能力等特別關切。
此次改革意義重大。美國已在建立數位資產明確規則方面落後於其他主要司法管轄區。歐盟的加密資產市場監管規定(MiCA)於2024年12月全面生效,打造出全球最全面的加密監管框架。同時,新加坡、英國、阿聯酋等國亦極力推進各自方案。如今問題不是美國該不該監管加密,而是如何監管,以及由誰主導。
本文將深入解析最新動態,探討法案在實務運作上會如何推動變革,及其對創新、市場、投資人與國際競爭產生的影響。我們會回顧美國走到今日的歷史進程,詳解立法機制,剖析對不同市場參與者的意涵,評估未來挑戰與風險,並將美國做法放到全球監管脈絡中比較。
歷史回顧:我們如何走到這裡
加密監管模糊的起源
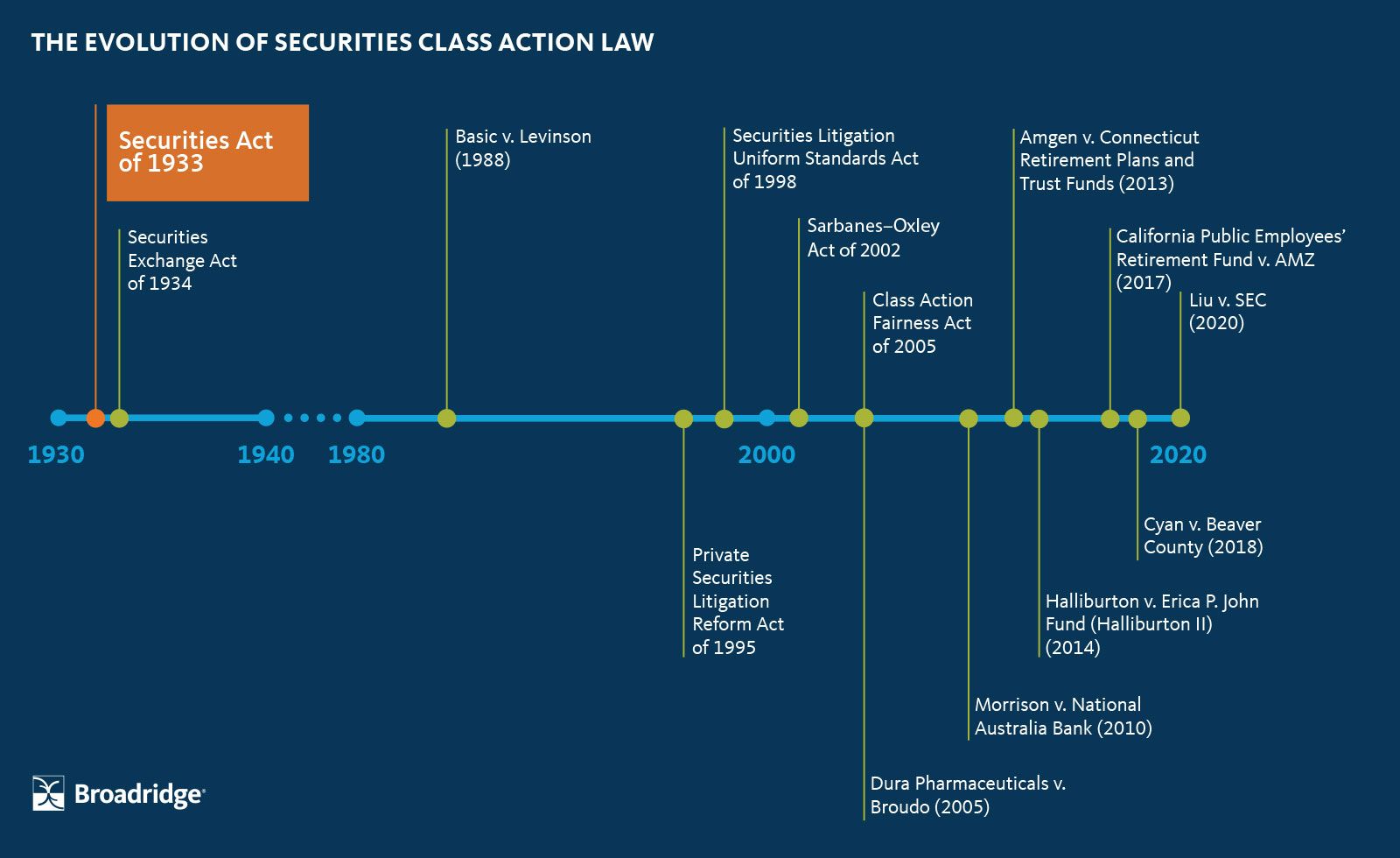
圍繞加密貨幣的監管混亂,源於法律根本不相容:比特幣2009年面世,但主要相關法律追溯到1930–40年代。《1933年證券法》、《1934年證券交易法》和《1936年商品交易法》都是為實體股票憑證、穀物期貨與集中交易所設計,未曾考慮去中心化、點對點網絡,以及商品、貨幣、證券及支付系統界線模糊的狀況。
2000年《商品期貨現代化法案》樹立先例,對部分場外衍生品進行去監管,並豁免某些數位金融工具納入傳統商品監管。該法賦予CFTC監管商品期貨及選擇權,SEC則維持證券監督權限。但加密資產卻未明確歸屬任何一類。比特幣交易該算證券發行?商品交易?還是資金匯款?抑或三者皆是?
多年來,這種模糊幾乎沒有產生嚴重後果。加密市場規模小且偏重零售,監管機構多採觀望,允許產業自行發展,偶爾僅對詐騙與風險提出警語。情勢自2017年創新幣發行(ICO)熱潮、資金大量湧入後才開始改變。
SEC主導的執法
SEC率先並積極出擊。在不同政府領導下,該機關援引Howey測試——一套1946年最高法院用以判定何謂投資合約的標準——認定ICO大多數代幣屬於未註冊證券。SEC展開大規模執法行動,要求許多項目向SEC註冊、歸還資金或繳納巨額罰款。
主席Gary Gensler 2021年上任後立場更趨強硬。Gensler為前MIT區塊鏈教授,主張絕大多數加密資產本質為證券,現行證券法律已足夠規範數位資產;他反對立新法,堅稱「加密產業失敗、詐欺和破產不是沒規則,而是業者拒絕遵守規則」。
這導致多宗高知名度訴訟。SEC於2023年起訴Coinbase涉嫌未註冊證券交易所、經紀商與清算機構身份,同樣也對Binance、Kraken等大型平台提訴,明確傳達訊息:不照證券法規則則面臨嚴厲執法。
CFTC的平行監督
CFTC態度略異。SEC聚焦於判斷代幣是否證券,CFTC則直接認定比特幣、以太坊屬大宗商品,特別是在衍生性商品市場。CFTC主張比特幣等數位資產為商品,當在期貨及選擇權市場交易時須受《商品交易法》規範。
CFTC執法以嚴查未註冊衍生性商品交易所為主。2023年,該單位起訴Binance及創辦人趙長鵬、前首席合規官Samuel Lim,指控其非法經營數位資產衍生品交易且刻意規避美國法。和解方案要求Binance支付近30億美元,其中13.5億為CFTC史上最高罰金,刷新紀錄。
隔年CFTC追討金額更甚。CFTC 與FTX及Alameda Research達成和解,須支付127億美元賠償及追繳不當得利,打破歷來紀錄。這些龐大案件展現CFTC執法能力,卻也引發其是否有足夠資源承擔擴充後職權之疑慮。
整體而言,2023財年CFTC 96件執法行動中有47件涉及數位資產,佔總案件逾49%;2024年,數位資產相關事件帶來近75%金額賠付,高達170億美元。儘管缺乏現貨市場明文授權,CFTC已然成為美國加密主要執法機構。
推動立法解決方案
監管重疊與不確定性,促使各界呼籲國會解決。業界認為雙重監管產生難以承擔的合規壓力。發幣方面臨同一資產因銷售對象、交易平台而被SEC當作證券或被CFTC當作商品的風險,交易所難以判斷不同產品適用何規則。
早期立法推動進展有限。參議員Kirsten Gillibrand與Cynthia Lummis 2022年提出「負責任金融創新法案」,盼建構完整監管框架,最終也僅停留委員會討論。其他提案亦因黨爭及產業與消費者團體遊說而未果。
轉機自眾議院開始。眾議員Glenn Thompson與Patrick McHenry主導推進「21世紀金融創新與科技法案(FIT21)」,規劃明確分劃SEC與CFTC的監管界線,對符合去中心化標準的數位資產進行分流... standards would be regulated as commodities by the CFTC, while those controlled by centralized entities would remain securities under SEC oversight.
標準將由CFTC作為商品進行監管,而由中心化實體控制的資產則仍然為證券,並接受SEC的監督。
FIT21 passed the House in May 2024 by a vote of 279-136, with 71 Democrats joining Republicans in support. It marked the first time comprehensive crypto legislation had cleared a chamber of Congress. However, the Senate took no action on the bill, and it died at the end of the congressional session.
FIT21於2024年5月在眾議院以279票對136票的結果通過,其中有71名民主黨議員和共和黨人一同支持。這是美國國會首次有完整的加密貨幣立法在其中一個議院獲得通過。然而,參議院並未對該法案採取行動,法案也於本屆國會會期結束時失效。
The House tried again in 2025 with the CLARITY Act, a refined version of FIT21. Passed in July 2025 with 294 votes in favor, including 78 Democrats, the legislation demonstrated even stronger bipartisan support. But it still required Senate action to become law.
眾議院於2025年再次嘗試,提出了CLARITY法案,這是FIT21的改良版本。該法案於2025年7月以294票贊成(其中包括78名民主黨人)通過,展現出更強烈的兩黨支持。但法案要成為法律,仍需參議院的通過。
The Trump Factor
川普因素
The political landscape shifted significantly with President Donald Trump's return to office in January 2025. Having previously expressed skepticism about cryptocurrencies, Trump reversed course and vowed to make America the "crypto capital of the planet". His administration actively lobbied Congress to pass comprehensive crypto legislation before the August 2025 recess.
隨著唐納·川普總統於2025年1月重返白宮,政治局勢顯著轉變。川普先前曾對加密貨幣表現懷疑,但他隨即改變立場,並誓言要讓美國成為「全球加密貨幣之都」。川普政府積極遊說國會,要求在2025年8月國會休會前通過全面加密立法。
This pressure bore fruit. In July 2025, Congress passed and Trump signed the Guiding and Establishing National Innovation for U.S. Stablecoins Act (GENIUS Act), establishing the first federal framework for payment stablecoins. The law marked a historic milestone: the first major crypto legislation to become law in the United States.
這項壓力終於開花結果。2025年7月,國會通過並由川普簽署《美國穩定幣國家創新引導及建立法案(GENIUS Act)》,建立了美國首個有關支付型穩定幣的聯邦監管框架。這部法律成為歷史性里程碑:為美國首部成為法律的主要加密立法。
The Trump administration's enthusiasm for crypto regulation stemmed partly from ideological alignment with the industry's focus on financial innovation and deregulation. But it also reflected practical concerns. Without clear rules, the U.S. risked losing its competitive edge to jurisdictions like the EU, Singapore, and the UAE that were actively courting crypto businesses with regulatory certainty.
川普政府對加密監管的熱情,部分源自其與產業在金融創新和放寬管制上的理念一致。但這同時也是出於務實的考量——如果沒有明確規則,美國將有失競爭優勢,落後於歐盟、新加坡、阿聯酋等積極以監管明確性吸引加密業者的司法管轄區。
The administration endorsed giving the CFTC primary authority over spot crypto markets. Officials argued the agency's principles-based approach and focus on market integrity made it better suited than the SEC for overseeing trading platforms and commodity transactions. Critics, however, noted that the president's family held significant personal investments in crypto ventures, raising conflict-of-interest concerns.
政府支持將加密現貨市場的主要監管權賦予CFTC。官員認為,CFTC以原則為本、重視市場誠信的方式,比SEC更適合監管交易平台和商品交易。然而,批評者指出,總統家族在加密企業有大量個人投資,引發利益衝突疑慮。
What is the Draft Legislation?
什麼是此項草案立法?
The Boozman-Booker Discussion Draft
Boozman-Booker 討論版草案
The November 2025 draft represents months of quiet bipartisan negotiation between Senate Agriculture Committee Chairman John Boozman, an Arkansas Republican, and Senator Cory Booker, a New Jersey Democrat. Unlike the House's CLARITY Act, which covers both SEC and CFTC jurisdiction, the Senate Agriculture Committee's draft focuses specifically on the CFTC's new authorities. It will eventually need to merge with separate legislation from the Senate Banking Committee, which oversees the SEC, to create a comprehensive framework.
2025年11月的草案代表了兩黨經數月低調協商,由參議院農業委員會主席、阿肯色州共和黨人John Boozman,與新澤西州民主黨參議員Cory Booker合作擬定。不同於眾議院的CLARITY法案涵蓋SEC與CFTC職權,本草案專注於CFTC新權限。未來仍需與參議院銀行委員會(負責SEC監管)另案合併,才能建立完整的法規框架。
The timing is deliberate. The draft builds upon the House CLARITY Act while addressing concerns raised by Democrats and some moderate Republicans about enforcement capacity and consumer protection. Senator Booker noted that the discussion draft is "a first step" and significant work remains before advancing the legislation out of committee, particularly regarding resources for the CFTC, preventing regulatory arbitrage, and ensuring guardrails against corruption.
時間點的選擇也是經過深思熟慮。該草案以眾議院的CLARITY法案為基礎,並回應了民主黨及部分溫和派共和黨人對執法能力與消費者保護的關切。Booker參議員指出,本討論版只是「第一步」,未來法案要順利出委員會,還有許多重要工作要做,特別是CFTC資源配置、防止監管套利,以及反貪腐機制設計等。
Key Provisions and Definitions
主要條文與定義
At the heart of the legislation is a formal legal definition of "digital commodity". The bill describes digital commodities as fungible digital assets that can be exclusively possessed and transferred person-to-person without necessary reliance on an intermediary, and are recorded on a public, distributed blockchain or similar decentralized system. This definition deliberately excludes most tokenized securities while capturing Bitcoin, Ethereum, and similar decentralized cryptocurrencies.
本法案核心在於明確界定"數位商品"的法律定義。法案將數位商品定義為:可替代、可單獨持有且能點對點轉移、無需依賴中介並記錄於公共分散式區塊鏈或類似去中心化系統的數位資產。該定義有意排除大部分代幣化證券,同時涵蓋比特幣、以太幣及類似的去中心化加密貨幣。
The definition matters enormously because it determines regulatory jurisdiction. Assets classified as digital commodities would fall under CFTC oversight for spot trading, meaning the agency would regulate how they are bought, sold, and exchanged on trading platforms. Assets that do not meet the digital commodity definition — particularly those that represent ownership stakes, profit-sharing rights, or other characteristics of traditional securities — would remain under SEC jurisdiction.
此定義意義重大,因其決定監管歸屬。被歸類為數位商品的資產,其現貨交易將由CFTC監督,涵蓋其在交易所的買賣與交換方式。不符合數位商品定義的資產——特別是代表所有權、分潤權利或具傳統證券特徵者——則維持在SEC管轄範圍下。
The draft explicitly protects self-custody rights, a priority for the crypto community. Individuals could hold and transact digital assets directly through hardware or software wallets without being treated as money transmitters under federal law. Software developers would also gain protection from regulation simply for publishing code or running blockchain infrastructure, though the draft clarifies this is "not a safe harbor for operating DeFi interfaces."
草案明確保障自我託管權利,這對加密社群而言至關重要。個人可透過硬體或軟體錢包直接持有並交易數位資產,而不會被聯邦法律視為資金傳遞者。軟體開發者僅因發布程式碼或運營區塊鏈基礎架構,也將受規範豁免保護,但草案強調「不適用於DeFi介面營運的避風港」。
Registration Requirements and Market Structure
登記要求與市場結構
The bill would establish a formal registration system for digital commodity trading platforms, similar to how traditional commodity exchanges must register with the CFTC. Platforms facilitating spot trading in Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other digital commodities would need to register and comply with rules on anti-fraud measures, recordkeeping, fund segregation, and dispute resolution. This represents a fundamental shift: currently, crypto exchanges operate largely outside the traditional regulatory perimeter for commodity markets.
法案將建立數位商品交易平台的正式登記制度,類似於傳統商品交易所須向CFTC登記。目前推動比特幣、以太幣等數位商品現貨交易的平台,必須登記並遵守反詐欺、帳簿紀錄、客戶資金隔離及爭議解決等規定。這帶來根本改變——目前大多數加密貨幣交易所其實大多於傳統商品市場監管範圍外營運。
Separate registration frameworks would apply to brokers and dealers in digital commodities. The bill includes bracketed sections — legislative shorthand indicating unresolved policy questions — around whether the CFTC should have broad exemption powers for certain types of brokers or dealers. This remains a point of negotiation, with industry advocates seeking flexibility for smaller market participants while consumer protection advocates want comprehensive oversight.
針對數位商品經紀人與自營商,則設有獨立登記架構。法案中有「中括號」註明尚未定案的政策問題——CFTC是否應對特定類型的經紀人/交易商具有廣泛豁免權限,目前仍在協商中。業界倡議者期盼小型業者具彈性,消費者保護派則希望加強全面監管。
Customer protection rules would require trading platforms to segregate customer funds from the platform's own operational money, preventing the type of commingling that contributed to FTX's collapse. Platforms would need clear disclosure requirements for retail investors, making explicit the risks of digital commodity trading, custody arrangements, insurance coverage (if any), and potential conflicts of interest.
客戶保護規則要求交易平台必須隔離客戶資金,不得與營運資金混合使用,以防止類似FTX崩潰的情況發生。平台需對散戶明確揭露數位商品交易風險、託管安排、相關保險(如有)及潛在利益衝突。
The bill creates a 270-day transition period after enactment, allowing existing operators to continue functioning while awaiting registration approval. This gradual implementation aims to prevent market disruption while ensuring firms have adequate time to build compliance infrastructure.
法案訂定施行後270天過渡期,讓現有業者在申請登記審核期間可維持正常運作。這種漸進式上路安排,兼顧防止市場動盪與企業建構合規體系所需緩衝時間。
Funding and Resources
資金與資源
Recognizing the CFTC's limited resources, the draft proposes a dedicated funding stream for the new spot market regime. Registration fees collected from digital commodity platforms, brokers, and dealers would go directly to the CFTC without requiring further congressional appropriation. This follows the model established by the FIT21 and CLARITY Acts, which proposed capping CFTC fee revenue at $40 million annually.
考量CFTC資源有限,草案提議成立專屬經費來源於新現貨市場制度。數位商品平台、經紀人與自營商繳納的登記費將直接撥至CFTC,無需再經國會追加預算。這延續FIT21及CLARITY法案所設年收費上限4,000萬美元的模式。
The resource question looms large in the debate. The SEC employs approximately 4,500 staff members focused on securities regulation, enforcement, examinations, and rulemaking. The CFTC, by contrast, has roughly 700 employees overseeing all U.S. commodity derivatives markets. Critics worry that adding oversight of the massive spot crypto market — valued in the trillions of dollars with millions of retail participants — could overwhelm the smaller agency.
「資源問題」始終是辯論焦點。SEC大約有4,500名員工,專職證券監管、執法、檢查及制定規則;而CFTC僅有約700人負責全美所有商品衍生品市場。批評者擔心,若再讓CFTC監管規模達數兆美元、參與者數百萬的加密現貨市場,規模較小的CFTC恐無法負荷。
Senator Booker's statement acknowledged these concerns directly, noting he is "specifically concerned about the lack of resources and the bipartisan commissioners at the CFTC". The issue may become a key negotiating point as the bill advances, with Democrats likely to demand substantial funding increases and staffing commitments as a condition for their support.
Booker參議員亦正面回應此憂慮,強調他"特別擔心CFTC人力與資源不足,以及該機構兩黨委員人數"。未來法案推進時,這將成重要協商點,民主黨料將以大幅增加經費與人力配置作為支持條件。
Relationship with SEC Authority
與SEC職權之關係
The draft requires coordination between the CFTC and SEC through joint rulemaking on overlapping issues. This includes portfolio margining of securities and digital commodities, oversight of intermediaries that operate in both markets, and establishment of the boundaries
草案要求CFTC與SEC協調,針對業務重疊議題共同制定規則,包括證券與數位商品的組合保證金安排、同時營運於兩市場的中介機構監管,以及相關職權界線的確立。between each agency's jurisdiction. The coordination mandates echo provisions in the Dodd-Frank Act, which required similar cooperation between agencies after the 2008 financial crisis.
在各機關的職權範圍之間。這些協調規定呼應了《多德-法蘭克法案》的條文,該法在2008年金融危機後就要求各機關之間的類似合作。
Securities-classified tokens — those meeting the Howey test as investment contracts — would remain under SEC jurisdiction for both primary issuance and secondary trading. The draft acknowledges that some digital assets may start as securities (when first sold in a centralized offering) but later transition to commodities (once the underlying network achieves sufficient decentralization). The agencies would need to develop joint guidance on how and when such transitions occur.
證券型代幣——即符合豪威測試、屬於投資合約的代幣——在初級發行和次級市場交易上,將維持在美國證券交易委員會(SEC)的監管範圍內。草案也承認,部分數位資產可能在初次以集中方式發行時屬於證券,但隨著其底層網路達到足夠的去中心化後,會轉變為商品。相關機關將需共同制定指引,說明這種轉換發生的時機與方式。
Some sections include bracketed minority views from Democratic committee members, indicating disagreement over which committee has jurisdiction over certain provisions. For instance, Democrats on the Agriculture Committee believe provisions on blockchain developer immunity properly belong under the Banking Committee's oversight. These jurisdictional disputes will need resolution before the bill advances.
部分章節含有括號標記的民主黨委員少數意見,顯示部分條款的管轄權歸屬仍有爭議。例如,農業委員會的民主黨成員認為,有關區塊鏈開發者豁免的條款,應由銀行委員會負責監督。這些職權爭議必須先解決,法案才能繼續推進。
DeFi: The Unresolved Question
Perhaps the draft's most notable feature is what it leaves unanswered about decentralized finance (DeFi). The entire section on DeFi oversight currently reads "Seeking further feedback," with numerous bracketed provisions indicating ongoing debate. DeFi protocols — which enable peer-to-peer trading, lending, and other financial services without traditional intermediaries — present unique regulatory challenges.
或許草案最受矚目的地方,在於其對去中心化金融(DeFi)所遺留的未解問題。針對DeFi監管的整個章節,目前僅寫著「徵求進一步意見」,並有多處括號刮註,顯示相關討論仍在持續。DeFi協定能讓用戶在沒有傳統中介機構的情況下進行點對點交易、借貸及其他金融服務,因此帶來獨特的監管挑戰。
Should DeFi protocols themselves be subject to registration if they facilitate digital commodity trading? What about the developers who build them? The liquidity providers who fund them? The governance token holders who vote on protocol changes? These questions lack clear answers in traditional commodity or securities law, and legislators are still grappling with how to address them without stifling innovation or driving development offshore.
若DeFi協定促成數位商品交易,本身是否應登記註冊?開發這些協定的工程師是否需要受管?資助協定的流動性提供者呢?參與協定治理、投票表決的治理代幣持有人又該納入監管嗎?這些問題在傳統商品或證券法下都沒有明確答案,立法者仍在摸索,如何兼顧監管與創新發展,避免把開發推向海外。
The draft's caution on DeFi reflects genuine uncertainty about the right regulatory approach. Overly broad rules could make it impossible to operate decentralized protocols from the U.S., pushing innovation to friendlier jurisdictions. But exempting DeFi entirely could create massive regulatory loopholes, allowing billions of dollars in transactions to occur beyond the reach of anti-fraud, anti-money laundering, and consumer protection rules.
對DeFi保留審慎態度,可以看出目前對於正確監管手段確實存在極大不確定性。過於寬泛的規則可能使DeFi協定難以在美國境內運作,把創新推向監管友善的海外地區;而完全豁免DeFi,則可能製造巨大的監管漏洞,讓數十億美元的交易逃避防詐、反洗錢以及消費者保護法規。
How Will It Work in Practice?
The New Regulatory Architecture

If enacted, the legislation would create a fundamentally different regulatory landscape for digital assets. The CFTC would gain explicit statutory authority to regulate spot digital commodity markets, moving beyond its current jurisdiction over only derivatives. This expansion would require the agency to build out entirely new regulatory frameworks, examination programs, enforcement strategies, and industry guidance.
若法案通過,將為數位資產創造一個全新的監管架構。商品期貨交易委員會(CFTC)將獲明文授權,可以監管現貨數位商品市場,不再侷限於目前僅能監管衍生品的職權。為此,該機關需建立全新的監理框架、稽核計劃、執法策略及業界指引。
Digital commodity trading platforms would face a comprehensive set of obligations. They would need to register with the CFTC, implement anti-fraud and anti-manipulation controls, maintain detailed transaction records, segregate customer assets from firm capital, establish robust cybersecurity programs, adopt dispute resolution mechanisms, and provide clear disclosures to retail customers about risks, fees, and terms of service.
數位商品交易平台將面臨一套完整的合規規定。它們必須向CFTC登記,執行防詐及防操縱機制,保存詳細交易紀錄,將客戶資產與自有資金分離,建立健全的資安措施,採納糾紛處理機制,並向零售客戶充分披露風險、費用及服務條款。
Broker-dealers would operate under separate rules tailored to their role as intermediaries. They would need to meet capital requirements ensuring they can fulfill customer obligations, implement supervisory systems monitoring employee conduct, manage conflicts of interest, and maintain records of all customer interactions and transactions. These requirements mirror, to some extent, the obligations already imposed on securities broker-dealers by the SEC, but would be adapted for the unique characteristics of digital commodities.
經紀商將遵循專門針對其中介角色設計的規定。他們需符合淨資本要求,確保有能力履行客戶義務,建立內控監督員工行為、管理利益衝突機制,保存所有客戶互動與交易記錄。這些要求在某種程度上參照了SEC對證券經紀商的監管義務,但會依數位商品的獨特性調整。
Classification and the Decentralization Question
The most consequential aspect of the new regime involves how tokens are classified. Under current law, classification often depends on subjective judgments about whether a token sale constitutes an investment contract. The new framework would establish more objective criteria, focusing on factors like network decentralization, control over governance, and the expectation of profits from others' efforts.
這套新制度最具影響力的環節是,如何界定各類代幣的屬性。根據現行規範,分類往往取決於主觀判斷——代幣銷售是否屬於投資合約。新框架則試圖建立較客觀的評估標準,強調網路去中心化程度、治理權控管,以及是否仰賴他人努力來獲利等因素。
Bitcoin and Ethereum would clearly qualify as digital commodities given their high degree of decentralization. No single entity controls either network, both have distributed governance, and neither depends on a central issuer's efforts for value appreciation. Other established proof-of-work and proof-of-stake networks with sufficient validator distribution would likely also qualify.
比特幣與以太坊由於高度去中心化,顯然屬於數位商品。這兩個網路沒有單一控制者,治理分散,也無需中央發行方努力以支撐其價值。其他已發展出的PoW或PoS公鏈,只要驗證者夠分散,也可能歸為此類。
Newer tokens present more complexity. A project might launch with a centralized team controlling most governance tokens, making it an investment contract (and thus a security) under SEC jurisdiction. Over time, as the team distributes tokens more broadly and implements decentralized governance, the project could transition to digital commodity status under CFTC oversight. The agencies would need to establish clear guidance on when and how such transitions occur.
較新發行的代幣狀況則更複雜。某些專案初期由集中化團隊掌控大部分治理代幣,屬於投資合約(因此歸SEC管轄)。隨著團隊廣泛分發代幣,建立去中心化治理後,該專案可望轉為數位商品,移交CFTC監督。機關間必須明確指引何時、如何判斷這種屬性轉換。
Investor Protections and Disclosure
Disclosure requirements would mark a significant change for the crypto industry. Trading platforms would need to provide customers with detailed information about how assets are held, whether customer funds are insured or guaranteed (typically they are not), the platform's financial condition, potential conflicts of interest (such as proprietary trading), and comprehensive fee schedules.
揭露義務將為加密產業帶來重大變革。交易平台需向用戶說明資產如何保管、客戶資金是否有保險或擔保(通常沒有)、平台財務狀況、潛在利益衝突(如自營交易),以及完整的費率標準。
These disclosures would need to be clear, prominent, and accessible to retail investors. The CFTC would likely require platforms to use plain English explanations rather than dense legal or technical jargon. Customers would need to affirmatively acknowledge understanding the risks before opening accounts, similar to the process for opening traditional brokerage accounts.
這些揭露資訊必須明確、顯眼且易於一般投資人理解。CFTC預料會要求用純白話(非法規術語或技術用語)說明。用戶開戶前須主動確認了解各項風險,和傳統券商開戶流程類似。
Custody and segregation rules aim to prevent another FTX-style collapse. Customer assets would need to be held separately from the platform's own funds, clearly identified as customer property, and protected from claims by the platform's creditors in bankruptcy. Regular attestations by independent auditors would verify that customer assets are fully reserved and accessible.
資產託管與分離要求,目的在防堵另一個FTX事件發生。用戶資產必須與平台自有資金嚴密分離,清楚標示屬於客戶財產。萬一平台破產,客戶資產不得被平台債權人主張。獨立會計師要定期驗證資產是否全額備齊且隨時可動用。
Transition Mechanics
The 270-day transition period would begin upon enactment. During this time, the CFTC would need to issue interim final rules establishing registration procedures, application requirements, compliance standards, and examination priorities. Existing platforms could continue operating while awaiting approval of their registration applications, creating a grandfathering mechanism that prevents market disruption.
施行後將有270天的過渡期。在此期間,CFTC要訂出臨時最終規則,包括註冊流程、申請文件、合規標準和查核要點。既有平台可在等待註冊核可時繼續運作,形成一種舊制保留機制,避免市場動盪。
Platforms would need to submit comprehensive registration applications including information about their organizational structure, key personnel, custody arrangements, cybersecurity systems, financial resources, and compliance programs. The CFTC would review applications, request additional information, conduct examinations of applicants' systems and controls, and grant or deny registration based on whether applicants meet statutory and regulatory standards.
平台需繳交完整登記資料,包括組織架構、主要人員、託管方式、資安設施、財務資源及合規措施。CFTC將審閱申請、要求補件、稽核申請人的系統與管控流程,最後依其是否符合法規標準決定是否核發登記資格。
Some firms might face difficult choices during the transition. Platforms currently offering both digital commodities and securities-classified tokens would need to either separate their operations into distinct entities (one registered with the CFTC, another with the SEC) or choose to focus on one asset class. Compliance costs could push smaller platforms to consolidate or exit the market.
部分業者在過渡期會面臨抉擇。目前同時提供數位商品及證券型代幣的平台,要嘛將業務切分為兩家公司(分別向CFTC及SEC登記),要嘛聚焦於其中一類資產。合規成本可能會壓縮小型業者,只能選擇併購或退出市場。
Global Context and Cross-Border Issues
The U.S. framework would need to coordinate with international approaches, particularly the EU's MiCA regulation. Many crypto platforms operate globally, serving customers across multiple jurisdictions. A platform registered with the CFTC for U.S. customers might simultaneously operate under MiCA in Europe, FCA regulation in the UK, and MAS oversight in Singapore.
美國架構還需與國際監理措施協調,特別是歐盟的MiCA規則。許多加密平台跨國經營,同時服務多地用戶。某平台如果在美國向CFTC登記,也可能受歐洲MiCA、英國FCA、新加坡MAS等監管。
Cross-border coordination would address issues like information sharing between regulators, recognition of foreign regulatory approvals, and prevention of regulatory arbitrage. The legislation explicitly contemplates international harmonization efforts, though the specific mechanisms remain to be developed through agency rulemaking and bilateral or multilateral agreements.
跨境協調主要聚焦監理機關間的資訊分享、對國外監管認證的認可以及防止監管套利。法案明定會推動國際監管協調,但具體機制還有待各機構透過規章、雙邊或多邊協議訂立。
The dollar-dominated nature of crypto markets gives the U.S. outsized influence. Stablecoins like USDC and USDT, which are pegged to the U.S. dollar and widely used in crypto trading, fall partly under U.S. regulatory jurisdiction regardless of where the issuing platform is located. This creates natural leverage for U.S. regulators to shape global standards through their domestic framework.
加密市場以美元為主,讓美國監管有巨大影響力。像USDC、USDT等美元穩定幣,即使發行平台設在海外也受美國法規部分約束。美國因此能憑本國監管制度帶動國際標準的定型。
Why It Matters: Implications for Industry, Innovation & Markets
For the Crypto Industry: The End of Regulatory Uncertainty?
The industry has long argued that regulatory clarity would unlock innovation and investment。在沒有明確規則的情況下,許多傳統金融機構選擇觀望,不願冒風險涉足灰色地帶市場,以免遭到執法行動。銀行對於託管加密資產或向客戶提供加密服務持觀望態度。機構投資者縮限了他們的曝險部位。支付處理商則避免促成加密貨幣交易。
一個明確的CFTC監管框架可能會改變這種局面。銀行將可以有信心地為數位商品提供託管服務,而不必擔心因處理未註冊證券而被SEC執法。傳統交易所則可將數位商品產品與股票、債券並列上市。退休基金與捐贈基金可將加密資產納入多元資產組合分散風險。支付網絡也能將數位商品整合進支付軌道。
對自我託管明文保護對加密社群的理念基礎意義重大。去中心化倡議者認為,擁有自己私鑰——即無需依賴中介便能控制數位資產——是加密貨幣存在的根本意義。將自我託管權利編入聯邦法,顯示政府監管未必會抹煞讓加密貨幣與眾不同的點對點、免信任特性。
開發者保護措施可激勵開源創新。目前,軟體開發者對於開發DeFi協議或其它加密基礎建設是否會讓自己暴露於匯款人規範或其它法律責任下感到不確定。若對純開發工作(區別於運營平台或服務)提出明確的安全保障,程式設計師便可無憂地貢獻於區塊鏈生態系,而不必擔心誤觸法律風險。
然而,新架構同時也會帶來龐大的合規成本。向CFTC註冊需建立合規部門、實作監控系統、聘請法務與風控人員,並接受定期檢查。規模較小的平台可能難以負擔,市場因此有機會出現整併,僅剩資金雄厚的交易所能達到監管標準。
關於代幣分類:商品 vs. 證券
從證券轉為商品分類將徹底改變代幣經濟學與市場結構。證券發行須廣泛揭露資訊、向SEC註冊、持續申報及受限於交易規則。這些要求既昂貴又曠日廢時,因此許多代幣項目乾脆避開美國市場,或將代幣銷售限定給合格投資人與海外買家。
商品分類則能大幅降低這些門檻。數位商品可直接向美國散戶投資人發行,無需證券註冊,但平台仍需CFTC註冊,並須遵守客戶保護規定。代幣發行者可在多個平台同時上市,無需面對各交易所專屬的上幣要求。次級市場可更自由交易,提升流動性與價格發現效率。
創投投資模式料將跟著改變。過去VC對代幣項目投資謹慎,因為若SEC其後認定為證券,投資人可能面臨賠償義務。有明確商品分類後,創投資金更有機會流向建構於去中心化網絡的項目,進而加速DeFi、Web3應用和區塊鏈基礎設施創新。
這套分類框架也將影響項目設計代幣分配模式。過去做初始代幣發行(ICO)往往近似證券發行未能通過審查;未來項目可直接在達到去中心化標準的區塊鏈上發代幣,即時被認定為數位商品。這將帶動更負責任的發行模式,項目必須展示真正的去中心化,而非讓創辦團隊集中控制。
關於投資人保護:情況複雜
消費者維權者擔心,將監管轉至CFTC恐削弱投資人保護措施。CFTC過去聚焦於機構衍生品市場,參與者普遍專業且資源充足。而加密現貨市場的散戶投資人風險承擔能力、辨識平台風險的能力不足,更易淪為詐騙、缺乏法律救濟資源。
草案中的揭露與託管要求可解決部分疑慮。強制資金分離能防止平台挪用客戶資產。定期審計能確保客戶資金全額備付。資訊揭露讓投資人明白風險、費用與合約條款。這些規定和證券監理類似,但無法完全取代SEC全面的投資人保護體系。
執法權限也是一大考量。SEC可依證券法提起詐欺訴訟,為投資人爭取三倍賠償和其它強力救濟;CFTC的商品詐欺執法雖然有力,但結構不同。集體訴訟、私人索賠權、舉證標準可能因案件究竟屬於證券詐欺還是商品詐欺而不同。
CFTC資源有限令人憂慮其稽查頻率與執法力度。全美僅700名員工肩負所有商品衍生品市場與現貨加密新任務,機構恐難以定期審查每個註冊平台。若審查間隔過長,問題恐積壓無法及時偵測,可能讓詐欺或不當行為作大害投資人,直到監管機構介入已經太遲。
關於市場結構:交易所、DeFi與資產代幣化
加密貨幣交易所將面臨最直接的營運變革。如Coinbase、Kraken和Gemini等主流平台,早已具備完善合規基礎,因此註冊CFTC未必會本質上顛覆其商業模式。但正式監管框架將帶來合法性與法律明確性,有助擴展服務及用戶基礎。
海外交易所則面臨更複雜抉擇。像Binance這類因監管不明而縮減或退出美國市場的平台,需評估CFTC註冊是否值得重返美國。美國市場規模巨大令人嚮往,但需考量合規成本、過往行為被追溯執法的風險,以及其它司法管轄區可能條件更優。
DeFi協議則是最棘手課題。草案並未明確納入DeFi監管,導致根本性的不確定性未解。自動化做市商、允許以加密資產作為抵押品借貸、還有提供合成資產曝險的衍生協議,都和受監管的交易所與經紀商服務類似。那麼他們是否該相同監管?對於無中控營運者的協議,監管如何執行?
創新與監管的張力在DeFi領域達到高點。過度嚴苛監管恐使美國難以發展去中心化服務,促使技術流向海外,削弱美國區塊鏈領導地位。而完全棄管則恐形成系統性風險,放任詐欺與市場操縱,破壞為中心化平台設立的保護措施。
傳統資產(股票、債券、不動產、商品)的代幣化可望在新架構下加速。如果代幣化證券的監理歸屬明確(SEC監督),而數位資產交易基礎設施日益健全(CFTC規範的平台),金融機構或將積極推廣發行代幣化產品。最終可能革新證券的發行、轉讓與結算方式。
關於創新:釋放潛力還是形成阻力?
支持者認為,監管明確性本身就是最重要的創新推手。開發者無需再擔憂無預警的執法。新創公司可放心向美國投資人募資。大型金融機構也能在合法保障下進入市場。這種組合能推動加密大規模採用——正如90、2000年代明確的網路監管促成網路服務蓬勃發展一樣。
美國之所以能長年領先金融與科技創新,正是因為其流動性強的資本市場、創業文化、完善法治體系,以及明確的——property rights. Extending that framework to digital assets could cement American dominance in blockchain technology, cryptocurrency infrastructure, and crypto-financial services. The alternative — regulatory hostility or prolonged uncertainty — risks allowing other countries to capture leadership in what many see as a transformative technology.
產權。將這一框架延伸至數位資產,可能鞏固美國在區塊鏈技術、加密貨幣基礎設施及加密金融服務領域的主導地位。另類選擇——監管敵意或長期不確定性——則有可能讓其他國家搶佔這一被許多人視為變革性科技的主導權。
Critics counter that excessive regulation could stifle experimentation. Registration requirements, compliance costs, and prescriptive rules about market structure might freeze the industry in its current form, preventing the type of rapid iteration that has characterized crypto's first decade. The most innovative projects might simply launch offshore, beyond U.S. regulatory reach, depriving American investors and developers of participation.
批評者則反駁,過度監管可能會扼殺創新實驗。註冊要求、合規成本、以及對於市場結構的規定,可能使行業停留在現有樣貌,無法持續進行加密產業首十年所展現的高速迭代。最具創新性的項目或許會選擇直接在海外上線,避開美國監管,從而讓美國投資人及開發者無法參與其中。
The impact on token design could cut both ways. Clear rules about what qualifies as a digital commodity versus a security would shape how projects structure governance, distribute tokens, and implement economic incentives. Some designs might become more common because they fit regulatory requirements. Others might be abandoned as noncompliant. Whether this channeling effect helps or hinders innovation depends on whether the regulatory categories align well with productive uses of the technology.
這對於代幣設計的影響可能是雙向的。明確規範數位商品與證券資格的規則,將決定項目方如何設計治理架構、分發代幣並實施經濟激勵。有些設計因為符合法規規定而變得更普遍,另一些則可能因不合規而被放棄。這種引導作用究竟有利還是阻礙創新,取決於監管分類與科技實際用途的契合程度。
Risks & Challenges
風險與挑戰
Institutional and Political Hurdles
制度與政治障礙
The CFTC's resource constraints represent the most frequently cited concern. Senator Booker explicitly flagged this issue in his statement accompanying the draft release. With approximately 700 employees, the agency currently oversees derivatives markets for agricultural commodities, metals, energy products, interest rates, equities, and foreign exchange. Adding oversight of the entire spot cryptocurrency market — potentially valued in the trillions of dollars with millions of retail participants — would multiply the agency's responsibilities.
CFTC 的資源限制是最常被提及的擔憂。參議員 Booker 在草案發布聲明中特別指出此問題。該機構約有 700 名員工,目前已監管著農產品、金屬、能源產品、利率、股票及外匯的衍生品市場。若還要納入全體現貨加密貨幣市場的監督——該市場規模可能達數兆美元且有數百萬散戶參與——將大幅增加機構負擔。
The funding mechanism in the bill — registration fees capped at $40 million annually — may not suffice. The SEC spends hundreds of millions of dollars annually on examinations and enforcement related to broker-dealers, exchanges, and trading platforms. The CFTC would need to build similar capacity for crypto markets, including hiring specialized staff who understand blockchain technology, developing surveillance systems to detect market manipulation, and conducting examinations of dozens of registered platforms.
草案中的資金來源——每年註冊費上限為 4000 萬美元——可能不足以應付所需開支。SEC 每年僅針對券商、交易所、交易平台的監管與執法行動,就花費數億美元。CFTC 若要監管加密貨幣市場,同樣須建立完善體系,包括聘用精通區塊鏈技術的專業人員、開發監控市場操縱的系統,並對數十家註冊平台進行查核。
Political obstacles loom. Senator Elizabeth Warren and some progressive Democrats have voiced strong opposition to shifting oversight to the CFTC, arguing it would weaken investor protection. Warren has described crypto as rife with fraud, money laundering, and abuse, and she prefers maintaining SEC authority with its stronger enforcement tools and investor protections.
政治障礙日益明顯。參議員 Elizabeth Warren 與部分進步派民主黨人已強烈反對將監管權轉交 CFTC,理由是這將削弱投資人保護。Warren 將加密產業描述為充斥詐欺、洗錢和濫用,她更傾向於維持 SEC 的主導地位,以確保強大執法和投資人保護工具。
President Trump's personal crypto investments create political complications. Critics argue his family's holdings in crypto ventures represent conflicts of interest that could bias his administration's regulatory preferences. Democrats may demand strong conflict-of-interest provisions, independent oversight of rulemaking, or other safeguards as a condition for supporting the legislation.
川普總統個人的加密投資使政治情勢更複雜。批評者認為他家族在加密公司持股,引發利益衝突疑慮,可能導致其政府在監管政策上傾向特定取向。民主黨人因此可能要求加入嚴格的利益衝突條款、規則制訂的獨立監督機制,或其他保障措施,作為支持立法的前提。
Classification Risks and Residual Ambiguity
分類風險與剩餘模糊地帶
Despite the effort to establish clear definitions, classification disputes would inevitably continue. The line between digital commodities and securities depends on factors like decentralization, control, and the expectation of profits from others' efforts. These factors can be ambiguous and may change over time as projects evolve.
儘管致力於建立明確定義,分類爭議仍將無可避免地持續發生。數位商品和證券間的界線取決於去中心化程度、控制權、以及對他人努力產生獲利的期待等因素。然而,這些指標本身模糊,並且隨著項目發展會不斷變化。
A token might be issued initially through a centralized offering that constitutes a security, but later transition to commodity status as the network decentralizes. The legislation contemplates this possibility but leaves critical details to agency rulemaking. When exactly does the transition occur? Who determines whether sufficient decentralization has been achieved? What happens if the agencies disagree?
一個代幣在發行初期可能以集中方式進行,屬於證券,但隨著網絡去中心化後又轉為商品。法案雖然預見這種可能性,卻把關鍵細節留給政府機關定義:究竟轉換點何時到來?誰決定去中心化程度是否充足?如果監管機關對此產生歧見又該怎麼辦?
The decentralization test itself presents challenges. How many validators or nodes are required? What if control is theoretically distributed but effectively concentrated through voting coalitions or economic incentives? What about Layer 2 protocols built on top of decentralized base layers? These questions lack obvious answers and will require agencies to develop detailed, technically sophisticated guidance.
去中心化測試本身就充滿挑戰。需要多少個驗證者或節點才算充足?如果理論上分散,實際上卻又透過投票聯盟或經濟誘因而出現權力集中呢?若是在去中心化底層上發展的 Layer 2 協議,又該如何判斷?這些問題並無明確答案,監管機關將需要制定細緻且技術性極高的指引。
Projects might structure themselves specifically to qualify as digital commodities, potentially gaming the rules. A project could distribute tokens widely and implement decentralized governance on paper while maintaining de facto control through other mechanisms. Detecting and addressing such arrangements would require regulatory judgment calls that could themselves become sources of litigation and uncertainty.
部分項目可能為了符合法規而刻意設計成數位商品,存在套利法規之虞。項目方或許聲稱廣泛分發代幣並設置去中心化治理,卻仍透過其他方式維持實質控制權。要發現並處理此類情況,需要監管機關的判斷,而這本身又可能成為引發訴訟與不確定性的來源。
Compliance Costs and Market Fragmentation
合規成本與市場碎裂
Registration and compliance requirements would impose substantial costs, particularly on smaller platforms. Building anti-fraud surveillance systems, maintaining detailed transaction records, implementing fund segregation, conducting regular audits, and staffing compliance departments all require significant capital investment. Platforms might need to spend millions of dollars annually to maintain regulatory compliance.
註冊及合規要求會帶來重大成本負擔,尤其對於規模較小的平台而言。建立防詐監控系統、維持詳細交易紀錄、實施資金隔離、定期審計,以及設立合規部門等,都需投入大量資本。平台每年光是維持合規,可能就需花費數百萬美元。
These costs could lead to market consolidation. Large, well-funded exchanges like Coinbase could absorb compliance expenses as a cost of doing business, potentially strengthening their competitive position. Smaller platforms with lower trading volumes might find the costs prohibitive, forcing them to exit the market, merge with larger competitors, or move operations offshore.
這些成本可能促使市場逐漸集中化。資金雄厚的大型交易所如 Coinbase,能將合規花費視為營運成本,進一步強化自身競爭力。交易量較低的小型平台則可能難以負擔這些支出,被迫退出市場、與更大業者合併,或將業務移往海外。
State-federal conflicts could create additional complexity. Some states have enacted their own cryptocurrency regulations through money transmitter laws, consumer protection statutes, and state securities rules. A platform registered with the CFTC for digital commodity trading might still need to comply with varying state requirements, creating a patchwork of overlapping obligations. The draft bill does not preempt state law, leaving this tension unresolved.
聯邦與州之間的衝突則讓情況更加複雜。部分州以資金傳輸者法、消費者保護法與州版證券法另立加密規範。一家在 CFTC 註冊的數位商品交易平台,仍可能需同時面對各州不同的法律義務,導致合規責任重疊。草案並未優先於州法,這項緊張關係至今未解。
Cross-border issues compound the challenges. A U.S.-based platform with CFTC registration might face different requirements in Europe under MiCA, in the UK under FCA rules, and in Asia under various regional frameworks. Maintaining compliance with multiple regulatory regimes simultaneously requires sophisticated legal infrastructure and could force platforms to fragment their operations geographically.
跨境問題使困難更加複雜。美國平台即使已通過 CFTC 註冊,在歐洲(MiCA)、英國(FCA)及亞洲各地,仍需面對不同規範。要同時遵循多地監管體系,須建立精良法律結構,還可能因此被迫讓平台業務地理分散。
Innovation and Offshore Migration Risks
創新流失及離岸風險
Restrictive regulations could push innovation beyond U.S. borders. If compliance costs are too high or rules too restrictive, developers and startups might simply locate in more favorable jurisdictions. Countries like Singapore, Switzerland, and the UAE have actively courted crypto businesses with clear rules, tax incentives, and streamlined approval processes.
限制性規範可能讓創新流向美國境外。若遵從成本過高或規則過於嚴苛,開發者和新創公司很可能會選擇遷徙至更加友善的司法管轄區。如新加坡、瑞士、阿聯酋等國,皆以明確規則、稅務優惠、精簡核可流程積極吸引加密產業。
The DeFi problem is particularly acute. If DeFi protocols face the same registration and compliance requirements as centralized platforms, developers may conclude that building decentralized systems from the U.S. is impractical. They could relocate to jurisdictions with DeFi-friendly approaches or design their protocols to be truly decentralized and ungovernable, operating beyond the reach of any regulatory system.
DeFi (去中心化金融)問題尤為嚴峻。如果 DeFi 協議要比照中心化平台接受註冊與合規要求,開發者可能會認為根本無法在美國構建分散系統。他們可能因此轉移到對 DeFi 友善的國家,或選擇設計徹底去中心化、難以監管的協議,進而規避任何法規體系的覆蓋。
Token issuers might launch offshore to avoid classification disputes and compliance burdens. Rather than navigating the complexities of commodity versus security classification in the U.S., projects could conduct token sales exclusively to non-U.S. investors, establish operations in crypto-friendly jurisdictions, and build global user bases that happen to exclude Americans. This would deprive U.S. investors and developers of participation in potentially valuable innovations.
代幣發行方則可能直接在海外上線以避免分類糾紛與合規壓力。不用在美國承受商品或證券分類疑慮,項目方可選擇只向非美國投資人開放銷售,業務據點設立於加密友善國家,面向全球發展卻排除美國人。這會讓美國投資人與開發者無法參與潛在價值巨大的創新項目。
The risk of regulatory overreach extends to traditional financial innovation as well. If banks find crypto custody too complicated or risky under the new framework, they might avoid offering such services despite customer demand. If payment networks decide CFTC compliance is too burdensome, they might refuse to facilitate crypto transactions. The result could be a regulatory regime that theoretically allows crypto innovation but practically makes it too difficult to pursue.
監管過度之風險同樣蔓延至傳統金融創新。如果銀行在新法規下認為加密託管服務過於複雜或風險太高,即使市場有需求,也可能因此不提供。若支付網絡覺得遵從 CFTC 規範過於繁瑣,他們也可能拒絕加密貨幣支付。這會導致一個理論上允許加密創新、實際操作卻困難重重的監管體系。
Enforcement Gaps and Systemic Risks
執法缺口與系統性風險
Former CFTC Chair Timothy Massad warned that the new regime could create enforcement gaps, particularly around consumer protection. The CFTC's enforcement focus has historically centered on market manipulation, fraud in derivatives trading, and registration violations. Its consumer protection authority in spot commodity markets is less developed than the SEC's securities investor protection framework.
前 CFTC 主席 Timothy Massad 警告新監管體系可能產生執法缺口,尤其是在消費者保護方面。CFTC 傳統上執法重心在市場操縱、衍生品詐欺和註冊違規。其對現貨商品市場的消費者保護權限,遠不如 SEC 對證券投資人的保護架構來得成熟。
The agency would need to build out new enforcement capabilities focused on retail 該機關還需要建立針對散戶相關的新執法能力。investors. This includes systems for receiving and investigating customer complaints, examining platforms for compliance with disclosure and custody requirements, detecting Ponzi schemes and other fraud, and pursuing cases that often involve small individual losses but large aggregate harm.
投資人。這包括接收與調查客戶投訴的系統、檢查平台是否遵守揭露和託管要求、偵測龐氏騙局及其他詐欺行為,以及追查那些雖然單筆損失金額不大、但整體加總後造成重大危害的案件。
Systemic risk concerns persist. Crypto markets have experienced spectacular failures, from the Mt. Gox hack to the FTX collapse. The new framework addresses some vulnerabilities through fund segregation and custody requirements. But interconnections between platforms, opacity in DeFi protocols, and the potential for rapid contagion when confidence erodes all pose ongoing systemic risks that commodity regulation may not fully address.
系統性風險的疑慮依然存在。加密市場曾爆發數起重大失敗事件,從 Mt. Gox 遭駭到 FTX 崩潰。新架構透過資金隔離與託管要求針對部分脆弱點加以補強,但平台間的高度連結性、去中心化金融(DeFi)協議的缺乏透明度,以及市場信心動搖時可能出現的迅速連鎖反應,都構成持續性的系統性風險,這些未必能完全靠商品型監管來解決。
The global nature of crypto markets complicates enforcement. Bad actors can operate from jurisdictions beyond U.S. reach, serve American customers through VPNs and proxy services, and move assets across chains and through mixers to evade detection. The CFTC's international coordination capabilities would need substantial enhancement to effectively police global crypto markets that touch U.S. investors.
加密貨幣市場的全球性本質讓監管執法更加複雜。惡意行為者可以在美國司法權無法觸及的地區運作,透過 VPN 和代理服務向美國客戶提供服務,並利用鏈間轉移及資產混合工具逃避偵查。若要有效監管與美國投資人相關的全球加密市場,美國商品期貨交易委員會(CFTC)亟需大幅提升其國際協調能力。
Global Perspective: How U.S. Fits With the World
全球觀點:美國在國際中的定位
The EU's MiCA: A Comprehensive Model
歐盟 MiCA:全面性的監管典範
The European Union's Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation represents the most comprehensive crypto regulatory framework globally. MiCA became fully applicable across all 27 EU member states on December 30, 2024, establishing harmonized rules for crypto-asset issuers and service providers. The regulation covers authorization requirements, operating conditions, consumer protection measures, and market abuse prevention.
歐盟的加密資產市場監管規則(MiCA)被視為目前全球最全面的加密監管架構。MiCA 自2024年12月30日起於27個歐盟成員國全面實施,為加密資產發行人和服務供應商訂定一致的規範。這些規範涵蓋授權標準、營運條件、消費者保護措施及防制市場操作等項目。
MiCA classifies digital assets into three categories: asset-referenced tokens (stablecoins backed by baskets of assets), e-money tokens (stablecoins pegged to single fiat currencies), and other crypto-assets (including utility tokens and unclassified digital assets). Each category faces tailored requirements. Stablecoin issuers must maintain liquid reserves, publish regular disclosure, meet capital requirements, and undergo supervision by the European Banking Authority if they reach certain size thresholds.
MiCA 將數位資產區分為三大類:資產參照型代幣(由一攬子資產支持的穩定幣)、電子貨幣型代幣(掛鉤單一法幣的穩定幣)、以及其他加密資產(包含用途型代幣及未分類數位資產)。每種類型都有對應監管要求。穩定幣發行人必須維持高度流動的準備金、定期揭露資訊、符合資本要求,且當規模達一定標準時,將受歐洲銀行管理局監督。
Crypto-asset service providers (CASPs) must obtain licenses from national regulators to operate in the EU. Licensed CASPs benefit from passporting rights, allowing them to operate across all member states without separate authorizations in each country. Services covered include exchange operation, custody, portfolio management, investment advice, and order execution. Requirements include governance standards, operational resilience, customer protection, and market abuse prevention.
加密資產服務供應商(CASPs)必須向各國主管機關申請執照才可在歐盟經營。取得執照的業者享有「護照」權益,可在全體成員國無須逐國申請即可提供服務,涵蓋交易所經營、資產託管、投資組合管理、投資諮詢及委託下單等服務。其要求包括公司治理標準、營運韌性、消費者保護與防範市場造市等。
MiCA's implementation included transitional periods allowing existing providers time to adapt. Member states could adopt grandfathering provisions permitting service providers already operating under national law to continue for up to 18 months while seeking MiCA authorization. This gradual approach aims to prevent market disruption while ensuring compliance.
MiCA 的實施設有過渡期,讓現存業者有時間調整。各成員國可採「既有業者條款」,允許已依本國法規營運的服務業者在申請 MiCA 執照期間,最多可繼續經營18個月。這種漸進的方式有助於避免市場劇烈動盪,同時達到合規目的。
Early impacts have been significant. Several non-compliant stablecoins have been delisted from European exchanges as CASPs move to restrict access to tokens issued by entities without proper EU authorization. The European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) has stated that restrictions on non-MiCA compliant stablecoins should be complete, with full compliance expected by the end of Q1 2025.
初期影響已相當明顯。部分未合規的穩定幣已被歐洲交易所下架,因服務業者逐步限制未獲歐盟授權機構發行的代幣。歐洲證券及市場管理局(ESMA)已表示,對於非 MiCA 合規穩定幣的限制應全面落實,預計至2025年第一季結束前,市場將實現完全合規。
UK, Singapore, and Asian Approaches
英國、新加坡與亞洲其他監理作法
The United Kingdom's Financial Conduct Authority has developed a "same risk, same regulation" model for crypto assets. Crypto firms must meet standards similar to traditional financial institutions, including capital requirements, governance standards, and consumer protection measures. The approach seeks to integrate crypto into the existing financial regulatory framework rather than creating an entirely new regime.
英國金融行為監管局(FCA)推動「同風險,同監理」模式來管理加密資產。加密業者須遵守與傳統金融機構相當的資本、治理與消費者保護標準。這種作法力求將加密產業納入既有金融法規架構,而非另立新規。
The UK is developing specific rules for stablecoins, following the success of the GENIUS Act in the U.S. and MiCA in the EU. The FCA has also launched sandboxes for innovative crypto products, allowing firms to test new services under regulatory supervision before full market launch. This balanced approach aims to foster innovation while maintaining oversight and protecting consumers.
英國正仿照美國 GENIUS 法案及歐盟 MiCA 的成功經驗,制定針對穩定幣的專法。FCA 也設立加密創新沙盒,允許業者在主管機關監督下試水新產品,再全面推向市場。這種平衡方式致力於促進創新,同時維持監管與消費者保障。
Singapore's Monetary Authority (MAS) has established a sophisticated framework emphasizing reserve requirements, regular audits, and institutional-grade custody for crypto service providers. The Payment Services Act regulates crypto payment services, while the Securities and Futures Act covers security tokens. MAS has finalized stablecoin frameworks with particular focus on systemic stablecoins that could impact financial stability.
新加坡金融管理局(MAS)建立了一套高度進階的監理架構,強調儲備金、定期稽核及機構級託管標準。支付服務法規範加密支付,證券及期貨法則納管證券型代幣。MAS 並完成穩定幣監理規則,特別針對攸關金融穩定的系統性穩定幣給予更嚴格規範。
Singapore actively courts crypto businesses through clear rules, reasonable licensing timelines, and business-friendly tax treatment. Major exchanges and projects have established operations in Singapore, attracted by regulatory certainty and government support for financial technology innovation. The approach balances openness to innovation with robust anti-money laundering standards and consumer protection.
新加坡積極招商加密業者,提供明確法規、合理執照時程及友善稅制。受惠於法規確定性與政府對金融科技創新的扶持,多家大型交易所與專案紛紛落戶新加坡。這種兼顧創新與嚴格反洗錢及消費者保護的政策,造就新加坡成為亞洲重要加密中心。
Hong Kong has launched regulatory sandboxes for digital assets, allowing new products to be tested under supervision. The Securities and Futures Commission licenses crypto exchanges and requires them to meet standards for custody, cybersecurity, and investor protection. Hong Kong's approach reflects its position as a major financial center seeking to maintain relevance in the digital asset era.
香港推行了數位資產監管沙盒計畫,讓新產品可在監理單位監督下試行上路。證券及期貨事務監察委員會負責加密交易所發牌,並要求在資產託管、網路安全及投資人保護等方面達到高標準。香港的作法體現其國際金融中心地位,希望在數位資產時代維持競爭力。
Japan, one of the earliest countries to regulate cryptocurrency exchanges, has mature frameworks covering exchange licensing, stablecoin issuance, and custody requirements. The Financial Services Agency oversees crypto businesses, requiring registration, regular audits, and compliance with anti-money laundering rules. Japan's experience — including lessons from the Mt. Gox collapse — has informed its cautious but sophisticated regulatory approach.
日本是最早對加密交易所施行監管的國家之一,已建立包括交易所執照、穩定幣發行及託管義務的完整制度。金融廳主導加密業者之註冊、定期審核及反洗錢合規。從 Mt. Gox 崩潰等事件中吸取教訓後,日本的監理態度謹慎而精密。
The United Arab Emirates: Aggressive Competition
阿拉伯聯合大公國:積極搶占競爭優勢
The UAE, particularly Dubai, has positioned itself as a global crypto hub through aggressive regulatory innovation and business incentives. The Dubai Virtual Assets Regulatory Authority (VARA) has established clear rules for crypto businesses while offering favorable tax treatment and streamlined approval processes.
阿聯酋,尤其是杜拜,透過積極的監管創新與營商誘因,定位自己為全球加密樞紐。杜拜虛擬資產監管局(VARA)已為加密業者訂立明確法規,同時提供優惠稅制及簡化審批流程。
VARA's framework aligns with many MiCA principles while maintaining flexibility to attract businesses. Licensed entities can offer a full range of crypto services including exchange operation, custody, advisory services, and lending. Dubai's approach combines clear regulation with business-friendly policies, creating an environment attractive to both crypto startups and established firms seeking operational flexibility.
VARA 架構參考 MiCA 多項原則,並保有高度彈性,專為吸引企業導入。持牌業者可經營全方位加密服務,包括交易所、託管、諮詢及放貸。杜拜透過清晰規範與友善營商政策兼容並蓄,吸引新創與成熟企業設點並靈活運作。
The UAE's success in attracting crypto businesses highlights the competitive dynamics of global regulation. Countries that establish clear, balanced frameworks early can capture significant market share as businesses relocate to favorable jurisdictions. The UAE's gains have come partly at the expense of regions with uncertain or hostile regulatory environments.
阿聯酋能成功吸引加密企業,凸顯全球監管競逐的本質。率先打造兼備明確性與平衡性的早期法規國家,能在業者紛紛尋找友善司法區時搶下龐大市佔率。阿聯酋的躍進,也伴隨著一些監管不明或敵對地區市場份額的流失。
Implications for International Harmonization
國際規範協調的啟示
The diversity of global approaches creates both challenges and opportunities. Crypto markets are inherently global — tokens trade 24/7 across borders, users access platforms from anywhere with internet, and capital flows freely across jurisdictions. Divergent regulations create compliance complexity but also allow for regulatory arbitrage and experimentation.
全球各國監理模式多元,既帶來挑戰,也伴隨機會。加密市場天生具備全球性,代幣24小時跨國交易,用戶只需網路即可連結平台,資金更可任意跨境流動。規範分歧雖增加合規成本,也使監管套利與新制試驗成為可能。
If the U.S. establishes a CFTC-led framework while the EU maintains MiCA and Asia pursues various approaches, platforms will need to navigate multiple regimes simultaneously. This could be manageable for large, well-resourced firms but prohibitive for smaller startups. The result might be a crypto market dominated by a few global platforms that can afford comprehensive compliance while smaller, regional players serve local markets.
若美國採由 CFTC 主導的方案、歐盟維持 MiCA、亞洲走向多軌並行,平台業者將被迫同時應對多重監理。大型資本充裕企業或可應付,小型新創恐難以負荷。結果將可能演變為少數具全球合規能力的平台寡占國際市場,而本地及中小型業者僅能深耕區域市場。
International coordination efforts would benefit from U.S. leadership. The Financial Stability Board, International Organization of Securities Commissions, and other international bodies have been developing high-level principles for crypto regulation. The U.S. adopting a clear framework would allow American regulators to actively shape global standards rather than reacting to frameworks developed elsewhere.
美國帶頭的國際協調將帶來正面助益。金融穩定委員會、國際證券監理組織及其他國際機構也都已著手制訂加密資產監管原則。若美國制定明確框架,將使美方監理者由被動接受他人規定,轉為主動塑造國際標準。
Conversely, if the U.S. lags in establishing clear rules, other jurisdictions may set the template. MiCA is already influencing discussions in Latin America, Africa, and other regions considering crypto regulation. The standard-setting role could shift to Europe, diminishing U.S. influence over the evolution of global digital asset markets.
反之,若美國遲遲未能落實明確規範,國際標準制訂權恐將旁落他國。MiCA 已開始影響拉丁美洲、非洲及其他考慮監管加密的地區。屆時,設定標準的主導權可能移轉歐洲,使美國在全球數位資產市場的影響力下降。
What to Watch: Indicators & Timeline
關注重點:指標與時程
Legislative Milestones and Timeline
立法進程與時間表
The Boozman-Booker draft represents [the first step in a lengthy legislative...]
Boozman-Booker 草案代表著[一項漫長立法歷程的第一步...] process](https://finance.yahoo.com/news/bipartisan-senate-proposal-seeks-extend-050509130.html)。參議院農業委員會將徵詢利害關係人的意見、舉辦聽證會以審查條文並接收證詞、舉行修正會議讓委員會成員能提出修正案,並最終表決是否將法案提交至參議院全院審查。
參議院銀行委員會的同步行動同樣關鍵。雖然農業委員會的草案涵蓋了CFTC的監管,銀行委員會的配套法案則須處理 SEC 對證券類代幣的管轄權,包括發行人規定,以及機構間的協調。銀行委員會已於2025年7月公佈了《負責任金融創新法案》(RFIA)的討論稿,但在兩個委員會的法案能合併前,仍有許多細節尚待完成。
參議院的通過時程已多次延宕。川普總統原本希望能在2025年8月完成立法,但該最後期限過去後,僅有GENIUS法案(穩定幣立法)獲得通過。隨後的九月與十一月目標也皆未實現。現階段預測可能要到2025年底或2026年初才有進展。
若參議院最終通過自身版本,與眾議院CLARITY法案之間的差異需進行協調。這可能透過正式的協商委員會來談判折衷版,或者某一院接受對方版本並加以修改。考量其中的技術複雜性及政治敏感性,協調程序可能需時數月之久。
產業指標觀察重點
登記模式將揭示市場對新框架的反應。若立法施行,觀察者應追蹤有多少交易所於過渡期間向CFTC登記,哪些平台選擇專注於數位商品,哪些同時提供商品及證券服務,以及是否有新進入者專為CFTC體系設計平台。
代幣分類決策將提供該商品/證券框架實務運作的關鍵數據。核心問題包括:CFTC與SEC願接受哪些代幣為數位商品,項目如何規劃其代幣發行以符合商品待遇,以及分類爭議是否引發訴訟以釐清或模糊法律標準。
執法行動將展現監管優先順序與能力。早期執法案件可揭示CFTC主要著力於防詐、操縱市場、登記合規,抑或其他事務。執法頻率與規模也顯示該機構資源是否充裕,或因新職責而力有未逮。
市場指標,包括數位資產價格、交易量與資金流向,將反映產業信心。若監管明朗化促使機構採用,可能出現受監管平台的交易量增加,加密金融產品成長,及機構資金流入數位資產。反之,若交易量下降或資金流出,或意味合規成本大於預期效益。
創投投資趨勢可顯示新框架對創新的激勵效果。美國本土加密新創募資激增則意味監管明確釋放投資潛力。若仍偏好赴海外專案,或加密創投低迷,則可能代表監管仍過於不明或繁重。
市場信號與全球定位
國際動態將影響美國競爭力。重點包括大型平台是否擴展美國業務或轉向其他司法管轄區,發行方選擇於美國啟動項目,還是迴避美國市場,以及美國在區塊鏈技術領導地位能否鞏固或流失。
全球代幣與加密產品的上市情況可顯示市場整合或分裂趨勢。依照美國規定發行之代幣是否同時能於歐盟MiCA平台上市?亞洲交易所是否接受CFTC監管資產?這些答案將揭露法規架構究竟互通還是造成全球市場割裂。
穩定幣採用率則反映GENIUS法案與潛在商品監管規範的實際效果。由GENIUS規範實體所發行的美元穩定幣若呈現成長,即證明監管策略可行。若資金轉向非美國穩定幣或使用率下滑,則可能過度監管所致。
開發者活動指標,如美國區塊鏈專案的GitHub提交數、美國地區加密會議及黑客松的參與度,以及新創總部地點,都可觀察美國是否持續領先加密創新。技術人才外流到監管友善的國家將成為負面警訊。
失敗情境與替代方案
若法案無法推進,監管不確定性的現狀將持續。SEC會繼續主張大多數代幣為證券的廣泛管轄權,CFTC僅能有限監管衍生品市場,且缺乏對現貨市場的明確權力。執法案件將繼續透過訴訟界定監管界線,而非立法程序。
失敗也可能造成州層級監管割裂。有些州可能自行立法設立全方位加密規範,產生如數據隱私法般的地區碎片化。這對全美經營的企業造成高昂合規成本,更損及美國全球競爭力。
局部立法成功仍有可能。國會或僅通過部分條款,如CFTC資金擴充或穩定幣規範,而較大範圍的市場結構問題仍懸而未決。這種漸進方式可先解決最迫切問題,並為日後推進立法累積動能。
若立法停滯,主管機構訂立規則可部分彌補空缺。CFTC與SEC可發布聯合指引,釐清各自管轄範圍,建立協作流程,以行政行動提升監管確定性,雖然不如法律改革全面,但強化機關協作仍可減少不確定性。
結論:數位資產市場的關鍵時刻
將加密貨幣監管重心由SEC轉移至CFTC,將是數位資產短暫歷史上最具深遠影響的監管變革之一。若能通過,Boozman-Booker架構將建立數位商品現貨市場首個聯邦全面監管體系,解決多年來的管轄爭議,並讓美國有能力在區塊鏈科技及加密金融服務領域與全球競爭。
這些影響遠超官僚體系本身。將代幣分類為商品而非證券,將改變項目的募資、治理結構設計、以及與投資人互動的方式。交易所登記將強化加密平台的正當性,同時帶來實質監督與消費者保護。明確的託管、揭露與營運規範也將使傳統金融機構更有信心進軍加密市場。
但重大不確定性依舊存在。CFTC的資源有限,令人質疑其現行人力與預算能否有效監管龐大的加密市場。對DeFi的規範幾乎未觸及,數十億美元的去中心化交易尚處法律灰色地帶。因項目方測試商品證券界線,分類爭議勢必持續出現。
全球背景使議題更加迫切。歐盟的MiCA架構已為歐洲加密市場帶來監管明確性,吸引企業進駐,並讓歐洲成為潛在標準制定者。新加坡、阿聯酋等其他國家亦發展出兼顧創新與監管的成熟模式。美國若繼續延宕制定明確規範,勢將失去金融創新領導地位。
對於加密產業各方—無論是開發區塊鏈協議的工程師、發行代幣的創業家、配置數位資產的投資人,還是考慮加密服務的傳統金融機構—未來數月將至關重要。現在確定的規則,將決定數位資產市場未來十年之發展軌跡,也將決定加密能否主流化或維持邊緣地位、創新是茁壯還是外移,美國能否繼續立足全球金融中心,抑或讓位於國際競爭者。
該法案目前仍為草案,往後仍需重大協商、修正與完善,方能——bill reaches the president's desk. 產業利益相關者將會遊說,以爭取有利條款。消費者倡議人士則會推動更強力的保障措施。國會議員將努力回應選民關切並考慮政治因素。最終結果若有出爐,可能與目前提案有顯著差異。
What seems certain is that the era of regulatory ambiguity is ending. 無論是透過 Boozman-Booker 架構、替代性的立法途徑,或是結合法規與主管機關的規則制定,美國都將為加密貨幣市場建立更明確的規則。現在的問題不是「要不要監管」,而是「如何監管」──以及所選擇的方式是否能促進創新、競爭以及投資人保護,這些正是美國金融市場一向的特質。
For readers in the crypto ecosystem, this is a moment demanding attention, engagement, and preparedness. 密切關注立法進展。參與意見表達過程。為未來可能的規範要求做好合規基礎建設。思考各種監管結果將如何影響商業模式與策略。今年華盛頓做出的決策,將會在未來數年間形塑整個產業。
加密貨幣革命始終不僅關乎科技本身。它更在於重新想像價值的儲存、傳遞及治理方式。現在逐步成形的監管架構,將決定這場革命是否會於美國本土、在美國規則下、由美國參與展開──還是將於他處發生,而美國只能在這一場數位時代最具變革性的金融創新浪潮中被迫旁觀。





