For more than a decade, Bitcoin has worn the mantle of "digital gold" - a scarce, decentralized store of value positioned as an analog to the precious metal that has anchored human commerce for millennia. The comparison made intuitive sense: both assets feature fixed supply constraints, resist centralized control, and promise protection against fiat currency debasement. Yet as 2025 unfolds, this narrative is showing its age.
Bitcoin's price briefly topped $125,000 in October, establishing new all-time highs. Meanwhile, institutional adoption accelerated, with corporate treasuries now holding over one million BTC worth approximately $117 billion. The approval of spot Bitcoin ETFs in early 2024 brought Bitcoin firmly into traditional finance, with BlackRock's iShares Bitcoin Trust amassing more than $50 billion in assets under management by mid-2025.
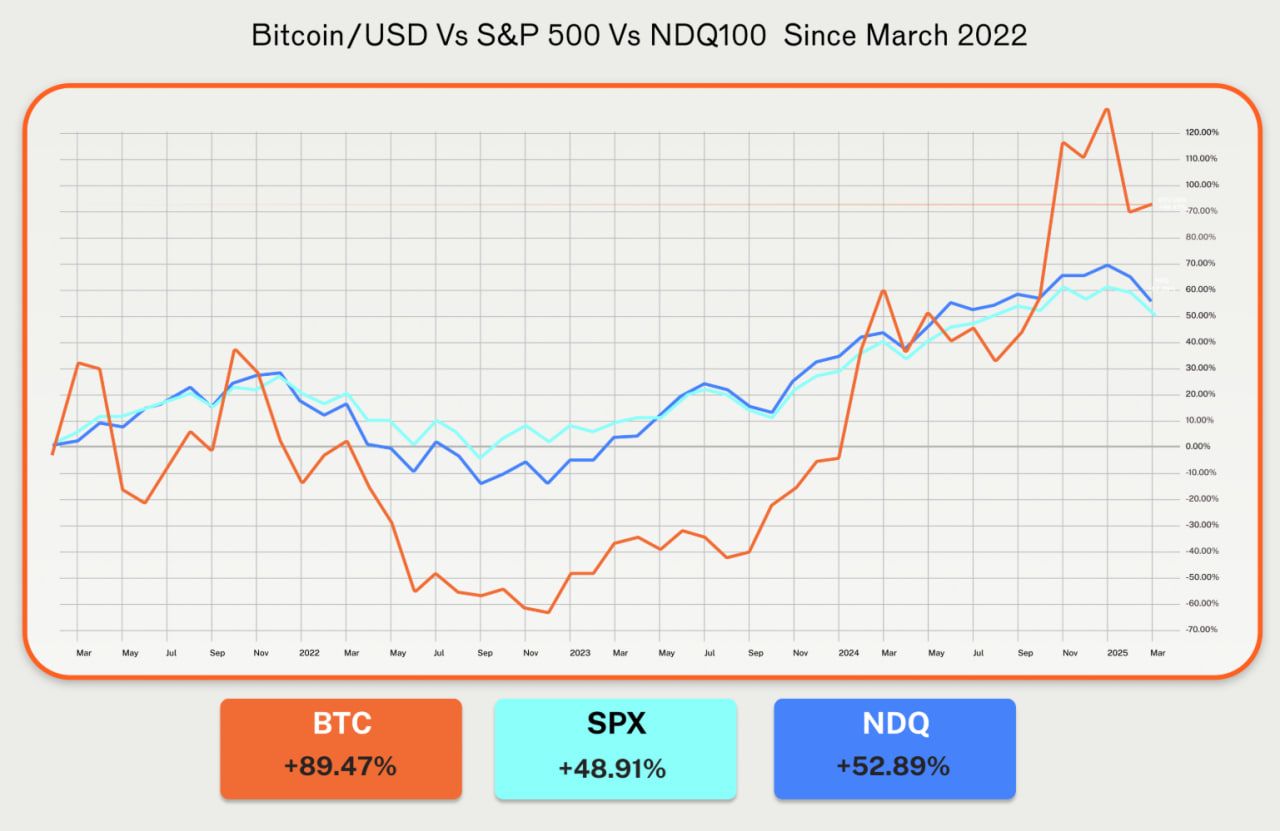
But something curious happened in 2025: gold outperformed Bitcoin. While the precious metal surged more than 50% since January, Bitcoin gained approximately 15% over the same period, according to market data. Bitcoin's correlation with the Nasdaq reached as high as 0.8 early in the year, far exceeding its 0.2 correlation with gold. The cryptocurrency that was supposed to be "digital gold" increasingly behaved like a leveraged technology stock.
This disconnect raises fundamental questions. As the global monetary system confronts unprecedented challenges - ballooning sovereign debt, persistent inflation fears, geopolitical fractures, and the erosion of dollar hegemony - is Bitcoin's story shifting? Are we witnessing not the fulfillment of the "digital gold" thesis, but its transformation into something more complex and potentially more significant?
Below we explore how Bitcoin's narrative is evolving beyond its characterization as mere "digital gold." We also examine what its next monetary role might be, how that transformation is unfolding technologically, institutionally, and macro-economically, and why it matters for understanding the architecture of value in the digital age. Through fact-based analysis drawing on institutional research, market data, and emerging infrastructure developments, we'll consider whether Bitcoin is positioned to become something more than a passive store of value - and what comes next in its monetary evolution.
The "Digital Gold" Narrative: Origins and Rationale
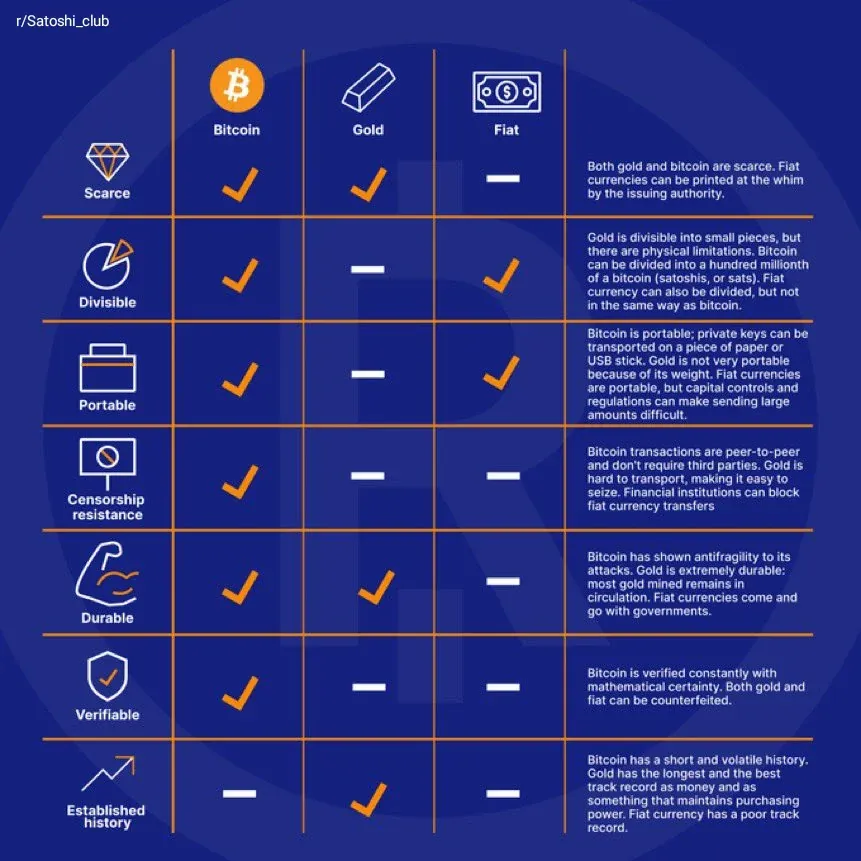
The comparison between Bitcoin and gold emerged organically from Bitcoin's fundamental characteristics. Both assets share key attributes that have historically defined sound money: scarcity, durability, divisibility, portability, and resistance to confiscation or debasement by central authorities.
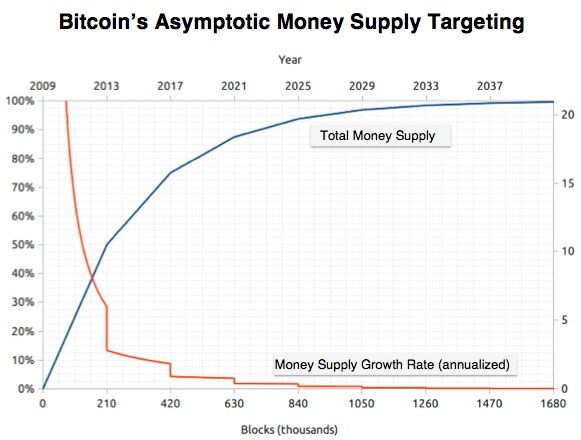
Bitcoin's fixed supply of 21 million coins, embedded immutably in its protocol, creates absolute scarcity that even gold cannot match. While gold's supply increases by approximately 1-2% annually through mining, Bitcoin's issuance follows a predetermined schedule, with new supply diminishing through programmatic "halvings" every four years. The April 2024 halving reduced miner rewards to 3.125 BTC per block, bringing Bitcoin's annual inflation rate below that of gold for the first time in its history.
Decentralization formed another pillar of the digital gold thesis. Like gold, Bitcoin operates outside the control of any single nation-state or central bank. No entity can arbitrarily increase its supply, freeze holdings, or reverse transactions. This positioned Bitcoin as a potential hedge against government overreach and monetary mismanagement - precisely the fears that drove gold's 5,000-year track record as a store of value.
The narrative gained particular resonance following the 2008 financial crisis and subsequent rounds of quantitative easing. As central banks flooded the system with newly created currency, investors sought assets that could preserve purchasing power. Gold rallied to record highs above $1,900 per ounce in 2011. Bitcoin, launched in 2009 as a direct response to the financial crisis, offered a digital alternative with superior portability and divisibility.
Institutional voices reinforced the parallel. Deutsche Bank analysts described Bitcoin's trajectory as following gold's historical path "from skepticism to widespread acceptance." The bank projected that Bitcoin could join gold on central bank balance sheets by 2030, driven by shared characteristics of scarcity and low correlation with traditional assets.
Corporate adoption followed this logic. MicroStrategy, which began accumulating Bitcoin in August 2020, positioned its strategy explicitly as a hedge against dollar debasement. By late 2025, the company held 628,946 BTC valued at $73.6 billion, representing nearly 3% of Bitcoin's total supply. CEO Michael Saylor repeatedly framed Bitcoin as "digital property" superior to fiat reserves, echoing gold's historical role as treasury ballast.
Yet the digital gold narrative always contained tensions. Bitcoin's volatility dwarfed that of gold. While gold's annual price volatility typically ranges between 14-16%, Bitcoin's has historically exceeded 45-65%, according to market analysts. Such wild price swings challenged Bitcoin's utility as a stable store of value, particularly for risk-averse institutions and central banks.
The analogy also overlooked Bitcoin's distinct technological properties. Gold is inert, a passive asset with limited utility beyond jewelry and industrial applications. Bitcoin, by contrast, exists as programmable digital infrastructure. Its blockchain enables not just value storage but potentially complex financial operations - lending, derivatives, yield generation - that gold cannot support natively.
Regulatory uncertainty further complicated the comparison. Gold enjoys clear legal status and deep, liquid markets spanning centuries. Bitcoin remained subject to evolving and often contradictory regulatory frameworks, with some jurisdictions embracing it and others restricting or banning its use. This created counterparty and jurisdictional risks absent from physical gold.
Perhaps most significantly, Bitcoin's behavior increasingly diverged from gold's in practice. The correlation between Bitcoin and the Nasdaq 100 reached 0.5 by mid-2025, and had spiked to 0.8 earlier in the year. Bitcoin increasingly moved in tandem with technology stocks, responding to the same macroeconomic drivers - interest rates, liquidity conditions, risk appetite - that affected growth equities. Meanwhile, its correlation with gold remained weak, hovering around 0.2.
By 2025, the digital gold narrative appeared strained. Bitcoin had achieved remarkable institutional validation through spot ETF approvals and corporate treasury adoption. Yet it behaved less like gold and more like a high-beta tech asset. This disconnect suggested that Bitcoin's monetary role was evolving beyond the simple store-of-value function that the gold comparison implied.
Macro & Monetary Context: Why Change Might Be Coming
Bitcoin's evolution cannot be separated from the broader monetary dynamics reshaping global finance. The macroeconomic environment of the mid-2020s has created conditions that both validate and complicate Bitcoin's original value proposition.
Fiat currency debasement has accelerated dramatically. U.S. federal debt surpassed $35 trillion in 2025, while global debt exceeded $300 trillion according to Institute of International Finance data cited in market analyses. This debt overhang limits central banks' ability to normalize monetary policy without risking financial instability or sovereign debt crises.
The result is a persistent backdrop of what Bitcoin advocates call the "debasement trade" - the strategy of holding hard assets to protect against fiat currency dilution. This narrative, long championed by Bitcoin proponents, gained mainstream traction in 2025 as prominent economists acknowledged currency debasement concerns publicly for the first time.
Yet Bitcoin's relationship with inflation proved more nuanced than the simple digital gold thesis suggested. Research from Fidelity Digital Assets found that Bitcoin's highest correlation came not with inflation metrics directly, but with measures of liquidity - particularly broad money supply measures like M2. Bitcoin's price movements could be explained largely by changes in global money supply rather than consumer price inflation per se.
This insight reframed Bitcoin's monetary role. Rather than simply hedging against rising consumer prices, Bitcoin responded to liquidity conditions and real yields. When central banks expanded money supply and suppressed real interest rates, capital flowed into Bitcoin. When they tightened monetary policy and drained liquidity, Bitcoin suffered.
The Federal Reserve's policy trajectory illustrated this dynamic. After aggressive tightening in 2022-2023 pushed policy rates above 5%, the Fed began cutting rates in September 2025, implementing two consecutive 25-basis-point reductions. These cuts signaled a return to accommodative policy, increasing global liquidity and reducing real yields. Bitcoin responded positively, consolidating above $110,000 as capital rotated back into risk assets.
But the macro environment also highlighted Bitcoin's persistent correlation with risk assets, particularly technology stocks. As one analysis noted, "Bitcoin's correlation with broader equity markets such as the Nasdaq 100 and S&P 500 has increased notably." This correlation suggested Bitcoin might be less a hedge against traditional markets than a leveraged play on liquidity conditions affecting all risk assets.
Geopolitical dynamics added another dimension. Central banks purchased over 1,045 tons of gold in 2024, marking the third consecutive year above 1,000 tons. This buying, concentrated among developing nations seeking to reduce dollar dependence, drove gold to new all-time highs. Bitcoin, despite its decentralized and censorship-resistant properties, attracted relatively limited central bank interest.
The divergence reflected different institutional needs. Central banks require deep liquidity, price stability, and universal acceptance - qualities gold possesses after millennia of use. Bitcoin's volatility, uncertain regulatory status, and relatively shallow markets made it unsuitable for large-scale reserve diversification, despite its theoretical advantages.
Yet the U.S. government's policy shift created a potential inflection point. In March 2025, President Trump established a Strategic Bitcoin Reserve via executive order, consolidating approximately 198,000 BTC in federal holdings. While primarily symbolic, the move represented "the first time Bitcoin is formally recognized as a reserve asset of the United States government," according to S&P Global Ratings analysis.
This political validation could influence other nations. Multiple countries introduced bills allowing central banks to hold Bitcoin reserves, including Argentina, Brazil, Hong Kong, and Japan. Russia's parliament called for exploring Bitcoin as a hedge against sanctions. El Salvador continued accumulating BTC, holding over 6,100 coins worth approximately $550 million.
The broader monetary context suggested Bitcoin might be entering a transitional phase. The asset had proven its resilience as a store of value, surviving multiple crypto winters and regulatory crackdowns. Institutional infrastructure matured through ETFs, custody solutions, and corporate treasury adoption. Yet Bitcoin's role remained ambiguous - neither pure digital gold nor conventional risk asset, but something in between.
As the next monetary cycle takes shape, Bitcoin faces a critical juncture. Will it remain primarily a speculative asset correlated with technology stocks? Will it achieve true reserve status alongside gold? Or might it evolve into something different entirely - not just passive store of value but active financial infrastructure? The answer may lie in technological developments transforming Bitcoin from static asset to productive capital.
Infrastructure & Utility: From Passive Store to Active Asset
Bitcoin's monetary evolution depends critically on its technological capabilities. While the base layer prioritizes security and decentralization at the expense of transaction throughput and programmability, a new wave of infrastructure is transforming Bitcoin from passive store of value into dynamic, yield-generating asset.
Layer-2 solutions represent the primary technical innovation expanding Bitcoin's utility. These protocols process transactions off the main blockchain while anchoring security back to Bitcoin's base layer, dramatically increasing throughput and functionality without compromising Bitcoin's core conservative design.
The Lightning Network, launched in 2018, pioneered Bitcoin Layer-2 scaling. By establishing payment channels between users that settle net balances on-chain only when channels close, Lightning enables near-instant, low-cost transactions. As of mid-2025, the network secured between $400-500 million in BTC liquidity and powered real-world payment applications, particularly for cross-border remittances in emerging markets.
Lightning's infrastructure continued maturing through 2025. Key upgrades including splicing, Taproot integration, and Atomic Multi-Path Payments improved reliability and reduced friction. Major exchanges integrated Lightning support, while Coinbase partnered with infrastructure company Lightspark to enable Lightning payments directly from user accounts. Payment processor Strike expanded merchant adoption, demonstrating Lightning's viability for everyday commerce.
Yet Lightning's design optimizes for payments, not decentralized finance. Its smart contract capabilities remain minimal, suited for simple channel scripts rather than complex financial logic. This limitation created space for more ambitious Layer-2 projects bringing DeFi functionality to Bitcoin.
Stacks emerged as a leading smart contract platform for Bitcoin. Using a novel Proof of Transfer mechanism, Stacks anchors its blockchain to Bitcoin while enabling programmable applications. The 2024 Nakamoto upgrade introduced Bitcoin finality, ensuring Stacks transactions inherit Bitcoin-level security once confirmed on the base chain. This architecture supports DeFi protocols, NFTs, and programmable assets that would be impossible on Bitcoin's conservative base layer.
Rootstock (RSK) took a different approach, implementing Ethereum Virtual Machine compatibility as a Bitcoin sidechain. This allows developers to deploy Solidity smart contracts secured by Bitcoin miners, creating a bridge between Bitcoin's security and Ethereum's mature developer ecosystem. As of 2025, Rootstock hosted $245 million in total value locked across 20 decentralized applications.
Newer projects pushed Bitcoin scaling further. Bitlayer implemented BitVM, a "third generation Bitcoin bridge" using cryptographic challenge-response models rather than multisignature custodians. Starknet announced plans to become the first Layer-2 settling on both Bitcoin and Ethereum, positioning itself as a unifying execution layer. Botanix launched an EVM-compatible mainnet in 2025, while projects like Merlin Chain leveraged ZK-Rollup technology to compress transaction data.
These infrastructure developments enabled Bitcoin Finance (BTCFi) - decentralized financial services native to Bitcoin. BTCFi transforms Bitcoin from static asset into productive capital through lending, staking, derivatives, and yield generation.
The numbers illustrate explosive growth. According to DefiLlama data, BTCFi's total value locked skyrocketed from just $304 million in January 2024 to over $7 billion by December 2024 - a 22x increase in one year. By mid-2025, BTCFi TVL climbed to $8.6 billion, with combined market capitalization of BTCFi tokens exceeding $1.1 billion.
Bitcoin staking formed the foundation of BTCFi's growth. Babylon pioneered trustless Bitcoin staking, allowing BTC holders to secure Proof-of-Stake networks without wrapping tokens or surrendering custody. By mid-2025, over $5-6 billion in BTC was staked through Babylon, representing approximately 80% of total BTCFi TVL. This positioned Babylon as the dominant Bitcoin staking infrastructure, with PoS chains integrating it to inherit Bitcoin's economic weight.
Solv Protocol took a multi-chain approach to Bitcoin yield aggregation. Through its SolvBTC token - a native Bitcoin derivative pegged 1:1 to BTC - the platform unlocked idle Bitcoin across multiple blockchains. By mid-2025, Solv attracted around $2 billion in TVL, ranking among the top three BTCFi protocols. The platform offered diversified yield sources spanning staking rewards, node operations, and trading strategies, creating a "BTC balance treasure" allowing holders to earn returns while maintaining Bitcoin exposure.
Lending protocols brought capital efficiency to Bitcoin holders. Platforms like Maple Finance extended institutional credit, while retail-focused protocols enabled overcollateralized borrowing against BTC. In 2025, Maple expanded its institutional lending model to Bitcoin through partnership with Bitcoin Layer-2 network Core DAO, allowing institutions to earn returns while holding Bitcoin.
Yield-trading protocols added sophisticated financial tools. Pendle, with over $5.6 billion in TVL and $53.9 billion in trading volume as of 2025, allowed users to split yield-bearing tokens into Principal Tokens and Yield Tokens, enabling fixed-yield positions or speculation on yield fluctuations. Collaboration between Solv and Pendle enabled Bitcoin users to earn nearly 10% fixed annual percentage yield.
This infrastructure transformation fundamentally altered Bitcoin's function. Rather than simply storing value, Bitcoin could now generate value through productive deployment. Holders could earn staking rewards, provide liquidity to earn trading fees, lend assets to earn interest, or deploy sophisticated yield strategies - all while maintaining exposure to Bitcoin's price appreciation.
Institutional interest followed. Custody banks and fintechs explored Bitcoin yield products, with $175 million invested in BTCFi during the first half of 2025 across 32 venture capital rounds. Major financial institutions including Coinbase and JPMorgan moved into Bitcoin yield, validating BTCFi as a legitimate institutional market.
The implications extended beyond individual yield generation. As one analysis noted, "BTCFi represents a natural evolution for Bitcoin from a passive store of value to a productive financial asset." By bringing Bitcoin into the modern DeFi economy while maintaining its security and brand, BTCFi could unlock Bitcoin's massive capital and network effects for next-generation financial products.
Yet infrastructure development faced challenges. Bitcoin Layer-2s exhibited greater technical complexity than Ethereum Layer-2s, which share Ethereum's programming environment. Bitcoin solutions required learning different languages and architectures - Stacks used its Clarity language, Rootstock implemented separate EVM infrastructure, while projects like RGB employed unfamiliar client-side validation. This fragmentation complicated development and interoperability.
Security risks remained paramount. Smart contract vulnerabilities, bridge exploits, and custody failures plagued DeFi across chains. Bringing these risks to Bitcoin-native protocols required extreme caution. Surveys indicated that nearly 36% of potential users avoided BTCFi due to trust issues, while others cited security and liquidity concerns.
Nonetheless, the infrastructure trajectory appeared clear. Bitcoin was "outgrowing the 'digital gold' narrative," as Core DAO contributor Brendon Sedo observed. The question was no longer whether Bitcoin could support financial functionality, but how quickly that functionality would mature and scale. As infrastructure proliferated and institutional capital flowed in, Bitcoin's transformation from passive asset to active financial network accelerated.
Institutional & Reserve Dynamics: What's Changing in Finance
Bitcoin's institutional adoption in 2024-2025 marked a watershed moment, fundamentally altering the asset's market structure and legitimacy. The approval of spot Bitcoin ETFs, corporate treasury strategies, and emerging sovereign reserve discussions collectively represent a paradigm shift in how traditional finance views Bitcoin.
The January 2024 SEC approval of 11 spot Bitcoin ETFs catalyzed institutional adoption. These products provided regulated, familiar vehicles for accessing Bitcoin without navigating custody complexities or regulatory uncertainty. The impact proved immediate and dramatic.
BlackRock's iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT) attracted $50+ billion in assets under management within a year, representing "the most successful crypto ETF launch in history." Daily inflows approached $10 billion in early 2025, with total ETF inflows reaching $6.96 billion by mid-year. By Q2 2025, the collective spot Bitcoin ETF market held approximately $58-86 billion in assets, with institutions holding roughly 33% of total ETF shares.
These flows created structural demand distinct from retail speculation. Unlike individual investors buying Bitcoin directly, ETF flows represented institutional asset allocation decisions - pension funds, endowments, family offices, and registered investment advisors incorporating Bitcoin into diversified portfolios. A Coinbase/EY-Parthenon survey found that 83% of institutional investors planned to increase crypto allocations in 2025, with 59% intending to allocate over 5% of assets under management to digital assets.
The institutional infrastructure matured rapidly. Major custody providers including Fidelity Digital Assets and Coinbase Prime implemented sub-second transaction capabilities, reducing operational risk for institutional clients. Regulatory clarity improved as the SEC dropped lawsuits against exchanges like Coinbase and Gemini, while the OCC and FDIC confirmed in March 2025 that U.S. banks no longer needed advance permission to engage with cryptocurrency.
Corporate treasury adoption accelerated in parallel. By Q3 2025, 172 public companies held over one million BTC worth $117 billion, up 39% in company count and 21% in holdings from the previous quarter. This represented a fundamental shift from traditional treasury practices prioritizing cash and short-term securities.
MicroStrategy exemplified the treasury strategy. The company acquired 257,000 BTC in 2024 alone, establishing a $2+ billion Bitcoin treasury. By mid-2025, its holdings reached 628,946 BTC valued at approximately $73.6 billion. CEO Michael Saylor's thesis positioned Bitcoin as superior store of value compared to fiat, with the company raising capital through convertible bonds to purchase additional BTC.
The corporate adoption model extended beyond pure-play Bitcoin companies. Technology firms, pharmaceuticals, and diverse industries explored Bitcoin treasury allocations. Windtree Therapeutics allocated $520 million for cryptocurrency holdings, while Sharps Technology committed $400 million for asset acquisition, demonstrating diversification beyond Bitcoin to other cryptocurrencies.
The strategic rationale combined multiple factors. Bitcoin's fixed supply offered inflation hedging as global debt exploded. The asset provided portfolio diversification with low correlation to bonds and moderate correlation to equities. Companies with Bitcoin exposure experienced stock performance correlation with BTC price - MicroStrategy's 650% gain since early 2024 far exceeded Bitcoin's 160% rise, driven by market speculation on its Bitcoin holdings.
Access to capital markets enabled aggressive accumulation. Companies like MicroStrategy raised funds via convertible bonds at historically low interest rates, using proceeds to acquire Bitcoin at favorable prices. This created leveraged exposure - if Bitcoin appreciated, equity holders benefited disproportionately. The strategy attracted both Bitcoin advocates and traditional investors seeking crypto exposure through publicly traded equities.
Yet the model carried significant risks. Bitcoin's volatility created balance sheet fluctuations requiring accounting adjustments. Companies with high leverage faced insolvency risk if Bitcoin prices reversed sharply. Equity issuance diluted existing shareholders. MicroStrategy's market-to-net-asset-value ratio of 1.61 as of August 2025 indicated its stock traded at a 61% premium to underlying Bitcoin holdings, raising valuation concerns.
The institutional evolution extended to retirement accounts. Fidelity introduced Bitcoin ETF options in select 401(k) plans, while specialty providers like ForUsAll offered cryptocurrency investment options in multiple employer plans. Major administrators including Schwab and Vanguard evaluated inclusion of Bitcoin ETFs, though adoption remained gradual as fiduciaries navigated liability concerns.
Perhaps most significantly, sovereign reserve discussions gained traction. The U.S. Strategic Bitcoin Reserve, established in March 2025, held approximately 198,000 BTC. While modest relative to gold reserves, the symbolic recognition proved meaningful. Deutsche Bank projected Bitcoin could join gold on central bank balance sheets by 2030, emphasizing that volatility reduction and regulatory clarity were prerequisites.
Actual central bank adoption remained limited but emerging. El Salvador's 6,102 BTC holdings represented 28% of the small nation's GDP, demonstrating commitment despite Bitcoin volatility. The Czech National Bank governor floated allocating up to 5% of reserves into Bitcoin to diversify from dollars and euros. Ukraine's parliament introduced legislation instructing its central bank to hold Bitcoin alongside gold for post-war reconstruction.
Yet mainstream central banks remained skeptical. A February 2025 survey of economists by the University of Chicago found not a single respondent agreed that borrowing money to create strategic crypto reserves would benefit the economy or that holding crypto would lower risk in international reserve portfolios. Central banks continued favoring gold, which offered deeper liquidity, universal acceptance, and millennia-proven stability.
The institutional transformation nonetheless marked Bitcoin's transition from fringe asset to pillar of modern finance. ETF infrastructure, corporate treasury strategies, and sovereign reserve discussions collectively created what one analysis called "self-reinforcing cycle of scarcity and demand." With institutional investors controlling 18% of Bitcoin's supply and long-term holders increasing stakes by 10.4% year-over-year, effective circulating supply was shrinking even as demand expanded.
This institutional foundation distinguished the 2024-2025 cycle from previous speculative manias. Rather than retail FOMO driving parabolic rallies followed by crashes, sustained institutional accumulation created a structural price floor. As one observer noted, "Bitcoin's institutionalization is a tailwind that transcends market cycles." The question was whether this institutional adoption would ultimately validate Bitcoin as digital gold, or transform it into something more ambitious - a global reserve asset and financial infrastructure layer.
Comparative Asset Case: Bitcoin vs Gold vs Other Stores of Value
Understanding Bitcoin's evolving monetary role requires rigorous comparison with established stores of value, particularly gold. While the digital gold narrative drew obvious parallels, the divergence between these assets in 2024-2025 revealed fundamental differences in market positioning and institutional acceptance.
Gold's performance in 2025 surprised market participants. The precious metal surged more than 50% from January, reaching near-record highs above $3,900 per troy ounce by October 2025. This rally reflected sustained central bank buying, geopolitical uncertainty, and safe-haven demand amid U.S. fiscal concerns. By contrast, Bitcoin gained approximately 15% over the same period, underperforming dramatically despite institutional adoption narratives.
The divergence stemmed from different buyer profiles and motivations. Central banks, the marginal buyers driving gold higher, purchased 1,045 tons in 2024 - the third consecutive year exceeding 1,000 tons. This accumulation, concentrated among developing nations seeking to reduce dollar dependence, reflected gold's unique properties: universal acceptance, deep liquidity, millennia-proven stability, and absence of counterparty risk.
Bitcoin lacked these institutional credentials. While 13 nations held Bitcoin as of late 2024, most holdings resulted from law enforcement seizures rather than deliberate reserve strategy. Central banks require assets suitable for multi-billion-dollar positions with minimal market impact. Gold's daily trading volume exceeds $200 billion, dwarfing Bitcoin's liquidity. Gold reserves can be mobilized instantly through established swap lines and repo markets. Bitcoin's infrastructure, while maturing, cannot yet support central bank-scale operations.
Volatility constituted another critical distinction. Gold's 30-day volatility typically ranges 14-16%, providing relative stability suitable for reserve assets. Bitcoin's volatility, while declining, remained significantly higher. Deutsche Bank noted that Bitcoin's 30-day volatility hit historic lows in August 2025 even as prices exceeded $123,500, suggesting maturation toward lower volatility. Yet this still exceeded gold's stability, limiting Bitcoin's appeal for conservative reserve managers.
Supply dynamics revealed both convergence and divergence. Bitcoin's fixed 21 million supply cap provided absolute scarcity. After the April 2024 halving, Bitcoin's issuance rate fell below gold's long-term supply growth for the first time. This hard cap distinguishes Bitcoin from all physical commodities - gold deposits can be discovered, mining technology improved, or asteroids mined in the future. Bitcoin's supply remains cryptographically constrained.
Yet this advantage appeared theoretical rather than practical for most institutional buyers. Gold's 1-2% annual supply growth over centuries proved sufficient stability for reserve purposes. The marginal difference between gold's gradual inflation and Bitcoin's fixed supply mattered less than other factors like volatility, liquidity, and regulatory clarity.
Correlation analysis illuminated divergent market positioning. Research found that Bitcoin's correlation with the S&P 500 stood at just 12% since 2020, while gold showed 14% equity correlation. Both assets offered diversification benefits. However, Bitcoin's correlation with the Nasdaq reached 0.5-0.8 during 2025, significantly higher than gold's tech stock correlation. This suggested Bitcoin behaved more like a leveraged technology bet than a safe-haven asset during risk-off periods.
The macroeconomic sensitivity differed markedly. Fidelity Digital Assets research identified broad money supply measures (M2) as Bitcoin's highest correlation factor, with R-squared values indicating much of Bitcoin's price change could be explained by money supply fluctuations. Gold, by contrast, responded to different drivers - real yields, currency fluctuations, geopolitical risk premiums - creating complementary rather than substitutive dynamics.
This complementarity led Deutsche Bank to conclude that "Bitcoin and gold will continue to coexist as complementary hedges against inflation and geopolitical risk." Both assets offered scarcity and independence from traditional monetary systems, but served different institutional needs and market functions.
Real estate and other hard assets provided additional comparison points. Real estate offered yield through rental income but lacked portability and divisibility. Transaction costs and illiquidity made real estate unsuitable for rapid reallocation. Commodities like oil or agricultural products had utility value but lacked durability as stores of value. None provided Bitcoin's unique combination of digital portability, programmatic scarcity, and censorship resistance.
Yet these alternatives enjoyed regulatory clarity, established legal frameworks, and institutional familiarity Bitcoin still lacked. Real estate investment trusts (REITs) and commodity futures operated within well-understood regulatory regimes. Bitcoin's legal status remained fluid across jurisdictions, with some countries embracing it while others banned or restricted its use.
The investment case ultimately depended on time horizon and institutional constraints. For central banks requiring stable, liquid reserves deployable in crisis, gold remained superior. For corporations seeking portfolio diversification and inflation hedging with higher risk tolerance, Bitcoin offered attractive asymmetry. For individual investors comfortable with volatility, Bitcoin's upside potential exceeded gold's modest annual returns.
Long-term supply-demand dynamics favored Bitcoin theoretically. With institutional investors controlling 18% of supply and long-term holders steadily accumulating, effective circulating supply continued shrinking. If institutional adoption accelerated while supply remained fixed, price appreciation could eventually reduce volatility through higher market capitalization and liquidity depth.
This created potential for convergence over decades. As Bitcoin's market capitalization approached and potentially exceeded gold's $15+ trillion total value, volatility might compress toward gold's range. Regulatory frameworks would mature, institutional infrastructure would deepen, and psychological barriers would diminish. Under this scenario, Bitcoin could plausibly join gold as a recognized central bank reserve asset by the 2030s, as Deutsche Bank projected.
Yet critical uncertainties remained. Would regulatory frameworks harmonize globally or fragment further? Would quantum computing threaten Bitcoin's cryptographic security? Would superior cryptocurrency designs displace Bitcoin's network effects? Would central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) satisfy institutional demand for digital monetary alternatives? These questions suggested Bitcoin's ultimate role alongside gold remained far from predetermined.
Risks and Obstacles to the Next Phase
Bitcoin's transformation from speculative asset to monetary infrastructure faces formidable obstacles. Understanding these risks proves essential for realistic assessment of Bitcoin's potential evolution beyond digital gold.
Regulatory risk tops the list of challenges. While the U.S. political environment shifted favorably in 2024-2025, with the Trump administration establishing a Strategic Bitcoin Reserve and regulatory agencies adopting crypto-friendly stances, global regulatory fragmentation persists. China maintains its ban on cryptocurrency trading and mining. The European Union's MiCA framework provides clarity but imposes strict compliance requirements that strained smaller firms. Emerging markets exhibit wildly varying approaches, from El Salvador's Bitcoin adoption to India's restrictive stance.
This regulatory patchwork creates jurisdictional arbitrage opportunities but prevents Bitcoin from achieving the universal acceptance required for global reserve asset status. Central banks cannot hold reserves subject to seizure or ban in major jurisdictions. Cross-border capital flows face friction from incompatible compliance regimes. Financial institutions must navigate conflicting requirements across markets, limiting Bitcoin's integration into traditional finance.
The regulatory landscape could deteriorate rapidly. A major hack, consumer protection failure, or terrorist financing incident could trigger global crackdown. U.S. political winds could shift again, with future administrations reversing crypto-friendly policies. A February 2025 survey of economists found zero support for Bitcoin reserves among mainstream academics, suggesting intellectual resistance persists despite institutional adoption.
Environmental concerns constitute another significant obstacle. Bitcoin mining's energy consumption has drawn sustained criticism from environmental advocates, policymakers, and ESG-focused investors. While proponents argue Bitcoin mining increasingly uses renewable energy and can stabilize electricity grids by monetizing stranded energy, public perception remains negative.
Institutional investors face ESG mandates limiting exposure to carbon-intensive assets. European regulations require climate-related disclosures that could discourage Bitcoin holdings. If environmental opposition gains political traction, mining bans or carbon taxes could threaten Bitcoin's security model. China's 2021 mining ban demonstrated how quickly regulatory environments can shift, forcing hash rate migration despite Bitcoin's decentralized nature.
Technological scaling challenges persist despite Layer-2 progress. Bitcoin's base layer processes approximately 7-10 transactions per second, far below Visa's thousands of transactions per second throughput. While Lightning Network and other Layer-2s address this limitation, they introduce complexity, security assumptions, and user experience friction.
The fragmentation across Layer-2 solutions - Stacks, Rootstock, Lightning, Bitlayer, and others - created interoperability challenges. Developers must learn multiple architectures and languages. Users face confusing choices between platforms with different security models and trust assumptions. This fragmentation could prevent network effects from consolidating around Bitcoin, allowing competitors to offer superior user experiences.
Security risks extend beyond the base protocol. BTCFi protocols introduce smart contract vulnerabilities, bridge exploits, and custody risks. Nearly 36% of potential users avoid BTCFi due to trust concerns, while others cite security and liquidity worries. High-profile hacks or protocol failures could undermine institutional confidence in Bitcoin's productive capabilities, pushing institutions back toward passive holding strategies.
Competition from alternative assets threatens Bitcoin's market position. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) could satisfy institutional demand for digital monetary alternatives without Bitcoin's volatility or regulatory uncertainty. Over 130 countries explored CBDCs as of 2025, with China's digital yuan already deployed at scale. While CBDCs lack Bitcoin's decentralization and censorship resistance, they offer government backing, regulatory clarity, and payment system integration that Bitcoin cannot match.
Stablecoins present another competitive threat. Stablecoin payment volumes grew to $19.4 billion year-to-date in 2025, demonstrating demand for digital dollars. For payments and DeFi applications, stablecoins offer Bitcoin's digital properties without price volatility. The July 2025 GENIUS Act allowing banks to issue stablecoins under federal supervision could entrench dollar-denominated digital assets, reducing Bitcoin's utility for transactions.
Newer cryptocurrencies with superior technical capabilities could displace Bitcoin's network effects. Ethereum's transition to Proof-of-Stake reduced its energy consumption by 99%+, addressing Bitcoin's primary environmental criticism. Layer-1 blockchains like Solana offer drastically higher throughput. If institutional users prioritize functionality over Bitcoin's first-mover advantage and brand recognition, capital could rotate toward technically superior alternatives.
Market structure risks emerged from institutional adoption itself. ETFs concentrate Bitcoin holdings with regulated intermediaries, creating potential vulnerability to regulatory actions. The OCC or SEC could reverse policies allowing bank Bitcoin custody or ETF offerings. Exchange-traded funds do not immunize crypto from macro shocks, as evidenced by February 2025's record $3.54 billion monthly outflow from Bitcoin ETFs.
Corporate treasury concentration poses systemic risks. MicroStrategy's massive holdings create correlation between its equity performance and Bitcoin price. If the company faced financial distress requiring Bitcoin liquidation, the impact could cascade through markets. Over 172 companies now hold Bitcoin, creating interconnected risks if macro conditions force simultaneous selling.
Volatility remains Bitcoin's fundamental challenge for reserve asset status. Despite declining over time, Bitcoin's price swings still exceed 45-65% annually compared to gold's 14-16%. Central banks require stable reserves deployable in crises without triggering price disruptions. Bitcoin's volatility makes it unsuitable for large-scale reserve allocations absent dramatic volatility reduction.
Liquidity constraints could cap institutional adoption. While Bitcoin markets handle billions in daily volume, this remains small relative to foreign exchange or government bond markets. Large institutional orders risk significant market impact. Gold's multi-trillion-dollar market and established lending/repo infrastructure provide liquidity depth Bitcoin cannot yet match. Academic studies concluded Bitcoin remains "less stable and liquid than gold or government bonds, which makes it unsuitable for large allocations."
Quantum computing presents a long-term existential threat. Bitcoin's cryptographic security depends on the computational difficulty of factoring large numbers and solving discrete logarithm problems. Sufficiently powerful quantum computers could break these cryptographic schemes, allowing attackers to forge signatures or steal funds. While quantum threats remain theoretical and distant, their eventual emergence could require disruptive protocol changes or even render Bitcoin's security model obsolete.
The cumulative weight of these obstacles suggests Bitcoin's evolution is far from assured. Technological, regulatory, environmental, competitive, and market structure challenges could prevent Bitcoin from achieving reserve asset status or broad productive utility. Even optimistic scenarios require navigating a narrow path between competing risks and coordination challenges across global stakeholders.
What Comes Next: Scenarios for Bitcoin's Monetary Role
Bitcoin's future monetary role remains radically uncertain. Rather than offering false precision through price predictions, we can outline plausible scenarios based on key variables: institutional adoption trajectory, regulatory evolution, technological scaling, and macroeconomic conditions.
Scenario 1: Status Quo - Persistent Digital Gold
In this scenario, Bitcoin remains primarily a speculative store of value asset, maintaining its digital gold narrative without fundamental transformation. Institutional adoption plateaus at current levels, with Bitcoin ETFs providing sufficient access for investors seeking cryptocurrency exposure. Corporate treasuries hold modest allocations as portfolio diversifiers, but Bitcoin never achieves mainstream reserve status.
Regulatory frameworks stabilize without harmonizing globally, creating persistent jurisdictional friction. Central banks continue favoring gold and fiat reserves, viewing Bitcoin as too volatile and insufficiently liquid for large-scale adoption. BTCFi infrastructure matures modestly but remains niche, with most holders maintaining passive positions.
Bitcoin's correlation with technology stocks persists, cementing its position as a high-beta risk asset rather than safe-haven store of value. Prices exhibit continued volatility, cycling between speculative manias and corrections without achieving the stability required for monetary system integration. Market capitalization grows gradually but never approaches gold's multi-trillion-dollar dominance.
Under this scenario, Bitcoin succeeds as a digital commodity and speculative investment but fails to transcend its niche. The "digital gold" narrative proves both Bitcoin's strength and its limitation - providing a compelling story for individual investors but insufficient legitimacy for institutional monetary infrastructure.
Key indicators to monitor:
- ETF inflows stabilizing or declining after initial enthusiasm
- Central bank Bitcoin holdings remaining below 1% of reserves
- BTCFi TVL growth decelerating
- Bitcoin correlation with Nasdaq remaining above 0.5
- Annual volatility persisting above 40%
Scenario 2: Evolved Role - Productive Capital Network
The second scenario envisions Bitcoin's transformation into productive financial infrastructure, moving beyond passive store of value toward yield-generating, utility-rich monetary network. BTCFi adoption accelerates dramatically, with total value locked reaching $50-100 billion by 2027-2028 as infrastructure matures and institutional products proliferate.
Layer-2 scaling solutions achieve technical breakthroughs, delivering seamless user experiences rivaling traditional finance while maintaining Bitcoin's security guarantees. Lightning Network processes hundreds of millions of transactions, Stacks and Rootstock support sophisticated DeFi protocols, and interoperability between Layer-2s improves dramatically.
Corporate treasuries increasingly treat Bitcoin not as passive reserves but as productive capital. Rather than simply holding BTC, companies deploy Bitcoin into yield strategies, lending protocols, and liquidity provision. Institutional yield products proliferate, with major financial institutions offering Bitcoin-based structured products, derivatives, and income-generating accounts.
Regulatory clarity improves in major jurisdictions, with harmonized frameworks providing legal certainty for Bitcoin custody, lending, and derivatives. The U.S., European Union, and select Asian markets establish clear rules enabling institutional participation while maintaining compliance standards.
Bitcoin's market capitalization expands toward $3-5 trillion by 2030, driven by sustained institutional accumulation and productive use cases. Volatility compresses toward 20-30% annually as market depth increases and speculative dynamics moderate. Bitcoin maintains higher volatility than gold but achieves sufficient stability for diversified reserve allocations.
A minority of progressive central banks begin experimental Bitcoin allocations, typically 1-3% of reserves. Countries facing sanctions, capital controls, or currency instability adopt Bitcoin more aggressively. While Bitcoin doesn't replace gold, it establishes a complementary role as digital reserve asset for a multipolar monetary system.
Key indicators to monitor:
- BTCFi TVL exceeding $50 billion by 2028
- Major banks offering Bitcoin custody and yield products
- 3+ central banks holding Bitcoin as deliberate reserve strategy
- Bitcoin volatility falling below 30% annually
- Lightning Network processing 100+ million transactions monthly
Scenario 3: Displaced Role - Competitive Disruption
The third scenario considers Bitcoin failing to evolve successfully, with competitive alternatives or technological limitations preventing its ascent beyond speculative asset. Newer cryptocurrencies with superior scaling, lower energy consumption, and better user experience capture institutional adoption flows.
Central Bank Digital Currencies gain overwhelming traction, with major economies deploying CBDCs that satisfy demand for digital money without Bitcoin's volatility or regulatory ambiguity. Payment networks integrate CBDCs seamlessly, while capital controls and surveillance capabilities allow governments to discourage Bitcoin usage.
Stablecoins dominate crypto-based DeFi, with dollar-denominated tokens providing Bitcoin's digital properties without price volatility. The GENIUS Act's stablecoin framework creates regulated digital dollar infrastructure that marginalizes Bitcoin for payment use cases.
BTCFi fails to achieve sustainable product-market fit. Security incidents, smart contract failures, or user experience friction prevent mass adoption. Institutional investors conclude Bitcoin's productive capabilities don't justify additional complexity and risk compared to passive ETF holdings.
Regulatory environments fragment further or turn hostile. Environmental concerns gain political momentum, leading to mining restrictions or carbon taxes in key jurisdictions. The U.S. reverses crypto-friendly policies in response to financial stability concerns or political shifts.
Bitcoin's correlation with technology stocks strengthens, making it increasingly redundant with existing equity exposure. During major market downturns, Bitcoin fails to demonstrate safe-haven properties, undermining the digital gold narrative. Institutional enthusiasm wanes as Bitcoin proves neither effective inflation hedge nor uncorrelated portfolio diversifier.
Key indicators to monitor:
- BTCFi TVL stagnating or declining
- Major regulatory reversals in U.S. or Europe
- Central banks explicitly rejecting Bitcoin reserves
- Competing cryptocurrencies capturing >30% of institutional flows
- Bitcoin correlation with Nasdaq exceeding 0.7 persistently
Scenario 4: Transformational Integration - Global Reserve Asset
The most ambitious scenario envisions Bitcoin achieving true global reserve asset status, joining gold as accepted component of central bank reserves and international monetary architecture. This requires confluent developments across technology, regulation, institutions, and geopolitics.
Layer-2 solutions achieve dramatic scaling breakthroughs, enabling Bitcoin to process transaction volumes comparable to traditional payment networks while maintaining decentralization and security. User experience improvements make Bitcoin-based financial services indistinguishable from conventional banking, removing adoption barriers.
Regulatory frameworks harmonize globally through international cooperation, establishing clear standards for Bitcoin custody, taxation, and reporting. G20 nations negotiate multilateral agreements treating Bitcoin as legitimate reserve asset, removing legal uncertainties.
Geopolitical dynamics accelerate Bitcoin adoption. Dollar weaponization concerns drive de-dollarization initiatives, with emerging economies seeking neutral reserve alternatives. Bitcoin's political neutrality and censorship resistance make it attractive for countries excluded from Western financial systems. Multiple nations establish Strategic Bitcoin Reserves, creating competitive pressure for others to follow.
Institutional adoption reaches critical mass. Pension funds, endowments, and sovereign wealth funds allocate 5-10% of portfolios to Bitcoin. Corporate treasuries routinely hold Bitcoin as strategic reserves. Bitcoin ETFs become standard portfolio components, with $500+ billion in assets under management.
Bitcoin's market capitalization exceeds $10 trillion by 2030-2032, approaching half of gold's total value. This scale dramatically reduces volatility, with annual price fluctuations compressing toward 15-20% - still higher than gold but acceptable for diversified reserve allocations.
Central banks of major economies hold Bitcoin representing 2-5% of reserves, recognizing it as legitimate diversification tool. The IMF considers including Bitcoin in Special Drawing Rights baskets, providing multilateral legitimization. International monetary system evolves toward tripartite structure: dollar hegemony weakens, gold maintains traditional role, Bitcoin emerges as digital-native neutral reserve.
Key indicators to monitor:
- 10+ nations holding Bitcoin as official reserves
- IMF formal recognition of Bitcoin in global reserve system
- Bitcoin market cap exceeding $10 trillion
- Annual volatility below 20%
- BTCFi TVL exceeding $200 billion
- Regulatory harmonization across G20 nations
The probability and timeline for each scenario depends on variables beyond prediction. Regulatory decisions, technological breakthroughs, macroeconomic shocks, and competitive developments could rapidly shift trajectories. The most likely outcome may involve hybrid elements - Bitcoin achieving modest institutional adoption and productive utility without full reserve status, creating a new asset class distinct from both traditional safe havens and conventional risk assets.
Conclusion
Bitcoin's monetary narrative is undergoing fundamental transformation. The "digital gold" framework that dominated the past decade - positioning Bitcoin as scarce store of value analogous to precious metals - captured important truths about the asset's scarcity and decentralization. Yet this framing increasingly appears incomplete, if not constraining.
The divergence between Bitcoin and gold in 2025 crystallized this evolution. While gold surged 50%+ on central bank buying and safe-haven demand, Bitcoin's 15% gain and persistent correlation with technology stocks revealed an asset still finding its place in the global monetary order. Bitcoin behaved less like digital gold and more like a high-beta liquidity-sensitive asset, responding to the same macroeconomic forces driving risk appetite across markets.
Yet beneath this surface volatility, profound structural changes were accelerating. Layer-2 infrastructure transformed Bitcoin from passive store to active financial network. BTCFi protocols enabled yield generation, lending, derivatives, and sophisticated financial operations impossible on Bitcoin's conservative base layer. Total value locked expanded 22x in a single year, demonstrating explosive demand for productive Bitcoin deployment.
Institutional adoption achieved critical mass through spot ETF approvals and corporate treasury strategies. BlackRock's iShares Bitcoin Trust accumulated $50+ billion in assets, while corporations held over one million BTC worth $117+ billion. These flows created structural demand distinct from retail speculation, potentially establishing a durable price floor beneath Bitcoin's volatility.
Most significantly, sovereign reserve discussions moved from theoretical to practical consideration. The U.S. Strategic Bitcoin Reserve, Deutsche Bank's projection of Bitcoin on central bank balance sheets by 2030, and multiple nations exploring official holdings collectively represented Bitcoin's emergence from fringe asset toward legitimate monetary consideration.
Yet formidable obstacles remain. Regulatory fragmentation, environmental concerns, technological scaling challenges, competitive threats from CBDCs and stablecoins, and persistent volatility all threaten Bitcoin's ascent. Central banks continue overwhelmingly favoring gold, recognizing Bitcoin lacks the liquidity depth, price stability, and institutional frameworks required for large-scale reserve allocation.
The critical question is not whether Bitcoin will exactly replicate gold's monetary role, but whether it will carve out its own distinct function in a transforming global monetary system. The scenarios outlined above - from persistent niche asset to transformational global reserve - represent plausible trajectories rather than predictions.
What appears increasingly clear is that Bitcoin's story is shifting. Being "digital gold" may prove the beginning of Bitcoin's monetary evolution, not its culmination. The asset's technological capabilities exceed gold's passive storage function. Its decentralization offers properties no central bank digital currency can match. Its programmatic scarcity provides inflation hedging that no fiat currency can deliver.
As the next monetary cycle takes shape - characterized by ballooning sovereign debt, declining dollar hegemony, technological transformation of finance, and search for neutral reserve assets - Bitcoin's unique properties may position it to play a role that transcends simple analogies to gold or conventional assets.
For investors and policymakers, the implications are profound. Bitcoin may be transitioning from speculative asset class to architectural component of a new monetary system. Whether that transition succeeds depends on technological scaling, regulatory evolution, institutional adoption, and macroeconomic forces that remain in flux.
The digital gold narrative served Bitcoin well, providing an accessible framework for understanding its value proposition. But as Bitcoin's infrastructure matures, its productive capabilities expand, and its institutional integration deepens, a more complex and ambitious story is emerging. What comes after "digital gold" may be something the existing monetary lexicon cannot yet adequately describe - a programmatically scarce, censorship-resistant, yield-generating financial network that becomes foundational infrastructure for the digital economy.
The next five years will prove critical. Bitcoin stands at an inflection point, with infrastructure, regulation, and adoption either converging to create new monetary paradigm or fragmenting into failed promise. Monitoring the indicators outlined above - BTCFi growth, central bank holdings, volatility trends, regulatory developments, competitive dynamics - will illuminate which scenario is unfolding.
As the architecture of value shifts toward digital natives, Bitcoin's evolution beyond "digital gold" may define whether decentralized monetary alternatives can coexist with, complement, or ultimately challenge state-sponsored money. That evolution, still in its early chapters, represents one of the most consequential financial transformations of the 21st century.



