Decentralized finance options trading has undergone a dramatic transformation in 2025, with on-chain options volumes surging over 10x year-on-year to reach new heights while three pioneering protocols - Lyra (now Derive), Dopex (now Stryke), and Panoptic - fundamentally reshape how derivatives function in the blockchain ecosystem.
This revolution extends beyond simple digitization of traditional options, introducing entirely new paradigms like perpetual options without expiration dates, oracle-free pricing mechanisms, and capital-efficient liquidity models that challenge conventional financial theory.
The statistics paint a compelling picture of growth: DeFi derivatives trading volume reached $342 billion in December 2024, representing an 872% increase, while the broader DeFi ecosystem achieved $153 billion in total value locked by mid-2025. Yet options remain a specialized frontier within this expansion, representing both the greatest potential for innovation and the most complex technical challenges in decentralized finance.
Evolution of the decentralized options landscape
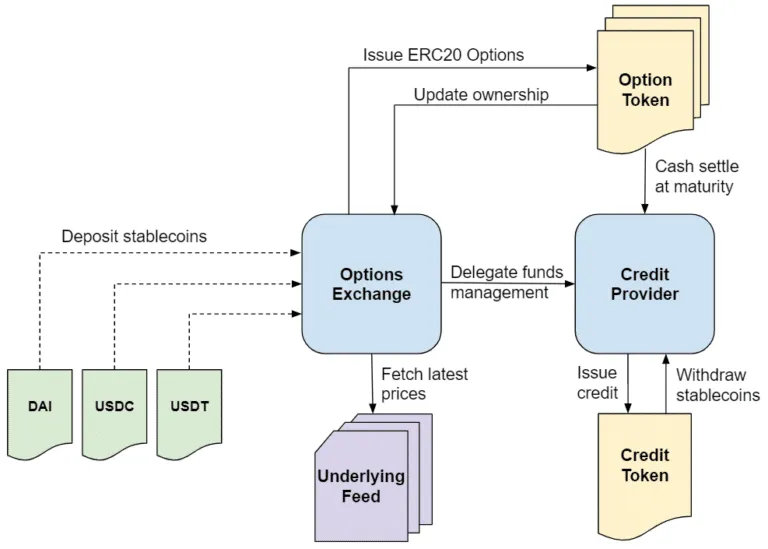
The journey from experimental protocols to sophisticated trading platforms reveals three distinct evolutionary phases that have shaped today's competitive landscape. The early development period from 2020 to 2022 featured infrastructure-focused protocols like Opyn and PsyOptions, which provided basic options creation and settlement capabilities but required manual market-making and over-the-counter trading for liquidity. These foundational protocols served as building blocks rather than direct trading venues, establishing the technical groundwork for more sophisticated systems.
The market expansion phase from 2022 to 2024 introduced Automated Market Maker-based platforms attempting to solve liquidity challenges through algorithmic pricing and automated provision. Lyra, Dopex, and Premia emerged as leaders during this period, though early AMM versions suffered from poor liquidity and high risks for providers. The breakthrough came with "second-wave" AMMs implementing delta hedging capabilities and more sophisticated risk management systems.
The current maturation phase beginning in 2025 has produced four distinct categories of protocols: order book systems like AEVO and Zeta, advanced AMMs including Lyra and Dopex, structured products from Ribbon and Friktion, and innovative AMM-powered solutions like Panoptic. This diversification reflects the market's evolution toward specialized solutions addressing different trader needs and risk profiles.
The transformation from experimental technology to institutional-grade infrastructure becomes evident in the numbers. Lyra processes over $100 million in total value locked with monthly trading volumes exceeding $369 million, while maintaining over 70% market share in decentralized options. Dopex's evolution to Stryke features concentrated liquidity AMMs providing up to 40x higher returns than standard trading fees when liquidity is utilized for options. Meanwhile, Panoptic's oracle-free perpetual options built directly on Uniswap V3 represent perhaps the most radical reimagining of options fundamentals.
Lyra's transformation into institutional-grade infrastructure
Lyra Finance's evolution to Derive represents one of the most successful transitions from experimental DeFi protocol to institutional-grade derivatives infrastructure. The protocol's journey from its 2021 launch as the first Layer 2-native options protocol to becoming the dominant decentralized options platform illuminates both the potential and challenges of building sophisticated financial products in decentralized systems.
The original Lyra V1 pioneered automated market making specifically designed for options, implementing dynamic Black-Scholes pricing with market-driven implied volatility surface mapping. This innovation solved the fundamental chicken-and-egg problem of options liquidity by eliminating the need for direct counterparties. Market Maker Vaults allowed liquidity providers to deposit stablecoins and automatically act as counterparties to options traders, while delta hedging through integration with Synthetix and GMX protected providers from directional risk.
The technical sophistication of Lyra's approach became apparent in its pricing accuracy, achieving parity with centralized exchanges like Deribit through advanced volatility surface modeling and real-time price discovery. The protocol's risk management system quantified vega risk and implemented dynamic fee structures to incentivize risk-reducing trades, demonstrating that decentralized systems could match traditional finance in sophistication.
However, the transition to Lyra V2, later rebranded as Derive, represents a fundamental architectural shift that challenges assumptions about decentralized systems. The move from AMM to gasless central limit order book with on-chain settlement combines the benefits of centralized exchange user experience with blockchain transparency and self-custody. The modular design features three core components: subaccounts implemented as ERC-721 NFTs holding user assets, managers defining margining rules, and assets representing tradeable instruments and collateral.
The Derive Chain, built as an optimistic rollup on the OP Stack, serves as the settlement layer enabling sub-second execution while maintaining decentralization. This infrastructure supports both standard rule-based margin and portfolio margin using scenario-based stress testing across 27+ volatility and spot shock scenarios. The sophisticated risk engine performs real-time margin calculations and liquidations on-chain, with partial liquidation mechanisms minimizing market impact while preserving user positions.
Performance metrics demonstrate the protocol's market dominance: over $1.5 billion in historical notional volume, monthly trading volumes reaching $369 million at their peak, and over 70,000 active users. The recent DRV token launch in January 2025 with a market cap exceeding $152 million fully diluted further validates institutional interest. However, geographic restrictions excluding major markets like the United States, Canada, and Australia limit addressable market expansion.
The practical implications for traders extend beyond simple fee reduction to fundamental improvements in user experience. Gasless transactions eliminate friction, while instant confirmations provide centralized exchange-like responsiveness. The unified interface supporting spot, perpetuals, and options trading through smart contract wallets and account abstraction significantly reduces onboarding complexity. Multi-asset collateral systems with risk-adjusted haircuts enable sophisticated portfolio margin strategies previously available only to institutional traders.
Yet challenges remain significant. Despite technical sophistication, liquidity gaps compared to Deribit's billion-dollar daily volumes persist. The protocol's dependency on external systems like Synthetix and GMX for hedging introduces counterparty risk, while the novel technology stack creates unknown risks that only time and stress testing will reveal. Limited validator participation in the Layer 2 system, with fewer than five external challengers according to L2BEAT analysis, raises centralization concerns that could undermine the decentralized value proposition.
Dopex's capital efficiency breakthrough
Dopex's transformation into Stryke represents perhaps the most innovative approach to solving DeFi options' fundamental capital efficiency problems. Founded by TzTok-Chad, the protocol has evolved from a traditional options exchange to a Liquidity Providing DeFi platform that maximizes capital utilization through revolutionary Concentrated Liquidity Automated Market Maker technology and Atlantic Options systems.
The CLAMM innovation addresses a core inefficiency in traditional AMM models where only active ranges earn fees in concentrated liquidity positions. Stryke's approach enables entire position ranges to be utilized for options trading, allowing liquidity providers to earn standard AMM trading fees when liquidity remains idle while earning premiums up to 40 times higher when utilized for options. This breakthrough eliminates the traditional choice between options market making and standard liquidity provision, enabling both simultaneously.
The technical mechanics reveal sophisticated engineering that transforms existing DEX liquidity into options underwriting without requiring migration. Users can deposit single-sided liquidity or existing Uniswap V3 range positions directly into the system. When options trades occur, the protocol dynamically utilizes this liquidity for physical settlement while automatically hedging directional exposure. The system ensures liquidity providers face no greater risks than standard DEX participation while earning significantly enhanced yields.
Atlantic Options represent Stryke's most groundbreaking innovation, allowing option collateral to be dynamically moved out of positions and used for other DeFi purposes before expiry. This capital efficiency breakthrough enables applications impossible in traditional options markets: liquidation protection for leveraged positions through GMX integration, leveraged bond protection, collateralized debt position protection, synthetic straddles, and protocol treasury management. The system achieves approximately 17-18% annual yields for Atlantic call writers with minimal risk, funded by traders seeking leveraged exposure.
The development timeline showcases rapid innovation from the 2019 conceptual stage through the 2021 launch of Single Staking Option Vaults to the 2024 rebrand and cross-chain expansion. The transition from DPX/rDPX dual tokens to the unified SYK governance model with 100 million total supply demonstrates institutional maturation. The conversion ratios of 1 DPX equals 100 SYK and 1 rDPX equals 13.333 SYK consolidated fragmented liquidity while simplifying governance participation.
Current partnerships highlight the protocol's ecosystem integration strategy. The PancakeSwap collaboration enables CLAMM options trading directly through familiar DEX interfaces across multiple chains. The Polygon deployment with native Atlantic Straddles provides additional chain-specific incentives, while the Unibot integration enables leveraged options trading up to 110x through Telegram interfaces. These partnerships demonstrate how DeFi protocols achieve scale through composability rather than isolated growth.
The practical trader implications extend far beyond traditional options benefits. Capital efficiency improvements enable 300-1000x leveraged exposure through CLAMM without liquidation risk, fundamentally changing position sizing dynamics. The dual yield generation from AMM fees and options premiums provides income streams unavailable in traditional markets. Cross-chain flexibility allows seamless trading across networks, while American-style options enable exercise flexibility that European-style contracts cannot match.
Fee structures reflect the protocol's focus on sustainable economics rather than unsustainable yield farming. Dynamic fee allocation sends 80% to xSYK holders, 10% to insurance funds, and 10% to protocol treasury, creating aligned incentives for long-term success. Options premiums calculated through advanced pricing models and Atlantic Options targeting approximately 35% annual yields for collateral providers demonstrate sustainable revenue generation rather than token emission-dependent models.
However, implementation complexity creates both opportunities and challenges. The sophisticated collateral management system requires careful risk monitoring to prevent under-collateralization during extreme market conditions. Cross-chain operations introduce bridge risks and potential liquidity fragmentation, while the innovative Atlantic Options model remains relatively untested during major market stress. The protocol's success depends heavily on maintaining technical sophistication while providing user experiences simple enough for mainstream adoption.
Panoptic's perpetual options paradigm shift
Panoptic represents the most radical reimagining of options fundamentals in the DeFi space, introducing perpetual options without expiration dates while eliminating oracle dependencies through direct integration with Uniswap V3's concentrated liquidity mechanism. Founded by Cornell University professor Guillaume Lambert and former Advanced Blockchain AG researcher Jesper Kristensen, the protocol has raised $11.5 million from tier-1 investors and launched on Ethereum mainnet in December 2024 following extensive beta testing.
The core innovation lies in recognizing that Uniswap V3 liquidity positions inherently mimic options payoff profiles. Concentrated liquidity positions function as short options, where providing liquidity in a specific range mirrors selling covered calls or cash-secured puts. Conversely, removing or "burning" liquidity positions creates long option exposures. This insight enables Panoptic to build options directly on existing DEX infrastructure rather than competing for separate liquidity pools.
The technical architecture consists of three primary components working in concert. The Semi-fungible Position Manager serves as the protocol's engine, managing Uniswap V3 positions as ERC1155 tokens with sophisticated accounting for complex multi-leg strategies. CollateralTrackers implemented as ERC4626 vaults manage liquidity and collateral requirements while enabling integration with other DeFi protocols. The PanopticPool acts as the conductor, orchestrating all protocol interactions and managing risk parameters across different token pairs.
The streaming premia model, dubbed "streamia," represents perhaps the most innovative pricing mechanism in DeFi derivatives. Instead of requiring upfront premium payments, positions start at zero cost and accumulate fees based on actual trading activity in the underlying Uniswap pool. Premium calculation equals the swap fees that borrowed liquidity positions would generate plus a Panoptic spread, creating path-dependent pricing that converges to Black-Scholes models over time through continuous theta integration.
This oracle-free approach eliminates manipulation risks that plague traditional options pricing while enabling options markets on long-tail assets without sufficient oracle coverage. The pricing mechanism inherently reflects actual trading activity rather than theoretical implied volatility, potentially providing more accurate price discovery during volatile conditions when oracle delays can cause significant discrepancies.
The practical implications for traders extend beyond simple cost reduction to fundamental changes in options strategy implementation. Perpetual options eliminate time decay concerns that dominate traditional options strategies, while undercollateralized positions up to 5x leverage enable capital-efficient exposure. The ERC1155 token standard supporting up to four options positions in single tokens simplifies complex multi-leg strategies like iron condors and ratio spreads.
Cross-margining capabilities efficiently manage collateral requirements across multiple positions, while the composability of ERC1155 tokens enables integration with other DeFi protocols for yield generation and risk management. The permissionless market creation allows options trading on any token pair with sufficient Uniswap V3 liquidity, democratizing access to derivatives previously available only for major assets.
The ecosystem impact extends beyond individual trading benefits to broader DeFi infrastructure improvement. By utilizing existing Uniswap V3 liquidity exceeding $3 billion rather than competing for separate pools, Panoptic enhances capital efficiency across the entire ecosystem. Liquidity providers can hedge impermanent loss through protective options while maintaining their underlying positions, reducing the traditional trade-off between yield generation and directional risk.
However, the innovative model introduces novel risks requiring careful consideration. The perpetual nature eliminates traditional options expiry disciplines that limit maximum losses in traditional structures. The path-dependent pricing model's behavior during extreme market conditions remains theoretical, particularly during periods when Uniswap trading activity diverges significantly from underlying asset fundamentals. The oracle-free pricing, while resistant to manipulation, could potentially disconnect from traditional options markets during periods of low DEX activity.
The growth trajectory through beta testing phases demonstrates institutional validation. Multiple successful trading epochs with substantial prize pools have attracted sophisticated traders, while the December 2024 mainnet launch represents a major milestone for DeFi derivatives innovation. The roadmap toward V2 in Q4 2025 and integration with Uniswap V4 positions the protocol as foundational infrastructure for next-generation DeFi financial products.
Comparative analysis reshaping derivatives markets
The convergence of Lyra's institutional-grade infrastructure, Stryke's capital efficiency innovations, and Panoptic's perpetual options paradigm creates a comprehensive ecosystem that addresses different trader needs while collectively reshaping expectations for decentralized derivatives. Each protocol's approach illuminates distinct philosophical and technical directions that together demonstrate the maturation of DeFi options from experimental technology to sophisticated financial infrastructure.
Architectural approaches reveal fundamental design philosophies that extend beyond simple technical implementation. Lyra's transition from AMM to order book represents the centralized exchange convergence theory, where decentralized protocols achieve mainstream adoption by replicating familiar user experiences while maintaining blockchain benefits. The gasless trading, instant confirmations, and institutional-grade matching engine provide the performance characteristics professional traders demand while preserving self-custody and transparency.
Stryke's concentrated liquidity AMM approach embodies the composability maximization philosophy, where protocols achieve competitive advantages through deep integration with existing DeFi infrastructure rather than building isolated systems. The ability to transform existing Uniswap V3 positions into options underwriting without migration requirements demonstrates how DeFi protocols can enhance rather than compete with existing liquidity. This approach potentially offers more sustainable growth paths than protocols requiring separate liquidity bootstrapping.
Panoptic's perpetual options model represents the financial innovation maximization approach, where blockchain capabilities enable entirely new financial products impossible in traditional systems. The oracle-free pricing and perpetual structure challenge fundamental assumptions about options markets while leveraging unique blockchain characteristics like programmable money and composable protocols.
Liquidity provision models demonstrate different solutions to the same fundamental challenge of sustainable market making in volatile environments. Lyra's Market Maker Vaults with automated delta hedging protect providers from directional risk while enabling sophisticated pricing models. The integration with Synthetix and GMX for hedging creates a complex but potentially robust risk management system that could scale with institutional adoption.
Stryke's dual-yield model enables providers to earn both AMM fees and options premiums without choosing between strategies, potentially achieving higher risk-adjusted returns than either approach individually. The Atlantic Options innovation that allows collateral utilization for other DeFi activities while maintaining options exposure could fundamentally change capital efficiency calculations across the entire DeFi ecosystem.
Panoptic's approach of directly utilizing Uniswap V3 liquidity eliminates the need for separate liquidity incentivization while enabling impermanent loss hedging. This model could prove most sustainable long-term if it successfully demonstrates that existing DEX liquidity can efficiently price options without dedicated market makers.
User experience philosophies reflect different approaches to mainstream adoption. Lyra's institutional focus with advanced margin systems, sophisticated risk management, and professional trading tools targets experienced traders and institutions comfortable with complex derivatives strategies. The protocol's success validates demand for professional-grade DeFi options infrastructure.
Stryke's integration approach through familiar DEX interfaces and mobile trading via Telegram demonstrates mass market accessibility strategies. By abstracting options complexity behind familiar interfaces, the protocol potentially reaches traders who would not engage with traditional options platforms. The cross-chain deployment strategy addresses network effects and scaling challenges through geographic and technological diversification.
Panoptic's educational focus with interactive interfaces and strategy visualization attempts to democratize options knowledge while providing powerful tools for sophisticated users. The perpetual structure eliminates expiry complexity that intimidates new options traders while maintaining strategic flexibility for advanced users.
Risk management approaches reveal different priorities in balancing innovation with prudent risk controls. Lyra's comprehensive approach with portfolio margin, scenario analysis, and partial liquidation mechanisms represents institutional-grade risk management adapted for DeFi. The protocol's proven track record through various market cycles provides confidence in the risk systems' effectiveness.
Stryke's focus on eliminating liquidation risk through American-style options and Atlantic Options collateral flexibility prioritizes user protection over capital efficiency optimization. This approach could prove superior during extreme market conditions when traditional liquidation mechanisms fail or create cascade effects.
Panoptic's undercollateralized positions up to 5x leverage with automated liquidation systems balance capital efficiency with risk management. The protocol's novel approach requires extensive stress testing to validate effectiveness during various market scenarios.
The collective impact on traditional derivatives markets extends beyond simple competition to fundamental questions about optimal market structure. The three protocols demonstrate that different approaches can coexist and serve different market segments while collectively expanding the addressable market for derivatives trading. Traditional finance participants increasingly monitor these innovations for potential application in conventional markets, particularly around capital efficiency and risk management techniques.
Practical implications across trader categories
The maturation of DeFi options protocols creates distinct value propositions for different trader categories, from individual retail participants to sophisticated institutional market makers. Understanding these practical implications requires examining how each protocol addresses specific needs while considering the broader ecosystem effects that emerge from increased sophisticated derivatives usage in decentralized systems.
Retail traders benefit most significantly from reduced barriers to entry and enhanced capital efficiency that traditional options markets cannot match. Minimum investment requirements in DeFi options often start around $50 compared to institutional-focused minimums in traditional markets, while 24/7 trading availability and global accessibility eliminate geographic and temporal constraints. The elimination of know-your-customer requirements and credit checks democratizes access for users excluded from traditional derivatives markets.
Stryke's integration with familiar DEX interfaces enables retail traders to access options strategies through platforms they already understand, reducing the learning curve that traditionally limits options adoption. The mobile integration through Unibot allows sophisticated leveraged trading through Telegram interfaces, bringing institutional-quality execution to mobile users. American-style exercise flexibility provides forgiveness for timing mistakes that European-style options penalize.
Panoptic's educational approach with interactive payoff diagrams and strategy visualization helps retail traders understand options mechanics without requiring extensive derivatives knowledge. The perpetual structure eliminates expiry timing concerns that create stress and potential losses for inexperienced traders. The ability to hedge impermanent loss while maintaining liquidity provider positions addresses a specific DeFi risk that traditional options cannot cover.
However, retail traders also face unique risks in DeFi options that traditional markets address through regulation and intermediary protection. Smart contract vulnerabilities could result in complete capital loss without insurance or regulatory recourse. The complexity of wallet management, gas fee calculation, and multi-chain operations creates technical barriers and potential user error risks. The lack of traditional customer support means retail traders must navigate problems independently or rely on community assistance.
Institutional traders and market makers represent the most sophisticated user category with specific requirements around risk management, compliance, and operational efficiency. Lyra's institutional focus addresses these needs through advanced portfolio margin systems, comprehensive risk analytics, and professional trading interfaces comparable to Bloomberg terminals. The protocol's proven ability to handle large position sizes while maintaining pricing accuracy validates its suitability for institutional capital.
The gasless trading and instant settlement capabilities eliminate traditional settlement risk and reduce operational complexity compared to traditional derivatives markets. Multi-asset collateral support enables sophisticated portfolio construction strategies impossible in single-collateral traditional systems. The transparency of on-chain settlement and risk management provides institutional-grade auditability that traditional markets often obscure.
Institutional adoption faces regulatory and operational challenges that retail traders can more easily navigate. Compliance requirements in traditional markets often conflict with DeFi's permissionless nature, while custody solutions must meet institutional security and insurance standards. The geographic restrictions implemented by major protocols to avoid regulatory conflicts limit institutional participation from major markets.
Professional market makers find unique opportunities in DeFi options that traditional markets cannot provide. The automated market making capabilities of protocols like Lyra enable continuous liquidity provision without human intervention, potentially improving capital efficiency compared to traditional market making strategies. The composability with other DeFi protocols enables risk management strategies impossible in traditional markets, such as dynamic hedging through perpetual swaps or yield optimization through lending protocols.
Stryke's CLAMM technology enables market makers to provide liquidity across both spot and options simultaneously, earning multiple revenue streams from the same capital. The Atlantic Options innovation allows sophisticated risk management strategies where the same collateral serves multiple purposes, potentially achieving higher risk-adjusted returns than traditional market making.
However, market makers also face novel risks specific to DeFi systems. Smart contract bugs could cause significant losses despite sophisticated risk management, while oracle failures or manipulation could create pricing discrepancies leading to adverse selection. The complexity of managing positions across multiple chains and protocols increases operational risk and capital requirements.
Hedge funds and asset managers represent an emerging category finding increasing utility in DeFi options for both alpha generation and risk management. The ability to implement complex strategies like volatility trading, basis trading between spot and derivatives, and cross-asset arbitrage provides alpha opportunities unavailable in traditional markets. The 24/7 nature of DeFi markets enables continuous strategy management and faster response to market opportunities.
The composability of DeFi options with lending protocols, yield farming, and other financial primitives enables strategy construction impossible in traditional markets. Yield optimization through automated position management and cross-protocol arbitrage can enhance returns while maintaining target risk profiles.
Cross-border capital flows represent another significant practical implication as DeFi options enable international diversification and arbitrage without traditional currency controls or regulatory restrictions. Institutional participants can achieve exposure to markets and strategies globally without establishing local entities or navigating complex regulatory frameworks in each jurisdiction.
The collective impact on traditional market participants extends beyond direct usage to competitive pressure and innovation inspiration. Traditional derivatives exchanges monitor DeFi innovations for potential implementation, while regulatory authorities examine DeFi options markets for policy implications. The demonstrated viability of oracle-free pricing, automated risk management, and cross-chain liquidity aggregation could influence traditional market structure evolution.
Ecosystem impact on DeFi and traditional finance
The emergence of sophisticated options protocols fundamentally alters the DeFi ecosystem's risk and return characteristics while creating spillover effects that influence traditional financial markets. These protocols serve as critical infrastructure enabling more sophisticated portfolio construction, risk management, and yield generation strategies across the broader decentralized finance landscape.
The integration patterns between options protocols and other DeFi primitives reveal how composability creates emergent behaviors impossible in traditional finance. Lending protocols like Aave and Compound now support yield-bearing tokens as collateral for options positions, enabling capital efficiency improvements where the same assets simultaneously earn lending yields and provide options margin. Flash loans enable complex cross-protocol arbitrage strategies that keep options prices aligned with underlying spot markets while providing additional yield opportunities for sophisticated traders.
Automated vault strategies combine options writing with yield farming to create structured products serving retail investors who lack the sophistication to manage complex derivatives positions directly. Protocols like Ribbon utilize infrastructure layers from Opyn with AMM pricing from various sources to create "set-and-forget" strategies that generate returns through systematic options selling. These products democratize access to options-based yield generation while creating consistent demand for underlying options infrastructure.
The risk diversification benefits extend throughout DeFi as protocols implement options-based hedging strategies for their treasury management and risk mitigation. Protocols holding large token positions can hedge price risk through protective puts, while those with stablecoin treasury exposure can generate additional yield through covered call strategies. This institutional adoption of options by DeFi protocols themselves creates a positive feedback loop driving further innovation and adoption.
Cross-chain bridge risks, historically a major concern in multi-chain DeFi, find partial mitigation through options strategies that provide insurance against bridge failures or cross-chain arbitrage opportunities that reduce reliance on single bridge providers. Intent-based trading systems that aggregate liquidity across chains enable options strategies that span multiple blockchain networks, creating more robust and capital-efficient derivatives markets.
The data availability and transparency characteristics of blockchain-based options create new possibilities for quantitative analysis and algorithm development. All trades, liquidations, and risk management activities occur transparently on-chain, enabling sophisticated backtesting and strategy development impossible with traditional options markets' limited data availability. Academic researchers and quantitative funds increasingly leverage this data for strategy development and market microstructure research.
Traditional finance integration accelerates as institutional participants recognize specific advantages of DeFi options infrastructure. The 24/7 trading availability particularly benefits global asset managers who previously faced timing constraints in traditional options markets. The elimination of counterparty credit risk through smart contract settlement provides advantages during periods of traditional market stress when counterparty concerns may limit trading activity.
Major asset managers increasingly explore hybrid strategies combining traditional and DeFi options to optimize execution and risk management. The ability to implement identical strategies in both traditional and DeFi markets enables sophisticated basis trading and arbitrage opportunities while providing diversification across market structure types. Some institutional participants report better execution and lower costs in DeFi options for certain strategy types, particularly those requiring frequent small adjustments.
The regulatory implications extend beyond DeFi-specific concerns to broader questions about optimal derivatives market structure. Regulatory authorities study DeFi options markets for insights into potential improvements for traditional markets, particularly around transparency, risk management, and settlement efficiency. The demonstrated viability of automated risk management and real-time margining could influence traditional market structure regulations.
However, the ecosystem impact includes significant challenges that could constrain growth or create systemic risks. The concentration of liquidity across relatively few protocols creates potential single points of failure that could affect multiple DeFi sectors simultaneously. The complexity of interactions between options protocols and other DeFi primitives makes system-wide risk assessment difficult, particularly during extreme market conditions when correlations may increase unexpectedly.
The regulatory uncertainty surrounding DeFi options creates compliance challenges for traditional finance participants seeking to integrate these innovations. Geographic restrictions implemented by major protocols limit addressable markets, while unclear tax treatment of DeFi options strategies creates uncertainty for institutional adoption. These regulatory constraints may limit the ecosystem's growth potential despite technical viability.
Scalability challenges remain significant as options trading generates substantial computational requirements for pricing, risk management, and settlement. Network congestion during volatile periods can increase transaction costs and reduce execution quality, while the complex state requirements for options positions may face practical limits on current blockchain infrastructure. Layer 2 solutions provide partial mitigation but introduce additional complexity and potential risks.
The cultural and educational barriers to options adoption in DeFi remain substantial despite improved user interfaces and educational resources. Options strategies require significantly more financial sophistication than simple spot trading or lending, limiting the addressable user base. The permanent loss risks from options selling strategies may not be well understood by retail participants attracted by high yields, potentially leading to unsustainable adoption patterns.
Technical innovations transforming derivatives pricing
The technical foundations underlying DeFi options represent breakthrough innovations in automated market making, risk management, and pricing accuracy that address fundamental challenges in traditional derivatives markets. These innovations extend beyond simple blockchain implementation of existing models to entirely new approaches that leverage unique blockchain characteristics like programmable money, composable protocols, and transparent state management.
Advanced AMM designs have evolved from simple constant product models to sophisticated systems that accurately price complex derivatives while managing multiple risk factors simultaneously. Lyra's dynamic Black-Scholes implementation with market-driven implied volatility surface mapping demonstrates how AMMs can achieve pricing accuracy comparable to traditional market makers while operating autonomously. The system continuously adjusts volatility parameters based on supply and demand dynamics, creating price discovery mechanisms that respond to market conditions without human intervention.
The development of concentrated liquidity AMMs specifically for derivatives represents another significant innovation. Stryke's CLAMM technology enables liquidity providers to concentrate capital in specific price ranges while automatically utilizing that liquidity for options underwriting. This dual-purpose approach achieves capital efficiency improvements of up to 40x compared to traditional AMM models while providing options-specific risk management features.
Hybrid orderbook-AMM systems like Lyra's V2 architecture combine the efficiency of automated market making with the precision of traditional orderbooks. The gasless central limit order book with on-chain settlement provides institutional-grade execution while maintaining transparency and self-custody. This architectural innovation addresses previous trade-offs between decentralization and performance that limited institutional adoption.
Oracle integration and manipulation resistance represent critical technical innovations addressing fundamental vulnerabilities in DeFi derivatives. Traditional approaches using simple price feeds proved vulnerable to flash loan attacks and other manipulation strategies that could cause significant losses for options protocols. Modern systems implement multiple layers of protection including time-weighted average prices, median filtering, and cross-oracle consensus mechanisms.
Chainlink's decentralized oracle network architecture provides manipulation-resistant price data through multiple independent nodes fetching and verifying data from numerous sources. The redundancy and cryptographic verification eliminate single points of failure while providing the high-frequency updates required for accurate options pricing. Integration with additional oracle providers like Pyth Network creates further redundancy and provides specialized financial market data directly from trading firms.
Panoptic's oracle-free approach represents perhaps the most radical innovation, eliminating oracle dependency entirely through direct integration with Uniswap V3 trading activity. The streaming premia model that prices options based on actual trading fees rather than theoretical implied volatility creates entirely new pricing paradigms while eliminating manipulation risks that plague oracle-based systems. This innovation enables options markets on long-tail assets without sufficient oracle coverage while providing pricing accuracy that reflects actual market activity.
Risk management innovations address the complex challenges of managing derivatives exposure across multiple protocols and assets. Modern DeFi options protocols implement real-time portfolio margin calculations using scenario analysis across dozens of volatility and price shock scenarios. These systems provide risk assessment capabilities comparable to institutional trading systems while operating transparently on-chain.
Automated liquidation systems have evolved from simple threshold-based mechanisms to sophisticated systems that minimize market impact while maintaining protocol solvency. Partial liquidation capabilities preserve user positions during temporary market stress while preventing system-wide failures. Competition among multiple liquidators ensures efficient execution while MEV protection mechanisms prevent value extraction that could reduce liquidation effectiveness.
Cross-chain risk management represents emerging innovation as protocols expand across multiple blockchain networks. Unified risk monitoring systems aggregate exposure across different chains while providing coordinated risk management responses. Intent-based execution systems enable complex strategies that span multiple networks while minimizing bridge risks and execution complexity.
Advanced pricing models specifically designed for blockchain environments address unique characteristics of DeFi markets including liquidity fragmentation, gas cost considerations, and MEV extraction risks. Path-dependent pricing models like Panoptic's streamia accumulate fees based on actual trading activity rather than time-based theta decay, potentially providing more accurate pricing during volatile conditions.
Dynamic fee structures that adapt to market conditions help manage volatility impact while incentivizing beneficial trading behavior. These systems can increase fees during high volatility periods to compensate liquidity providers for increased risk while reducing fees during stable periods to encourage trading activity. Some protocols implement negative fees for trades that reduce portfolio risk, effectively paying users to improve system stability.
Multi-asset collateral systems enable sophisticated portfolio construction strategies impossible in traditional single-collateral options systems. Risk-adjusted haircuts based on asset volatility and correlation enable efficient capital utilization while maintaining prudent risk management. These systems support complex cross-asset strategies while providing flexibility for users with diverse portfolio holdings.
The technical infrastructure improvements extend to user interface innovations that make complex derivatives accessible to broader user bases. Interactive payoff diagrams provide real-time visualization of strategy outcomes across different market scenarios, while automated strategy optimization helps users construct efficient positions. These educational tools combined with simplified execution interfaces reduce barriers to derivatives adoption.
Smart contract architecture innovations address scalability and composability challenges that limit traditional blockchain applications. Modular designs enable rapid feature additions without core contract changes, while standardized interfaces enable seamless integration with other DeFi protocols. Gas optimization techniques reduce transaction costs while maintaining security and functionality.
The emergence of intent-based execution represents a paradigm shift from specifying transaction mechanics to describing desired outcomes. Users can specify complex multi-step strategies that solvers compete to execute efficiently, potentially achieving better execution while reducing user complexity. This innovation could dramatically simplify access to sophisticated derivatives strategies while improving execution quality through professional competition.
Risk considerations and regulatory framework evolution
The risk landscape for DeFi options encompasses traditional derivatives risks alongside novel technological and regulatory uncertainties that require sophisticated understanding and management. These risks span multiple categories including smart contract vulnerabilities, market structure risks, operational challenges, and evolving regulatory requirements that collectively create complex risk management requirements for market participants.
Smart contract risk represents the most fundamental technical challenge as options protocols require complex logic for pricing, risk management, and settlement that creates large attack surfaces for potential exploits. Historical precedent demonstrates that even audited protocols can contain vulnerabilities leading to significant losses, with several major options protocols experiencing exploits resulting in millions of dollars in losses. The composition of multiple smart contracts across different protocols for advanced strategies compounds these risks exponentially.
Mitigation strategies have evolved significantly as the industry matures. Multiple audit requirements from reputable firms like OpenZeppelin, ConsenSys Diligence, and Cyfrin provide increasing confidence in contract security. Bug bounty programs incentivize ongoing security research by offering substantial rewards for vulnerability discovery. Formal verification processes for critical contract functions provide mathematical certainty about contract behavior under specific conditions.
However, smart contract risk remains elevated for newer protocols and novel architectures. Panoptic's innovative perpetual options model, while theoretically sound, lacks extensive battle-testing during extreme market conditions. The protocol's complex integration with Uniswap V3 creates interdependencies where bugs in either system could affect the other. Similarly, Stryke's Atlantic Options innovation creates novel risk scenarios that historical testing cannot fully address.
Oracle risk and manipulation represent critical vulnerabilities that could cause immediate and substantial losses through mispriced options. Flash loan attacks enabling temporary price manipulation have historically caused significant losses across various DeFi protocols. Traditional time-weighted average price oracles provide some protection but may lag significantly during volatile periods, potentially causing unfair liquidations or enabling arbitrage extraction.
Advanced oracle protection mechanisms including median-based aggregation, multiple independent price sources, and manipulation-resistant algorithms provide increased security. Research demonstrates that median-based methods resist manipulation more effectively than arithmetic means used in traditional TWAP systems. Multiple oracle providers with different data sources create redundancy that reduces single points of failure.
Panoptic's oracle-free approach eliminates these risks entirely but introduces novel uncertainties about pricing accuracy during periods when Uniswap trading activity diverges from fundamental asset values. The path-dependent pricing model's behavior during extreme market conditions where trading may cease entirely remains untested in practice.
Liquidity risk in DeFi options differs significantly from traditional markets due to the automated market making systems and concentrated liquidity provision models. Liquidity providers face impermanent loss risks that can be severe during volatile conditions, with academic research demonstrating potential losses exceeding 70% for highly volatile trading pairs. The complexity of options market making amplifies these risks as providers must manage both price risk and time decay simultaneously.
Modern protocols implement sophisticated protection mechanisms for liquidity providers including automated delta hedging, dynamic fee structures, and impermanent loss protection through derivatives strategies. However, these protections add complexity and may fail during extreme conditions when hedging mechanisms become inadequate or counterparties become unreliable.
Liquidation risk represents another significant concern as the complexity of options positions makes accurate real-time risk assessment challenging. Network congestion during volatile periods could prevent timely liquidation execution, while oracle delays might cause unfair liquidations or inadequate risk management. MEV extraction by searchers could reduce liquidation effectiveness by front-running or back-running liquidation transactions.
Advanced liquidation systems implement partial liquidations to minimize user impact while maintaining protocol solvency. Competition among multiple liquidators ensures execution efficiency while automated systems reduce reliance on human intervention. However, these systems require extensive stress testing to validate effectiveness during various market scenarios.
Regulatory uncertainty represents perhaps the most significant long-term risk as DeFi options operate in legal gray areas across most jurisdictions. The U.S. regulatory framework continues evolving with the House Discussion Draft Bill establishing CFTC authority over digital commodities while preserving SEC antifraud enforcement. However, specific treatment of DeFi options remains unclear with potential for retroactive enforcement or sudden regulatory changes.
The CFTC's precedent in Ooki DAO demonstrates that decentralized structures provide no regulatory immunity, with DAOs considered legal persons under commodity exchange laws. This precedent creates compliance obligations for protocol developers and potentially for token holders participating in governance. Geographic restrictions implemented by major protocols indicate recognition of regulatory risks but may limit addressable markets and protocol growth potential.
International regulatory approaches vary significantly with some jurisdictions providing clearer frameworks while others maintain restrictive positions. The European Union's MiCA regulation provides comprehensive digital asset frameworks, while Singapore offers progressive sandbox approaches for institutional participants. However, regulatory arbitrage creates operational complexity for global protocols and users.
Operational risks encompass the technical infrastructure dependencies that DeFi options require for reliable operation. RPC provider reliability affects protocol accessibility, while frontend interfaces face DNS attacks and phishing risks. Wallet security becomes critical for users managing complex multi-asset positions across multiple protocols. Cross-chain bridge security remains a major concern with historical losses exceeding $2 billion from bridge exploits.
Governance risks affect protocol evolution and user protection as major protocol changes could substantially alter risk characteristics or user protections. Token-based governance systems may concentrate control among large holders while potentially excluding smaller users from important decisions. Emergency pause mechanisms provide protection against immediate threats but create centralization concerns that could undermine decentralized value propositions.
The interconnected nature of DeFi protocols creates systemic risks where failures in one protocol could cascade through integrated systems. Options protocols' dependencies on lending protocols, oracle providers, and underlying DEXs create complex failure scenarios that may be difficult to predict or manage. The concentration of liquidity among relatively few major protocols amplifies these systemic risks.
Risk assessment tools and monitoring systems provide increasing sophistication for managing these complex risks. Real-time portfolio risk dashboards enable continuous monitoring of exposure across multiple protocols and positions. Automated alert systems provide warnings before risk thresholds are exceeded while liquidation calculators help users understand downside scenarios. However, the complexity of DeFi options strategies may exceed many users' ability to assess risks accurately, potentially leading to inappropriate position sizing or inadequate risk management.
Future outlook and emerging trends
The trajectory of DeFi options trading points toward fundamental shifts in market structure, user experience, and institutional adoption that could reshape both decentralized and traditional derivatives markets. Current developments in intent-based execution, cross-chain infrastructure, artificial intelligence integration, and regulatory clarity create convergent forces that may accelerate mainstream adoption while introducing new categories of financial products impossible in traditional systems.
Intent-based trading represents perhaps the most transformative trend as it shifts focus from transaction mechanics to outcome specification. Rather than managing complex multi-step transactions across different protocols, users specify desired results while professional solvers compete to achieve optimal execution. DeGate's implementation supporting cross-chain intent-based trading across Solana, Base, BNB Smart Chain, Arbitrum, Avalanche, Optimism, and Polygon demonstrates the potential for seamless multi-network strategies without technical complexity.
This evolution addresses current barriers to sophisticated derivatives strategies by abstracting technical complexity while potentially improving execution quality through professional competition. Advanced users could specify complex options strategies with desired risk-return characteristics while solvers handle optimal implementation across multiple protocols and chains. The gas abstraction enabled by USDC settlements could eliminate transaction cost unpredictability that currently complicates strategy planning.
Cross-chain infrastructure development enables global liquidity aggregation that could address current fragmentation limiting DeFi options growth. Application-specific chains like dYdX's Cosmos-based implementation provide ultra-fast derivatives trading while maintaining decentralization principles. Layer 2 scaling solutions continue reducing transaction costs while increasing throughput, with some implementations achieving sub-second confirmations comparable to traditional exchanges.
Chain abstraction initiatives aim to eliminate user awareness of underlying blockchain complexity while maintaining security and decentralization benefits. Users could access options strategies across any blockchain network through unified interfaces while protocols optimize execution across different networks based on liquidity, costs, and performance characteristics. This development could significantly expand addressable markets by eliminating technical barriers that currently limit adoption.
Artificial intelligence integration represents emerging innovation that could enhance risk management, pricing accuracy, and strategy optimization. Machine learning algorithms already optimize routing across multiple execution venues in traditional markets, with similar applications emerging in DeFi. AI-driven risk management systems could provide real-time portfolio optimization while predictive analytics enhance volatility forecasting and options pricing accuracy.
Automated market making with AI-powered pricing and liquidity provision could improve capital efficiency while reducing risks for liquidity providers. These systems could dynamically adjust parameters based on market conditions while implementing sophisticated hedging strategies automatically. However, AI integration also introduces risks including algorithm bias, unexpected behavior during market stress, and potential coordination failures between different AI systems.
Institutional adoption patterns suggest increasing sophistication and scale as regulatory clarity improves and infrastructure matures. Major financial institutions including Goldman Sachs enhance crypto trading capabilities while custody solutions from firms like Anchorage Digital provide institutional-grade security. Bitcoin and Ethereum ETF approvals legitimize digital assets for institutional allocators while creating demand for sophisticated risk management tools including options strategies.
Professional trading tools development focuses on institutional requirements including advanced options Greeks calculations, comprehensive portfolio analytics, and regulatory compliance integration. Cross-chain portfolio management tools enable institutional-scale operations across multiple blockchain networks while automated reporting facilitates regulatory compliance and audit requirements.
The development of hybrid models combining DeFi innovation with traditional finance compliance could accelerate institutional adoption. Permissioned DeFi pools provide blockchain benefits while meeting regulatory requirements, with some implementations already controlling substantial volume. Tokenization of traditional assets for DeFi options trading could expand addressable markets while providing familiar regulatory frameworks for institutional participants.
Regulatory framework evolution shows increasing sophistication as authorities develop specific approaches to DeFi derivatives. The U.S. Congressional Discussion Draft establishing CFTC and SEC coordination represents significant progress toward regulatory clarity. However, implementation details and enforcement approaches remain unclear, creating continued uncertainty for market participants.
International regulatory competition may benefit DeFi options development as jurisdictions compete for blockchain innovation leadership. Progressive frameworks in jurisdictions like Singapore, Switzerland, and parts of Europe provide clearer operating environments while potentially attracting protocol development and institutional adoption. However, regulatory arbitrage creates complexity for global protocols serving users across multiple jurisdictions.
Technical innovation continues advancing with emerging developments including improved consensus mechanisms, enhanced privacy features, and better interoperability protocols. Zero-knowledge proof integration could enhance privacy while maintaining transparency requirements. Quantum computing resistance becomes increasingly relevant as quantum capabilities advance, requiring protocol upgrades to maintain security assumptions.
The integration of traditional asset tokenization with DeFi options could dramatically expand addressable markets by enabling options trading on tokenized stocks, bonds, commodities, and real estate. This development could bring traditional finance sophistication to DeFi while providing blockchain benefits including transparency, automation, and global accessibility.
Market structure evolution may favor protocols that achieve sustainable economic models without token emission dependency. Protocols demonstrating consistent profitability through transaction fees and genuine value creation appear better positioned for long-term success than those relying on unsustainable incentive programs. The maturation toward sustainable economics represents critical progress for long-term viability.
The emergence of new derivative products leveraging unique blockchain capabilities could create entirely new market categories. Perpetual options without expiration dates, as pioneered by Panoptic, represent one example of innovation impossible in traditional markets. Weather derivatives based on oracle data, prediction markets with options characteristics, and complex structured products combining multiple DeFi primitives could expand derivatives utility beyond traditional financial hedging.
However, significant challenges remain including scalability limitations, user experience complexity, and regulatory uncertainty that could constrain growth potential. The technical infrastructure requirements for sophisticated options trading may face practical limits on current blockchain architecture, while user education barriers limit addressable market expansion. Success will likely require continued innovation balancing sophistication with accessibility while navigating evolving regulatory requirements.
The convergence of traditional finance expertise with DeFi innovation, supported by clearer regulatory frameworks and institutional infrastructure, positions sophisticated decentralized derivatives as critical components of future financial systems. The success of current protocols in demonstrating technical viability and economic sustainability provides foundation for broader adoption, while continued innovation addresses remaining limitations and expands possible use cases.
Final thoughts
The transformation of DeFi options trading from experimental protocols to sophisticated financial infrastructure represents one of the most significant innovations in modern finance, with Lyra, Stryke, and Panoptic collectively demonstrating that decentralized systems can match or exceed traditional derivatives markets in technical sophistication while providing unique advantages impossible in conventional financial systems.
Lyra's evolution to Derive showcases the institutional convergence pathway where decentralized protocols achieve mainstream adoption through familiar user experiences combined with blockchain benefits. The protocol's proven ability to handle substantial volume while maintaining pricing accuracy comparable to established exchanges validates the technical viability of sophisticated DeFi derivatives. However, geographic restrictions and regulatory uncertainty limit addressable market expansion despite technical success.
Stryke's capital efficiency innovations through CLAMM technology and Atlantic Options demonstrate how DeFi protocols can enhance existing infrastructure rather than compete with it. The ability to provide simultaneous spot and options liquidity while enabling dynamic collateral utilization creates economic advantages impossible in traditional markets. This approach potentially offers more sustainable growth paths through composability rather than isolated liquidity competition.
Panoptic's perpetual options paradigm challenges fundamental assumptions about derivatives markets while demonstrating how blockchain capabilities enable entirely new financial products. The oracle-free pricing mechanism and direct Uniswap V3 integration create unprecedented transparency and manipulation resistance while potentially achieving superior capital efficiency. However, the innovative model requires extensive real-world testing to validate behavior during extreme market conditions.
The collective impact extends beyond individual protocol success to broader ecosystem transformation as options infrastructure enables sophisticated risk management, yield generation, and portfolio construction strategies throughout DeFi. The integration with lending protocols, cross-chain bridges, and other financial primitives creates emergent behaviors and improved capital efficiency that benefit the entire decentralized finance ecosystem.
Technical innovations including advanced AMM designs, oracle-free pricing mechanisms, automated risk management systems, and cross-chain liquidity aggregation represent fundamental advances in derivatives market structure that could influence traditional finance evolution. The demonstrated viability of real-time risk management, transparent settlement, and automated market making provides potential models for conventional market improvement.
However, significant challenges persist including liquidity fragmentation across protocols, regulatory uncertainty in major markets, technical complexity barriers limiting mainstream adoption, and novel risks from untested systems during extreme market conditions. The concentration of activity among relatively few protocols creates potential single points of failure that could affect multiple DeFi sectors simultaneously.
The regulatory landscape shows increasing sophistication with authorities developing specific frameworks for DeFi derivatives, though implementation remains uncertain and potentially fragmented across jurisdictions. The balance between innovation encouragement and investor protection will likely determine whether DeFi options achieve mainstream institutional adoption or remain specialized tools for sophisticated participants.
Looking forward, the convergence of intent-based execution, cross-chain infrastructure, artificial intelligence integration, and regulatory clarity creates potential for rapid mainstream adoption while introducing new categories of financial products impossible in traditional systems. The success of current protocols provides foundation for broader ecosystem development, while continued innovation addresses remaining limitations.
The evidence suggests that DeFi options have successfully transitioned from experimental technology to viable financial infrastructure capable of serving sophisticated institutional and retail participants. While challenges remain significant, the demonstrated technical capabilities, growing institutional interest, and continued innovation position these protocols as critical components of future financial system evolution. The question appears to be not whether DeFi options will achieve broader adoption, but rather how quickly regulatory clarity and infrastructure maturity will enable that transition while maintaining the innovative advantages that distinguish decentralized systems from traditional alternatives.



