The SEC suspended trading in QMMM Holdings after shares surged nearly 2,000 percent following a questionable $100 million crypto allocation announcement - marking the most dramatic intervention yet in a regulatory crackdown examining over 200 publicly traded companies pursuing similar strategies.
This case crystallizes mounting tensions as corporate cryptocurrency treasuries balloon past $112 billion while regulators intensify scrutiny of social media-driven stock manipulation that threatens investor protection. The suspension signals that while corporate crypto adoption continues accelerating - with holdings now exceeding one million Bitcoin - the path forward demands stricter governance, transparency, and compliance, fundamentally reshaping how companies can legitimately integrate digital assets into balance sheets.
QMMM's spectacular rise from under twelve dollars in early September to an intraday peak of $303 on announcement day exemplifies the dangerous intersection between crypto hype and vulnerable micro-cap stocks. The company, a Hong Kong-based digital advertising firm with just $2.7 million in annual revenue and persistent losses, announced plans to allocate $100 million to Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Solana despite holding only $498,000 in cash.
The SEC explicitly cited "potential manipulation effectuated through recommendations made to investors by unknown persons via social media" designed to artificially inflate price and volume. What makes this case particularly significant is its timing: the suspension came amid Wall Street Journal revelations that regulators were investigating suspicious trading patterns across hundreds of companies that pivoted to crypto treasury strategies in 2025, with many experiencing abnormal volume spikes and price surges before public announcements.
In this article we examine the most comprehensive regulatory examination of the corporate crypto phenomenon since MicroStrategy pioneered the Bitcoin treasury model in 2020, raising fundamental questions about whether SEC interventions will discourage corporate digital asset adoption or force healthier, more compliant practices that ultimately legitimize the strategy.
How the SEC wields suspension authority to protect markets
The Securities and Exchange Commission derives its trading suspension power from Section 12(k) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, which authorizes the agency to halt trading for up to ten business days when necessary to protect investors and the public interest. This authority requires no advance warning, no hearing, and imposes no burden of proof beyond identifying potential manipulation or inadequate public information. The suspension itself does not constitute a finding of wrongdoing, but rather creates a cooling-off period during which regulators investigate suspicious activity and investors reassess positions without the pressure of rapidly moving markets.
The legal threshold for suspension is deliberately low. The SEC need only cite concerns about "accuracy of publicly available information" or potential manipulation to freeze trading immediately. During the suspension period, affected companies cannot trade on any exchange or over-the-counter market, effectively locking shareholders into positions while regulatory examination proceeds. After the suspension expires, companies face significant challenges: trading typically resumes on less liquid OTC markets with severely depressed valuations, institutional investors often exit entirely, and the stigma of suspension creates lasting reputational damage regardless of whether formal charges follow.
Historical precedent shows the SEC has wielded this authority increasingly against crypto-related stock promotions. The Long Island Iced Tea case from 2017 established the template: a struggling beverage company announced a pivot to blockchain technology and name change to Long Blockchain Corp, triggering a 380 percent single-day surge despite having no actual blockchain operations. The stock soared from $2.45 to $9.49 as retail investors piled in based purely on the blockchain association. The SEC suspended trading in February 2018, and subsequent investigation revealed insider trading by executives who tipped associates before the announcement. The company was eventually delisted, its registration revoked, and three individuals faced criminal charges including securities fraud. By July 2021, the SEC charged that company leadership made "a series of public statements designed to mislead investors and take advantage of general investor interest in bitcoin and blockchain technology."
Similar patterns emerged with Riot Blockchain, formerly Bioptix, a biotech company that saw shares jump 400 percent after announcing a blockchain pivot in October 2017. On-line Plc, a British firm, gained 394 percent simply by adding "blockchain" to its corporate name. In each case, the fundamental business remained unchanged while the crypto association alone drove speculative frenzy. These precedents informed the SEC's approach to QMMM: a micro-cap company with declining core operations suddenly announcing a crypto allocation far exceeding its cash position, accompanied by extraordinary social media promotion and parabolic price action.
The SEC's enforcement playbook for crypto-related manipulation evolved significantly under Chair Gary Gensler's tenure from April 2021 through January 2025. During this period, the agency initiated 125 cryptocurrency-related enforcement actions, resolving 98 cases with $6.05 billion in penalties - nearly four times the amount collected under prior leadership. Gensler's approach emphasized treating most crypto assets as securities subject to existing regulations rather than creating new frameworks. This enforcement-first strategy generated significant industry friction but established that crypto exposure does not exempt companies from traditional securities laws.
The transition to Chair Paul Atkins in January 2025 signaled a philosophical shift toward innovation-focused regulation, with Commissioner Hester Peirce leading a new Crypto Task Force to expedite clearer rulemaking. However, the QMMM suspension and broader investigation demonstrate that enforcement against fraud and manipulation continues unabated regardless of broader policy evolution. Securities lawyer commentary emphasizes this distinction: while regulators may create clearer pathways for legitimate crypto adoption, they simultaneously intensify scrutiny of schemes exploiting crypto narratives to manipulate stock prices.
The anatomy of QMMM's spectacular rise and suspicious fall
QMMM Holdings Limited went public on Nasdaq in July 2024 through an initial public offering that raised $8.6 million at four dollars per share. The company, incorporated in the Cayman Islands with principal operations in Hong Kong, operated for eighteen years as ManyMany Creations, providing digital advertising, virtual avatar technology, and projection mapping services to luxury brands, real estate developers, and theme parks. Despite its established niche, financial performance deteriorated: fiscal 2024 revenue declined to $2.7 million while net losses widened to $1.58 million. By early 2025, the company faced Nasdaq minimum bid price deficiency notices, placing it at risk of delisting.
On September 9, 2025, QMMM announced via GlobeNewswire its "strategic entry into the cryptocurrency sector," detailing plans to establish a $100 million diversified cryptocurrency treasury targeting Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Solana. The press release described ambitions to develop AI-powered crypto analytics platforms, decentralized data marketplaces, DAO treasury management agents, and smart contract vulnerability detection tools. CEO Bun Kwai proclaimed that "global adoption of digital assets and blockchain technology is accelerating at an unprecedented pace" and positioned the move as bridging "the digital economy with real-world applications."
The market reaction was immediate and extreme. QMMM shares opened September 9 at eleven dollars, surged to an intraday peak of $303, and closed at $207 - a single-day gain between 1,737 and 2,144 percent depending on calculation method. Trading volume exploded by over 1,000 percent as the stock's market capitalization ballooned from approximately $141 million to $11.84 billion at the closing price. Circuit breakers triggered multiple times as volatility halts paused trading four times over the following week. By September 27, the stock had pulled back to $119.40 but remained up approximately 1,736 percent from its early-month baseline.
Critical analysis revealed glaring inconsistencies between the announcement and financial reality. QMMM's fiscal 2024 financial statements showed only $497,993 in cash and cash equivalents. The company provided no explanation for how it would fund a $100 million allocation - a sum representing 200 times its available cash and 37 times its annual revenue. In June 2025, QMMM had conducted a desperate secondary offering at twenty cents per share, raising $8 million but severely diluting shareholders by nearly quadrupling share count. This reflected a company struggling for survival, not one positioned to deploy nine-figure cryptocurrency investments.
The social media environment surrounding QMMM's surge exhibited classic pump-and-dump characteristics. Reddit threads celebrated QMMM as a "sleeper bet poised to ride the next crypto wave." Twitter activity spiked with promotional posts emphasizing the crypto pivot while ignoring fundamental business weakness. StockTwits sentiment remained "extremely bullish" even during price declines, with message volume up "thousands of percent." Some users warned of manipulation - one StockTwits contributor explicitly called it a "pump and dump scam" likely to crash to thirty dollars - but these cautions were drowned out by promotional fervor.
The SEC's September 29 suspension order specifically cited "potential manipulation in the securities of QMMM effectuated through recommendations, made to investors by unknown persons via social media to purchase the securities of QMMM, which appear to be designed to artificially inflate the price and volume." The language emphasizes three critical elements: the recommendations came from "unknown persons" rather than identifiable market participants, they utilized social media platforms for broad reach, and they appeared designed for artificial inflation rather than reflecting genuine investment analysis. Securities lawyer Carl Capolingua noted that "if the SEC can link those unknown persons responsible for promoting buying the company's stock back to employees, or worse, to management, then the penalties can be severe, including large fines or jail time."
The trading suspension runs through October 10, 2025, providing regulators ten business days to investigate the identity of promoters, examine trading records for coordination, and determine whether company insiders participated in or benefited from the manipulation. When trading resumes, QMMM faces an uncertain future: the company must address how it actually plans to fund crypto purchases, explain the timing and sources of promotional activity, and convince investors that legitimate business strategy rather than stock promotion motivated the announcement. Historical precedent suggests few companies recover from such suspensions.
The explosive growth of corporate cryptocurrency treasuries
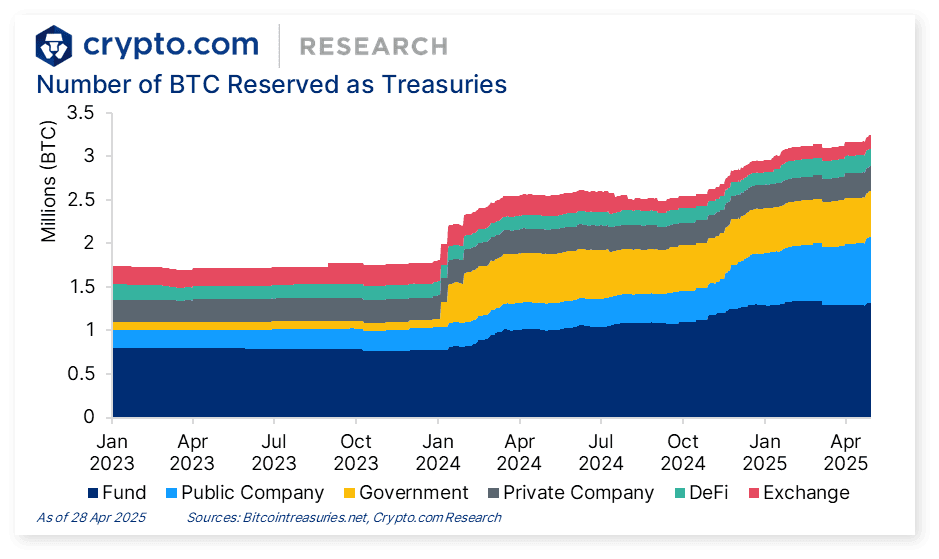
Nearly 200 publicly traded companies now hold over $112 billion in cryptocurrency assets as of September 2025, representing one of the most dramatic shifts in corporate treasury management in modern financial history. This movement began modestly in August 2020 when MicroStrategy, a business intelligence software company, purchased $250 million worth of Bitcoin as a treasury reserve asset. CEO Michael Saylor articulated a thesis that Bitcoin represented "superior money" and a better store of value than cash, which faced debasement through monetary expansion and negative real interest rates.
MicroStrategy's bet proved spectacularly successful. The company continued accumulating Bitcoin through equity offerings, convertible notes, and cash flow, amassing between 632,000 and 640,000 BTC by September 2025 - holdings worth approximately $73 billion at current prices. The company formally rebranded as "Strategy" in February 2025, signaling its identity shift from software firm to Bitcoin treasury company. Strategy's stock price surged 2,919 percent from August 2020 through September 2025, dramatically outperforming major technology stocks including Nvidia, Tesla, and Microsoft over the same period. The company now holds approximately three percent of Bitcoin's 21 million total supply and trades at a 112 percent premium to its Bitcoin net asset value, reflecting investor willingness to pay substantial premiums for leveraged Bitcoin exposure through public equities.
Corporate Bitcoin holdings across all publicly traded companies now exceed 1 million BTC, representing approximately 4.7 percent of total supply and valued between $115 and $120 billion. The concentration remains extreme: Strategy alone accounts for over 60 percent of the top ten corporate holders. Marathon Digital Holdings, a Bitcoin mining company that accumulates production rather than selling immediately, holds approximately 52,000 BTC worth $6 billion. Tesla maintains 11,509 BTC valued at $1.24 billion after selling 75 percent of its holdings during the 2022 bear market - a decision that cost the company approximately $3.5 billion in foregone gains had it maintained its full position.
The corporate Bitcoin adoption trajectory accelerated dramatically in 2024 and 2025. Only 64 public companies held Bitcoin at the start of 2024, a figure that grew to 79 by Q1 2025 and exploded past 200 by September 2025. This 166 percent year-over-year growth rate reflects both genuine strategic adoption by established companies and opportunistic pivots by struggling firms seeking stock price appreciation. Bernstein Private Wealth Management projects that public companies globally could allocate as much as $330 billion to Bitcoin over the next five years, suggesting the trend remains in early stages despite recent growth.
Beyond Bitcoin, corporate Ethereum holdings have surged past $10 billion across approximately 13 publicly traded companies. BitMine Immersion Technologies leads with 2.4 million ETH worth approximately $10 billion, aiming to acquire five percent of total Ethereum supply. SharpLink Gaming, led by Ethereum co-founder Joseph Lubin as chairman, holds between 361,000 and 839,000 ETH valued at $1.3 to $3.4 billion. The company stakes 95 percent of holdings to generate yield and is building Ethereum-powered stablecoin payment systems for its iGaming platforms. Bit Digital pivoted entirely from Bitcoin to Ethereum, selling its entire BTC treasury and raising $172 million to purchase 120,000 ETH, positioning itself as a pure-play Ethereum treasury company.
Solana represents the newest frontier for corporate treasuries, with total holdings exceeding $2.5 billion across eight major public companies. Forward Industries raised $1.65 billion to acquire 6.8 million SOL, backed by Galaxy Digital, Jump Crypto, and Multicoin Capital. Upexi accumulated 1.9 million SOL over four months in 2025 with strategic advice from BitMEX founder Arthur Hayes, staking holdings for seven to eight percent annual yield. SOL Strategies operates Solana validators with assets under delegation of 3.6 million SOL, generating dual revenue from treasury appreciation and validator operations.
The diversity of companies adopting crypto treasuries has expanded well beyond technology firms. Semler Scientific, a medical device company, holds 4,449 BTC worth $510 million. GameStop, the video game retailer that became a 2021 meme stock phenomenon, announced in May 2025 it had acquired 4,710 BTC. Allied Gaming & Entertainment saw shares surge 105 percent intraday after announcing a Bitcoin and Ethereum treasury strategy. Even healthcare company MEI Pharma announced crypto purchases, though regulators flagged unusual call option activity before the public disclosure.
However, not all corporate crypto strategies succeed. Tesla's sale of 75 percent of its Bitcoin holdings in Q2 2022, near the bear market bottom, exemplifies the risk of panic selling during volatility. The company sold approximately $936 million worth of Bitcoin at prices between $20,000 and $30,000 per coin - holdings that would be worth roughly $5 billion at current prices. Some 2025 crypto treasury adopters now trade below their Bitcoin net asset value, with 25 percent of public Bitcoin holders experiencing market capitalizations less than the value of their crypto holdings alone. This negative premium suggests investor skepticism about management's ability to create value beyond simply holding cryptocurrency.
The stock market reaction to crypto treasury announcements has become remarkably predictable yet increasingly scrutinized. Animoca Brands research found that companies announcing crypto treasury strategies surged an average of 150 percent within 24 hours of disclosure in 2025. Brera Holdings skyrocketed 464 percent after announcing plans to rebrand as Solmate and transition to a Solana-based digital asset treasury. Allied Gaming surged 105 percent intraday on its Bitcoin-Ethereum announcement. However, Smart Digital Group crashed 87 percent in a single day after its crypto announcement met with investor skepticism about vague details and questionable execution, demonstrating that markets can distinguish between credible strategies and opportunistic pivots.
Social media amplification and the mechanics of market hype
Social media platforms have fundamentally transformed how stock manipulation operates, replacing traditional "boiler room" operations with viral promotion campaigns that reach millions of potential investors within minutes at minimal cost. Academic research published in Technological Forecasting and Social Change documented that publicly traded companies announcing blockchain initiatives experience substantial stock price premiums and sustained volatility increases, with the largest gains coming from highly speculative motives like coin creation and corporate name changes rather than substantive business integration.
The Long Island Iced Tea to Long Blockchain case from 2017 established the template. When the beverage company announced its blockchain pivot and name change on December 21, 2017, shares jumped 289 percent to 380 percent despite the company having no blockchain operations, expertise, or revenue. The announcement itself - containing only vague references to "evaluating potential opportunities" - sufficed to trigger explosive retail investor interest. Subsequent SEC investigation revealed that leading shareholder Eric Watson tipped off broker Oliver Barret-Lindsay about the impending announcement, who then tipped friend Gannon Giguiere. Giguiere purchased 35,000 shares and sold within two hours of the public announcement, realizing $160,000 in illicit profits from a textbook insider trading scheme.
Reddit's WallStreetBets community, which exploded from obscurity to 13.3 million members by end of 2022, demonstrated the power of coordinated social media trading. While the community's GameStop short squeeze in January 2021 involved legitimate market dynamics exploiting over-leveraged institutional positions, the tactics popularized there - "diamond hands" culture encouraging holding stocks regardless of fundamentals, detailed "due diligence" posts mixing analysis with hype, and meme-driven promotion creating in-group identity - became templates for manipulation. Similar communities emerged focused specifically on crypto-related stocks, promoting QMMM and similar companies as vehicles for capturing crypto upside through equity markets.
Twitter and X serve as primary amplification channels for stock promotion. Research from USC's Information Sciences Institute tracked crypto pump-and-dump operations by detecting coordinated tweeting activity with direct correlation to cryptocurrency price movements. Machine learning algorithms identified clusters of accounts communicating with each other and posting identical promotional content within narrow timeframes. Academic research published in International Review of Financial Analysis found that Twitter effectively garners attention for pump-and-dump schemes, with notable effects on abnormal returns before pump events. Critically, investors relying on Twitter exhibited delayed selling behavior during post-dump phases, resulting in significant losses compared to other participants who recognized manipulation patterns.
Telegram and Discord enable even more sophisticated coordination through private groups with thousands of members. The CFTC's 2018 customer advisory documented typical pump-and-dump countdown messaging: "15 mins left before the pump! Get ready to buy," followed by "5 minutes till pump, next message will be the coin!" Instructions to "Tweet about us" amplified reach beyond the private groups to broader audiences. These operations complete entire pump-and-dump cycles in as little as eight minutes, exploiting thin liquidity in low-cap cryptocurrencies and stocks.
The SEC's December 2022 charges against eight social media influencers illustrated the scale and sophistication of these schemes. The defendants cultivated a combined 1.5 million followers on Twitter and Discord, promoting themselves as successful traders with market expertise. They purchased stocks before publicly recommending them to followers, posted price targets and statements like "buying, holding, adding," then sold shares when follower demand drove prices up - all without disclosing their dump plans. When accused of dumping, one defendant explicitly stated "I don't dump on anyone... I have diamond hands" while simultaneously selling. The scheme generated approximately $100 million in fraudulent profits over two years.
The mechanics of exploiting thin liquidity in micro-cap and penny stocks are well-documented. Stocks with market capitalizations below $50 million and those trading under five dollars per share feature low trading volumes, making price manipulation relatively inexpensive. A coordinated buying campaign by a few hundred or thousand retail investors can drive prices up 100 to 300 percent in hours. Manipulators employ sophisticated tactics including bid support to create artificial price floors, coordinated trading across multiple accounts to simulate broader market interest, and strategic selling that gradually dumps positions without triggering panic.
Chinese experimental research published in International Review of Economics and Finance provided causal evidence by posting 20,000 messages with strong sentiment but no fundamental information on the EastMoney Guba forum for 100 CSI 300 stocks. The posted messages led to a 0.26 percent rise in same-day stock returns, demonstrating that "stock prices can be manipulated by simply posting messages without any fundamental information." The effect was driven primarily by positive sentiment messages, and the study concluded that markets with high retail investor participation are particularly vulnerable.
Academic research comparing social media coverage to traditional news media coverage found opposite effects on stock volatility: news media coverage predicted decreases in subsequent volatility and turnover, while social media coverage predicted increases in both metrics. This pattern aligns with an "echo chamber" model where social media repeats existing news but a subset of traders interpret these repetitions as new information, generating excessive trading activity and volatility disconnected from fundamental developments.
For QMMM specifically, the social media environment exhibited all the classic manipulation red flags. Promotional posts emphasized the crypto narrative while ignoring the massive disconnect between announced allocation size and available capital. Message volume spiked thousands of percent on StockTwits concurrent with the price surge. Reddit discussions celebrated QMMM as a hidden opportunity despite the company's tiny revenue base and persistent losses. Twitter activity focused on price targets and momentum rather than business analysis. The SEC's identification of "unknown persons" making recommendations via social media suggests a coordinated campaign rather than organic investor interest - precisely the pattern that triggers regulatory intervention.
Regulatory crackdown and the debate over chilling effects

The QMMM suspension represents just one data point in a much broader regulatory investigation that threatens to reshape corporate crypto adoption. On September 26, 2025, the Wall Street Journal revealed that the SEC and FINRA were examining over 200 companies that announced crypto treasury strategies in 2025, investigating unusual trading patterns before announcements, abnormally high trading volumes, sharp price increases preceding public disclosures, and potential violations of Regulation Fair Disclosure. This probe represents the most comprehensive regulatory examination of the corporate crypto phenomenon since its emergence in 2020.
Regulation Fair Disclosure, or Reg FD, prohibits companies from selectively disclosing material nonpublic information to certain investors who could trade on it before public announcement. The pattern regulators identified across numerous 2025 crypto treasury companies showed suspicious activity: stocks doubling or tripling in the days before public crypto announcements, unusual option activity with heavy call buying, and "clustered trading" suggesting coordinated purchases based on leaked information. This pattern implies either insider trading by company executives and their associates or strategic leaking of announcement details to preferred investors.
Several specific cases demonstrate the pattern. SharpLink Gaming's stock jumped 433 percent on heavy volume before its May 28, 2025 Ethereum treasury announcement. MEI Pharma shares nearly doubled in the four days before its Litecoin purchase disclosure, accompanied by unusual call option activity. Mill City Ventures, Kindly MD, and Empery Digital all experienced significant pre-announcement spikes flagged by surveillance systems. Trump Media & Technology Group saw volatility before its May 27 disclosure of a $2 billion Bitcoin commitment, drawing regulatory attention despite the company's political prominence.
FINRA's role in the investigation involves sending detailed questionnaires to flagged companies, asking about the timing of board decisions, which executives and board members knew about crypto plans in advance, trading activity in company stock by insiders and their associates, and communications between management and investors before announcements. David Chase, a former SEC enforcement lawyer, noted that "when those FINRA letters go out, it really stirs the pot. It's typically the first step in an investigation." Companies receiving such letters face the choice of cooperating fully, which may expose wrongdoing, or resisting, which signals potential problems and intensifies scrutiny.
Nasdaq itself has responded to the crypto treasury trend by tightening requirements. The exchange now requires shareholder approvals before companies can issue new equity to fund crypto reserve purchases and has warned it will delist companies that fail to comply with these enhanced requirements. This policy targets a common financing pattern where companies announce crypto strategies, experience stock surges, then immediately issue shares at elevated prices to fund the purchases - a sequence that benefits selling shareholders and company executives with stock compensation but dilutes existing investors.
The enforcement climate under SEC Chair Paul Atkins, who assumed leadership in January 2025, represents a complex evolution from his predecessor Gary Gensler's aggressive enforcement approach. Atkins and Commissioner Hester Peirce, who leads the new Crypto Task Force, have signaled openness to creating clearer regulatory frameworks that enable innovation. Peirce apologized in a September 25, 2025 speech for the SEC's past stance that hindered innovation and urged the crypto industry to seize opportunities created by the new environment. However, both officials have made clear that fraud and manipulation enforcement will continue unabated regardless of broader policy evolution toward crypto-friendly regulation.
This creates a bifurcated environment where legitimate corporate crypto strategies may face clearer regulatory pathways and reduced compliance uncertainty, while manipulative schemes exploiting crypto narratives for stock promotion face intensified enforcement. Securities lawyers emphasize this distinction: companies with genuine treasury strategies, proper board governance, strong internal controls, transparent disclosure, and arms-length financing arrangements have less to fear from regulatory scrutiny than those with suspicious pre-announcement trading, vague business plans, and inconsistencies between announced strategies and financial capacity.
The debate over potential chilling effects centers on whether aggressive enforcement discourages beneficial innovation. Industry advocates argue that regulatory uncertainty and enforcement risk deter legitimate companies from adopting crypto treasuries even when strategically sound. They point to the fragmented U.S. regulatory landscape - with the SEC, CFTC, FinCEN, state regulators, and banking authorities all claiming jurisdiction over different aspects of crypto activity - as creating compliance complexity that favors only the largest, most resourced companies. Smaller firms that might benefit from crypto treasury strategies lack the legal budgets to navigate this complexity, potentially missing opportunities to strengthen balance sheets and attract investor interest.
Conversely, investor protection advocates argue that the 2025 explosion of crypto treasury announcements - with over 200 companies pivoting to crypto strategies in a single year - exhibits clear signs of faddish behavior driven by stock promotion rather than sound financial management. They note that 25 percent of public companies holding Bitcoin now trade below their Bitcoin net asset value, indicating market skepticism about management's value creation beyond passive cryptocurrency holdings. The pattern of struggling companies with declining core businesses suddenly announcing crypto pivots mirrors the 2017 blockchain bubble, when adding "blockchain" to a company name sufficed to trigger triple-digit stock gains.
Grant Thornton's crypto policy outlook suggested that "a lighter regulatory touch and specific crypto legislation could drive cryptocurrency adoption and sector growth," arguing that clear rules legitimize the industry and attract institutional capital. However, Brookings Institution countered that "today's crypto policy choices are occurring against the backdrop of rising bitcoin prices and a regulatory environment where oversight is weakening and political entanglements are deepening - raising legitimate concerns about regulatory capture, ethical conflicts, and public accountability."
The International Monetary Fund emphasized that effective regulation should pursue consistent objectives across jurisdictions: protecting consumers and investors, preserving market integrity against fraud and manipulation, preventing money laundering and terrorism financing, and safeguarding financial stability. The IMF warned that the actual or intended use of crypto assets attracts attention from multiple domestic regulators with fundamentally different frameworks and objectives, creating coordination challenges that manipulators exploit.
Perhaps the most compelling argument for stricter oversight comes from market surveillance firms tracking the negative premium phenomenon. When 25 percent of Bitcoin treasury companies trade below net asset value, it signals that markets do not trust management to deploy capital effectively or create shareholder value beyond passive crypto holdings. This discount persists despite crypto price appreciation, suggesting reputational damage from the association with speculative schemes. If stricter enforcement and clearer compliance standards separate legitimate strategies from promotional schemes, the resulting credibility could actually increase institutional investor participation in well-governed crypto treasury companies.
Understanding manipulation risks at the crypto-corporate intersection
The intersection of securities regulation and cryptocurrency markets creates unique manipulation vulnerabilities that traditional enforcement frameworks struggle to address. Stock markets operate under comprehensive surveillance systems with trade reporting, audit trails, broker-dealer supervision, and civil and criminal penalties for manipulation. Cryptocurrency markets, particularly for smaller altcoins, operate with minimal oversight, limited transparency, and frequent cross-border transactions that complicate enforcement. When these two ecosystems meet through corporate crypto holdings, manipulators exploit regulatory gaps and information asymmetries.
The classic pump-and-dump scheme adapted to crypto treasury stocks follows a predictable pattern. Promoters identify a small-cap company with weak financial performance, limited institutional ownership, and low trading volumes - characteristics that enable price manipulation with relatively modest capital. They approach company management with a proposal to announce a crypto treasury strategy, often providing convertible debt financing or agreeing to purchase shares at premiums to market. The announcement gets drafted with crypto buzzwords, ambitious language about AI integration and Web3 adoption, and allocation figures designed to impress rather than reflect available capital.
Before public announcement, promoters position themselves in the stock through purchases spread across multiple accounts to avoid triggering unusual activity alerts. They coordinate with social media promoters who control large followings on Twitter, Reddit, Telegram, and Discord. Some promoters create sophisticated infrastructure including dedicated websites, promotional videos, and fake analyst reports to lend credibility. The announcement timing gets coordinated with social media campaigns beginning immediately upon release, with countdown posts building anticipation, coordinated buying pressure in the opening minutes, and promotional posts emphasizing price targets and momentum.
The stock surges on the announcement day, often triggering exchange-mandated volatility halts that paradoxically increase attention rather than dampening enthusiasm. Retail investors seeing 100 to 200 percent gains fear missing out and chase the price higher throughout the day and following sessions. Meanwhile, promoters gradually sell their holdings into the buying frenzy, carefully managing sell volume to avoid triggering panic. Within days or weeks, promotional activity ceases, buying pressure evaporates, and the stock collapses - often declining 70 to 90 percent from peak levels. Late-arriving retail investors suffer catastrophic losses while promoters realize substantial profits.
Several factors make crypto treasury stocks particularly vulnerable to this manipulation pattern. First, the crypto narrative alone generates speculative interest from retail investors attracted to potential cryptocurrency upside. Many retail investors maintain crypto holdings and follow crypto markets closely, creating a large potential audience predisposed to view crypto exposure positively. Second, the complexity of evaluating crypto treasury strategies creates information asymmetries that favor sophisticated promoters over retail investors. Most investors lack the expertise to assess whether announced crypto allocations are financially realistic, strategically sound, or properly structured from tax and accounting perspectives.
Third, the accounting treatment of cryptocurrency holdings under generally accepted accounting principles creates opportunities for misleading disclosure. Until December 2024, companies had to treat crypto assets as intangible assets subject to impairment testing but could not recognize gains without selling. The FASB's ASU 2023-08 now requires fair value measurement with changes reflected in net income each period, improving transparency but also increasing earnings volatility. Companies can emphasize unrealized gains during bull markets to present favorable narratives while downplaying the volatility risks that materialize during bear markets.
Fourth, the leverage dynamics of corporate crypto treasuries create attraction for certain investor profiles while obscuring risks for others. Strategy's success at raising capital through convertible debt and equity offerings to purchase more Bitcoin demonstrates that leverage applied to Bitcoin appreciation can generate extraordinary returns. The company's introduction of "Bitcoin yield" as a key performance indicator - measuring BTC per share growth rather than traditional financial metrics - reflects this refocusing on cryptocurrency accumulation rather than underlying business operations. However, leverage amplifies losses equally during downturns, and the permanent nature of balance sheet Bitcoin holdings means companies cannot easily exit positions without taking losses and disappointing investors.
Fifth, the international nature of many crypto treasury companies complicates regulatory oversight. QMMM's Cayman Islands incorporation with Hong Kong operations exemplifies structures designed to limit regulatory exposure. Cayman Islands exempted companies face minimal disclosure requirements and no corporate taxation, creating incentives for financial engineering that prioritizes founder and promoter benefits over shareholder protection. When suspicious activity emerges, U.S. regulators must coordinate with foreign authorities who may lack comparable enforcement resources or priorities.
The options market interaction with crypto treasury stocks creates additional manipulation potential. Unusual call option activity before announcements, as regulators flagged with MEI Pharma, suggests parties with advance knowledge of announcements positioning for leveraged gains. Options markets in micro-cap stocks typically have minimal liquidity and wide bid-ask spreads, making unusual activity easier to detect but also easier to profit from given leverage. Buying call options before positive announcements and puts before negative announcements allows manipulators to multiply returns beyond stock gains alone.
Market surveillance systems operated by exchanges and regulators detect many manipulation patterns through statistical analysis of trading volumes, price movements, and correlations with external events. However, detection occurs with lag - often days or weeks after suspicious activity - and proving manipulation requires connecting trading patterns to communications and coordination evidence. The use of encrypted messaging apps, international participants, and nominee accounts frustrates investigation efforts. Even when manipulation gets detected, penalties often represent small fractions of ill-gotten gains, creating insufficient deterrence.
The QMMM case illustrates these dynamics comprehensively. A micro-cap company with declining revenues and minimal cash announces a crypto allocation exceeding its financial capacity by 200 times. Social media promotion from "unknown persons" drives parabolic price action disconnected from any fundamental analysis. Trading volumes explode while volatility triggers multiple circuit breakers. The company provides no credible explanation for funding sources. Regulatory suspension occurs after shares already surged 2,000 percent, meaning promoters likely captured substantial profits during the run-up. Even if the SEC identifies and charges manipulators, recovering investor losses remains difficult as profits get dissipated across multiple jurisdictions and accounts.
Global regulatory divergence and competitive dynamics
Regulatory approaches to corporate cryptocurrency holdings vary dramatically across major jurisdictions, creating competitive dynamics that influence where companies incorporate, where trading occurs, and what strategies prove viable. The European Union's Markets in Crypto-Assets regulation, or MiCA, represents the most comprehensive harmonized framework globally and became fully applicable December 30, 2024. MiCA establishes clear requirements for crypto asset service providers, detailed stablecoin reserve and disclosure mandates, and unified rules across all 27 EU member states.
MiCA requires stablecoin issuers to maintain one-to-one reserve backing with high-quality liquid assets including cash and government bonds, segregate reserves legally and operationally from corporate funds, and hold 30 percent of asset-referenced token reserves and 60 percent of e-money token reserves in EU bank accounts. Issuers must publish detailed white papers covering token characteristics, risks, reserve composition, technology specifications, and environmental impact. Quarterly audits and monthly public disclosures of reserve management practices ensure transparency. Token holders can redeem at par value within five business days at any time, and "significant" stablecoins exceeding ten million holders, five billion euros market capitalization, or 2.5 million daily transactions face enhanced capital requirements.
The practical impact of MiCA is already visible. Tether's USDT, the largest stablecoin by market capitalization, faces restrictions on major EU exchanges due to non-compliance with MiCA requirements. Circle's USDC and EURC position themselves as MiCA-compliant alternatives, potentially gaining European market share. Nine major European banks announced plans to launch a MiCA-compliant euro stablecoin. The regulation is expected to reduce fraud by 60 percent according to industry estimates while enabling 84 percent of issuers to align with compliance requirements. Some 75 percent of European financial firms report exploring crypto assets under the clearer MiCA framework.
Singapore's Monetary Authority implements a structured Payment Services Act framework requiring all digital payment token service providers to obtain licenses, with 33 licensed as of September 2025. Capital requirements include S$250,000 minimum for corporations. The MAS mandates 90 percent cold storage of customer assets, daily reconciliation, and independent custody separation from trading functions. Singapore's first-dollar know-your-customer requirements impose due diligence from the first transaction without de minimis thresholds, stricter than FATF standards. However, Singapore prohibits public advertising of cryptocurrencies in mass media and by social media influencers, limiting marketing to firms' own channels.
Singapore's Project Guardian represents the institutional focus of its approach, bringing together over 40 global financial institutions to explore tokenization of fixed income, foreign exchange, and asset management through regulated frameworks. The Guardian Fixed Income Framework and Guardian Funds Framework released in November 2024 provide structured pathways for institutional adoption. This approach emphasizes wholesale market development over retail speculation, reflected in the licensing of major institutional players including Gemini, OKX, Upbit, BitGo, and GSR during 2024. Singapore consistently ranks as the leading Asia-Pacific jurisdiction for crypto innovation combined with investor protection.
Hong Kong's Securities and Futures Commission operates a principles-based Virtual Asset Trading Platform licensing regime mandatory since June 2023. The ASPIRe Framework announced in February 2025 expands oversight across five pillars covering access, safeguards, products, infrastructure, and relationships. This includes new licensing for over-the-counter trading services, cryptocurrency custodians, and regulation of online influencers promoting crypto assets. Hong Kong approved Asia's first spot Bitcoin and Ethereum exchange-traded funds and maintains a clear distinction between professional investor and retail rules. The framework requires 98 percent of client assets in cold storage, independent audits, and segregation from corporate funds.
Hong Kong's comparative positioning aims at balanced institutional adoption with retail protection. The framework is more retail-protective than Singapore's but less prescriptive than EU MiCA. This middle ground attracted major platforms including Crypto.com and Bullish to pursue licensing while maintaining Hong Kong's role as an Asian financial hub. The absence of capital gains taxation for corporations holding crypto, combined with clear regulatory pathways, positions Hong Kong competitively for corporate treasury adoption relative to jurisdictions with adverse tax treatment.
The United Arab Emirates, particularly Dubai, has emerged as perhaps the most permissive major jurisdiction. The Virtual Assets Regulatory Authority framework established in February 2023 requires licensing but operates with founder-friendly approaches designed to attract crypto businesses globally. A September 2024 cooperation agreement between Dubai's VARA and the federal Securities and Commodities Authority enables UAE-wide licensing through VARA registration. Critically, the UAE maintains zero personal income tax and zero capital gains tax on cryptocurrency earnings for individuals, with only nine percent corporate tax on profits exceeding approximately $100,000. Value-added tax on crypto transactions for individuals was eliminated in October 2024.
The UAE government itself holds approximately 6,300 Bitcoin worth $700 to $740 million, ranking as the sixth-largest government holder globally. Binance estimates approximately $40 billion in Bitcoin holdings across UAE entities. Crypto ownership rates reach 25.3 percent of the population, the highest globally. This combination of regulatory clarity, tax advantages, and government support created explosive growth in crypto businesses relocating to Dubai, though questions persist about the long-term sustainability of zero-tax models and the quality of supervision relative to more established financial centers.
Japan maintains an established regulatory framework dating to 2017 requiring crypto exchange registration with the Financial Services Agency. The current tax treatment creates significant friction: individuals face taxation as ordinary income at rates up to 55 percent, while corporations face 30 percent unrealized gains tax on crypto holdings. However, proposed 2025 reforms would implement a flat 20 percent capital gains tax on sales aligned with other investment income and eliminate unrealized gains taxation for corporations. These changes, if legislated, would substantially improve the environment for corporate crypto holdings. Japan's $14 trillion in household savings represents a massive potential source of capital if regulatory and tax barriers diminish. Progressive stablecoin frameworks and institutional adoption through platforms like Progmat demonstrate Japan's movement toward mainstream integration.
The United States maintains a fragmented approach across multiple agencies creating compliance complexity. The SEC regulates crypto assets deemed securities, the CFTC oversees derivatives, FinCEN enforces anti-money laundering requirements, state regulators oversee money transmission, and banking regulators influence bank relationships with crypto firms. The GENIUS Act signed in July 2025 establishes federal stablecoin regulation requiring one-to-one reserve backing, prohibiting interest payments, and creating dual federal-state oversight depending on issuer size. However, comprehensive crypto market structure legislation remains pending.
The SEC's April 2025 guidance on corporate crypto disclosure requires detailed business descriptions covering development stage versus operational status, comprehensive risk factors including volatility and regulatory uncertainty, security characteristics explaining rights and technical requirements, management backgrounds, and material conflicts of interest. Financial reporting follows FASB's ASU 2023-08 requiring fair value measurement with quarterly changes reflected in net income. The ongoing SEC and FINRA investigation of over 200 corporate crypto firms adds enforcement uncertainty despite policy evolution toward clearer frameworks under Chair Atkins.
This global regulatory divergence creates arbitrage opportunities and competitive pressures. Companies incorporate in jurisdictions offering favorable tax treatment like the UAE or Cayman Islands while maintaining operations elsewhere. Regulatory clarity in Singapore and the EU attracts institutional capital uncomfortable with U.S. fragmentation. However, the largest capital pools remain in the United States, and accessing U.S. investors typically requires SEC compliance regardless of incorporation jurisdiction. China's comprehensive ban on crypto trading and mining drove activity offshore to Kazakhstan, the United States, and Southeast Asia, demonstrating that overly restrictive regimes cannot eliminate activity but merely displace it.
Academic analysis by the Atlantic Council tracking 75 countries found cryptocurrency adoption rates weakly correlated with regulatory restrictiveness. Even countries with bans maintain high adoption rates, suggesting prohibition proves generally ineffective. The most successful frameworks combine clear rules enabling innovation with investor protection measures preventing fraud - the balance Singapore and the evolving EU MiCA framework appear to achieve. Overly permissive regimes like the UAE attract activity but face questions about supervision quality and long-term stability. Overly restrictive approaches like China's ban or fragmented approaches like the U.S. current state create regulatory arbitrage without meaningfully protecting investors or preventing adoption.
Scenarios for the future of corporate digital asset strategies
The regulatory inflection point marked by the QMMM suspension and broader investigation of 200 companies creates three primary scenarios for corporate crypto treasury evolution, each with distinct implications for market structure, investor protection, and institutional adoption.
The base case scenario envisions regulatory legitimization through stricter oversight that paradoxically accelerates institutional adoption by creating clear compliance pathways and separating legitimate strategies from manipulative schemes. In this scenario, the SEC and FINRA investigations result in enforcement actions against the most egregious manipulators while simultaneously the Crypto Task Force issues clearer guidance on acceptable corporate crypto treasury practices. Companies with robust governance, realistic financing plans, transparent disclosure, and alignment between announced strategies and business fundamentals face minimal disruption. Those with suspicious pre-announcement trading, impossible financial commitments, or connections to promotional schemes face delisting, penalties, and potential criminal charges.
This bifurcation benefits well-capitalized companies with experienced management and institutional investor bases. Strategy's continued success at raising tens of billions through convertible debt for Bitcoin purchases demonstrates that sophisticated capital markets participants will fund crypto strategies they view as credible. Metaplanet's rise from $15 million to $7 billion market capitalization in one year while Bitcoin only doubled shows that proper execution of the treasury model generates extraordinary shareholder returns. Companies following these templates - establishing clear Bitcoin yield metrics, maintaining transparent reporting, securing institutional-grade custody, implementing strong internal controls - attract capital even amid broader regulatory scrutiny.
Bernstein's projection of $330 billion in corporate Bitcoin allocations over the next five years assumes this legitimization pathway materializes. The projection envisions corporate treasuries becoming standard asset class considerations alongside bonds, equities, and real estate for diversified balance sheet management. EY's finding that 83 percent of institutional investors plan to increase digital asset allocations in 2025 supports this trajectory. Sygnum Bank's research suggesting 2025 may mark the year crypto achieves standard asset class status in institutional portfolios reflects growing conviction that regulatory clarity enables mainstream adoption.
However, this scenario requires resolution of several structural challenges. The U.S. must clarify the fragmented regulatory landscape, ideally through comprehensive legislation establishing which agency has primary jurisdiction over different crypto activities. Accounting standards need further evolution to address the volatility that fair value measurement introduces into earnings. Tax policy must resolve uncertainties around the Corporate Alternative Minimum Tax potentially applying to unrealized crypto gains starting in 2026, which analysts warn could create "hefty tax implications" for major holders like Strategy. Banking regulators need to provide clear guidance enabling crypto companies to maintain accounts without fear of sudden relationship termination.
The bull case scenario envisions these challenges getting resolved favorably, unleashing a wave of mainstream institutional adoption that dwarfs current activity. In this scenario, corporate Bitcoin holdings reach the $330 billion Bernstein projection by 2028 rather than 2030, with acceleration coming from Fortune 500 companies that currently avoid crypto due to regulatory uncertainty. Ethereum and Solana treasury adoption expands from $12 billion currently to $50 billion or more as institutional comfort with alternative layer-one protocols grows. Stablecoin integration into corporate treasury operations becomes routine, with companies using crypto-native payment rails for cross-border transactions, vendor payments, and working capital management.
DeFi market growth from $21 billion in 2025 to over $231 billion by 2030, averaging 53 percent compound annual growth as projected by Crypto.com, would support this scenario by creating yield opportunities for corporate treasuries beyond passive holdings. AI-driven risk management tools projected to launch by 2026 would address institutional concerns about volatility and security. Project Guardian's tokenization initiatives expanding from 40 institutions to hundreds would normalize on-chain capital markets. Bitcoin reaching $200,000 by early 2026 as Bernstein forecasts would vindicate early corporate adopters and accelerate bandwagon effects.
This scenario faces skepticism from analysts noting that 25 percent of current Bitcoin treasury companies already trade below net asset value despite Bitcoin appreciation. The negative premium suggests markets question whether corporate structures add value beyond individual Bitcoin ownership. If this skepticism persists or intensifies, the premium required to raise capital for crypto purchases increases, limiting the leverage that makes treasury strategies attractive. Additionally, the bull case assumes no major negative events like exchange failures, custody breaches, or protocol vulnerabilities that could trigger institutional flight despite regulatory clarity.
The bear case scenario envisions regulatory crackdown producing market consolidation and shakeout that discourages corporate adoption for years. In this scenario, SEC and FINRA investigations reveal widespread insider trading and Reg FD violations across dozens of companies. High-profile enforcement actions with eight-figure penalties and potential criminal charges for executives create chilling effects. Nasdaq and other exchanges delist numerous companies failing to meet enhanced governance requirements. Investor losses from collapsed promotional schemes generate political pressure for stricter rules preventing companies from holding speculative assets.
The accounting treatment creates additional pressure in this scenario. Strategy's declining Bitcoin yield - from 2.6 BTC per basis point in 2021 to 58 BTC in 2025 - reflects diminishing returns as holdings grow and capital requirements increase exponentially. Fair value accounting means that crypto market corrections immediately flow through corporate earnings, creating quarterly volatility that conflicts with traditional corporate communication strategies. The 2026 implementation of Corporate Alternative Minimum Tax potentially applying to unrealized gains forces some companies to sell crypto holdings to fund tax payments, creating selling pressure during downturns.
Banking relationships deteriorate in this scenario as regulators indicate displeasure with financial institutions supporting crypto activities. Companies struggle to maintain accounts, custody relationships, and payment processing. The concerns expressed by Brookings Institution about "regulatory capture, ethical conflicts, and public accountability" leading to insufficient oversight materialize through major market failures. Public pension funds and endowments that began allocating to crypto treasury stocks suffer losses triggering political backlash. Congress passes restrictive legislation limiting corporate crypto holdings to small percentages of assets or prohibiting them entirely for certain company types.
This scenario would not eliminate corporate crypto holdings entirely - Strategy and core believers would persist regardless - but would freeze growth and potentially force some exits. The pattern would mirror the 2022 bear market when numerous companies that announced crypto holdings during the 2021 bull market quietly divested during the crash. However, the higher baseline of adoption in 2025 compared to 2022 and the structural changes in custody, accounting, and institutional infrastructure make a complete reversal less likely than during previous cycles.
The most probable outcome combines elements of all three scenarios: regulatory legitimization for well-governed strategies, continued institutional adoption at measured pace, and market consolidation that eliminates speculative excess while preserving the innovation core. The QMMM suspension and broader investigation represent necessary corrections to a 2025 market that clearly featured excessive faddish behavior and manipulation. Companies announcing crypto strategies without financial capacity or business rationale deserve scrutiny and face appropriate consequences. However, companies like Strategy, Metaplanet, and others with multi-year track records, transparent operations, and sustained Bitcoin accumulation demonstrate that the treasury model can create genuine shareholder value when executed properly.
The key question becomes whether regulatory interventions can distinguish between these categories effectively. Overly broad enforcement that treats all crypto treasury companies suspiciously would damage legitimate innovators and drive activity offshore. Insufficient enforcement that allows manipulation to continue would undermine investor confidence and delay institutional adoption. The optimal outcome threads this needle through clear guidance, vigorous enforcement against fraud, and permissive posture toward compliant strategies - the approach Commissioner Peirce and Chair Atkins appear to pursue.
Balancing innovation imperatives with investor protection mandates
The QMMM case crystallizes fundamental tensions inherent in regulating financial innovation. Cryptocurrency and blockchain technology offer genuine potential to improve financial systems through faster settlement, reduced intermediary costs, programmable money, and democratized access to investment opportunities. Corporate adoption of crypto treasuries represents one pathway for traditional businesses to participate in and benefit from this technological evolution. Legitimate strategic rationales exist for companies to hold Bitcoin as an inflation hedge, Ethereum as infrastructure for blockchain applications, or stablecoins as payment rails.
However, the same innovation narrative that attracts genuine entrepreneurs and value creation also provides cover for fraud, manipulation, and exploitation of unsophisticated investors. The 2017 blockchain name-change bubble, the 2021 meme stock phenomenon, and the 2025 crypto treasury explosion share common patterns: struggling companies pivoting to trendy narratives, stock promoters coordinating through social media, retail investors suffering losses while insiders profit, and eventual regulatory intervention after damage occurs. Each cycle generates calls for stricter oversight to prevent recurrence and industry resistance arguing that regulation stifles innovation.
The data from the QMMM investigation supports aggressive regulatory intervention. A company with $2.7 million in revenue, $1.58 million in annual losses, and under $500,000 in cash announcing a $100 million crypto allocation represents an obvious disconnect that should trigger immediate scrutiny. The 2,000 percent stock surge driven by social media promotion from "unknown persons" fits every element of classic pump-and-dump schemes. The pattern of suspicious pre-announcement trading across 200 companies investigated by SEC and FINRA suggests systematic abuse rather than isolated incidents. The fact that 25 percent of Bitcoin treasury companies trade below net asset value indicates market recognition that many strategies create no value beyond passive crypto holdings.
Yet the existence of manipulation does not invalidate the underlying strategy. Strategy's $8 billion gain on Bitcoin holdings year-to-date in 2025 and 2,919 percent stock appreciation since adopting the strategy in August 2020 demonstrate that leveraged Bitcoin exposure through corporate structures can generate extraordinary returns. The company's success at raising over $21 billion through convertible debt and equity offerings shows that sophisticated capital markets participants will fund strategies they view as credible. Metaplanet's market capitalization increase from $15 million to $7 billion while Bitcoin only doubled proves that proper execution generates premiums to underlying holdings.
The International Monetary Fund's framework for crypto regulation provides useful guidance: protect consumers and investors, preserve market integrity against fraud and manipulation, prevent money laundering and terrorism financing, and safeguard financial stability. These objectives apply uniformly whether regulatory approaches lean permissive or restrictive. The challenge lies in implementation through fragmented national regulatory systems with different legal frameworks, agency mandates, and enforcement capacities.
MiCA represents the most ambitious attempt at comprehensive harmonization, establishing clear rules across 27 EU member states for custody, disclosure, reserve requirements, and redemption rights. The regulation's focus on stablecoins reflects recognition that systemically important digital assets require bank-like supervision. Early results show Tether facing restrictions while Circle and European bank consortiums build compliant alternatives - exactly the market sorting that effective regulation should produce. The projected 60 percent fraud reduction and 84 percent issuer compliance rate suggest MiCA strikes a workable balance between investor protection and enabling innovation.
Singapore's approach emphasizes institutional market development over retail participation through stringent licensing, high capital requirements, robust custody standards, and marketing restrictions. The 33 licensed VASPs include institutional-grade platforms like Gemini, OKX, BitGo, and GSR rather than retail-focused exchanges. Project Guardian's 40-plus institutional participants exploring tokenization demonstrates that clear rules attract sophisticated capital even when retail access is limited. This institutional-first approach may prove more sustainable than retail-driven markets prone to manipulation and speculation.
Hong Kong's middle path between Singapore's institutional focus and broader retail access reflects its traditional role balancing mainland China relationships with international financial center status. The approval of spot Bitcoin and Ethereum ETFs alongside strict VATP licensing and 98 percent cold storage requirements shows how jurisdictions can enable access while maintaining controls. The ASPIRe Framework's expansion to OTC services, custody licensing, and influencer regulation demonstrates regulatory adaptation as markets evolve.
The U.S. fragmentation across SEC, CFTC, FinCEN, state regulators, and banking agencies creates compliance complexity that favors large, well-resourced firms over smaller innovators. However, this fragmentation also enables experimentation and prevents single-point regulatory failure. The evolution from Gensler's enforcement-heavy approach to Atkins and Peirce's innovation-focused strategy shows how leadership changes can shift policy without legislative action. The GENIUS Act's stablecoin framework and expected comprehensive market structure legislation may resolve the worst fragmentation while preserving beneficial regulatory competition.
The Atlantic Council's finding that cryptocurrency adoption rates correlate weakly with regulatory restrictiveness suggests that prohibition proves ineffective while clear enabling frameworks accelerate institutional adoption. China's comprehensive ban drove mining operations to the United States, Kazakhstan, and other jurisdictions rather than eliminating activity. Nigeria's restrictions pushed trading to peer-to-peer platforms. Conversely, Singapore's clear licensing attracted major institutions despite high compliance costs. The EU's MiCA framework is accelerating rather than slowing institutional exploration.
For corporate crypto treasuries specifically, the path forward requires several elements. First, clear disclosure standards distinguishing between companies with track records of accumulation, proper custody, and transparent reporting versus those making opportunistic announcements without financial capacity or business rationale. Second, enforcement targeting manipulation schemes while avoiding overly broad actions that create uncertainty for compliant companies. Third, accounting standards evolution that addresses earnings volatility from fair value measurement without forcing economically irrational behavior. Fourth, tax policy clarity on whether unrealized gains face taxation and at what thresholds.
Fifth, custody standards requiring institutional-grade solutions with multi-signature controls, cold storage for majority of assets, insurance coverage, independent audits, and segregation from operational funds. Sixth, governance requirements including board oversight of crypto strategies, independent directors reviewing risk management, disclosure of conflicts between management compensation tied to stock price and decisions to announce crypto pivots, and shareholder approval for material allocations. Seventh, financing structure transparency distinguishing between companies funding purchases with existing cash flow versus those issuing dilutive equity or debt.
Companies following these practices - Strategy, Metaplanet, Coinbase, Galaxy Digital, and others with multi-year track records - face minimal risk from enhanced regulatory oversight. Those making announcements designed primarily to generate stock price surges rather than execute sustainable strategies face appropriate consequences. Market consolidation eliminating the bottom quartile trading below net asset value would strengthen rather than weaken the ecosystem by improving average quality and reducing association with speculative excess.
The most compelling argument for viewing stricter oversight as long-term legitimization rather than existential threat comes from institutional investor behavior. EY's finding that 83 percent of institutional investors plan to increase crypto allocations assumes clear regulatory frameworks enabling fiduciary compliance. Sygnum's argument that 2025 may mark crypto achieving standard asset class status depends on resolution of the regulatory uncertainty that prevented earlier adoption. Bernstein's $330 billion corporate allocation projection requires confidence that strategies won't face sudden prohibition or punitive treatment.
If the current regulatory inflection point produces clear rules, vigorous fraud enforcement, and permissive posture toward compliant strategies, the likely outcome is acceleration rather than deceleration of institutional adoption. Companies will understand what practices are acceptable, investors will have confidence in disclosure quality, custodians will provide institutional-grade infrastructure, and traditional financial institutions will integrate crypto services rather than avoiding them. The alternative - continued regulatory uncertainty combined with inadequate manipulation enforcement - produces the worst outcome: sophisticated participants capture opportunities while retail investors suffer losses and the technology's legitimate potential remains unrealized.
The QMMM suspension and broader investigation of 200 companies represent necessary corrections to a market exhibiting obvious excesses. A struggling Hong Kong advertising firm with minimal cash announcing an impossible crypto allocation and experiencing a 2,000 percent stock surge driven by anonymous social media promotion deserves regulatory intervention regardless of one's views on crypto generally. The question is whether interventions stop there, targeting clear manipulation, or expand to create chilling effects that discourage legitimate innovation.
Early indications suggest regulators understand this distinction. Commissioner Peirce's apology for past SEC approaches that hindered innovation and Chair Atkins' emphasis on creating clear frameworks rather than enforcement-only strategies signal awareness that effective regulation enables rather than prevents valuable activity. The continuation of fraud enforcement alongside policy evolution shows that these objectives are complementary rather than contradictory. Companies can innovate within clear rules while manipulators face consequences for exploiting ambiguity.
The corporate crypto treasury phenomenon ultimately tests whether regulatory systems can adapt to technological innovation at a pace that protects investors without preventing value creation. The traditional model of waiting for crises, then imposing reactive restrictions, then gradually loosening as industry matures creates unnecessary volatility and delays beneficial adoption. A more effective model establishes clear principles - transparency, custody standards, conflicts management, adequate capital - then allows innovation within those boundaries while enforcing vigorously against violations.
MiCA's comprehensive framework implemented before major failures rather than after represents this proactive approach. Singapore's institutional-first development prioritizing quality over quantity reflects similar thinking. The United States' current inflection point offers opportunity to establish clearer frameworks before rather than after the next major crisis. The QMMM suspension and broader investigation, while creating short-term uncertainty, may ultimately prove to be constructive corrections that accelerate long-term adoption by improving market quality and investor confidence. The companies that survive this scrutiny with reputations intact will find themselves in stronger competitive positions with clearer paths to institutional capital and mainstream legitimacy.






